一、Qwen1.5介绍
通义千问为阿里云研发的大语言系列模型。千问模型基于Transformer架构,在超大规模的预训练数据上进行训练得到。预训练数据类型多样,覆盖广泛,包括大量网络文本、专业书籍、代码等。同时,在预训练模型的基础之上,使用对齐机制打造了模型的chat版本。
| 模型 | 介绍 | 模型下载 |
|---|---|---|
| qwen1.5-110b-chat | 通义千问1.5对外开源的110B规模参数量的经过人类指令对齐的chat模型。 | 魔搭社区 |
| qwen1.5-72b-chat | 通义千问1.5对外开源的72B规模参数量的经过人类指令对齐的chat模型。 | 魔搭社区 |
| qwen1.5-32b-chat | 通义千问1.5对外开源的32B规模参数量的经过人类指令对齐的chat模型 | 魔搭社区 |
| qwen1.5-14b-chat | 通义千问1.5对外开源的14B规模参数量的经过人类指令对齐的chat模型。 | 魔搭社区 |
| qwen1.5-7b-chat | 通义千问1.5对外开源的7B规模参数量是经过人类指令对齐的chat模型。 | 魔搭社区 |
| qwen1.5-4b-chat | 通义千问1.5对外开源的4B规模参数量是经过人类指令对齐的chat模型。 | 魔搭社区 |
| qwen1.5-0.5b-chat | 通义千问1.5对外开源的0.5B规模参数量的经过人类指令对齐的chat模型。 | 魔搭社区 |
| [开源模型序列] |
二、本地部署Qwen1.5
由于资源问题,本机只能使用cpu运行qwen1.5_4b_chat,所以本次操作基于上述条件执行。
3.1 下载模型文件
可以Hugging Face Hub 下载模型,如果从 HuggingFace 下载比较慢,也可以从 ModelScope 中下载:
bash
#从ModelScope下载模型
git clone https://www.modelscope.cn/qwen/Qwen1.5-4B-Chat.git3.2 安装依赖
可以通过Conda 创建Python环境安装依赖。
bash
# vi requirements.txt
# basic requirements
fastapi>=0.110.0
uvicorn>=0.29.0
pydantic>=2.7.0
tiktoken>=0.6.0
sse-starlette>=2.0.0
transformers>=4.37.0
torch>=2.1.0
sentencepiece>=0.2.0
sentence-transformers>=2.4.0
accelerate
#安装依赖
pip install requirements.txt安装过程可能重新网络问题,无法下载相关文件,可以重复执行多次;也可以去PyPI下载相关whl文件,离线安装。
3.2 编码实现
通用python编码实现部署模型和提供RESTful API服务。
python
# 文件名:api-server-llm.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# This is a sample Python script.
import argparse
import datetime
import uuid
from threading import Thread
import os
from typing import List, Optional
from pydantic import BaseModel
# Press Shift+F10 to execute it or replace it with your code.
# Press Double Shift to search everywhere for classes, files, tool windows, actions, and settings.
import uvicorn
from fastapi import FastAPI, Request, Response
from fastapi.responses import JSONResponse
from sse_starlette.sse import EventSourceResponse
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM, TextIteratorStreamer
from utils import num_tokens_from_string
# 声明API
app = FastAPI(default_timeout=1000 * 60 * 10)
# chat消息
class ChatMessage(BaseModel):
# 角色
role: str = None
# chat内容
content: str = None
# chat请求信息
class ChatRequest(BaseModel):
# 对话信息
messages: List[ChatMessage]
# 模型平台
platform: str = None
# 具体模型名称
model: str = None
# 客户端id
clientId: str = None
stream: Optional[bool] = False
# 当前对话的模型输出内容
class ChatResponseChoice(BaseModel):
# 模型推理终止的原因
finishReason: str
# 消息内容
messages: ChatMessage
# tokens 统计数据
class ResponseUsage(BaseModel):
# 模型输入的 tokens 数量
outputTokens: int
# 用户输入的 tokens 数量
inputTokens: int
# chat返回信息
class ChatResponse(BaseModel):
clientId: str = None
usage: ResponseUsage
choices: List[ChatResponseChoice]
# 统一异常处理
@app.exception_handler(Exception)
async def all_exceptions_handler(request: Request, exc: Exception):
"""
处理所有异常
"""
return JSONResponse(
status_code=500,
content={
"msg": str(exc)
}
)
# 自定义中间件
@app.middleware("http")
async def unified_interception(request: Request, call_next):
# 在这里编写你的拦截逻辑
# 例如,检查请求的header或参数
# 如果不满足条件,可以直接返回响应,不再调用后续的路由处理
token = request.headers.get("Authorization")
# if token is None:
# return JSONResponse({"message": "Missing Authorization"}, status_code=401)
# 如果满足条件,则继续调用后续的路由处理
response = await call_next(request)
# 在这里编写你的响应处理逻辑
# 例如,添加或修改响应头
# 返回最终的响应
return response
# 监控
@app.get("/api/models")
async def models():
# 构造返回数据
response = {
"model": MODEL_NAME
}
return JSONResponse(response, status_code=200)
# 构造 回复消息对象
def create_chat_response(request_id: str, role: str, content: str, input_tokens: int, output_tokens: int,
finish_reason: str):
now = datetime.datetime.now() # 获取当前时间
time = now.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S") # 格式化时间为字符串
chat_message = {
"output": {
"choices": [{
"finish_reason": finish_reason,
"message": {
"role": role,
"content": content
}
}]
},
"request_id": request_id,
"usage": {
"input_tokens": input_tokens,
"output_tokens": output_tokens,
"total_tokens": (input_tokens + output_tokens)
},
"time": time
}
return chat_message
# 获取流式数据
def predict_stream(generation_kwargs: dict, request_id: str, input_tokens: int):
thread = Thread(target=model.generate, kwargs=generation_kwargs)
thread.start()
output_tokens = 0
for new_text in streamer:
output_tokens = output_tokens + num_tokens_from_string(str(new_text))
# 构造返回数据
yield str(create_chat_response(request_id=request_id, role="assistant", content=new_text,
input_tokens=input_tokens, output_tokens=output_tokens, finish_reason=""))
yield str(create_chat_response(request_id=request_id, role="assistant", content="", input_tokens=input_tokens,
output_tokens=output_tokens, finish_reason="stop"))
@app.post("/api/v1/chat/completions")
async def completions(request: ChatRequest):
# if MODEL_NAME != request.model:
# return JSONResponse({"msg": "模型异常!"}, status_code=500)
if len(request.messages) <= 0:
return JSONResponse({"msg": "消息不能为空!"}, status_code=500)
# 请求id
request_id = str(uuid.uuid4())
# 计算输入tokens
input_tokens = sum(num_tokens_from_string(message.content) for message in request.messages)
# 使用自带的聊天模板,格式化对话记录
text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(request.messages, tokenize=False, add_generation_prompt=True)
model_inputs = tokenizer(text, return_tensors="pt").to("cpu")
if request.stream:
print("----流式-----")
# 流式对象
generation_kwargs = dict(**model_inputs, streamer=streamer, max_new_tokens=4096,
pad_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id,
num_beams=1, do_sample=True, top_p=0.8,
temperature=0.3)
generate = predict_stream(generation_kwargs=generation_kwargs, request_id=request_id, input_tokens=input_tokens)
return EventSourceResponse(generate, media_type="text/event-stream")
print("----非流式-----")
# 非流式
generated_ids = model.generate(
model_inputs.input_ids
, max_new_tokens=512
)
generated_ids = [
output_ids[len(input_ids):] for input_ids, output_ids in zip(model_inputs.input_ids, generated_ids)
]
response = tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)[0]
# 计算输出tokens
output_tokens = num_tokens_from_string(response)
# 构造返回数据
result = create_chat_response(request_id=request_id, role="assistant", content=response, input_tokens=input_tokens,
output_tokens=output_tokens, finish_reason="stop")
return JSONResponse(result, status_code=200)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 定义命令行解析器对象
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='大语言模型参数解析器')
# 添加命令行参数、默认值
parser.add_argument("--host", type=str, default="0.0.0.0")
parser.add_argument("--port", type=int, default=8860)
parser.add_argument("--model_path", type=str, default="")
parser.add_argument("--model_name", type=str, default="")
# 从命令行中结构化解析参数
args = parser.parse_args()
# 模型路径
MODEL_PATH = args.model_path
MODEL_NAME = args.model_name
if len(MODEL_PATH) <= 0:
raise Exception("大语言模型路径不能为空!")
# 如果没有传入模型名称,则从路径中获取
if len(MODEL_NAME) == 0:
MODEL_DIR, MODEL_NAME = os.path.split(MODEL_PATH)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(MODEL_PATH, trust_remote_code=True)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
MODEL_PATH, trust_remote_code=True, device_map='auto'
).eval()
# 流式输出
streamer = TextIteratorStreamer(tokenizer=tokenizer, skip_prompt=True, skip_special_tokens=True)
# 启动 uvicorn 服务
uvicorn.run(app, host=args.host, port=args.port)3.3 运行服务
bash
# 运行脚本,指定模型路径
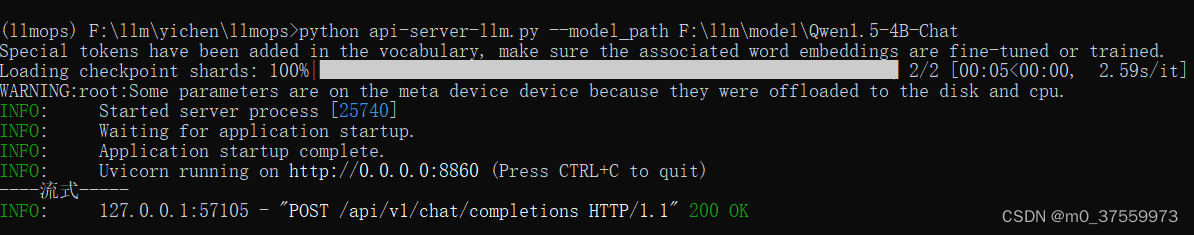
python api-server-llm.py --model_path=F:\llm\model\Qwen1.5-4B-Chat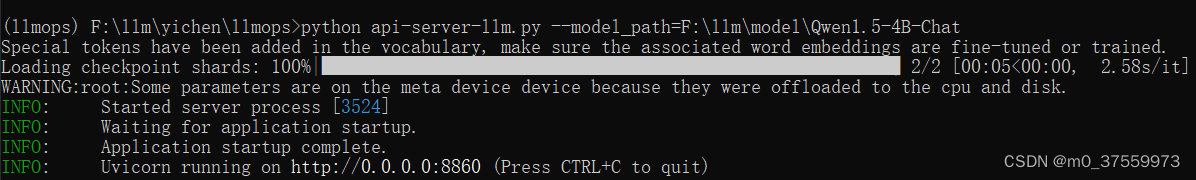
3.4 使用API访问
bash
curl -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" 'http://localhost:8860/api/v1/chat/completions' \
-d '{
"platform": "tongyi",
"model": "Qwen1.5-4B-Chat",
"stream":true,
"messages":[
{
"role": "user",
"content": "你好,你是谁?"
}
]
}'