顺序表的讲解与实现
- 一、顺序表的概念及结构
- 二、顺序表分类(C语言实现)
- 三、动态顺序表的实现(使用VS2022)
- 四、代码优化
- [五、完整 SeqList.c 代码](#五、完整 SeqList.c 代码)
一、顺序表的概念及结构
线性表 (linear list)是n个具有相同特性的数据元素的有限序列。 线性表是⼀种在实际中广泛使用的数据结构,常见的线性表:顺序表、链表、栈、队列、字符串 ... 线性表在逻辑上是线性结构 ,也就说是连续的一条直线。但是在物理结构上并不一定是连续的 ,线性表在物理上存储时,通常以数组和链式结构的形式存储。
二、顺序表分类(C语言实现)
顺序表和数组的区别
顺序表的底层结构是数组,对数组的封装,实现了常用的增删改查等接口。
顺序表分类
静态顺序表
概念:使用定长数组存储元素
c
#define N 10 // 长度恒定
typedef int SeqListDataType;
typedef struct SeqList
{
SeqListDataType arr[N]; // 长度恒定
int size;
} SeqList, *pSeqList;静态顺序表缺陷:空间给少了不够用,给多了造成空间浪费。
动态顺序表
概念:按需申请,避免空间进一步浪费
c
typedef int SeqListDataType;
typedef struct SeqList
{
SeqListDataType* arr; // 指针
int size; // 当前容量
int capacity; // 总容量
} SeqList, * pSeqList;三、动态顺序表的实现(使用VS2022)
这里以实现动态顺序表为例,开发工具为VS2022的C语言。
动态顺序表常用的增删改查等接口包括:
1.初始化、销毁、打印内容
2.检查扩容
3.尾部插入、尾部删除、头部插入、头部删除
4.指定插入、指定删除、查找
在 SeqList.h 中:
c
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// 初始化容量
#define INIT_CAPACITY 4
// 扩容倍率
#define EXPANSION_MULTIPLE 2
typedef int SeqListDataType;
typedef struct SeqList
{
SeqListDataType* arr;
int size;
int capacity;
} SeqList, * pSeqList;
// 初始化、销毁、打印
void SeqListInit(pSeqList ps);
void SeqListDestroy(pSeqList ps);
void SeqListPrint(pSeqList ps);
// 检查扩容
void CheckCapacity(pSeqList ps);
// 尾插尾删、头插头删
void SeqListPushBack(pSeqList ps, SeqListDataType x);
void SeqListPopBack(pSeqList ps);
void SeqListPushFront(pSeqList ps, SeqListDataType x);
void SeqListPopFront(pSeqList ps);
// 插入、删除、查找
void SeqListInsert(pSeqList ps, int pos, SeqListDataType x);
void SeqListErase(pSeqList ps, int pos);
int SeqListFind(pSeqList ps, SeqListDataType x);在 SeqList.c 中:
1.初始化、销毁、打印内容
c
#include "SeqList.h"
// 初始化、销毁、打印
void SeqListInit(pSeqList ps)
{
assert(ps); // 防止进入空指针
ps->arr = NULL;
ps->size = 0;
ps->capacity = 0;
}
void SeqListDestroy(pSeqList ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->arr);
ps->size = 0;
ps->capacity = 0;
}
void SeqListPrint(pSeqList ps)
{
assert(ps);
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; ++i)
{
printf("%d ", ps->arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}2.检查扩容
c
// 检查扩容
void CheckCapacity(pSeqList ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->size == ps->capacity)
{
int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? INIT_CAPACITY : ps->capacity * EXPANSION_MULTIPLE;
// ps->arr 为空时,realloc 会转为 malloc
SeqListDataType* temp = (SeqListDataType*)realloc(ps->arr, newCapacity * sizeof(SeqListDataType));
if (temp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc failed");
return;
}
// 更新
ps->arr = temp;
ps->capacity = newCapacity;
}
}3.尾部插入、尾部删除、头部插入、头部删除
尾部插入
c
void SeqListPushBack(pSeqList ps, SeqListDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
CheckCapacity(ps); // 检查容量,不足扩容
ps->arr[ps->size++] = x; // 尾插
}尾部删除
c
void SeqListPopBack(pSeqList ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size > 0); // 防止为空
--ps->size; // 直接--忽略掉当前位置
}头部插入
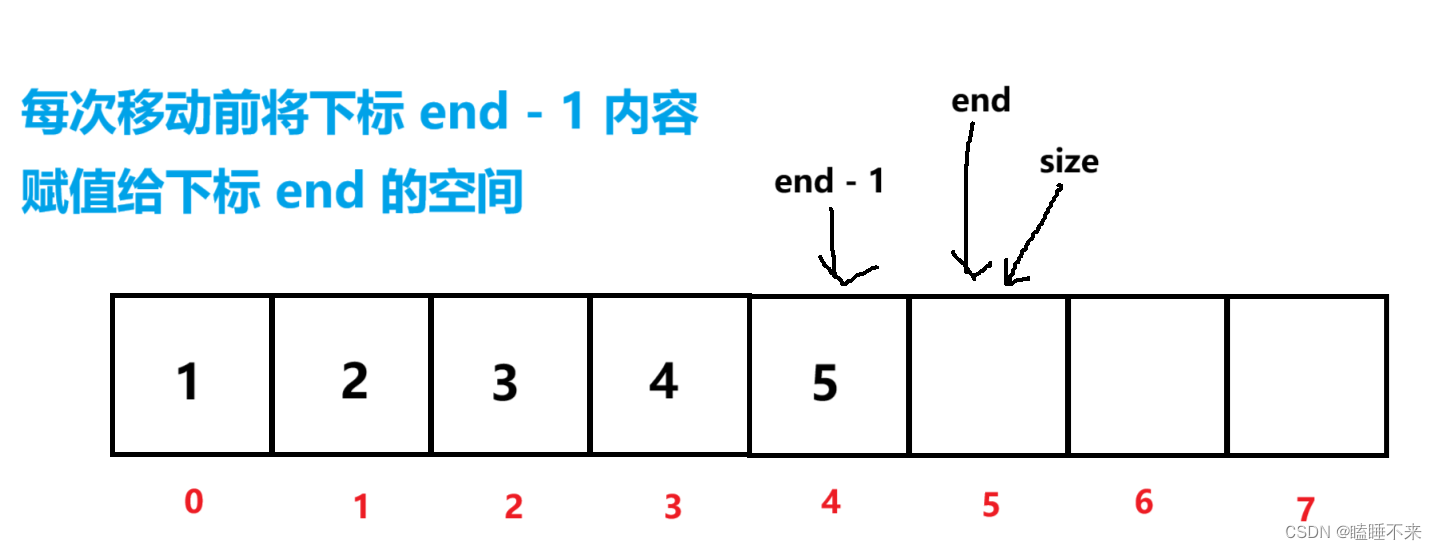
c
void SeqListPushFront(pSeqList ps, SeqListDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
CheckCapacity(ps);
for (int end = ps->size; end > 0; --end)
{
ps->arr[end] = ps->arr[end - 1];
}
ps->arr[0] = x;
++ps->size;
}
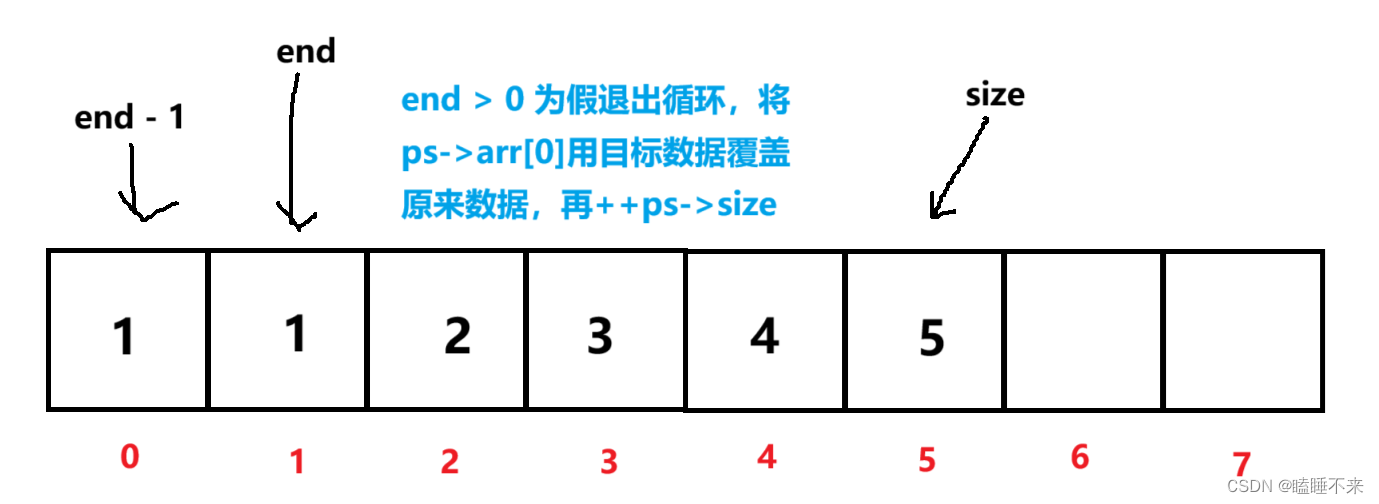
头部删除
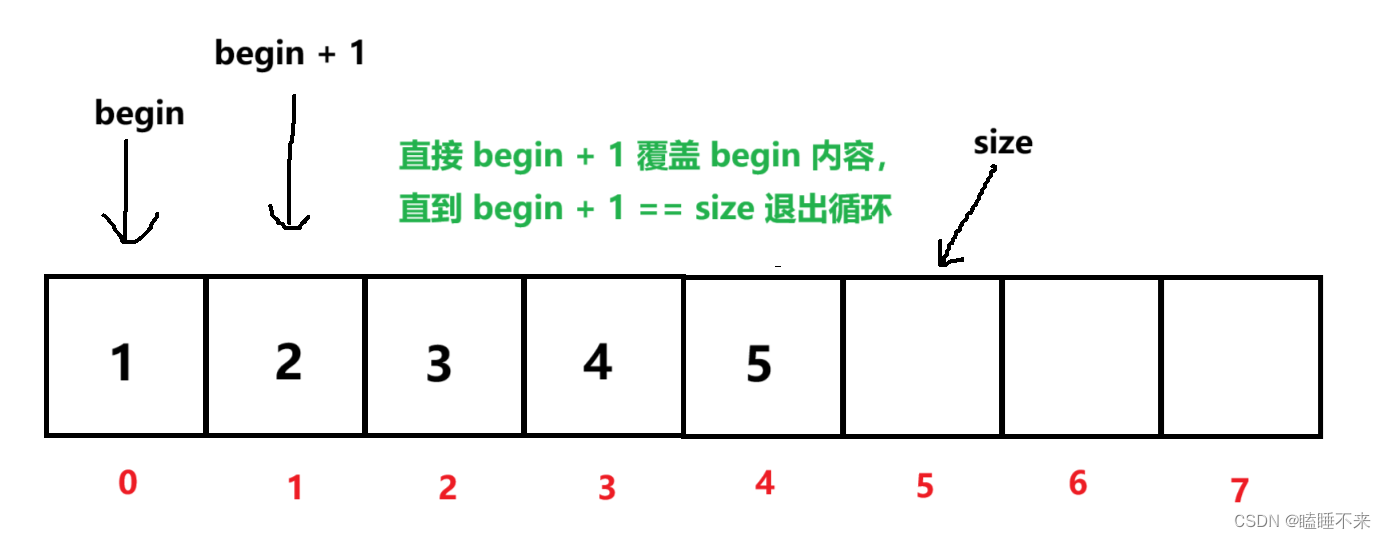
c
void SeqListPopFront(pSeqList ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size > 0);
for (int begin = 0; begin < ps->size - 1; ++begin)
{
ps->arr[begin] = ps->arr[begin + 1];
}
--ps->size;
}
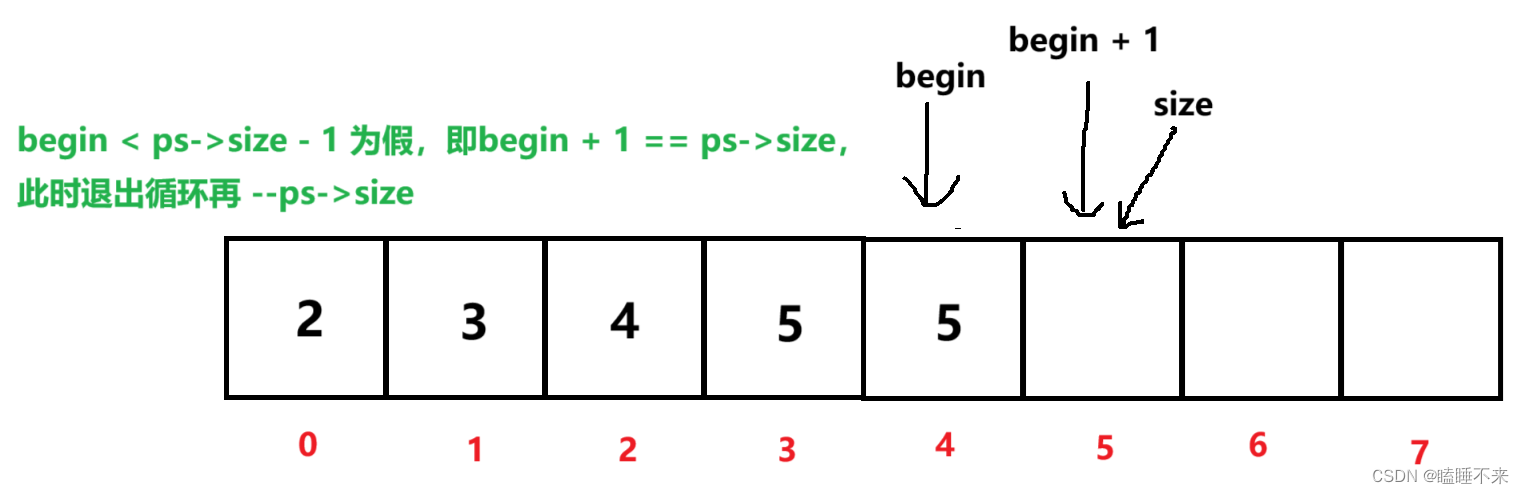
4.指定插入、指定删除、查找
指定插入
c
void SeqListInsert(pSeqList ps, int pos, SeqListDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
assert(0 <= pos && pos <= ps->size); // 当 pos == ps->size 可以实现尾插
CheckCapacity(ps);
for (int end = ps->size; end > pos; --end)
{
ps->arr[end] = ps->arr[end - 1];
}
ps->arr[pos] = x;
++ps->size;
}指定插入与头部插入同理,只需将结束位置改为 pos 指定的位置。
指定删除
c
void SeqListErase(pSeqList ps, int pos)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size > 0);
assert(0 <= pos && pos < ps->size); // 尾删不可删 pos == ps->size 位置上的
for (int begin = pos; begin < ps->size - 1; ++begin)
{
ps->arr[begin] = ps->arr[begin + 1];
}
--ps->size;
}指定删除与头部删除同理,只需将开始位置改为 pos 指定的位置。
查找
c
int SeqListFind(pSeqList ps, SeqListDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size > 0);
// 找到返回下标,反之返回 -1
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; ++i)
{
if (ps->arr[i] == x)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}四、代码优化
指定插入 包含 尾插头插,指定删除 包含 尾删头删 。可以复用两者,提高代码复用率。
c
// 尾插尾删、头插头删
void SeqListPushBack(pSeqList ps, SeqListDataType x)
{
SeqListInsert(ps, ps->size, x);
}
void SeqListPopBack(pSeqList ps)
{
SeqListErase(ps, ps->size - 1);
}
void SeqListPushFront(pSeqList ps, SeqListDataType x)
{
SeqListInsert(ps, 0, x);
}
void SeqListPopFront(pSeqList ps)
{
SeqListErase(ps, 0);
}五、完整 SeqList.c 代码
c
#include "SeqList.h"
// 初始化、销毁、打印
void SeqListInit(pSeqList ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->arr = NULL;
ps->size = 0;
ps->capacity = 0;
}
void SeqListDestroy(pSeqList ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->arr);
ps->size = 0;
ps->capacity = 0;
}
void SeqListPrint(pSeqList ps)
{
assert(ps);
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; ++i)
{
printf("%d ", ps->arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
// 检查扩容
void CheckCapacity(pSeqList ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->size == ps->capacity)
{
int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? INIT_CAPACITY : ps->capacity * EXPANSION_MULTIPLE;
// ps->arr 为空时,realloc 会转为 malloc
SeqListDataType* temp = (SeqListDataType*)realloc(ps->arr, newCapacity * sizeof(SeqListDataType));
if (temp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc failed");
return;
}
// 更新
ps->arr = temp;
ps->capacity = newCapacity;
}
}
// 尾插尾删、头插头删
void SeqListPushBack(pSeqList ps, SeqListDataType x)
{
SeqListInsert(ps, ps->size, x);
}
void SeqListPopBack(pSeqList ps)
{
SeqListErase(ps, ps->size - 1);
}
void SeqListPushFront(pSeqList ps, SeqListDataType x)
{
SeqListInsert(ps, 0, x);
}
void SeqListPopFront(pSeqList ps)
{
SeqListErase(ps, 0);
}
// 插入、删除、查找
void SeqListInsert(pSeqList ps, int pos, SeqListDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
assert(0 <= pos && pos <= ps->size);
CheckCapacity(ps);
for (int end = ps->size; end > pos; --end)
{
ps->arr[end] = ps->arr[end - 1];
}
ps->arr[pos] = x;
++ps->size;
}
void SeqListErase(pSeqList ps, int pos)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size > 0);
assert(0 <= pos && pos < ps->size);
for (int begin = pos; begin < ps->size - 1; ++begin)
{
ps->arr[begin] = ps->arr[begin + 1];
}
--ps->size;
}
int SeqListFind(pSeqList ps, SeqListDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size > 0);
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; ++i)
{
if (ps->arr[i] == x)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}