一、目录和文件
在当前目录下使用touch 创建一个名为 -a的文件:
touch -a ; // 错误,
touch -- -a//正确
touch ./-a 正确
ls -n可以看到对象的用户id,可以在/etc/passwd中查看,/etc/group可以看到组号
获取文件属性
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int stat(const char *pathname, struct stat *statbuf);
int fstat(int fd, struct stat *statbuf);
int lstat(const char *pathname, struct stat *statbuf);
#include <fcntl.h> /* Definition of AT_* constants */
#include <sys/stat.h>
int fstatat(int dirfd, const char *pathname, struct stat *statbuf,
int flags);
struct stat {
dev_t st_dev; /* ID of device containing file */ 包含这个文件的设备ID号
ino_t st_ino; /* Inode number */ ls -i可以看到inode号
mode_t st_mode; /* File type and mode */ 权限信息(16位)
nlink_t st_nlink; /* Number of hard links */ 硬链接数
uid_t st_uid; /* User ID of owner */ 用户id
gid_t st_gid; /* Group ID of owner */ 组id
dev_t st_rdev; /* Device ID (if special file) */ 设备的ID号
off_t st_size; /* Total size, in bytes */ 字节数
blksize_t st_blksize; /* Block size for filesystem I/O */ 块大小,一般512B
blkcnt_t st_blocks; /* Number of 512B blocks allocated */ 占的块数
/* Since Linux 2.6, the kernel supports nanosecond
precision for the following timestamp fields.
For the details before Linux 2.6, see NOTES. */
struct timespec st_atim; /* Time of last access */ 上次访问时间
struct timespec st_mtim; /* Time of last modification */上次修改时间
struct timespec st_ctim; /* Time of last status change */上次改变时间
#define st_atime st_atim.tv_sec /* Backward compatibility */
#define st_mtime st_mtim.tv_sec
#define st_ctime st_ctim.tv_sec
};
stat命令也可以查看信息
stat
将文件属性信息填入statbuf结构体,成功返回0.失败返回-1
fstat
传入文件描述符整形
lstat
传入链接文件
cpp
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
static off_t flen(const char *file)
{
struct stat st;
if(stat(file,&st)<0 )
{
perror("stat()");
exit(-1);
}
return st.st_size;
}
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
if(argc <2)
return -1;
off_t len = flen(argv[1]);
printf("%lld \n",(long long)len);
return 0;
}空洞文件
占用字节size大小,但是在linux下不占用磁盘空间,磁盘空间占用有:块大小*块总数。stat命令查看。
cpp
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int main(int argc,char *argv[] )
{
if(argc <2)
return -1;
int fd;
fd = open(argv[1],O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC,0600);
if(fd<0)
{
perror("open()");
return -1;
}
// lseek(fd,5*1,SEEK_SET);
lseek(fd,5LL*1024LL*1024LL*1024LL-1LL,SEEK_SET);//数字添加LL,防止计算过程中精度溢出
write(fd,"",1);//发生一次系统调用,否则不占用空间
close(fd);
return 0;
}文件访问权限
st_mode是一个16位的位图,用于表示文件的类型,文件访问权限及特殊的权限位,参考man手册:man 2 stat
umask
使用命令:umask 可以设置 默认是 0002
umask 0022
作用:防止产生权限过松的文件
文件权限管理
chmod
chmod命令更改文件的权限:chmod 777 temp.file 也可以使用 chmod a+x temp.file
chmod函数:int chmod(const char *pathname, mode_t mode);
fchmod
fchmod函数:int fchmod(int fd, mode_t mode);
粘住位
粘住位又叫做T位。现在不太常用。 ll / 查看tmp目录下的文件
drwxrwxrwt 19 root root 4096 Jun 5 04:53 tmp/ (权限最后是t代表是t位)
文件系统
文件或数据的存储和管理。
FAT
FAT16/32本质是:静态存储的单链表(闭源,害怕大文件)
UFS
(开源,不怕大文件),缺陷:不善于管理小文件
面试题:给一个无符号的32位数,什么方法获取二进制有多少零,多少一?
算法-求二进制数中1的个数 - 翰墨小生 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
硬链接与符号连接
硬链接
ln /tmp/bigfile /tmp/bigfile_link ln 源文件路径 目标文件路径
删除源文本不会影响硬链接文件
符号链接
ln -s /tmp/bigfile /tmp/bigfile_link ln 源文件路径 目标文件路径
符号链接文件的size为文件名长度,块大小为0,删除源文件链接文件不可以。
函数:
int link(const char *oldpath, const char *newpath); (链接)
int unlink(const char *pathname);(删除,系统调用,不可移植)
int remove(const char *pathname);(库函数-可移植)
int rename(const char *oldpath, const char *newpath);(系统调用)
硬链接计数为0时会删除数据,否则硬链接技计数-1
硬链接与目录项是同义词,建立连接有限制:不能给分区建立,不能给目录建立。符号连接:可以跨分区,可以给目录建立。
utime
更改时间:最后一次读和写的时间。
struct utimbuf {
time_t actime; /* access time */
time_t modtime; /* modification time */
};
int utime(const char *filename, const struct utimbuf *times);
目录的创建和销毁
mkdir int mkdir(const char *pathname, mode_t mode);
rmdir int rmdir(const char *pathname);
切换目录
int chdir(const char *path);
int fchdir(int fd);
改变工作路径
chroot假根技术,安全机制。
char *getcwd(char *buf, size_t size);
分析目录
glob
#include <glob.h>
int glob(const char *pattern, int flags,
int (*errfunc) (const char *epath, int eerrno),
glob_t *pglob);
void globfree(glob_t *pglob);
cpp
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <glob.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define PAT "/etc/a*.conf"
#define PAT "./" //不包括隐藏的文件
static int errfunc(const char*errpath,int eerrno)
{
fprintf(stderr,"%s \n",errpath);
fprintf(stderr,"errno = %s \n",strerror(eerrno));
return 0;
}
int main(int argc,char*argv[])
{
glob_t globres;
int err = glob(PAT,0,errfunc,&globres);
if(err)
{
printf("err glob %d \n",err);
exit(1);
}
for(int i=0;i<globres.gl_pathc;i++)
{
puts(globres.gl_pathv[i]);
}
globfree(&globres);
return 0;
}注意:glob第三个参数传递的是函数地址,函数中的名称一定要保持一致,否则会有警告。
opendir、closedir、readdir、rewinddir、seekdir、telldir
cpp
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <glob.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#define PAT "/etc"
#define PAT "./"
int main(int argc,char*argv[])
{
DIR* dp;
struct dirent*cur;
dp = opendir(PAT);
if(dp == NULL)
exit(1);
while(1)
{
cur = readdir(dp);
if(cur ==NULL)
break;
puts(cur->d_name);
}
closedir(dp);
return 0;
}du命令
查看文件/目录所占空间大小,默认以K为单位。stat中一个Block大小单位为一块512B。
mydu
cpp
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <glob.h>
#define PATHSIZE 1024
static int path_noloop(const char*path)
{
char*pos;
pos = strrchr(path,'/');
if(pos ==NULL)
{
exit(1);
}
if( strcmp(pos+1 ,".") ==0 || strcmp(pos+1,"..")==0 )
return 0;
return 1;
}
static int64_t mydu(const char*path)
{
struct stat st;//可以加static进行优化
char nextpath[PATHSIZE]; //可以加static进行优化
glob_t res;
int64_t sum;
if(lstat(path,&st)<0)//lstat解析连接文件
{
perror("lstat");
exit(1);
}
if(!S_ISDIR(st.st_mode))
{
//非目录
return st.st_blocks;
}
//目录
int ret;
strncpy(nextpath,path,PATHSIZE-1);
strncat(nextpath,"/*",PATHSIZE-1);
ret = glob(nextpath,0,NULL,&res);
strncpy(nextpath,path,PATHSIZE-1 );
strncat(nextpath,"/.*",PATHSIZE-1);
printf("nextpath = %s \n",nextpath);
ret = glob(nextpath,GLOB_APPEND,NULL,&res);
printf("glob =%d \n",ret);
if(ret)//特殊要求指定为追加
{
perror("glob()");
exit(1);
}
printf("res = %ld \n",res.gl_pathc);
sum = 0;
for(size_t i=0;i< res.gl_pathc;i++)
{
printf("res = %s \n",res.gl_pathv[i]);
if(path_noloop(res.gl_pathv[i]) )
{
sum += mydu(res.gl_pathv[i]);
}
}
sum+= st.st_blocks;
return sum;
}
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
if(argc <2)
{
fprintf(stderr,"Usage...\n");
return -1;
}
int64_t ret;
ret = mydu(argv[1]);
printf("block %ld \n",ret/2);
return 0;
}二、系统数据文件和信息
/etc/passed
可以看到当前linux下,用户名和用户id对象关系。
struct passwd *getpwnam(const char *name);
struct passwd *getpwuid(uid_t uid);
struct passwd {
char *pw_name; /* username */
char *pw_passwd; /* user password */
uid_t pw_uid; /* user ID */
gid_t pw_gid; /* group ID */
char *pw_gecos; /* user information */
char *pw_dir; /* home directory */
char *pw_shell; /* shell program */
};
cpp
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pwd.h>
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
if(argc <2)
{
return -1;
printf("Usage...\n");
}
struct passwd*pw;
pw = getpwuid(atoi(argv[1]) );
puts(pw->pw_name);
return 0;
}/etc/group
可以看到当前linux下,用户组直接的关系。
struct group *getgrnam(const char *name);
struct group *getgrgid(gid_t gid);
struct group {
char *gr_name; /* group name */
char *gr_passwd; /* group password */
gid_t gr_gid; /* group ID */
char **gr_mem; /* NULL-terminated array of pointers
to names of group members */
};
cpp
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <grp.h>
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
if(argc <2)
{
return -1;
printf("Usage...\n");
}
struct group*gr;
gr = getgrgid(atoi(argv[1]) );
puts(gr->gr_name);
return 0;
}/etc/shadow
一个很重要的文件,不可读,不可写,是属于密码的加密文件。
$1开头代表是MD5加密, +盐(杂字串)
$2开头代表是Blowfish 加密
$5开头代表是SHA-256 加密
$6开头代表是SHA-512 加密
struct spwd *getspnam(const char *name);
struct spwd *getspent(void);
void setspent(void);
void endspent(void);
struct spwd *fgetspent(FILE *stream);
struct spwd *sgetspent(const char *s);
int putspent(const struct spwd *p, FILE *stream);
int lckpwdf(void);
int ulckpwdf(void);
加密
char *
crypt(const char *phrase, const char *setting);
char *
crypt_r(const char *phrase, const char *setting, struct crypt_data *data);
char *
crypt_rn(const char *phrase, const char *setting, struct crypt_data *data, int size);
char *
crypt_ra(const char *phrase, const char *setting, void **data, int *size);
去除回显
char *getpass(const char *prompt);
cpp
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <shadow.h>
#include <crypt.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
char *pass;
struct spwd* showline;
if(argc <2)
{
printf("Usage...\n");
return -1;
}
pass = getpass("PassWorld:");
showline = getspnam(argv[1]);
printf("pass = %s \n",pass ) ;
char* cryped_pass = crypt(pass,showline->sp_pwdp); //加密
printf("%s \n",cryped_pass);
if( strcmp(showline->sp_pwdp,cryped_pass) ==0)
{
puts("OK");
}
else
puts("Error");
cryped_pass = crypt(pass,"$6$test$");
printf("%s \n",cryped_pass);
return 0;
}由于 /etc/shadow 文件只能root查看,所以执行此代码需要用root用户,否则会有权限问题,会core.
时间戳
cpp
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <time.h>
void test(int flag)
{
int a=10;
time_t t = time(NULL);
struct tm* tm;
if(flag)
{
tm = localtime(&t);
}
printf("a = %p \n",&a);
printf("t = %p \n",&t);
printf("tm = %p \n",&tm);
printf("tm = %d \n",tm->tm_year+1900);
printf("=============================\n");
}
#define FILENAME "/tmp/out"
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
#if 0
if(argc <2)
{
printf("Usage...\n");
return -1;
}
#endif
FILE*fp=fopen(FILENAME,"a+");
char buf[1024];
int count;
time_t stamp;
struct tm* tm;
while(1)
{
if( fgets(buf,sizeof(buf),fp) ==NULL)
break;
count++;
}
while(1)
{
time(&stamp);
tm = localtime(&stamp);
fprintf(fp,"%-4d%d-%d-%d %d:%d:%d\n",++count,tm->tm_year+1900,tm->tm_mon+1,tm->tm_mday,\
tm->tm_hour,tm->tm_min,tm->tm_sec);
fflush(fp);
sleep(1);
}
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
cpp
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <time.h>
#define FILENAME "/tmp/out"
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
#if 0
if(argc <2)
{
printf("Usage...\n");
return -1;
}
#endif
time_t stamp = time(NULL);
struct tm*tm = localtime(&stamp);
char timestr[1024];
strftime(timestr,1024,"Now:%Y-%m-%d ",tm);
puts(timestr);
tm->tm_mday +=100;
strftime(timestr,1024,"test:%Y-%m-%d ",tm);
puts(timestr);
mktime(tm); //会自动进位
strftime(timestr,1024,"100day:%Y-%m-%d ",tm);
puts(timestr);
return 0;
}三、进程环境
进程的终止
正常终止
从main函数返回
调用exit
调用_exit或_Exit
最后一个线程从启动例程返回
最有一个线程调用了pthread_exit
异常终止
调用abort
接到一个信号并终止
最后一个进行对其取消请求做出响应
钩子函数atexit
cpp
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void f1()
{
puts("f1() is working ");
}
void f2()
{
puts("f2() is working ");
}
void f3()
{
puts("f3() is working ");
}
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
puts("Begin");
atexit(f1);
atexit(f2);
atexit(f3);
puts("end");
return 0;
}命令行参数的分析
getopt
cpp
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <time.h>
/*
-y:year
-m:month
-d:day
-H hour
-M:minute
-S:second
*/
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
FILE*fp = stdout;
time_t stamp = time(NULL);
struct tm*tm = localtime(&stamp);
char timestr[1024];
int c;
char fmtstr[32];
fmtstr[0] = '\0';
while(1)
{
c = getopt(argc,argv,"-H:MSy:md"); //加冒号可以进行修饰字符串,-识别分选项传参
if(c<0)
break;
switch(c)
{
case 1:
if(fp == stdout)
{
fp = fopen(argv[optind-1],"w");
if(fp == NULL)
{
perror("fopen()");
fp = stdout;
}
}
break;
case 'H':
if(strcmp(optarg,"12")==0) //optarg是一个全局宏
strncat(fmtstr,"%I(%P) ",sizeof(fmtstr)-strlen(fmtstr)-1);
else if(strcmp(optarg,"24")==0 )
strncat(fmtstr,"%H ",sizeof(fmtstr)-strlen(fmtstr)-1);
else
fprintf(stderr,"Invaild argument");
break;
case 'M':
{
strncat(fmtstr,"%M ",sizeof(fmtstr)-strlen(fmtstr)-1);
break;
}
case 'S':
strncat(fmtstr,"%S ",sizeof(fmtstr)-strlen(fmtstr)-1);
break;
case 'y':
if(strcmp(optarg,"2")== 0)
strncat(fmtstr,"%y ",sizeof(fmtstr)-strlen(fmtstr)-1);
if(strcmp(optarg,"4")== 0)
strncat(fmtstr,"%Y ",sizeof(fmtstr)-strlen(fmtstr)-1);
break;
case 'm':
strncat(fmtstr,"%m ",sizeof(fmtstr)-strlen(fmtstr)-1);
break;
case 'd':
strncat(fmtstr,"%d ",sizeof(fmtstr)-strlen(fmtstr)-1);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
strncat(fmtstr,"\n",2);
strftime(timestr,1024,fmtstr,tm);
fputs(timestr,fp);
if(fp != stdout)
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}getopt_long
长格式,和上面用法一样。
环境变量
key=value,使用printenv、export可以查看。
cpp
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
extern char** environ;
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
#if 0
for(int i=0;environ[i] !=NULL;i++)
{
puts(environ[i]);
}
#endif
puts(getenv("USER"));
setenv("USER","test",1);//0不覆盖 1覆盖
puts(getenv("USER"));
return 0;
}C程序存储空间布局
64位程序内存空间分布128T,32位内存是4G
pmap命令可以查看。
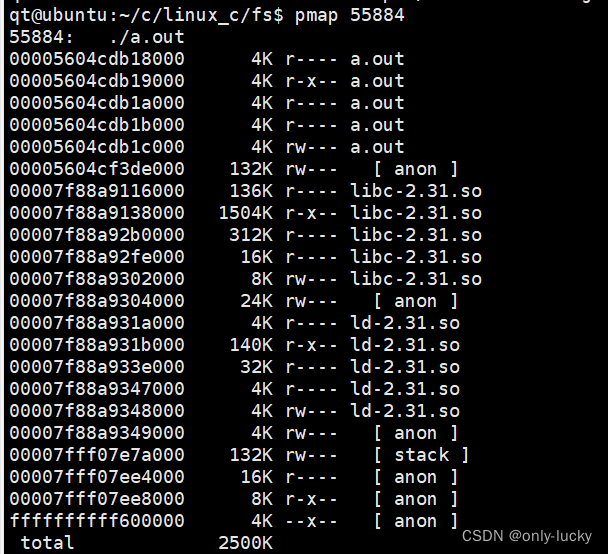
库
动态库、静态库、手工装载库
#include <dlfcn.h>
void *dlopen(const char *filename, int flags);
int dlclose(void *handle);
#define _GNU_SOURCE
#include <dlfcn.h>
void *dlmopen (Lmid_t lmid, const char *filename, int flags);
Link with -ldl.
void *dlsym(void *handle, const char *symbol);
char *dlerror(void);
函数跳转
#include <setjmp.h>
int setjmp(jmp_buf env); 设置跳转点
int sigsetjmp(sigjmp_buf env, int savesigs);
void longjmp(jmp_buf env, int val);跳转到指向位置
void siglongjmp(sigjmp_buf env, int val);
cpp
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <setjmp.h>
jmp_buf save;
void c()
{
printf("%s:Begin() \n",__FUNCTION__);
printf("%s:Jump now! \n",__FUNCTION__);
longjmp(save,6);
printf("%s:End() \n",__FUNCTION__);
}
void b()
{
printf("%s:Begin() \n",__FUNCTION__);
printf("%s:Call c() \n",__FUNCTION__);
c();
printf("%s:c() return \n",__FUNCTION__);
printf("%s:End() \n",__FUNCTION__);
}
void a()
{
int ret;
printf("%s:Begin() \n",__FUNCTION__);
ret = setjmp(save);
if(ret ==0)
{
printf("%s:Call b() \n",__FUNCTION__);
b();
printf("%s:b() return \n",__FUNCTION__);
}
else
{
printf("%s:Jumped back code = %d \n",__FUNCTION__,ret);
}
printf("%s:End() \n",__FUNCTION__);
}
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
printf("%s:Begin() \n",__FUNCTION__);
printf("%s:Call a() \n",__FUNCTION__);
a();
printf("%s:a() return \n",__FUNCTION__);
printf("%s:End() \n",__FUNCTION__);
return 0;
}资源的获取及控制
命令:ulimit -a
getrlimit():获取资源总量
setrlimit():设置资源总量
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <sys/resource.h>
int getrlimit(int resource, struct rlimit *rlim);
int setrlimit(int resource, const struct rlimit *rlim);
int prlimit(pid_t pid, int resource, const struct rlimit *new_limit,
struct rlimit *old_limit);
struct rlimit {
rlim_t rlim_cur; /* Soft limit */ 软限制
rlim_t rlim_max; /* Hard limit (ceiling for rlim_cur) */ 硬限制
};
普通用户不能升级硬限制,root用户可以。软限制不能超过硬限制。