文章目录
- 【分布式算法之一致性哈希】
- 为什么需要一致性哈希?
- [GoCache 实现](#GoCache 实现)
- 一致性哈希是分布式算法吗?
- [GoCache 与 Redis 的不同之处](#GoCache 与 Redis 的不同之处)
- 一致性哈希的作用
- 适用于哪些场景?
- 【缓存对外服务化】
- 服务端模块
- 安装工具(只需要做一次)
- [gRPC 代码生成](#gRPC 代码生成)
- 节点选择器
在 VSCode 中,可以使用以下快捷键打开左边的文件树(资源管理器):
Windows/Linux: Ctrl + B
macOS: Cmd + B
【分布式算法之一致性哈希】
在分布式缓存系统中,一致性哈希(Consistent Hashing) 是一种常用的负载均衡策略,用于解决缓存节点的动态扩展和缩容问题。它可以减少缓存失效率,提高缓存命中率,从而提高系统的可扩展性和稳定性。
为什么需要一致性哈希?
在分布式缓存系统中,多个服务器(缓存节点)存储不同的缓存数据,客户端需要决定将某个 key 存储在哪个缓存节点。最简单的方式是使用 取模(Modulo)分片:
对于分布式缓存来说,当一个节点接收到请求,如果该节点并没有存储缓存值,那么它面临的难题是,从谁那获取数据?自己,还是节点1, 2, 3, 4... 。假设包括自己在内一共有 10 个节点,当一个节点接收到请求时,随机选择一个节点,由该节点从数据源获取数据。
假设第一次随机选取了节点 1 ,节点 1 从数据源获取到数据的同时缓存该数据;那第二次,只有 1/10 的可能性再次选择节点 1, 有 9/10 的概率选择了其他节点,如果选择了其他节点,就意味着需要再一次从数据源获取数据,一般来说,这个操作是很耗时的。这样做,一是缓存效率低,二是各个节点上存储着相同的数据,浪费了大量的存储空间。
那有什么办法,对于给定的 key,每一次都选择同一个节点呢?使用 hash 算法能够做到这一点。那把 key 的每一个字符的 ASCII 码加起来,再除以 10 取余数可以吗?当然可以,这可以认为是自定义的 hash 算法。
go
// 传统哈希分片示例
func getShard(key string, nodeCount int) int {
hash := crc32.ChecksumIEEE([]byte(key))
return int(hash) % nodeCount
}节点数量变化了怎么办?

算法原理

步骤
一致性哈希算法将 key 映射到 232 的空间中,将这个数字首尾相连,形成一个环。
● 计算节点/机器(通常使用节点的名称、编号和 IP 地址)的哈希值,放置在环上 。
● 计算 key 的哈希值,放置在环上,顺时针寻找到的第一个节点,就是应选取的节点/机器。
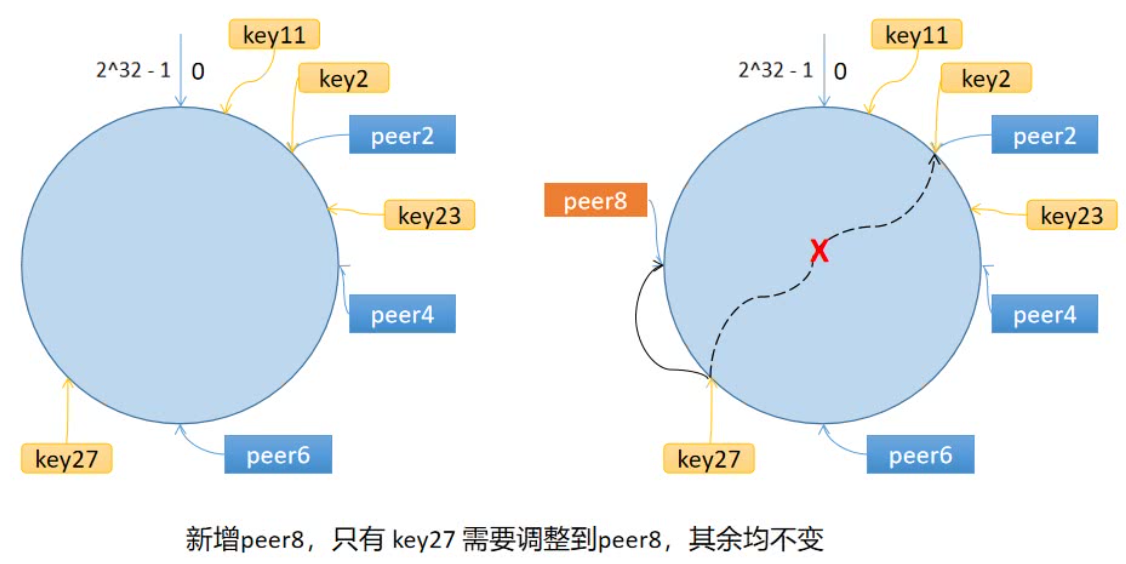
环上有 peer2,peer4,peer6 三个节点,key11,key2,key27 均映射到 peer2,key23 映射到 peer4。此时,如果新增节点/机器 peer8,假设它新增位置如图所示,那么只有 key27 从 peer2 调整到 peer8,其余的映射均没有发生改变。
也就是说,一致性哈希算法,在新增/删除节点时,只需要重新定位该节点附近的一小部分数据,而不需要重新定位所有的节点,这就解决了上述的问题。
数据倾斜问题

GoCache 实现
核心数据结构
go
type Map struct {
mu sync.RWMutex // 读写锁,保证并发安全
config *Config // 配置信息
keys []int // 哈希环上的所有虚拟节点位置,按顺序排列
hashMap map[int]string // 从哈希值到实际节点名称的映射
nodeReplicas map[string]int // 每个实际节点对应的虚拟节点数量
nodeCounts map[string]int64 // 记录每个节点处理的请求数
totalRequests int64 // 记录总请求数,用于负载均衡计算
}
节点管理
go
func (m *Map) Add(nodes ...string) error {
if len(nodes) == 0 {
return errors.New("no nodes provided")
}
m.mu.Lock()
defer m.mu.Unlock()
for _, node := range nodes {
if node == "" {
continue
}
// 为节点添加虚拟节点
m.addNode(node, m.config.DefaultReplicas)
}
// 重新排序
sort.Ints(m.keys)
return nil
}
func (m *Map) addNode(node string, replicas int) {
for i := 0; i < replicas; i++ {
hash := int(m.config.HashFunc([]byte(fmt.Sprintf("%s-%d", node, i))))
m.keys = append(m.keys, hash)
m.hashMap[hash] = node
}
m.nodeReplicas[node] = replicas
}
func (m *Map) Remove(node string) error {
if node == "" {
return errors.New("invalid node")
}
m.mu.Lock()
defer m.mu.Unlock()
replicas := m.nodeReplicas[node]
if replicas == 0 {
return fmt.Errorf("node %s not found", node)
}
// 移除节点的所有虚拟节点
for i := 0; i < replicas; i++ {
hash := int(m.config.HashFunc([]byte(fmt.Sprintf("%s-%d", node, i))))
delete(m.hashMap, hash)
for j := 0; j < len(m.keys); j++ {
if m.keys[j] == hash {
m.keys = append(m.keys[:j], m.keys[j+1:]...)
break
}
}
}
delete(m.nodeReplicas, node)
delete(m.nodeCounts, node)
return nil
}请求路由
go
// Get 获取节点
func (m *Map) Get(key string) string {
// 空 key 直接返回空
if key == "" {
return ""
}
m.mu.RLock()
// 没有节点时直接返回空
if len(m.keys) == 0 {
m.mu.RUnlock()
return ""
}
// key 先变成一个哈希值,再沿着环顺时针找到第一个"虚拟节点",它所属的真实节点就是目标节点
hash := int(m.config.HashFunc([]byte(key)))
// 二分查找
// 第一个满足 m.keys[i] >= hash 的下标 i,把它赋值给 idx
// 如果没有这样的索引,搜索将返回 len(m.keys)
idx := sort.Search(len(m.keys), func(i int) bool {
return m.keys[i] >= hash
})
// 处理边界情况
if idx == len(m.keys) {
idx = 0
}
node := m.hashMap[m.keys[idx]]
m.mu.RUnlock()
m.mu.Lock()
m.nodeCounts[node] = m.nodeCounts[node] + 1
m.mu.Unlock()
// 总请求数用 atomic,和 mu 解耦
atomic.AddInt64(&m.totalRequests, 1)
return node
}
负载均衡机制
go
// checkAndRebalance 检查并重新平衡虚拟节点
func (m *Map) checkAndRebalance() {
// 1. 样本量检查(用 atomic 读)
total := atomic.LoadInt64(&m.totalRequests)
if total < 1000 {
// 样本太少,不进行调整
return
}
// 2. 读节点数量 & nodeCounts,需要用锁保护 map
m.mu.RLock()
nodeCount := len(m.nodeReplicas)
if nodeCount == 0 {
m.mu.RUnlock()
return
}
// 计算负载情况
// 计算理论平均负载
avgLoad := float64(total) / float64(nodeCount)
if avgLoad == 0 {
m.mu.RUnlock()
return
}
var maxDiff float64
for _, count := range m.nodeCounts {
diff := math.Abs(float64(count) - avgLoad)
ratio := diff / avgLoad // 相对偏差比例
if ratio > maxDiff {
maxDiff = ratio
}
}
m.mu.RUnlock()
// 3. 判断是否超过不均衡阈值
if maxDiff <= m.config.LoadBalanceThreshold {
return
}
// 4. 负载不均衡,调整虚拟节点
m.rebalanceNodes()
}
// rebalanceNodes 重新平衡节点
func (m *Map) rebalanceNodes() {
// 独占整个 Map 的结构(keys / hashMap / nodeReplicas / nodeCounts)
m.mu.Lock()
defer m.mu.Unlock()
// 没有节点就不用算了,避免除 0
if len(m.nodeReplicas) == 0 {
return
}
// 读取总请求数(之前是 atomic.AddInt64),这里用 atomic.Load 保持一致
// total := atomic.LoadInt64(&m.totalRequests)
total := m.totalRequests
if total == 0 {
// 没有请求,也没啥可平衡的
return
}
// 理论上每个节点"应该"处理的平均请求数
avgLoad := float64(total) / float64(len(m.nodeReplicas))
if avgLoad == 0 {
// 理论上 total>0 时 avgLoad 不会是 0,这里只是兜底
return
}
// 先计算每个节点"应该"有多少虚拟节点,放在一个临时 map 里
// 这样在这一步不会改动 nodeCounts / nodeReplicas,避免遍历时写 map
newReplicas := make(map[string]int, len(m.nodeReplicas))
for node, currentReplicas := range m.nodeReplicas {
// 注意:这里从 nodeReplicas 遍历,而不是从 nodeCounts,
// 避免 Remove 之类的操作影响正在遍历的 map。
count := m.nodeCounts[node] // 如果没统计到就是 0
loadRatio := float64(count) / avgLoad
var replicas int
if loadRatio > 1 {
// 负载过高,减少虚拟节点
// 比如当前 100 个虚拟节点,loadRatio=2(负载是平均的 2 倍),新虚拟节点数 ≈ 50,减半
replicas = int(float64(currentReplicas) / loadRatio)
} else {
// 负载过低或刚好,增加一些虚拟节点
// loadRatio=1 → replicas=current
// loadRatio=0.5 → replicas≈1.5*current
// loadRatio=0 → replicas≈2*current
replicas = int(float64(currentReplicas) * (2 - loadRatio))
}
// 安全兜底:防止算出来 0 或负数
if replicas < 1 {
replicas = 1
}
// 限制在配置范围内
if replicas < m.config.MinReplicas {
replicas = m.config.MinReplicas
}
if replicas > m.config.MaxReplicas {
replicas = m.config.MaxReplicas
}
newReplicas[node] = replicas
}
// 用新的虚拟节点数量"重建"哈希环:
// 1. 清空 keys 和 hashMap
// 2. 清空 nodeReplicas
// 3. 再用 addNode 按 newReplicas 重建
m.keys = nil
m.hashMap = make(map[int]string, len(newReplicas)*m.config.MaxReplicas)
m.nodeReplicas = make(map[string]int, len(newReplicas))
for node, replicas := range newReplicas {
// addNode 会:
// - 按 node / i 生成虚拟节点 hash
// - 填充 m.keys / m.hashMap
// - 更新 m.nodeReplicas[node] = replicas
m.addNode(node, replicas)
}
// 重置统计:从这次重平衡之后重新开始采样
for node := range m.nodeCounts {
m.nodeCounts[node] = 0
}
atomic.StoreInt64(&m.totalRequests, 0)
// 最后把虚拟节点位置排个序,保证 Get 里的二分查找正常
sort.Ints(m.keys)
}负载均衡检查的详细流程:

重新平衡的详细算法:

一致性哈希是分布式算法吗?

GoCache 与 Redis 的不同之处

一致性哈希的作用

适用于哪些场景?
GoCache 是一个分布式缓存,适用于:

【缓存对外服务化】
每个 GoCache 进程在哈希环中都是其中的一个节点,环中不同节点要互相通信,因此必须对外提供服务。
服务端模块
服务端模块是缓存系统对外提供服务的核心,负责接收和处理来自其他节点的请求 这里 GoCache 使用的是 grpc 来进行节点间的通信,同时集成了服务注册发现、健康检查和安全传输等特性。
核心结构设计
go
// Server 定义缓存服务器
type Server struct {
pb.UnimplementedLCacheServer
addr string // 服务地址
svcName string // 服务名称
groups *sync.Map // 缓存组
grpcServer *grpc.Server // gRPC服务器
etcdCli *clientv3.Client // etcd客户端
stopCh chan error // 停止信号
opts *ServerOptions // 服务器选项
}
服务创建和生命周期管理
go
// NewServer 创建新的服务器实例
func NewServer(addr, svcName string, opts ...ServerOption) (*Server, error) {
options := DefaultServerOptions
for _, opt := range opts {
opt(options)
}
// 创建etcd客户端
etcdCli, err := clientv3.New(clientv3.Config{
Endpoints: options.EtcdEndpoints,
DialTimeout: options.DialTimeout,
})
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to create etcd client: %v", err)
}
// 创建gRPC服务器
var serverOpts []grpc.ServerOption
serverOpts = append(serverOpts, grpc.MaxRecvMsgSize(options.MaxMsgSize))
if options.TLS {
creds, err := loadTLSCredentials(options.CertFile, options.KeyFile)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to load TLS credentials: %v", err)
}
serverOpts = append(serverOpts, grpc.Creds(creds))
}
srv := &Server{
addr: addr,
svcName: svcName,
groups: &sync.Map{},
grpcServer: grpc.NewServer(serverOpts...),
etcdCli: etcdCli,
stopCh: make(chan error),
opts: options,
}
// 注册服务
pb.RegisterLCacheServer(srv.grpcServer, srv)
// 注册健康检查服务
healthServer := health.NewServer()
healthpb.RegisterHealthServer(srv.grpcServer, healthServer)
healthServer.SetServingStatus(svcName, healthpb.HealthCheckResponse_SERVING)
return srv, nil
}
// Start 启动服务器
func (s *Server) Start() error {
// 启动gRPC服务器
lis, err := net.Listen("tcp", s.addr)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to listen: %v", err)
}
// 注册到etcd
stopCh := make(chan error)
go func() {
if err := registry.Register(s.svcName, s.addr, stopCh); err != nil {
logrus.Errorf("failed to register service: %v", err)
close(stopCh)
return
}
}()
logrus.Infof("Server starting at %s", s.addr)
return s.grpcServer.Serve(lis)
}
缓存操作接口
go
// Get 实现LCache服务的Get方法
func (s *Server) Get(ctx context.Context, req *pb.Request) (*pb.ResponseForGet, error) {
group := GetGroup(req.Group)
if group == nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("group %s not found", req.Group)
}
view, err := group.Get(ctx, req.Key)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return &pb.ResponseForGet{Value: view.ByteSLice()}, nil
}
// Set 实现LCache服务的Set方法
func (s *Server) Set(ctx context.Context, req *pb.Request) (*pb.ResponseForGet, error) {
group := GetGroup(req.Group)
if group == nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("group %s not found", req.Group)
}
// 从 context 中获取标记,如果没有则创建新的 context
fromPeer := ctx.Value("from_peer")
if fromPeer == nil {
ctx = context.WithValue(ctx, "from_peer", true)
}
if err := group.Set(ctx, req.Key, req.Value); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return &pb.ResponseForGet{Value: req.Value}, nil
}
安装工具(只需要做一次)
bash
root@GoLang:~/proj1/GoDistributeCache# go install google.golang.org/protobuf/cmd/protoc-gen-go@latest
go: downloading google.golang.org/protobuf v1.36.10
root@GoLang:~/proj1/GoDistributeCache# go install google.golang.org/grpc/cmd/protoc-gen-go-grpc@latest
go: downloading google.golang.org/grpc/cmd/protoc-gen-go-grpc v1.6.0
go: downloading google.golang.org/grpc v1.77.0
bash
root@GoLang:~/proj1/GoDistributeCache# sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y protobuf-compiler
Hit:1 http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/ubuntu jammy InRelease
Get:2 http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/ubuntu jammy-updates InRelease [128 kB]
Get:3 http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/ubuntu jammy-backports InRelease [127 kB]
Get:4 http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/ubuntu jammy-security InRelease [129 kB]
Hit:5 https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu jammy InRelease
Get:6 http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 Packages [3,149 kB]
Get:7 http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main Translation-en [482 kB]
Get:8 http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 c-n-f Metadata [19.0 kB]
Get:9 http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/restricted amd64 Packages [5,022 kB]
Get:10 http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/restricted Translation-en [940 kB]
Get:11 http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/universe amd64 Packages [1,245 kB]
Get:12 http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/universe Translation-en [310 kB]
Get:13 http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/universe amd64 c-n-f Metadata [30.0 kB]
Get:14 http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/ubuntu jammy-security/main amd64 Packages [2,853 kB]
Get:15 http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/ubuntu jammy-security/main Translation-en [411 kB]
Get:16 http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/ubuntu jammy-security/restricted amd64 Packages [4,790 kB]
Get:17 http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/ubuntu jammy-security/restricted Translation-en [897 kB]
Get:18 http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/ubuntu jammy-security/universe amd64 Packages [1,007 kB]
Fetched 21.5 MB in 4s (5,437 kB/s)
Reading package lists... Done
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree... Done
Reading state information... Done
The following packages were automatically installed and are no longer required:
golang-1.18-go golang-1.18-src golang-src pkg-config
Use 'sudo apt autoremove' to remove them.
The following additional packages will be installed:
libprotobuf-dev libprotobuf-lite23 libprotobuf23 libprotoc23
Suggested packages:
protobuf-mode-el
The following NEW packages will be installed:
libprotobuf-dev libprotobuf-lite23 libprotobuf23 libprotoc23 protobuf-compiler
0 upgraded, 5 newly installed, 0 to remove and 27 not upgraded.
Need to get 3,125 kB of archives.
After this operation, 17.5 MB of additional disk space will be used.
Get:1 http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libprotobuf-lite23 amd64 3.12.4-1ubuntu7.22.04.4 [209 kB]
Get:2 http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libprotobuf23 amd64 3.12.4-1ubuntu7.22.04.4 [878 kB]
Get:3 http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libprotoc23 amd64 3.12.4-1ubuntu7.22.04.4 [662 kB]
Get:4 http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libprotobuf-dev amd64 3.12.4-1ubuntu7.22.04.4 [1,347 kB]
Get:5 http://mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/universe amd64 protobuf-compiler amd64 3.12.4-1ubuntu7.22.04.4 [29.2 kB]
Fetched 3,125 kB in 1s (3,793 kB/s)
Selecting previously unselected package libprotobuf-lite23:amd64.
(Reading database ... 94461 files and directories currently installed.)
Preparing to unpack .../libprotobuf-lite23_3.12.4-1ubuntu7.22.04.4_amd64.deb ...
Unpacking libprotobuf-lite23:amd64 (3.12.4-1ubuntu7.22.04.4) ...
Selecting previously unselected package libprotobuf23:amd64.
Preparing to unpack .../libprotobuf23_3.12.4-1ubuntu7.22.04.4_amd64.deb ...
Unpacking libprotobuf23:amd64 (3.12.4-1ubuntu7.22.04.4) ...
Selecting previously unselected package libprotoc23:amd64.
Preparing to unpack .../libprotoc23_3.12.4-1ubuntu7.22.04.4_amd64.deb ...
Unpacking libprotoc23:amd64 (3.12.4-1ubuntu7.22.04.4) ...
Selecting previously unselected package libprotobuf-dev:amd64.
Preparing to unpack .../libprotobuf-dev_3.12.4-1ubuntu7.22.04.4_amd64.deb ...
Unpacking libprotobuf-dev:amd64 (3.12.4-1ubuntu7.22.04.4) ...
Selecting previously unselected package protobuf-compiler.
Preparing to unpack .../protobuf-compiler_3.12.4-1ubuntu7.22.04.4_amd64.deb ...
Unpacking protobuf-compiler (3.12.4-1ubuntu7.22.04.4) ...
Setting up libprotobuf23:amd64 (3.12.4-1ubuntu7.22.04.4) ...
Setting up libprotobuf-lite23:amd64 (3.12.4-1ubuntu7.22.04.4) ...
Setting up libprotoc23:amd64 (3.12.4-1ubuntu7.22.04.4) ...
Setting up protobuf-compiler (3.12.4-1ubuntu7.22.04.4) ...
Setting up libprotobuf-dev:amd64 (3.12.4-1ubuntu7.22.04.4) ...
Processing triggers for man-db (2.10.2-1) ...
Processing triggers for libc-bin (2.35-0ubuntu3.11) ...
Scanning processes...
Scanning candidates...
Scanning linux images...
Running kernel seems to be up-to-date.
Restarting services...
systemctl restart unattended-upgrades.service
No containers need to be restarted.
No user sessions are running outdated binaries.
No VM guests are running outdated hypervisor (qemu) binaries on this host.
root@GoLang:~/proj1/GoDistributeCache# 
gRPC 代码生成
通过 protoc 编译器,你可以生成与服务定义对应的 Go 代码。例如,执行以下命令:
bash
root@GoLang:~/proj1/GoDistributeCache# protoc \
--go_out=. --go_opt=paths=source_relative \
--go-grpc_out=. --go-grpc_opt=paths=source_relative \
pb/gdc.proto
root@GoLang:~/proj1/GoDistributeCache# 这会生成两个文件:
pb/gdc.pb.go:包含消息类型(CacheRequest 和 CacheResponse)的定义。
pb/gdc_grpc.pb.go:包含服务接口的定义。
节点选择器

核心接口设计
go
// PeerPicker 定义了peer选择器的接口
type PeerPicker interface {
PickPeer(key string) (peer Peer, ok bool, self bool)
Close() error
}
go
// Peer 定义了缓存节点的接口
type Peer interface {
Get(group string, key string) ([]byte, error)
Set(ctx context.Context, group string, key string, value []byte) error
Delete(group string, key string) (bool, error)
Close() error
}
go
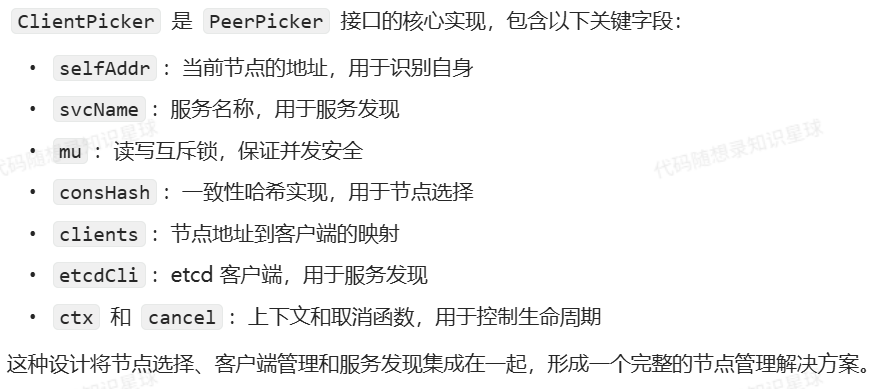
// ClientPicker 实现了PeerPicker接口
type ClientPicker struct {
selfAddr string
svcName string
mu sync.RWMutex
consHash *consistenthash.Map
clients map[string]*Client
etcdCli *clientv3.Client
ctx context.Context
cancel context.CancelFunc
}
服务发现与节点管理
go
// startServiceDiscovery 启动服务发现
func (p *ClientPicker) startServiceDiscovery() error {
// 先进行全量更新
if err := p.fetchAllServices(); err != nil {
return err
}
// 启动增量更新
go p.watchServiceChanges()
return nil
}
一致性哈希与节点选择
go
// PickPeer 选择peer节点
func (p *ClientPicker) PickPeer(key string) (Peer, bool, bool) {
p.mu.RLock()
defer p.mu.RUnlock()
if addr := p.consHash.Get(key); addr != "" {
if client, ok := p.clients[addr]; ok {
return client, true, addr == p.selfAddr
}
}
return nil, false, false
}
之后我会持续更新,如果喜欢我的文章,请记得一键三连哦,点赞关注收藏,你的每一个赞每一份关注每一次收藏都将是我前进路上的无限动力 !!!↖(▔▽▔)↗感谢支持!