文章目录
- 一、前言
- 二、技术思路及方案
-
- [2.1 实现思路](#2.1 实现思路)
- [2.2 实现方案](#2.2 实现方案)
-
- [2.2.1 nacos动态数据源实现类关系图](#2.2.1 nacos动态数据源实现类关系图)
- 三、功能实现
-
- [3.1 快速集成方案](#3.1 快速集成方案)
-
- [3.1.1 引入依赖](#3.1.1 引入依赖)
- [3.1.2 服务端熔断降级](#3.1.2 服务端熔断降级)
- [3.1.3 feign调用降级](#3.1.3 feign调用降级)
- 四、扩展
-
- [4.1 SPI机制](#4.1 SPI机制)
- [4.2 自定义Slot实现](#4.2 自定义Slot实现)
- [4.3 基于 Sentinel 实现 Feign 全局异常兜底](#4.3 基于 Sentinel 实现 Feign 全局异常兜底)
-
- [4.3.1 扩展SentinelFeign Builder](#4.3.1 扩展SentinelFeign Builder)
-
- [4.3.1.1 思路](#4.3.1.1 思路)
- [4.3.1.2 程序设计](#4.3.1.2 程序设计)
- [4.3.2 使用](#4.3.2 使用)
一、前言
关于Sentinel和Hystrix之间对比以及Sentinel原理在官方文档有详细文档,这里就不再做多余赘述,Sentinel常规集成通常是借助Sentinel Dashboard服务端整合实现服务的限流、熔断降级以及多维护的监控。但是项目当下已经集成promethus监控、aws云原生服务自带流量监控等,因此Sentinel Dashboard服务端提供的多维监控模项目需求优先级并不高。综合项目实际情况以及节约成本的理念我们提出:Spring Cloud + Sentinel + nacos 动态数据源模式(无Dashboard服务端)实现微服务的服务降级功能。
本文主要包含围Sentinel绕微服务的服务降级功能实现、自定义slot实现熔断降级预警功能以及基于-sentinel-实现-feign-全局异常兜底。
二、技术思路及方案
2.1 实现思路
从官方提供Sentinel整体架构可以看出Dashboard服务端在Sentinel整体架构中仅负责规则配置、实时监控、机器发现等辅助模块。
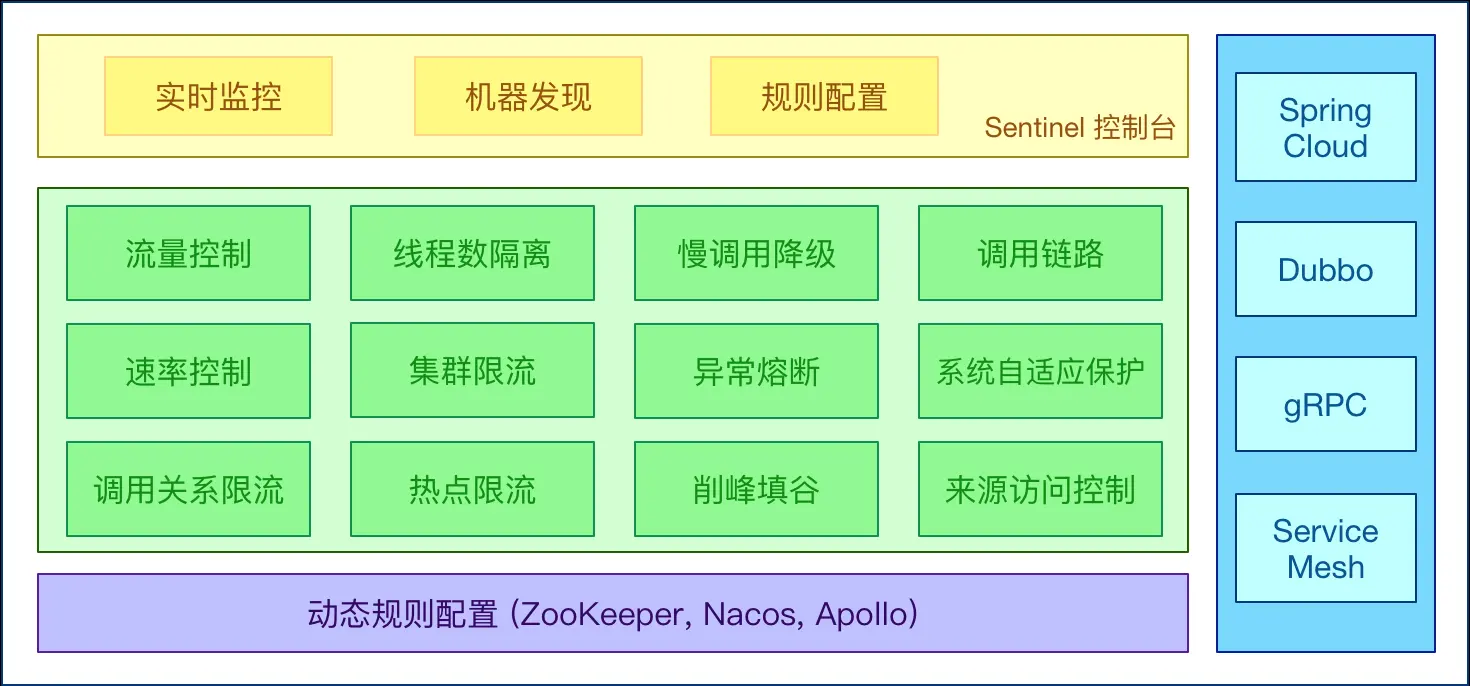
实际处理流控、熔断降级是Sentinel-core完成。因此剥离Dashboard服务端,独立实现服务的熔断降级功能是可行的。
调研官方文档不难发现,Sentinel针对Spring Cloud微服务提供了依赖:
- spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinel 微服务快速集成Sentinel提供支持
- spring-cloud-alibaba-sentinel-datasource Sentinel规则动态数据源支持自动化配置
- sentinel-datasource-nacos 提供了Sentinel规则动态数据源支持。
2.2 实现方案
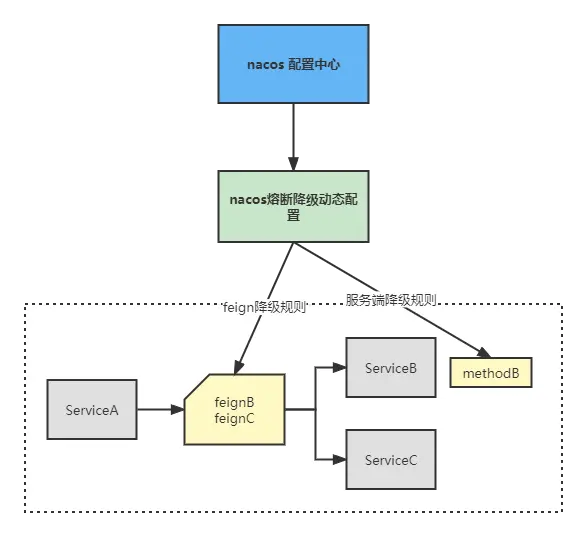
如上图,基于nacos配置中心实现Sentinel规则动态数据源管理,微服务启动时拉取熔断降级规则并维持心跳动态更新数据源配置。
2.2.1 nacos动态数据源实现类关系图
根据源码分析,可以看出nacos动态数据源实现如下:

从入口程序SentinelAutoConfiguration开始,应用程序从环境配置Properties获取指定的数据源配置,最终通过静态规则管理类DegradeRuleManager注册到数据源,从而实现动态刷新规则配置。
三、功能实现
3.1 快速集成方案
3.1.1 引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinel</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-alibaba-sentinel-datasource</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-datasource-nacos</artifactId>
</dependency>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinel 默认开启sentinel功能,引入依赖便可以使用sentinel,源码片段如下:
@Configuration(
proxyBeanMethods = false
)
@ConditionalOnProperty(
name = {"spring.cloud.sentinel.enabled"},
matchIfMissing = true
)
@EnableConfigurationProperties({SentinelProperties.class})
public class SentinelAutoConfiguration {spring-cloud-alibaba-sentinel-datasource依赖会从数据源中动态加载sentinel规则,源码片段如下:
# AbstractDataSourceProperties
public void postRegister(AbstractDataSource dataSource) {
switch(this.getRuleType()) {
case FLOW:
FlowRuleManager.register2Property(dataSource.getProperty());
break;
case DEGRADE:
DegradeRuleManager.register2Property(dataSource.getProperty());
break;
case PARAM_FLOW:
ParamFlowRuleManager.register2Property(dataSource.getProperty());
break;
case SYSTEM:
SystemRuleManager.register2Property(dataSource.getProperty());
break;
case AUTHORITY:
AuthorityRuleManager.register2Property(dataSource.getProperty());
break;
case GW_FLOW:
GatewayRuleManager.register2Property(dataSource.getProperty());
break;
case GW_API_GROUP:
GatewayApiDefinitionManager.register2Property(dataSource.getProperty());
}
}3.1.2 服务端熔断降级
@SentinelResource 可以作用于方法上的熔断降级保护,并提供可选的异常处理和 fallback 配置项。 @SentinelResource 注解包含以下属性:
- value:资源名称,必需项(不能为空),如果不填,会自动以全路径为key
- entryType:entry 类型,可选项(默认为 EntryType.OUT)
- blockHandler / blockHandlerClass: blockHandler 对应处理 BlockException 的函数名称,可选项。blockHandler 函数访问范围需要是 public,返回类型需要与原方法相匹配,参数类型需要和原方法相匹配并且最后加一个额外的参数,类型为 BlockException。blockHandler 函数默认需要和原方法在同一个类中。若希望使用其他类的函数,则可以指定 blockHandlerClass 为对应的类的 Class 对象,注意对应的函数必需为 static 函数,否则无法解析。
- fallback:fallback 函数名称,可选项,用于在抛出异常的时候提供 fallback 处理逻辑。fallback 函数可以针对所有类型的异常(除了 exceptionsToIgnore 里面排除掉的异常类型)进行处理。fallback 函数签名和位置要求:
- 返回值类型必须与原函数返回值类型一致;
- 方法参数列表需要和原函数一致,或者可以额外多一个 Throwable 类型的参数用于接收对应的异常
- fallback 函数默认需要和原方法在同一个类中。若希望使用其他类的函数,则可以指定 fallbackClass 为对应的类的 Class 对象,注意对应的函数必需为 static 函数,否则无法解析。
- defaultFallback(since 1.6.0):默认的 fallback 函数名称,可选项,通常用于通用的 fallback 逻辑(即可以用于很多服务或方法)。默认 fallback 函数可以针对所以类型的异常(除了 exceptionsToIgnore 里面排除掉的异常类型)进行处理。若同时配置了 fallback 和 defaultFallback,则只有 fallback 会生效。defaultFallback函数要求与fallback一致。
- exceptionsToIgnore(since 1.6.0):用于指定哪些异常被排除掉,不会计入异常统计中,也不会进入 fallback 逻辑中,而是会原样抛出。
这里补充说明下blockHandler和fallback触发机制
- fallback如上述所讲,是异常降级兜底函数,当资源函数出现异常将会进入fallback如上述所讲。
- blockHandler是当资源函数某项指标超过设定的规则时触发
| 异常 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| FlowException | 限流异常 |
| ParamFlowException | 热点参数限流的异常 |
| DegradeException | 降级异常 |
| AuthorityException | 授权规则异常 |
| SystemBlockException | 系统规则异常 |
代码示例
下面代码示例通过@SentinelResource 注解在方法上进行埋点,标记getBaseUserInfo1函数为Sentinel资源,并指定了兜底函数和降级函数。
public class DsUserBaseQueryApplicationImpl implements DsUserBaseQueryApplication {
@Override
@SentinelResource(value = "baseUserInfo", entryType = EntryType.IN, fallback = "defaultFallback", blockHandler = "exceptionHandler")
public String getBaseUserInfo1(String userId) {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(userId)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("userId is empty.");
}
return System.currentTimeMillis() + userId;
}
//默认的 fallback 函数名称
public String defaultFallback(String userId) {
log.info("Go to default fallback");
return "defaultFallback降级了";
}
// Block 异常处理函数,参数最后多一个 BlockException,其余与原函数一致.
public String exceptionHandler(String userId, BlockException ex) {
log.error("blockHandler服务降级了", ex);
// Do some log here.
return "Oops,blockHandler, error occurred at " + userId;
}
}增加动态数据源配置
动态数据源配置直接在SpringCloud配置模块增加sentinel.datasource数据源,支持flow限流规则和degrade降级规则。在flow/degrade层下添加具体的数据源配置介质,下面为基于nacos配置中心介质的动态数据源配置
#sentinel配置相关
spring:
cloud:
sentinel:
datasource:
flow:
nacos:
server-addr: ${spring.cloud.nacos.config.server-addr}
dataId: ${spring.application.name}-flow-rules
groupId: SENTINEL_GROUP
# 规则类型,取值见:
# org.springframework.cloud.alibaba.sentinel.datasource.RuleType
rule-type: flow
namespace: ${xxxx.sentinel.nacos.namespace}
degrade:
nacos:
server-addr: ${spring.cloud.nacos.config.server-addr}
dataId: global-sentinel-degrade-rules
groupId: SENTINEL_GROUP
rule-type: degrade
data-type: json
namespace: ${spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.namespace}指定资源熔断规则
上文通过动态数据源配置指定了nacos降级规则配置文件,配置文件采用json格式的数组配置,详细配置如下:
[
{
"resource":"baseUserInfo", # 资源名称
"grade":2, # 规则编号,2代表异常次数降级规则
"count":5, # 阈值
"timeWindow":10, # 降级窗口时间,单位s
"MinRequestAmount": 2 # 最小触发请求数
}
]降级规则结果验证测试
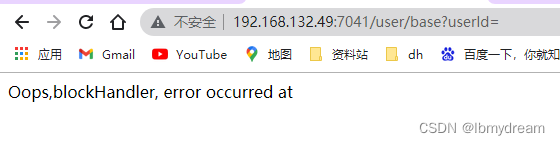
配置完降级规则启动服务,首次访问接口,参数传递为空,服务端资源出现异常,直接进入兜底函数。
http://192.168.132.49:7041/user/base?userId=下图为fallback兜底函数降级结果:

此后一秒内连续5次访问后,资源异常次数达到阈值,服务进入
blockHandler规则降级函数,并且在此后10秒内都会进入规则降级流程。下图为异常次数达到阈值后,进行blockHandler规则降级结果:
3.1.3 feign调用降级
开启sentinel feign支持
要启用sentinel feign降级功能需要在应用配置中显示关闭Spring Cloud 默认Hystrix降级开关 和 启用 feign sentinel 开启:
#打开sentinel对feign的支持
feign:
sentinel:
enabled: true
hystrix:
enabled: false开启feign支持后,应用启动将初始化sentinel feign 资源:
@Configuration(
proxyBeanMethods = false
)
@ConditionalOnClass({SphU.class, Feign.class})
public class SentinelFeignAutoConfiguration {
public SentinelFeignAutoConfiguration() {
}
@Bean
@Scope("prototype")
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
@ConditionalOnProperty(
name = {"feign.sentinel.enabled"}
)
public Builder feignSentinelBuilder() {
return SentinelFeign.builder();
}
}sentinel 对@FeignClient 注解中的所有属性,Sentinel 都做了兼容,查看源码片段:
if (Void.TYPE != fallback) {
Object fallbackInstance = this.getFromContext(beanName, "fallback", fallback, target.type());
return new SentinelInvocationHandler(target, dispatch, new feign.hystrix.FallbackFactory.Default(fallbackInstance));
} else if (Void.TYPE != fallbackFactory) {
FallbackFactory fallbackFactoryInstance = (FallbackFactory)this.getFromContext(beanName, "fallbackFactory", fallbackFactory, FallbackFactory.class);
return new SentinelInvocationHandler(target, dispatch, fallbackFactoryInstance);
} else {
return new SentinelInvocationHandler(target, dispatch);
}sentinel会根据定义的feing接口构建相应的资源,资源名策略定义:httpmethod:protocol://requesturl。
编码,定义feign调用服务端和调用方
# api 定义
@GetMapping(value = "/inner/user/base")
String getBaseUserInfo(@RequestParam("userId") String userId);
# feign api 定义
@FeignClient(contextId = "dsUserBaseApiClient", name = "xxxx", fallback = DsUserBaseApiClientFallback.class, configuration = FeignFallbackConfiguration.class)
public interface DsUserBaseApiClient extends DsUserBaseApi {
}
# feign 接口调用
@GetMapping(value = "/user/info")
public String getBaseUserInfo1(String userId) {
return client.getBaseUserInfo(userId);
}
# feign server 定义
@Override
public String getBaseUserInfo(String userId) {
log.info("降级测试start...");
try {
log.info("降级测试, 我开始休眠了...");
Thread.sleep(3 * 1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.info("降级测试, 我睡醒了...");
return baseQueryApplication.getBaseUserInfo(userId);
}配置feign超时规则
0-超时异常降级策略,阈值2000ms
[
{
"resource": "GET:http://demo-xxxx-server/inner/user/base",
"grade": 0,
"count": 2000,
"timeWindow":10
}
]项目默认超时时间10 * 1000MS,Server接口设置睡眠时间3 * 1000MS,阈值2 * 1000 ms,访问接口feign会正常返回。
使用Jmster进行压力测试,在50 * 50 循环调用过程,当feign调用平均响应时间超过设定的阈值后,将会提前进行熔断降级,调用feign接口定义的fallback函数,而不是一直等待服务端响应。
四、扩展
在 Sentinel 里面,所有的资源都对应一个资源名称(resourceName),每次资源调用都会创建一个 Entry 对象。Entry 可以通过对主流框架的适配自动创建,也可以通过注解的方式或调用 SphU API 显式创建。Entry 创建的时候,同时也会创建一系列功能插槽(slot chain):
- NodeSelectorSlot 负责收集资源的路径,并将这些资源的调用路径,以树状结构存储起来,用于根据调用路径来限流降级;
- ClusterBuilderSlot 则用于存储资源的统计信息以及调用者信息,例如该资源的 RT, QPS, thread count 等等,这些信息将用作为多维度限流,降级的依据;
- StatisticSlot 则用于记录、统计不同纬度的 runtime 指标监控信息;
- FlowSlot 则用于根据预设的限流规则以及前面 slot 统计的状态,来进行流量控制;
- AuthoritySlot 则根据配置的黑白名单和调用来源信息,来做黑白名单控制;
- DegradeSlot 则通过统计信息以及预设的规则,来做熔断降级;
- SystemSlot 则通过系统的状态,例如 load1 等,来控制总的入口流量;
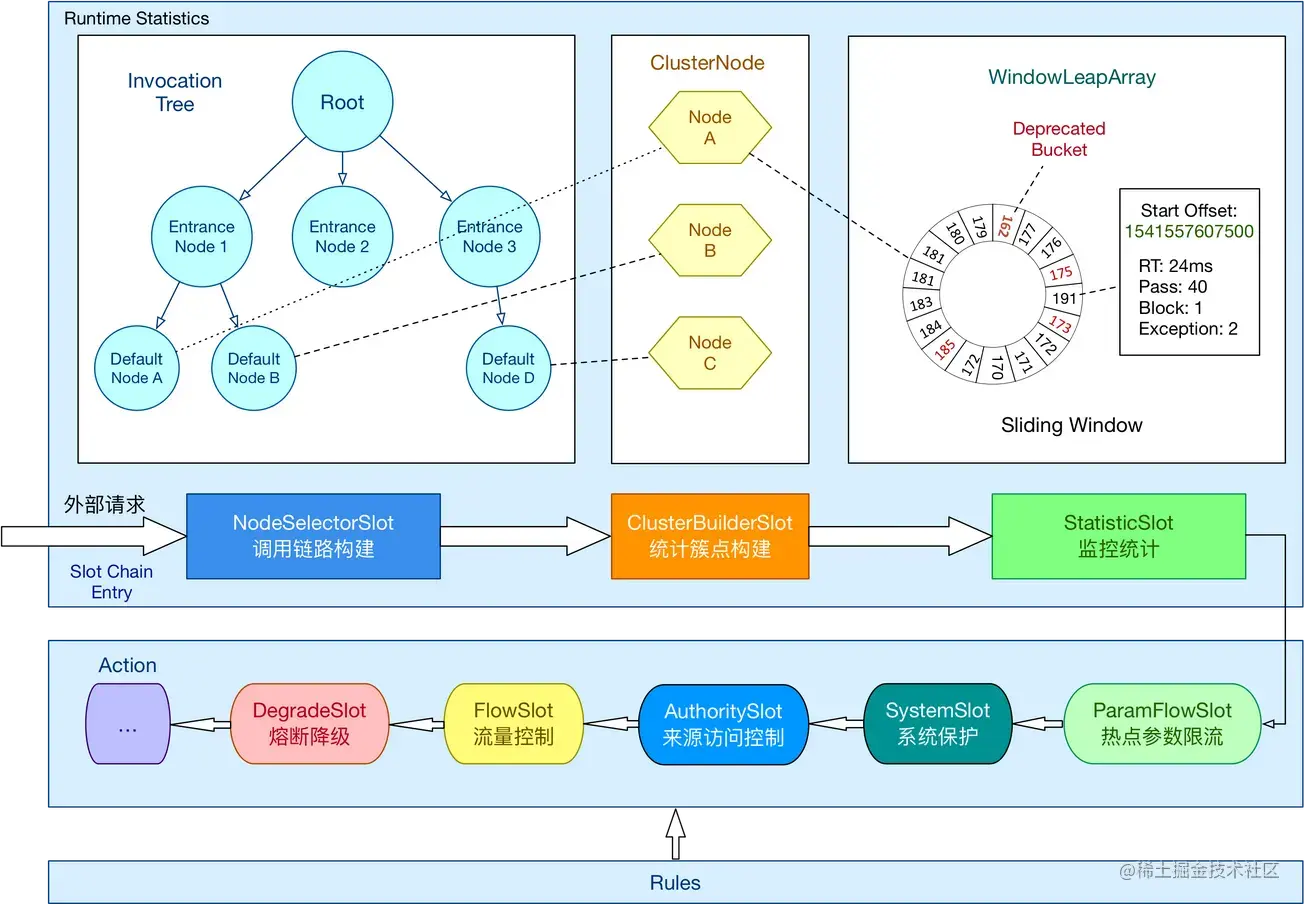
ProcessorSlotChain(核心骨架) :将不同的 Slot 按照顺序串在一起(责任链模式),从而将不同的功能(限流、降级、系统保护)组合在一起。slot chain 其实可以分为两部分:统计数据构建部分(statistic)和判断部分(rule checking)。
系统会为每个资源创建一套SlotChain。
Sentinel框架对feign适配自动为feign创建Entry,源码片段如下:
# SentinelInvocationHandler.invoke(...)
String resourceName = methodMetadata.template().method().toUpperCase() + ":" + hardCodedTarget.url() + methodMetadata.template().path();
Entry entry = null;
Object var12;
try {
Throwable ex;
try {
ContextUtil.enter(resourceName);
entry = SphU.entry(resourceName, EntryType.OUT, 1, args);
result = methodHandler.invoke(args);
return result;
} catch (Throwable var22) {
ex = var22;
if (!BlockException.isBlockException(var22)) {
Tracer.trace(var22);
}
}
if (this.fallbackFactory == null) {
throw var22;
}Sentinel框架通过AOP 切莫入口SentinelResourceAspect为@SentinelResource注解标记的资源自动创建Entry对象,源码片段如下:
@Around("sentinelResourceAnnotationPointcut()")
public Object invokeResourceWithSentinel(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
Method originMethod = this.resolveMethod(pjp);
SentinelResource annotation = (SentinelResource)originMethod.getAnnotation(SentinelResource.class);
if (annotation == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Wrong state for SentinelResource annotation");
} else {
String resourceName = this.getResourceName(annotation.value(), originMethod);
EntryType entryType = annotation.entryType();
int resourceType = annotation.resourceType();
Entry entry = null;
Object var10;
try {
Object var18;
try {
# 为资源构建 entry对象
entry = SphU.entry(resourceName, resourceType, entryType, pjp.getArgs());
Object result = pjp.proceed();
var18 = result;
return var18;
} catch (BlockException var15) {
var18 = this.handleBlockException(pjp, annotation, var15);
return var18;
} catch (Throwable var16) {
Class<? extends Throwable>[] exceptionsToIgnore = annotation.exceptionsToIgnore();
if (exceptionsToIgnore.length > 0 && this.exceptionBelongsTo(var16, exceptionsToIgnore)) {
throw var16;
}
}
if (!this.exceptionBelongsTo(var16, annotation.exceptionsToTrace())) {
throw var16;
}
this.traceException(var16);
var10 = this.handleFallback(pjp, annotation, var16);
} finally {
if (entry != null) {
entry.exit(1, pjp.getArgs());
}
}
return var10;
}
}4.1 SPI机制
Sentinel槽链中Slot执行顺序是固定的,但并不是绝对的。Sentinel将ProcessorSlot作为SPI接口进行扩展,使得SlotChain具备了扩展能力。用户可以自定义Slot并编排Slot间的顺序。

下图为Sentinel默认Slot链路实现:
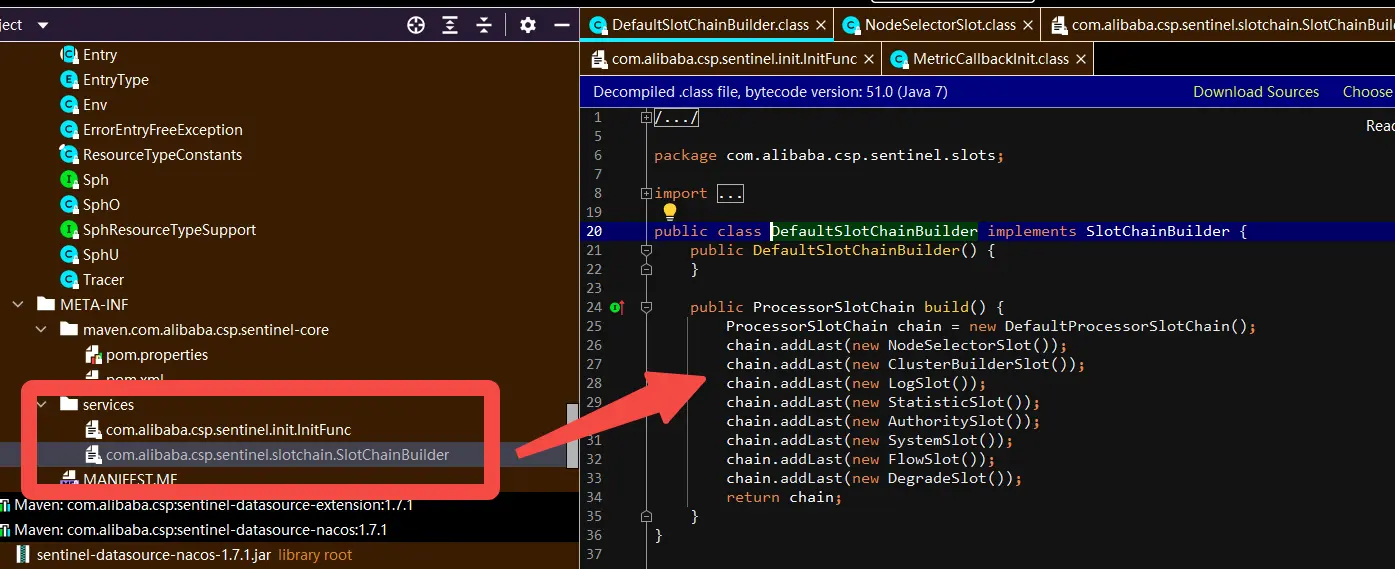
4.2 自定义Slot实现
熔断降级是保障微服务稳定性的重要手段,而在服务降级前提前预警,以便开发人员提前处理导致请求响应超时、接口异常等问题能够更加有效保障微服务的稳定性。
自定义Slot实现降级提前预警功能
熔断降级提前预警实现思路是分析了Sentinel默认ProcessorSlotChain构建思路并结合SPI机制,自定义熔断降级提前预警Slot并重新构建ProcessorSlotChain。代码实现如下:
# 降级预警实现
@Slf4j
public class DegradeEarlyWarningSlot extends AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot<DefaultNode> {
/**
* 从熔断降级规则管理器中提取降级规则并构建预警阈值规则
* @param resource
* @return
*/
private List<DegradeRule> getRuleProvider(String resource) {
List<DegradeRule> rules = DegradeRuleManager.getRules();
List<DegradeRule> earlyWarningRuleList = Lists.newArrayList();
for (DegradeRule rule : rules) {
DegradeRule earlyWarningRule = new DegradeRule();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(rule, earlyWarningRule);
double earlyWarningRuleCount;
if (rule.getGrade() == 2) { // 异常数取异常阈值-1
earlyWarningRuleCount = rule.getCount() - 1;
} else { // 异常比例 和 平均超时时间取阈值的80%作为提前预警阈值
earlyWarningRuleCount = rule.getCount() * 0.8;
}
earlyWarningRule.setCount(earlyWarningRuleCount);
earlyWarningRuleList.add(earlyWarningRule);
}
return earlyWarningRuleList.stream().filter(rule -> resource.equals(rule.getResource())).collect(Collectors.toList());
}
/**
* get origin rule
*
* @param resource
* @return
*/
private DegradeRule getOriginRule(String resource) {
List<DegradeRule> originRule = DegradeRuleManager.getRules()
.stream()
.filter(rule -> rule.getResource().equals(resource))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(originRule)) {
return null;
}
return originRule.get(0);
}
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode defaultNode, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable {
String resource = context.getCurEntry().getResourceWrapper().getName();
List<DegradeRule> rules = getRuleProvider(resource);
// 这里日志打印只是为了演示,后期计划集成disputhcer内存队列 + 飞书预警
if (rules != null) {
for (DegradeRule rule : rules) {
if (!rule.passCheck(context, defaultNode, count)) {
DegradeRule originRule = getOriginRule(resource);
String originRuleCount = originRule == null ? "未知" : String.valueOf(originRule.getCount());
log.info("DegradeEarlyWarning: 服务{} 资源{} 目前的熔断指标已经超过{},接近配置的熔断阈值:{},",
rule.getLimitApp(),
resource,
rule.getCount(),
originRuleCount);
break;
}
}
}
fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, defaultNode, count, prioritized, args);
}
@Override
public void exit(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, Object... args) {
this.fireExit(context, resourceWrapper, count, args);
}
}实现SlotChainBuilder,重新定义ProcessorSlotChain。
public class CustomerSlotChainBuilder implements SlotChainBuilder {
public CustomerSlotChainBuilder() {
}
public ProcessorSlotChain build() {
ProcessorSlotChain chain = new DefaultProcessorSlotChain();
chain.addLast(new NodeSelectorSlot());
chain.addLast(new ClusterBuilderSlot());
chain.addLast(new LogSlot());
chain.addLast(new StatisticSlot());
chain.addLast(new SystemSlot());
chain.addLast(new AuthoritySlot());
chain.addLast(new FlowSlot());
chain.addLast(new DegradeSlot());
# 在默认调用链基础上添加预警功能
chain.addLast(new DegradeEarlyWarningSlot());
return chain;
}
}添加SPI机制配置文件,在META-INF/services目录下定义一个名字为接口全限定名的文件,文件命名如下:
com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slotchain.SlotChainBuilder
com.xxxx.xx.common.sentinel.slot.CustomerSlotChainBuilder应用集成依赖添加预警功能
应用在pom文件中引入依赖,这里的依赖根据项目实际定义的基础包
<dependency>
<groupId>com.xxxx.framework</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.0.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>启动项目验证预警功能
2022-05-16 09:53:42.016 INFO [http-nio-7041-exec-1]c.m.s.d.application.impl.DsUserBaseQueryApplicationImpl.defaultFallback:46 -Go to default fallback
2022-05-16 09:53:45.902 INFO [http-nio-7041-exec-2]c.m.s.d.application.impl.DsUserBaseQueryApplicationImpl.defaultFallback:46 -Go to default fallback
2022-05-16 09:53:47.709 INFO [http-nio-7041-exec-3]c.m.s.d.application.impl.DsUserBaseQueryApplicationImpl.defaultFallback:46 -Go to default fallback
2022-05-16 09:53:49.001 INFO [http-nio-7041-exec-4]c.m.s.d.application.impl.DsUserBaseQueryApplicationImpl.defaultFallback:46 -Go to default fallback
2022-05-16 09:53:50.471 INFO [http-nio-7041-exec-5]c.m.saas.common.sentinel.slot.DegradeEarlyWarningSlot.entry:78 -DegradeEarlyWarning: 服务default 资源baseUserInfo 目前的熔断指标已经超过4.0,接近配置的熔断阈值:5.0,
2022-05-16 09:53:50.472 INFO [http-nio-7041-exec-5]c.m.s.d.application.impl.DsUserBaseQueryApplicationImpl.defaultFallback:46 -Go to default fallback
2022-05-16 09:53:51.923 ERROR[http-nio-7041-exec-6]c.m.s.d.appli根据上述日志可以看出当异常次数达到4时会提前预警。
4.3 基于 Sentinel 实现 Feign 全局异常兜底
Spring CLoud微服务间交互使用Feign技术框架,在网络请求时,可能会出现异常请求,如果还想再异常情况下使系统可用,那么就需要容错处理,使用FeignClient时可对fallback进行配置,但随着接口数不断增加,配置也越来越重复繁琐,且大多容错逻辑均一致,因此需要对容错配置进行代理,提供全局统一容错处理。
通过官方文档我们知道feign支持基于Hystrix fallbackFactory 和 fallback模式的,但是两者均需要定义相应的fallbackFactory 和 fallback处理类。参考官方示例:
@FeignClient(name = "hello", fallback = HystrixClientFallback.class)
protected interface HystrixClient {
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET, value = "/hello")
Hello iFailSometimes();
}
static class HystrixClientFallback implements HystrixClient {
@Override
public Hello iFailSometimes() {
return new Hello("fallback");
}
}
@FeignClient(name = "hello", fallbackFactory = HystrixClientFallbackFactory.class)
protected interface HystrixClient {
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET, value = "/hello")
Hello iFailSometimes();
}
@Component
static class HystrixClientFallbackFactory implements FallbackFactory<HystrixClient> {
@Override
public HystrixClient create(Throwable cause) {
return new HystrixClient() {
@Override
public Hello iFailSometimes() {
return new Hello("fallback; reason was: " + cause.getMessage());
}
};
}
}如上述示例,随着接口的增加势必会产生大量类似的模板代码。
4.3.1 扩展SentinelFeign Builder
4.3.1.1 思路
通过对 spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinel包源码分析,该包仅简单使用了四个类就实现对feign的支持。核心原理是通过自定义SentinelFeign构建器重新实现了feign对象初始化,添加了对Sentinel熔断限流的支持。查看核心源码如下:
public Feign build() {
super.invocationHandlerFactory(new InvocationHandlerFactory() {
public InvocationHandler create(Target target, Map<Method, MethodHandler> dispatch) {
Object feignClientFactoryBean = Builder.this.applicationContext.getBean("&" + target.type().getName());
Class fallback = (Class)Builder.this.getFieldValue(feignClientFactoryBean, "fallback");
Class fallbackFactory = (Class)Builder.this.getFieldValue(feignClientFactoryBean, "fallbackFactory");
String beanName = (String)Builder.this.getFieldValue(feignClientFactoryBean, "contextId");
if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName)) {
beanName = (String)Builder.this.getFieldValue(feignClientFactoryBean, "name");
}
if (Void.TYPE != fallback) {
Object fallbackInstance = this.getFromContext(beanName, "fallback", fallback, target.type());
return new SentinelInvocationHandler(target, dispatch, new feign.hystrix.FallbackFactory.Default(fallbackInstance));
} else if (Void.TYPE != fallbackFactory) {
FallbackFactory fallbackFactoryInstance = (FallbackFactory)this.getFromContext(beanName, "fallbackFactory", fallbackFactory, FallbackFactory.class);
return new SentinelInvocationHandler(target, dispatch, fallbackFactoryInstance);
} else {
return new SentinelInvocationHandler(target, dispatch);
}
}可以看出当未设置fallback 或者 fallbackFactory时,不会传递fallbackFactory到SentinelInvocationHandler。因此解决思路是:
- 自定义全局异常兜底处理函数CustomCommonFallbackFactory;
- 改写Feign build()逻辑,当未定义fallback 或者 fallbackFactory时,传入公共的CustomCommonFallbackFactory到SentinelInvocationHandler。
4.3.1.2 程序设计
自定义全局异常兜底处理函数CustomCommonFallbackFactory,具体实现如下:
@Slf4j
@AllArgsConstructor
public class CustomCommonFallback<T> implements MethodInterceptor {
private final Class<T> targetType;
private final String targetName;
private final Throwable cause;
@Nullable
@Override
public Object intercept(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects, MethodProxy methodProxy) {
String errorMessage = cause.getMessage();
log.error("Feign API Fallback:[{}.{}] serviceId:[{}] message:[{}]", targetType.getName(), method.getName(), targetName, errorMessage);
// BusinessException,直接返回
if (cause instanceof BusinessException) {
BusinessException be = (BusinessException) cause;
return Result.of(false, null, be.getCode(), be.getMsg(), null);
} else if (cause instanceof FeignException) {
FeignException exception = (FeignException) cause;
// 提取业务异常
return Result.of(false, null, exception.status(), exception.contentUTF8(), null);
} else {
// 提取原始异常
Throwable causeA = cause.getCause();
if (causeA != null && causeA instanceof ClientException) {
return Result.of(false, null, -1, String.format("%s服务已下线&服务状态不正常.", method.getName()), null);
} else {
return Result.of(false, null, -1, "系统未知异常.", null);
}
}
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) {
return true;
}
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) {
return false;
}
CustomCommonFallback<?> that = (CustomCommonFallback<?>) o;
return targetType.equals(that.targetType);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(targetType);
}
}
@AllArgsConstructor
public class CustomCommonFallbackFactory<T> implements FallbackFactory<T> {
private final Target<T> target;
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public T create(Throwable cause) {
final Class<T> targetType = target.type();
final String targetName = target.name();
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
enhancer.setSuperclass(targetType);
enhancer.setUseCache(true);
enhancer.setCallback(new CustomCommonFallback<>(targetType, targetName, cause));
return (T) enhancer.create();
}
}改写Feign build()逻辑,当未定义fallback 或者 fallbackFactory时,传入公共的CustomCommonFallbackFactory到SentinelInvocationHandler。这里需要注意,由于SentinelInvocationHandler访问权限限制包内访问,因此将新建的类放com.alibaba.cloud.sentinel.feign目录下。具体代码如下:
public final class CustomSentinelFeign {
private CustomSentinelFeign() {
}
public static CustomSentinelFeign.Builder builder() {
return new CustomSentinelFeign.Builder();
}
public static final class Builder extends feign.Feign.Builder implements ApplicationContextAware {
private Contract contract = new Contract.Default();
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
private FeignContext feignContext;
@Override
public feign.Feign.Builder invocationHandlerFactory(feign.InvocationHandlerFactory invocationHandlerFactory) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
@Override
public CustomSentinelFeign.Builder contract(Contract contract) {
this.contract = contract;
return this;
}
/**
* 自定义feign构建器,在模式SentinelFeign基础增加 CustomCommonFallbackFactory,
* 当feign配置不指定兜底函数将使用默认CustomCommonFallbackFactory
* @return
*/
@Override
public Feign build() {
super.invocationHandlerFactory(new InvocationHandlerFactory() {
public InvocationHandler create(Target target, Map<Method, MethodHandler> dispatch) {
Object feignClientFactoryBean = CustomSentinelFeign.Builder.this.applicationContext.getBean("&" + target.type().getName());
Class fallback = (Class) getFieldValue(feignClientFactoryBean, "fallback");
Class fallbackFactory = (Class) getFieldValue(feignClientFactoryBean, "fallbackFactory");
String beanName = (String) CustomSentinelFeign.Builder.this.getFieldValue(feignClientFactoryBean, "contextId");
if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName)) {
beanName = (String) CustomSentinelFeign.Builder.this.getFieldValue(feignClientFactoryBean, "name");
}
if (Void.TYPE != fallback) {
Object fallbackInstance = this.getFromContext(beanName, "fallback", fallback, target.type());
return new SentinelInvocationHandler(target, dispatch, new FallbackFactory.Default(fallbackInstance));
} else if (Void.TYPE != fallbackFactory) {
FallbackFactory fallbackFactoryInstance = (FallbackFactory) this.getFromContext(beanName, "fallbackFactory", fallbackFactory, FallbackFactory.class);
return new SentinelInvocationHandler(target, dispatch, fallbackFactoryInstance);
} else {
// 默认的 fallbackFactory
CustomCommonFallbackFactory customFallbackFactory = new CustomCommonFallbackFactory(target);
return new SentinelInvocationHandler(target, dispatch, customFallbackFactory);
}
}
private Object getFromContext(String name, String type,
Class fallbackType, Class targetType) {
Object fallbackInstance = feignContext.getInstance(name,
fallbackType);
if (fallbackInstance == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(String.format(
"No %s instance of type %s found for feign client %s",
type, fallbackType, name));
}
if (!targetType.isAssignableFrom(fallbackType)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(String.format(
"Incompatible %s instance. Fallback/fallbackFactory of type %s is not assignable to %s for feign client %s",
type, fallbackType, targetType, name));
}
return fallbackInstance;
}
});
super.contract(new SentinelContractHolder(contract));
return super.build();
}
private Object getFieldValue(Object instance, String fieldName) {
Field field = ReflectionUtils.findField(instance.getClass(), fieldName);
field.setAccessible(true);
try {
return field.get(instance);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
// ignore
}
return null;
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
feignContext = this.applicationContext.getBean(FeignContext.class);
}
}
}最后注入新定义的Bean
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnClass({SphU.class, Feign.class})
public class CustomFeignAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
@Scope("prototype")
@ConditionalOnClass({SphU.class, Feign.class})
@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "feign.sentinel.enabled")
@Primary
public Feign.Builder feignSentinelBuilder() {
return CustomSentinelFeign.builder();
}
}4.3.2 使用
要使用Sentinel全局异常兜底需要引入基础依赖包并且在配置文件中配置feign.sentinel.enabled=true,注释掉feign.hystrix.enabled=true
feign.sentinel.enabled=true
feign.hystrix.enabled=false
<dependency>
<groupId>com.xxxx.framework</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.0.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>定义feign不配置fullback
@FeignClient(contextId = "dsUserBaseApiClient", name = "demo-xxxx-server")
public interface DsUserBaseApiClient extends DsUserBaseApi {
}调用feign接口,当出现异常打印日志,可以看出定义的公共CustomCommonFallback触发生效。
2022-06-13 20:23:52.626 ERROR[http-nio-7042-exec-1]c.m.s.c.sentinel.feign.fallback.CustomCommonFallback.intercept:32 -Feign API Fallback:[com.xxxxx.saas.demoapi.feign.DsUserBaseApiClient.getBaseUserInfo] serviceId:[demo-xxxxx-server] message:[com.netflix.client.ClientException: Load balancer does not have available server for client: demo-xxxx-server]