链表反转--理解链表指针的基本操作
链表反转的方法--主要是理解链表指针
-
根据值创建新列表
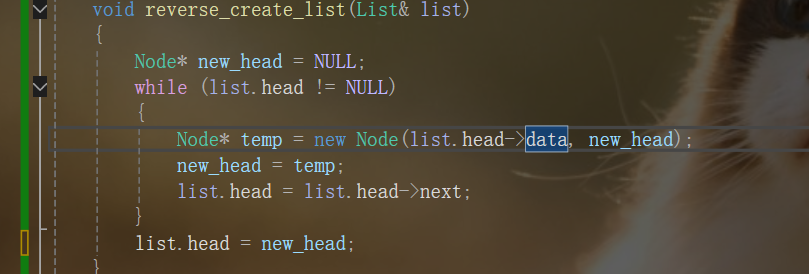
-
用一个链表指针代替整个新链表
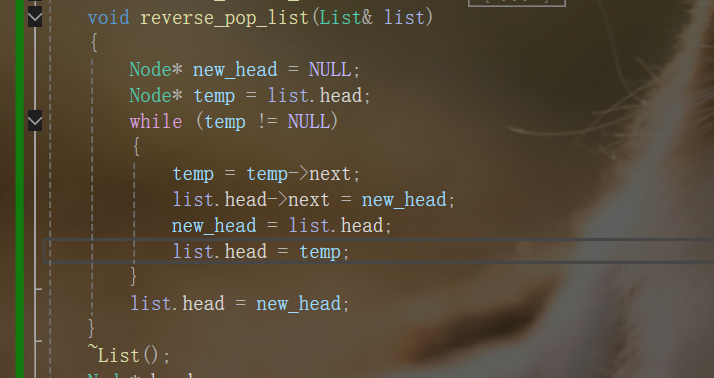
-
两个链表的赋值
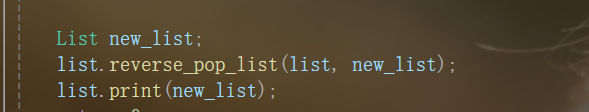
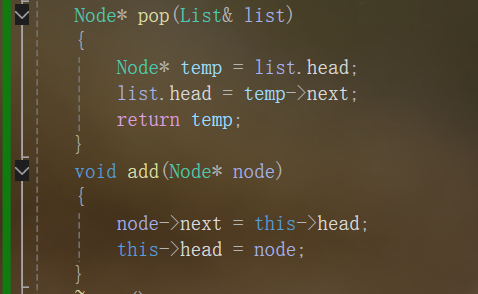

-
递归求解反向链表

-
用一个链表代替前后链表数据的跳动

链表心得
mad等号前面是指针指向,等号后面是节点
注意注意注意注意注意注意
mad等号前面是指针指向,等号后面是节点
其实对象作为虚拟头节点好理解一些
类指针如果没有初始化是不能够调用其中的属性
这种时候最好改的方式是变成类

这个就是错误的,改为类即可

类节点是对象和指针区别:
对象的话可以看着是一个存在的虚空节点
指针的话它其实就是头节点本身,不存在虚空节点这种说法
两者的区别可看,数据结构下面的链表和反转链表
cpp
//链表
#include <iostream>
#include<iterator>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
Node();
~Node();
Node(int data, Node* next);
int data;
Node* next;
private:
};
Node::Node(int data, Node* next)
:data(data), next(next)
{
}
Node::Node()
{
}
Node::~Node()
{
}
class Singlelist
{
public:
Singlelist();
~Singlelist();
void print();
void add(int data);
void iter_print();
//尾插
void add_tail(int data);
Node* index_find(int index)
{
int i = 0;
Node* p = &node_head;
for (; p != NULL;)
{
p = p->next;
if (i == index)
{
return p;
}
++i;
}
cout << "index out of range" << endl;
return NULL;
}
void inde_add(int index, int data)
{
if (index == 0)
{
add(data);
return;
}
Node* p = index_find(index - 1);
if (p == NULL)
{
cout << "index out of range" << endl;
return;
}
p->next = new Node(data, p->next);
}
void index_remove(int index)
{
if (node_head.next == NULL)
{
return;
}
if (index == 0)
{
node_head.next = node_head.next->next;;
return;
}
Node* p = index_find(index - 1);
if (p->next == NULL)
{
cout << "index out of range" << endl;
return;
}
p->next = p->next->next;
}
void merge(Singlelist& list2)
{
Node* p1 = &(this->node_head);
while (p1->next != NULL)
{
p1 = p1->next;
}
p1->next = list2.node_head.next;
list2.node_head.next = NULL;
}
Node node_head;
private:
};
Singlelist::Singlelist()
{
this->node_head.next = new Node(6666, NULL);
}
Singlelist::~Singlelist()
{
//删除节点
while (node_head.next != NULL)
{
Node* temp = node_head.next;
node_head.next = node_head.next->next;
delete temp;
temp = NULL;
}
}
void Singlelist::print()
{
Node p = node_head;
while (p.next != NULL)
{
cout << p.next->data << " " << endl;
p.next = p.next->next;
}
}
//头插
void Singlelist::add(int data)
{
node_head.next = new Node(data, node_head.next);
}
void Singlelist::iter_print()
{
for (Node* p = &node_head; p->next != NULL;)
{
cout << p->next->data << " ";
p = p->next;
}
}
void Singlelist::add_tail(int data)
{
Node* p = &node_head;
while (p->next != NULL)
{
p = p->next;
}
p->next = new Node(data, NULL);
}
int main2()
{
Singlelist list;
Singlelist list2;
list2.add_tail(1);
list2.add_tail(2);
list2.add_tail(3);
list2.add_tail(4);
list2.iter_print();
/*list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.add(4);
list.add(5);
list.print();*/
/*list.add_tail(6);
list.iter_print();*/
/*list.index_find(2);*/
list.add(3);
list.add(4);
list.add(5);
list.inde_add(1, 10);
cout << endl;
list.iter_print();
cout << endl;
list.index_remove(3);
list.iter_print();
cout << endl;
list.merge(list2);
list.iter_print();
return 0;
}
cpp
//反转链表
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
Node();
~Node();
Node(int data, Node* next = NULL) :data(data), next(next) {}
int data;
Node* next;
private:
};
Node::Node()
{
}
Node::~Node()
{
}
class List
{
public:
List() :head(NULL) {}
void print(List& list)
{
Node* temp = list.head;
while (temp != NULL)
{
cout << temp->data << " ";
temp = temp->next;
}
delete temp;
}
void reverse_create_list(List& list)
{
Node* new_head = NULL;
while (list.head != NULL)
{
Node* temp = new Node(list.head->data, new_head);
new_head = temp;
list.head = list.head->next;
}
list.head = new_head;
}
void reverse_pop_list(List& list, List& new_list)
{
while (list.head != NULL)
{
Node* temp = list.pop(list);
new_list.add(temp);
}
}
Node* reverse_recursion_list(Node* node)
{
if (node == NULL || node->next == NULL)
{
//这里需要返回的是节点而不是NULL
return node;
}
Node* new_head = reverse_recursion_list(node->next);
cout << new_head->data << " ";
node->next->next = node;
node->next = NULL;
return new_head;
}
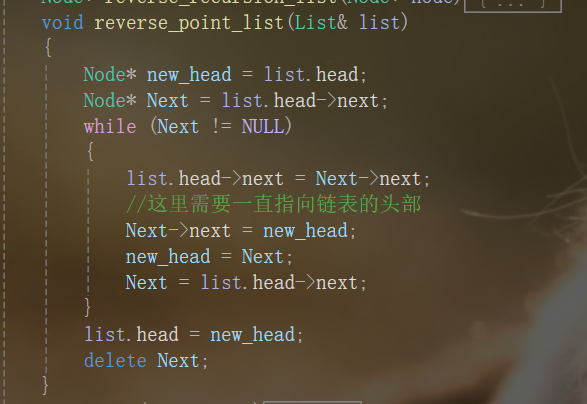
void reverse_point_list(List& list)
{
Node* new_head = list.head;
Node* Next = list.head->next;
while (Next != NULL)
{
list.head->next = Next->next;
//这里需要一直指向链表的头部
Next->next = new_head;
new_head = Next;
Next = list.head->next;
}
list.head = new_head;
delete Next;
}
Node* pop(List& list)
{
Node* temp = list.head;
list.head = temp->next;
return temp;
}
void add(Node* node)
{
node->next = this->head;
this->head = node;
}
~List();
Node* head;
private:
};
List::~List()
{
while (this->head != NULL)
{
Node* temp = this->head;
this->head = this->head->next;
delete temp;
}
cout << "List Destructor called" << endl;
}
int main()
{
List list;
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; )
{
list.head = new Node(i, list.head);
++i;
}
list.print(list);
cout << endl;
/*list.reverse_create_list(list);*/
/*List new_list;
list.reverse_pop_list(list, new_list);*/
/*list.head = list.reverse_recursion_list(list.head);*/
list.reverse_point_list(list);
list.print(list);
return 0;
}