目录
[spec = importlib.util.spec_from_file_location("example_module", "example.py")](#spec = importlib.util.spec_from_file_location("example_module", "example.py"))
[module = importlib.util.module_from_spec(spec)](#module = importlib.util.module_from_spec(spec))
spec.loader.exec_module(module)
创建模块规格对象:为py文件创建一个规格对象,包含文件的路径、名称、加载器等信息
绑定规格与对象:将规格信息绑定到对象中,此时module就具备了该py文件里所定义的类、函数等数据
[【import_chinese_file.py】 内容如下](#【import_chinese_file.py】 内容如下)
[运行【 import_chinese_file.py】 结果如下](#运行【 import_chinese_file.py】 结果如下)
背景
博主在设置Django绑定的定时任务,设计逻辑是一个py文件就是处理对应的定时任务,然后觉得用英文命名一个py文件可能没那么直观,所以想用中文来命名,就遇到了引入中文的py的问题,有了解决方法后就用文章记录下来
思路
不使用import直接导入中文py文件的模块(因为import 不能导入中文或特殊的符号),使用importlib进行处理模块的加载
importlib介绍
importlib 是 Python 提供的强大的动态导入模块库,主要用于动态导入模块和处理模块加载。
使用方法
1.导入内置库
importlib.util
2.创建模块规格对象
spec = importlib.util.spec_from_file_location("example_module", "example.py")
3.创建模块对象
module = importlib.util.module_from_spec(spec)
4.绑定规格与对象(执行对应的模块)
spec.loader.exec_module(module)
用法讲解
创建模块规格对象:为py文件创建一个规格对象,包含文件的路径、名称、加载器等信息
example_module:是自定义的模块名称,仅为标识,不会有具体影响
example.py:实际需要引入的py文件路径
spec = importlib.util.spec_from_file_location("example_module", "example.py")
创建模块对象:创建一个新的,空的模块对象
spec:对应的规格对象,一般搭配 importlib.util.spec_from_file_location() 使用
module = importlib.util.module_from_spec(spec)
绑定规格与对象:将规格信息绑定到对象中,此时module就具备了该py文件里所定义的类、函数等数据
注意:此时相当于已经执行了该py文件,例如py文件里面有print(1),将直接打印1
spec:规格对象
module:模块对象
spec.loader.exec_module(module)
具体示例
文件结构如下
【aa】文件夹下有【打印你好世界.py】文件,是用户引入的模块
【bb】文件夹的文件是进行引入的代码文件

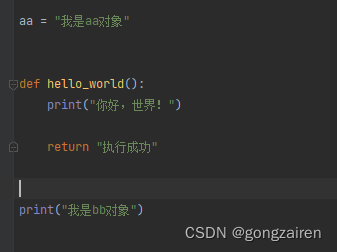
【打印你好世界.py】文件内容如下
【import_chinese_file.py】 内容如下
python
# 1.导入内置库
import importlib.util
import os
from pathlib import Path
# 具体需要引入的文件路径
file_path = os.path.join(Path(__file__).resolve().parent.parent, "aa", "打印你好世界.py")
# 创建规格对象
spec = importlib.util.spec_from_file_location("测试的中文模块", file_path)
# 创建模块对象
module = importlib.util.module_from_spec(spec)
# 绑定规格对象至模块中(执行对应模块)
spec.loader.exec_module(module) # 此时该模块已导入成功(相当于已运行该py文件)
# 获取py文件的aa对象
print(module.__getattribute__("aa"))
# 获取py文件的hello_world函数对象
print(module.__getattribute__("hello_world"))
# 执行py文件的hello_world函数
print(module.__getattribute__("hello_world")())
# 调用不存在的对象或函数
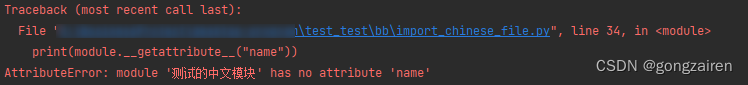
print(module.__getattribute__("name"))运行【 import_chinese_file.py】 结果如下

注意是先打印【我是bb对象】然后再打印【我是aa对象】,是因为执行 spec.loader.exec_module(module) 就已经运行了该py文件
如果调用py文件不存在的对象就会执行报下面的错误,这里就能看得到自定义的规格对象名称