一 最小距离累加和
1.1 描述
给定一个二维数组matrix,一个人必须从左上角出发,最后到达右下角
沿途只可以向下或者向右走,沿途的数字都累加就是距离累加和
返回最小距离累加和
1.2 分析
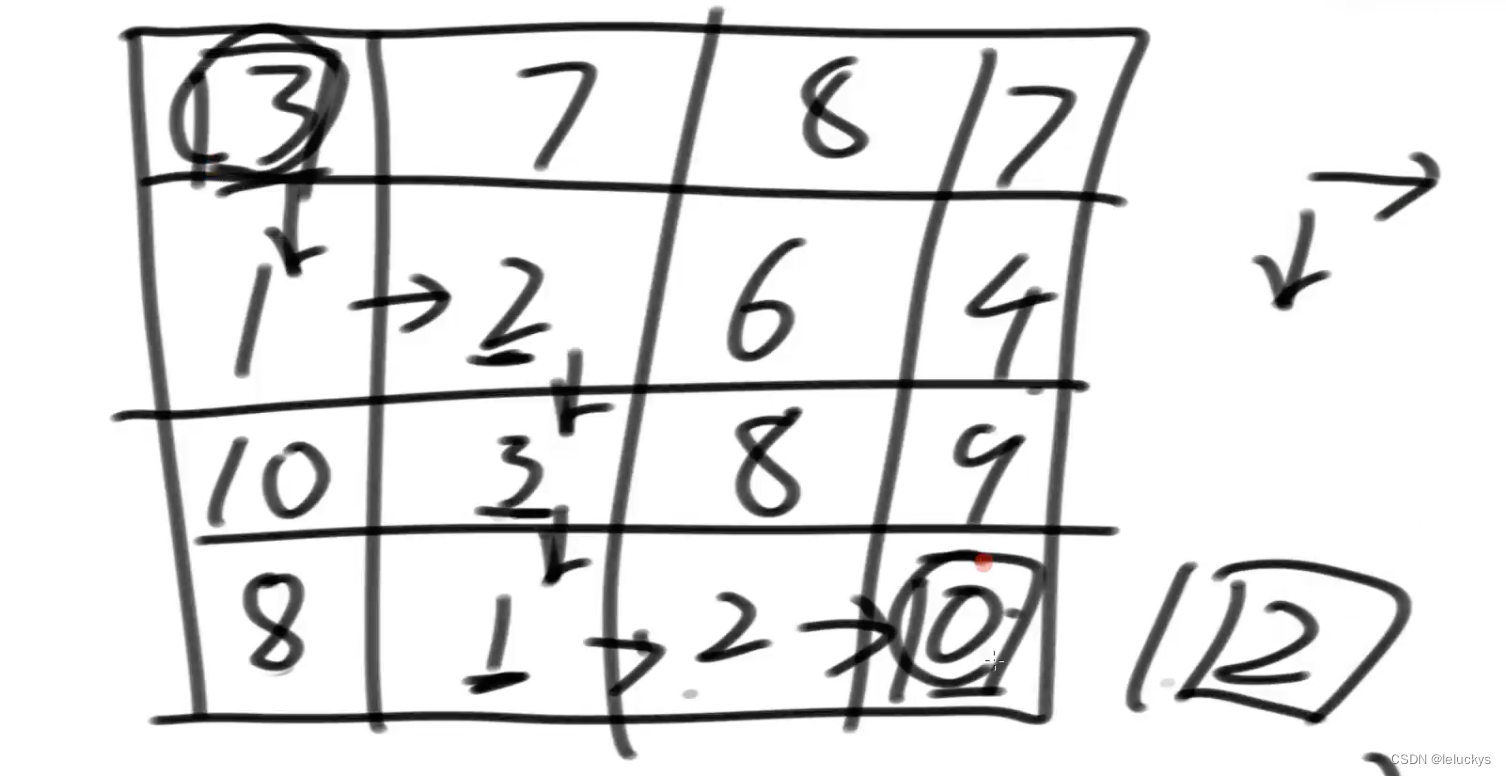
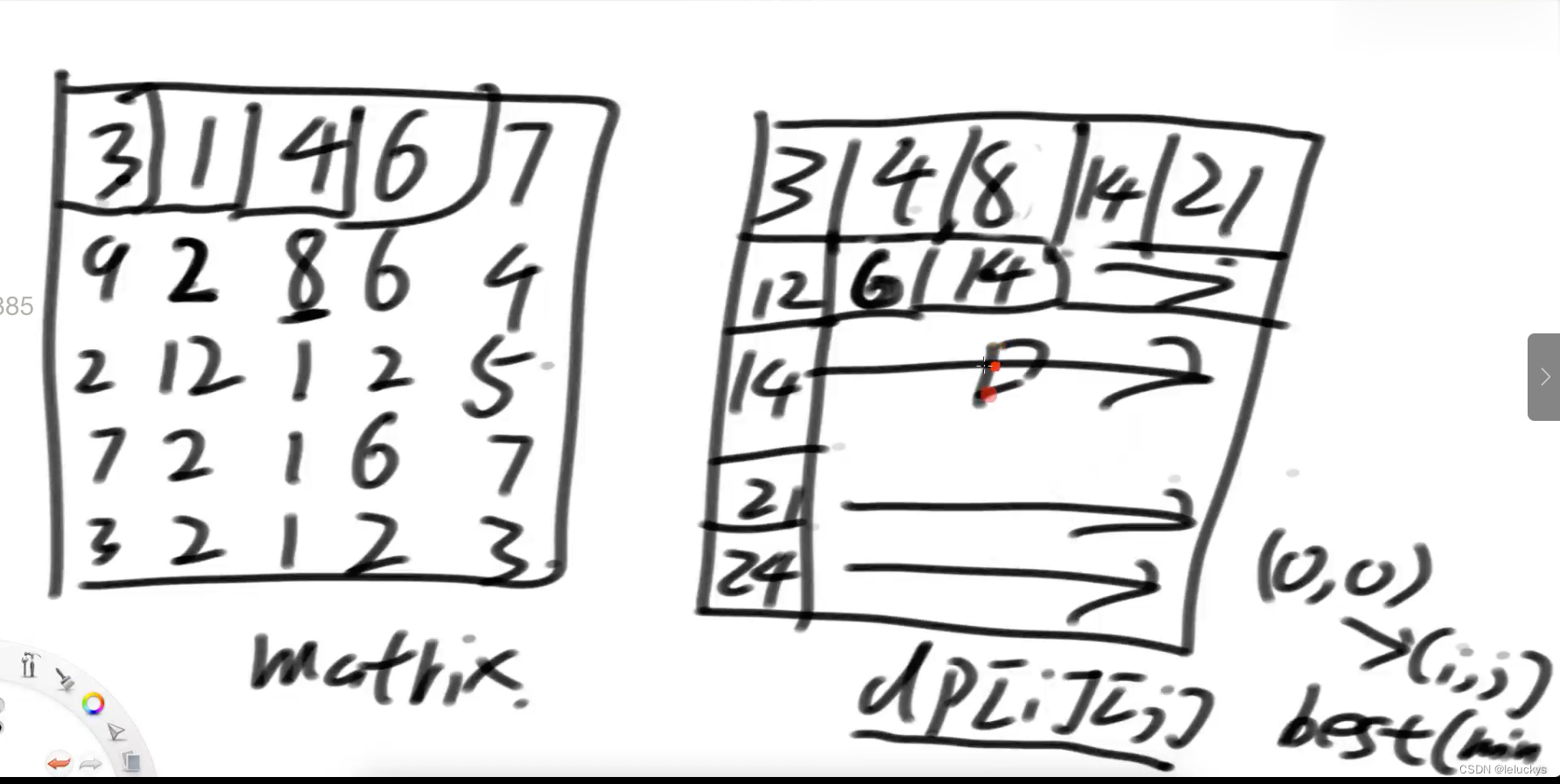
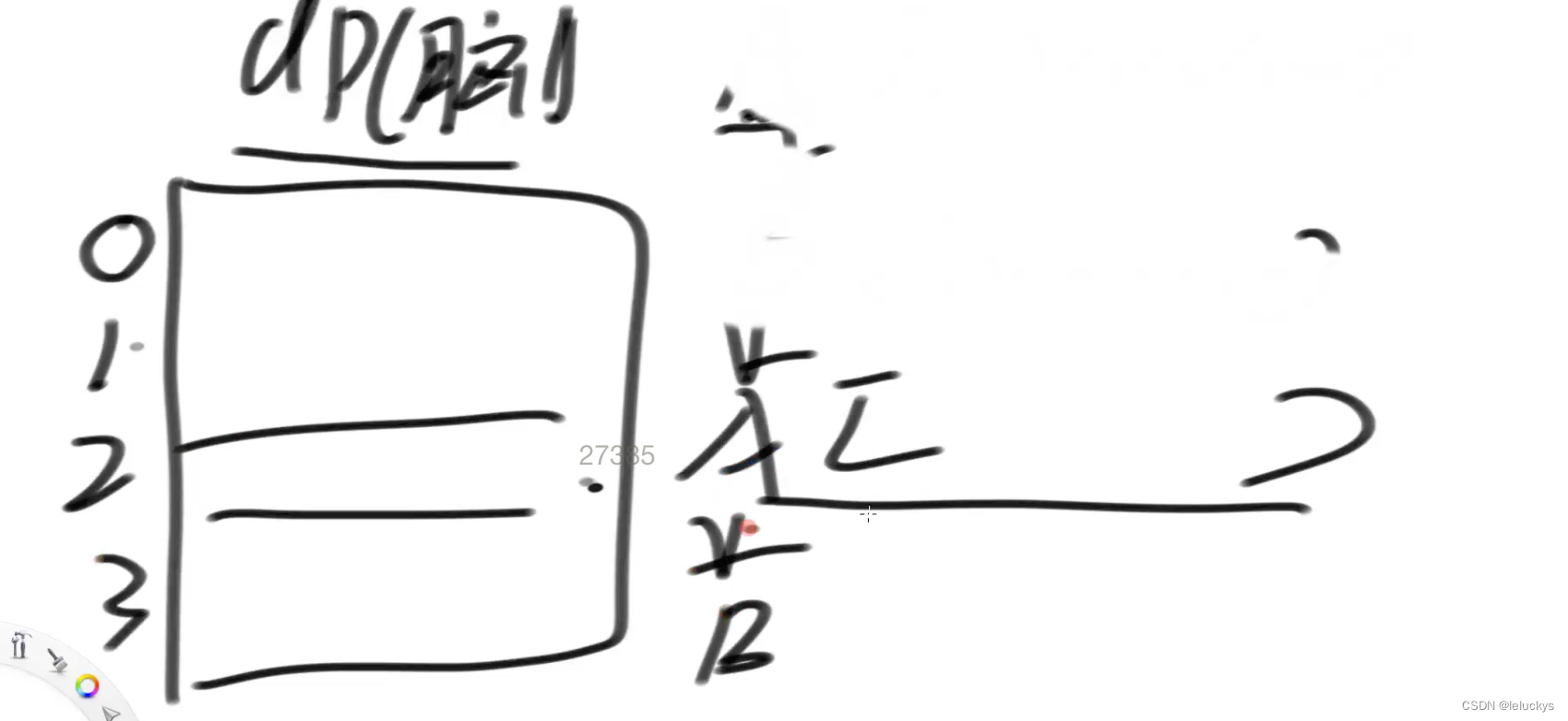
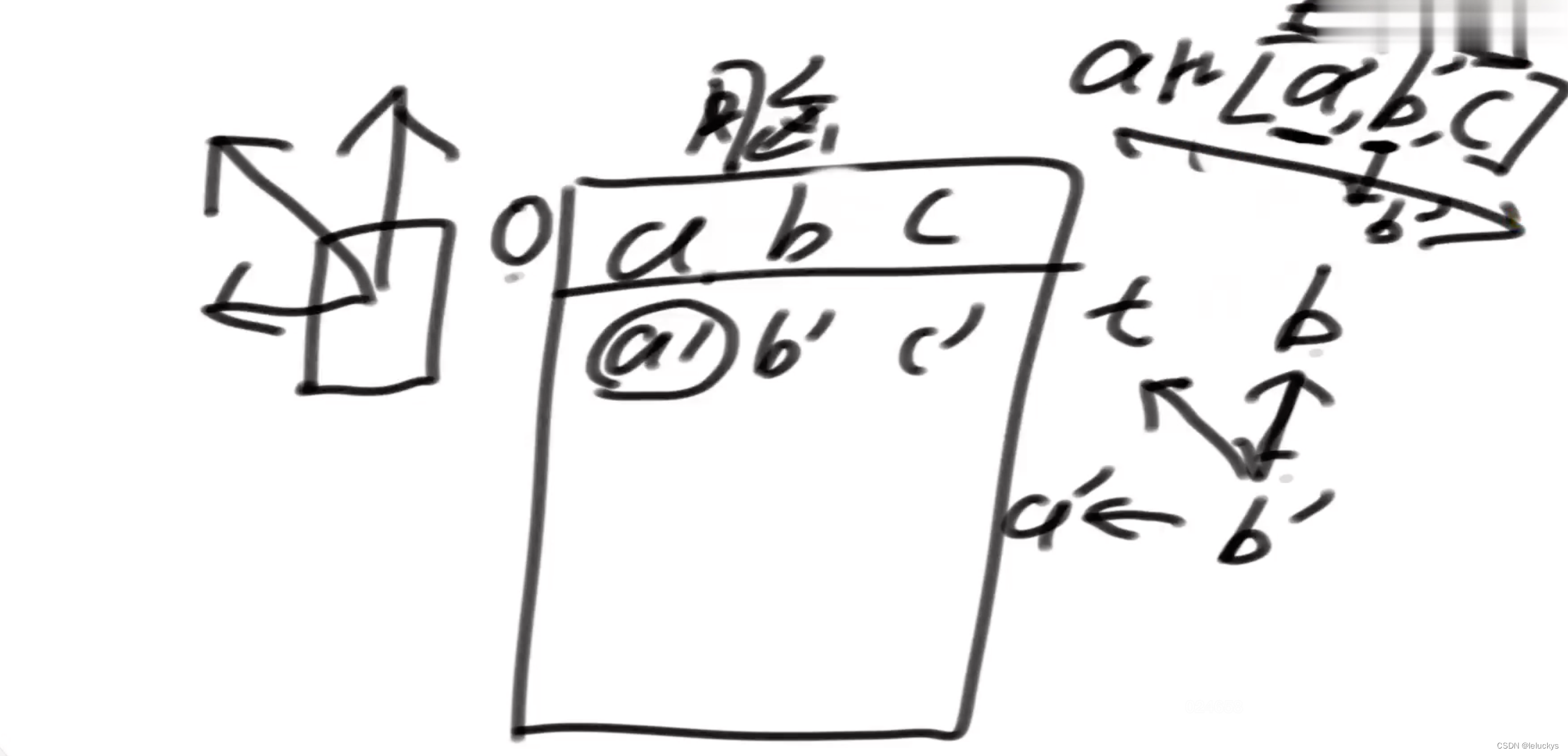
左边是原始矩阵,右边是我要的dp矩阵
下边的第一行和第一列只能从左往右和从上到下来
1.3 代码
java
public static int minPathSum1(int[][] m) {
if (m == null || m.length == 0 || m[0] == null || m[0].length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int row = m.length;
int col = m[0].length;
int[][] dp = new int[row][col];
dp[0][0] = m[0][0];
for (int i = 1; i < row; i++) {
dp[i][0] = dp[i - 1][0] + m[i][0];
}
for (int j = 1; j < col; j++) {
dp[0][j] = dp[0][j - 1] + m[0][j];
}
for (int i = 1; i < row; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < col; j++) {
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]) + m[i][j];
}
}
return dp[row - 1][col - 1];
}1.4 优化(空间压缩技巧)
空间优化,下一个只需要上一个就可以推出来来,下边的拿到了就把上边是释放掉
一个数组自我更新
1.5 优化代码
java
public static int minPathSum2(int[][] m) {
if (m == null || m.length == 0 || m[0] == null || m[0].length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int row = m.length;
int col = m[0].length;
int[] dp = new int[col];
dp[0] = m[0][0];
for (int j = 1; j < col; j++) {
dp[j] = dp[j - 1] + m[0][j];
}
for (int i = 1; i < row; i++) {
dp[0] += m[i][0];
for (int j = 1; j < col; j++) {
dp[j] = Math.min(dp[j - 1], dp[j]) + m[i][j];
}
}
return dp[col - 1];
}1.6 规律总结 空间压缩技巧
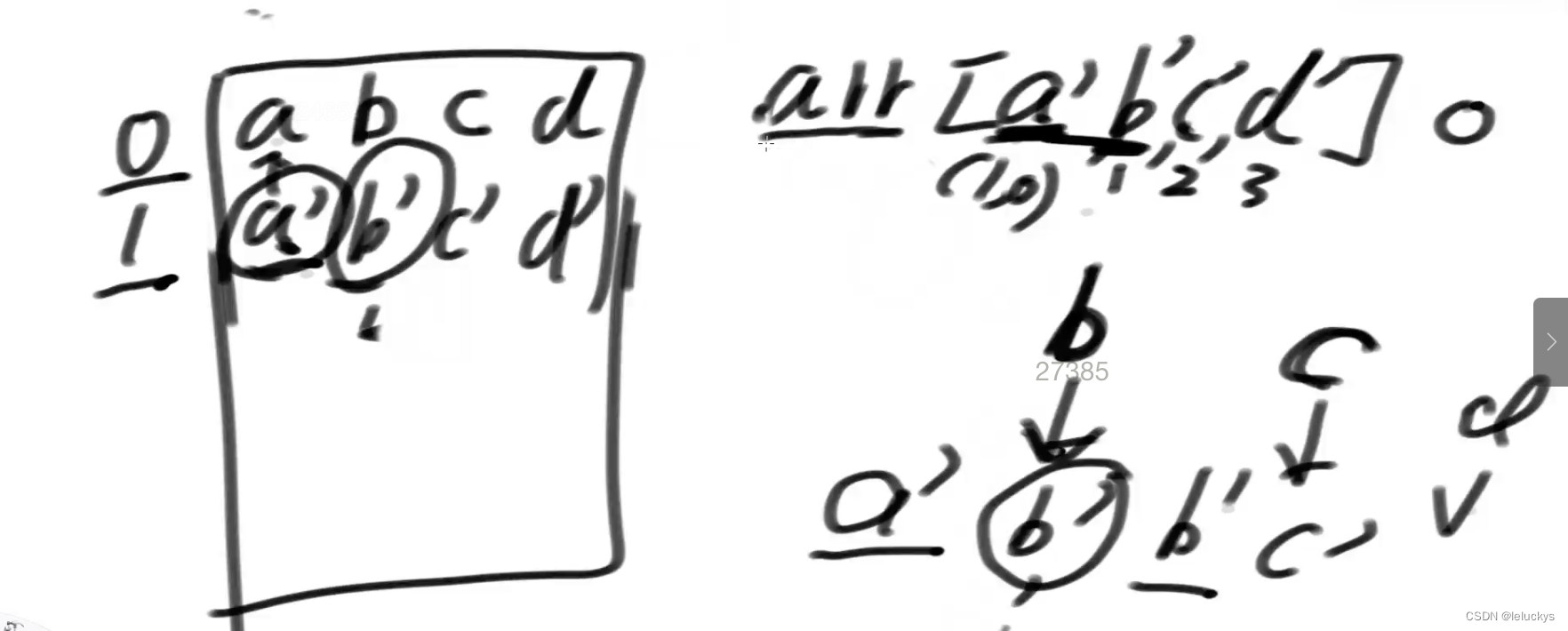
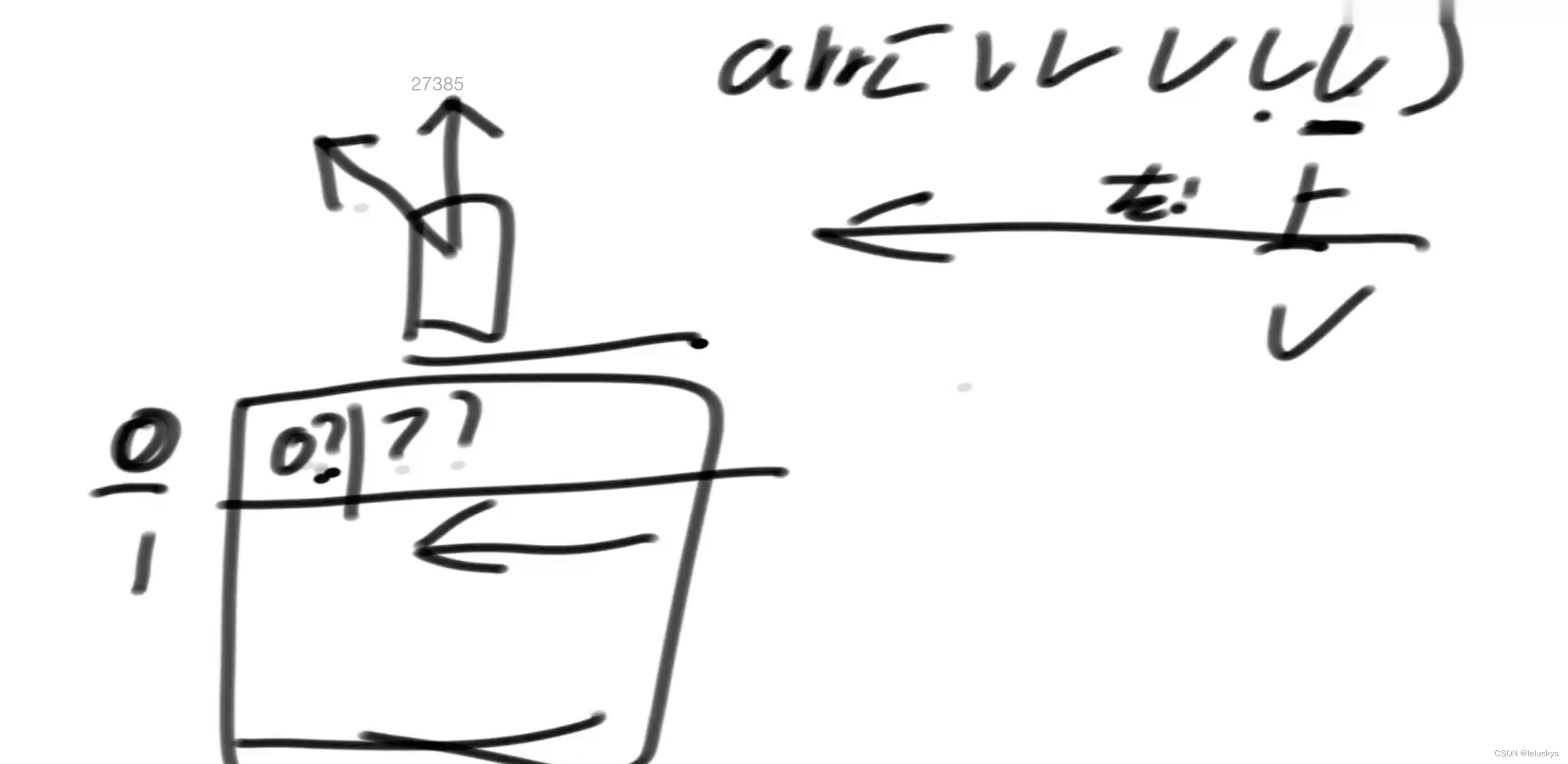
1.6.1 依赖上和左上的情况,0行的值可以算出来,从第一行开始从右开始更新
我的当前位置的上就是上的位置,左边的就是左上的值
1.6.1 依赖上,左上和左的情况
第0行的值可以算出来
第0列的也可以算出来
下面更新非0行0列的情况 例如 b计算b一匹
差左上的情况 当计算第0列的情况往回写进a的时候,拿一个临时变量把上一个记住,b一匹就可以计算了 左上是临时变量+左+右,当把b一匹往回写的时候,临时上次记录的a改为记录b,这个临时变量跟着从左往右走
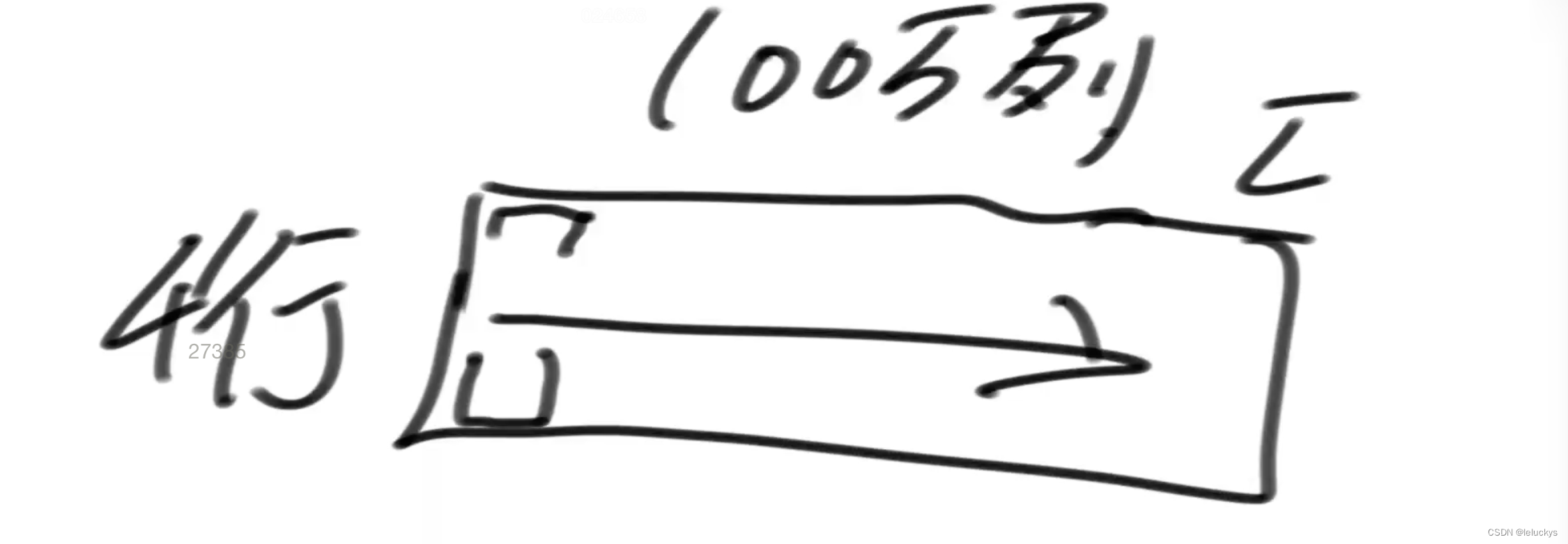
上面的情况至少得准备列的长度的数组
如 n x m的矩阵要准备m的长度数组,假如4行100万列怎么办,就反过来准备4个长度的数组
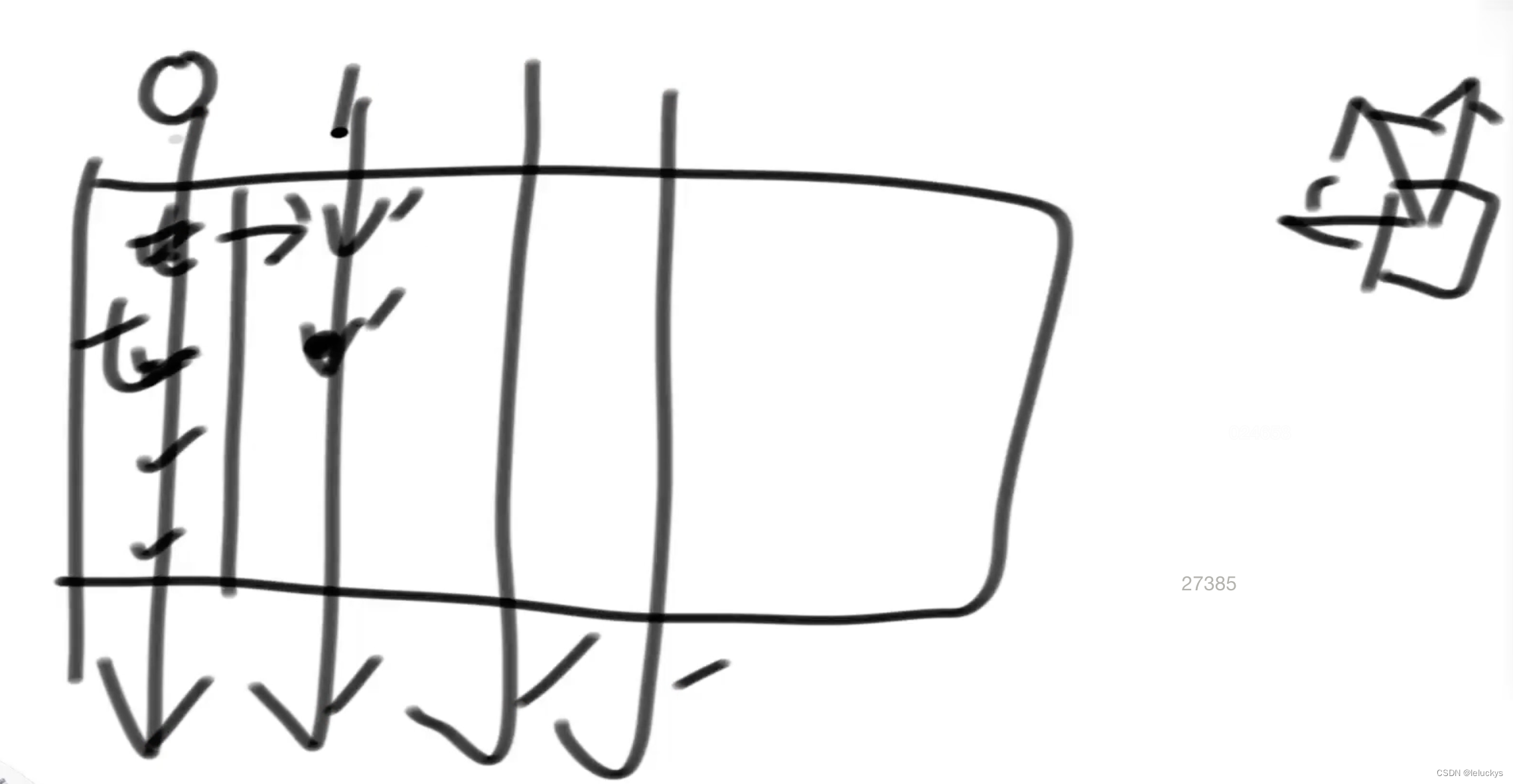
当列比较短的情况用列的数组去更新,当行比较短的情况用行的数组来更新
二 arr = {1,1,1},aim = 2 (从左往右模型尝试模型)
2.1 描述
arr是货币数组,其中的值都是正数。再给定一个正数aim。
每个值都认为是一张货币,
即便是值相同的货币也认为每一张都是不同的,
返回组成aim的方法数
例如:arr = {1,1,1},aim = 2
第0个和第1个能组成2,第1个和第2个能组成2,第0个和第2个能组成2
一共就3种方法,所以返回3
2.2 分析 尝试递归模型
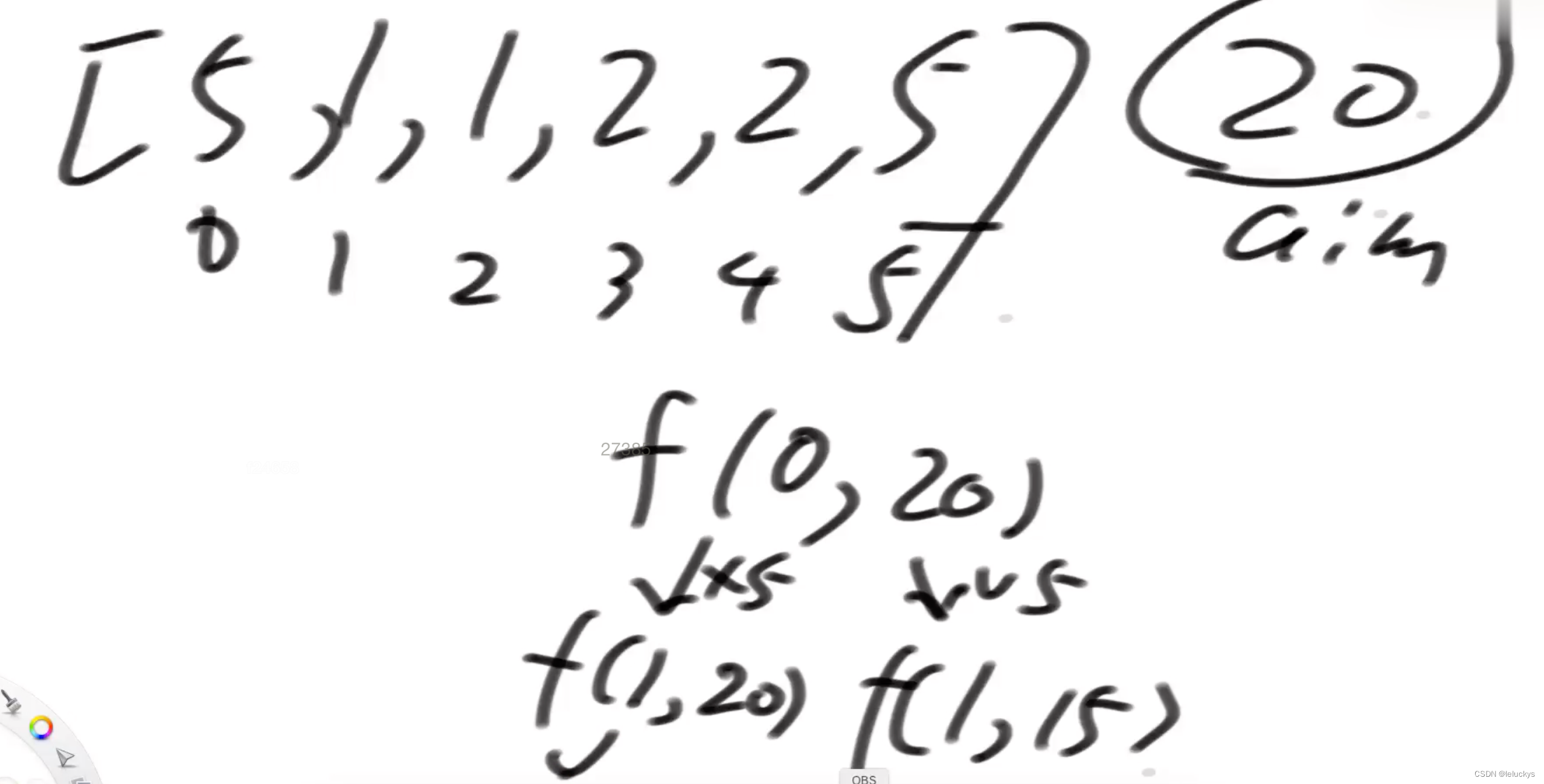
2.3 代码
java
public static int coinWays(int[] arr, int aim) {
return process(arr, 0, aim);
}
// arr[index....] 组成正好rest这么多的钱,有几种方法
public static int process(int[] arr, int index, int rest) {
if (rest < 0) {
return 0;
}
if (index == arr.length) { // 没钱了!
return rest == 0 ? 1 : 0;
} else {
return process(arr, index + 1, rest) + process(arr, index + 1, rest - arr[index]);
}
}2.4 改动态规划
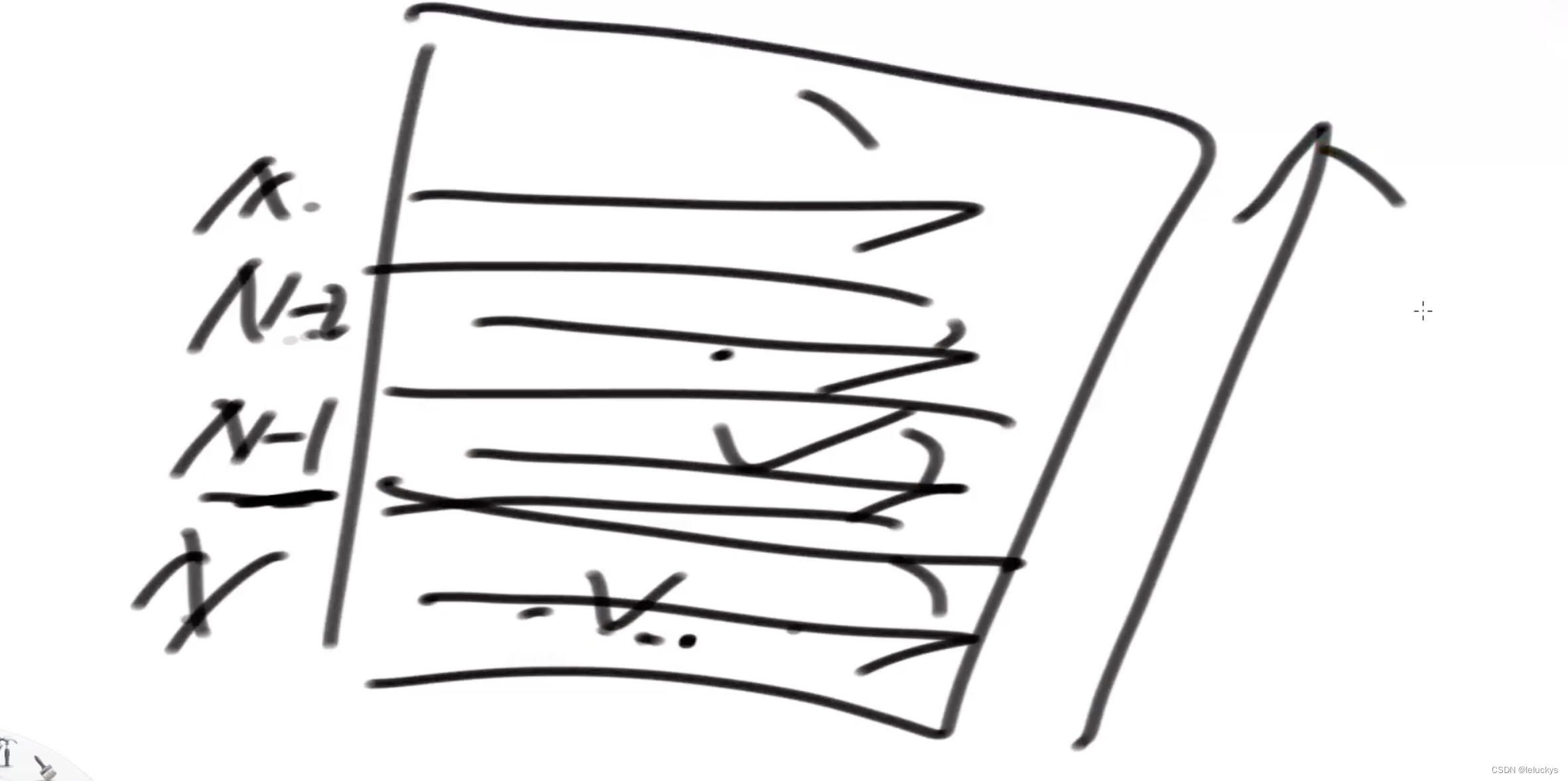
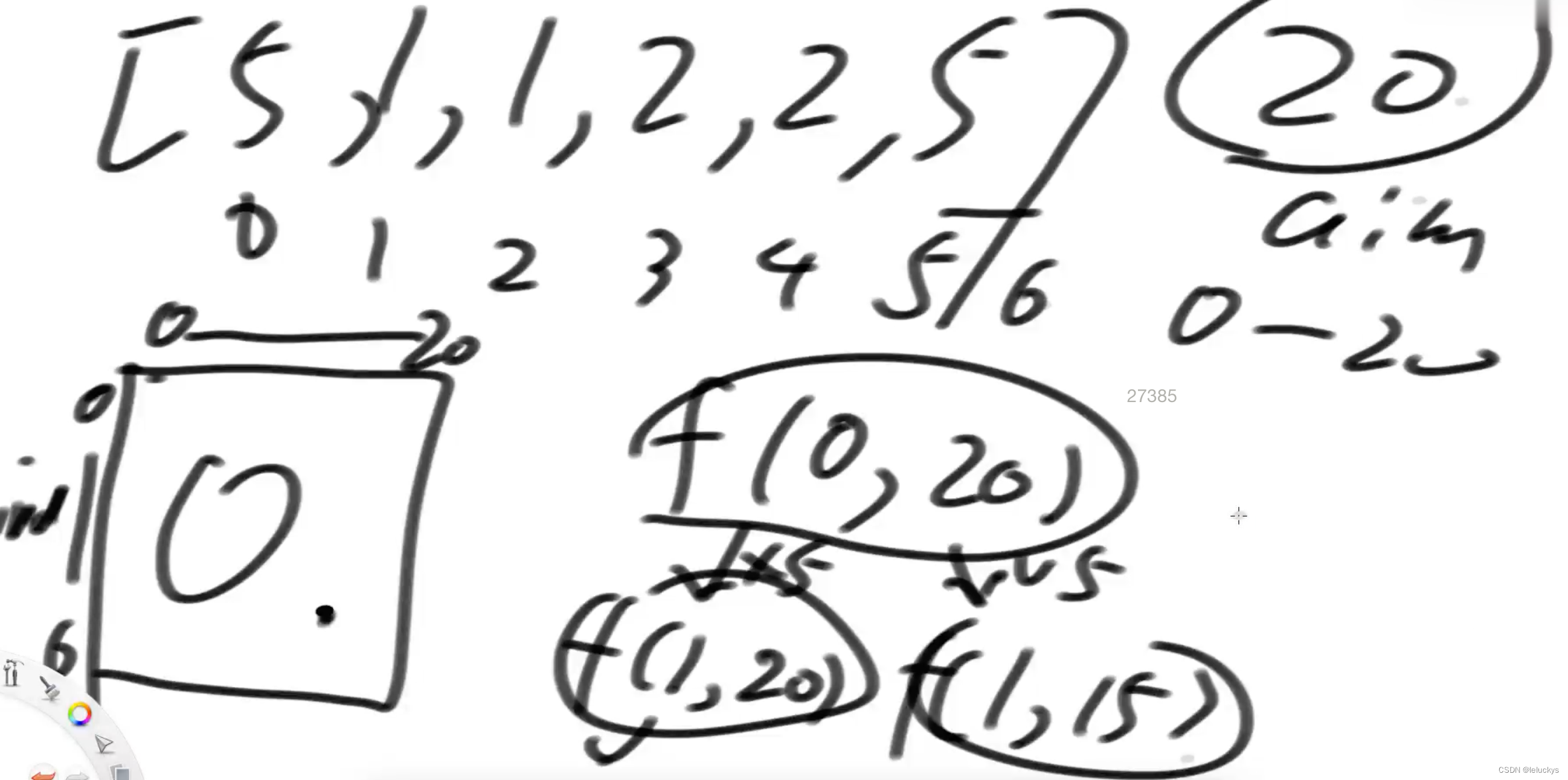

2.5 动态规划代码
java
public static int dp(int[] arr, int aim) {
if (aim == 0) {
return 1; }
int N = arr.length; int[][] dp = new int[N + 1][aim + 1]; dp[N][0] = 1; for (int index = N - 1; index >= 0; index--) {
for (int rest = 0; rest <= aim; rest++) {
dp[index][rest] = dp[index + 1][rest] + (rest - arr[index] >= 0 ? dp[index + 1][rest - arr[index]] : 0); }
}
return dp[0][aim];}三 arr是面值数组,其中的值都是正数且没有重复。再给定一个正数aim。( 从左往右模型)
3.1 描述
arr是面值数组,其中的值都是正数且没有重复。再给定一个正数aim。
每个值都认为是一种面值,且认为张数是无限的。
返回组成aim的方法数
例如:arr = {1,2},aim = 4
方法如下:1+1+1+1、1+1+2、2+2
一共就3种方法,所以返回3
3.2 分析
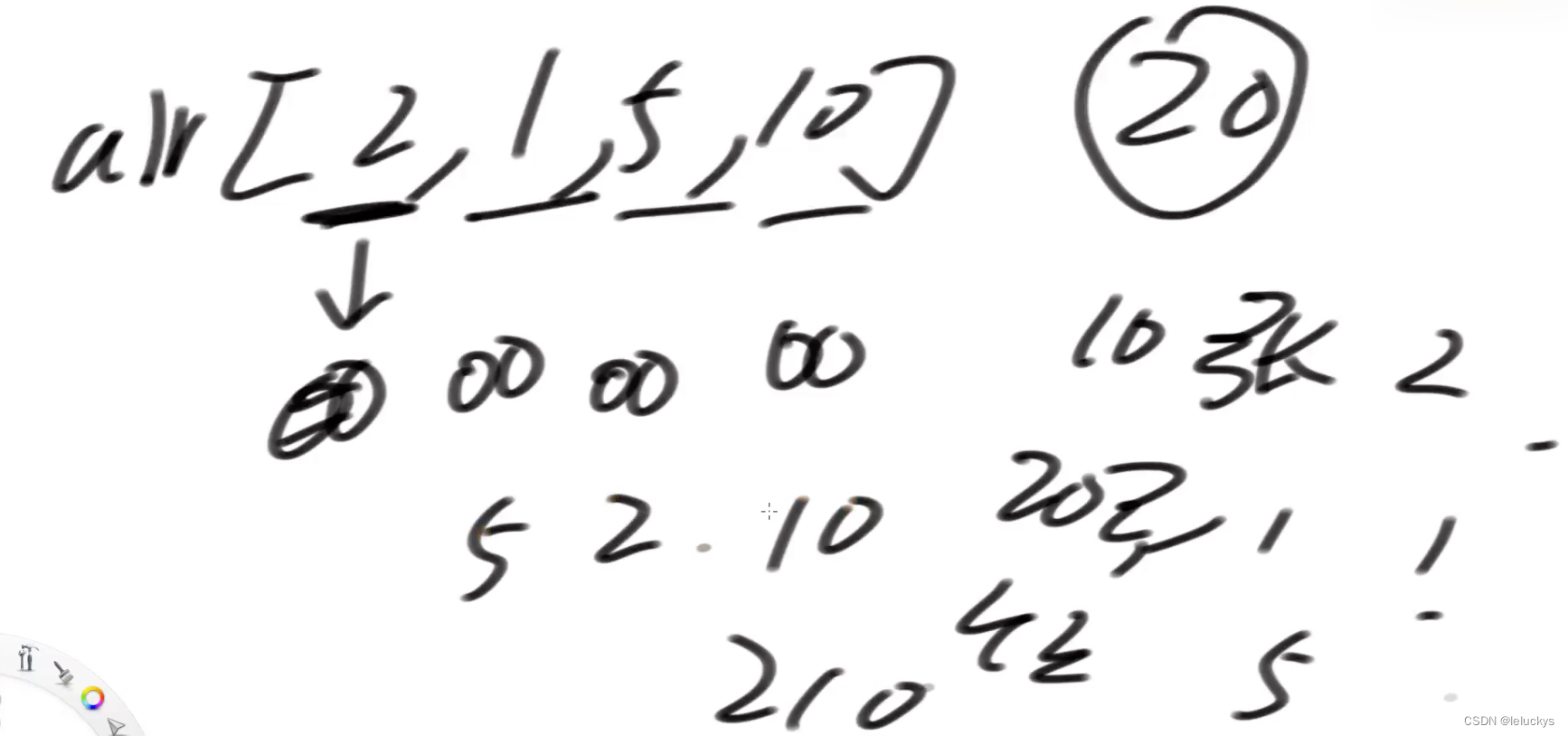
因为每一种面值有无数张,到每个index的时候就会叉出无数分支
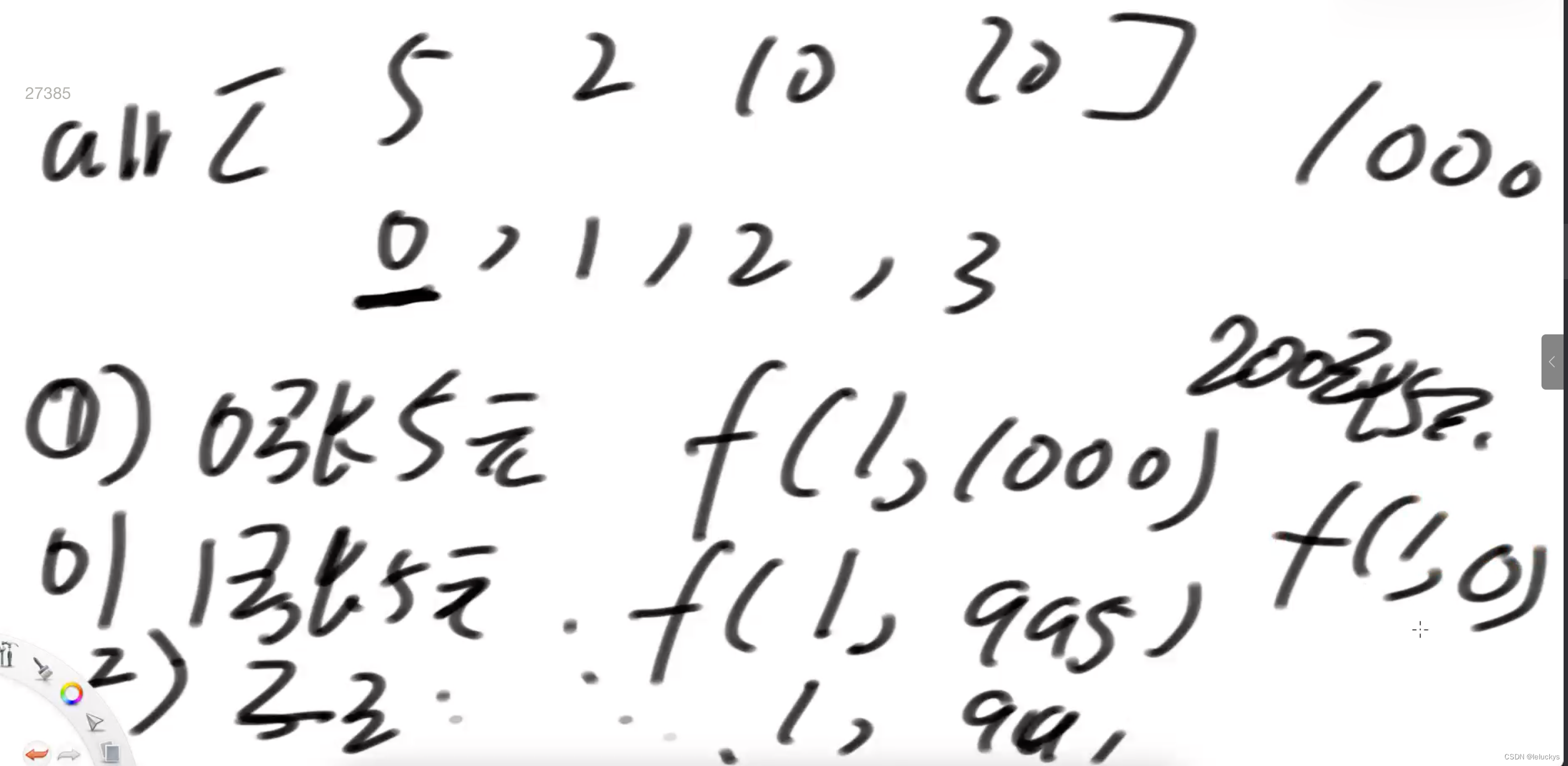
3.3 尝试代码
java
public static int coinsWay(int[] arr, int aim) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0 || aim < 0) {
return 0;
}
Info info = getInfo(arr);
return process(info.coins, info.zhangs, 0, aim);
}
// coins 面值数组,正数且去重
// zhangs 每种面值对应的张数
public static int process(int[] coins, int[] zhangs, int index, int rest) {
if (index == coins.length) {
return rest == 0 ? 1 : 0;
}
int ways = 0;
for (int zhang = 0; zhang * coins[index] <= rest && zhang <= zhangs[index]; zhang++) {
ways += process(coins, zhangs, index + 1, rest - (zhang * coins[index]));
}
return ways;
}3.4 有重复解
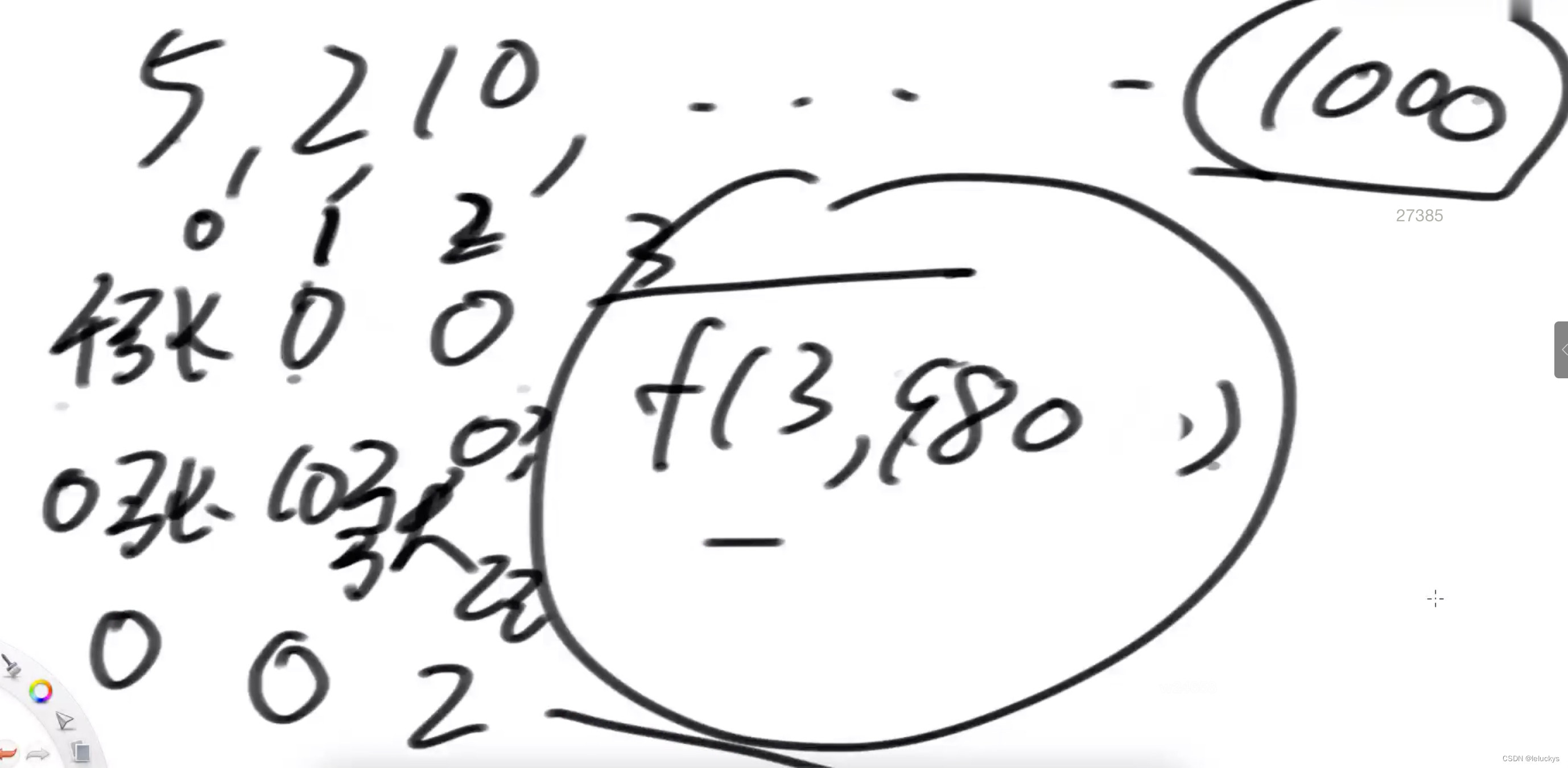
3.5 动态规划代码 (?下面有话动态规划二的版本的动态规划逻辑再理解 这个是通过画图标观察来的)
之前的题目求单独的每个格子没有for循环都是o(1),但是在这里求每个格子都得弄一个for循环
for (int zhang = 0; zhang * coins[index]
ways += dp[index + 1][rest - (zhang * coins[index])];
}
java
public static int dp1(int[] arr, int aim) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0 || aim < 0) {
return 0;
}
Info info = getInfo(arr);
int[] coins = info.coins;
int[] zhangs = info.zhangs;
int N = coins.length;
int[][] dp = new int[N + 1][aim + 1];
dp[N][0] = 1;
for (int index = N - 1; index >= 0; index--) {
for (int rest = 0; rest <= aim; rest++) {
int ways = 0;
for (int zhang = 0; zhang * coins[index] <= rest && zhang <= zhangs[index]; zhang++) {
ways += dp[index + 1][rest - (zhang * coins[index])];
}
dp[index][rest] = ways;
}
}
return dp[0][aim];
}
public static int dp2(int[] arr, int aim) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0 || aim < 0) {
return 0;
}
Info info = getInfo(arr);
int[] coins = info.coins;
int[] zhangs = info.zhangs;
int N = coins.length;
int[][] dp = new int[N + 1][aim + 1];
dp[N][0] = 1;
for (int index = N - 1; index >= 0; index--) {
for (int rest = 0; rest <= aim; rest++) {
dp[index][rest] = dp[index + 1][rest];
if (rest - coins[index] >= 0) {
dp[index][rest] += dp[index][rest - coins[index]];
}
if (rest - coins[index] * (zhangs[index] + 1) >= 0) {
dp[index][rest] -= dp[index + 1][rest - coins[index] * (zhangs[index] + 1)];
}
}
}
return dp[0][aim];
}
// 为了测试
public static int[] randomArray(int maxLen, int maxValue) {
int N = (int) (Math.random() * maxLen);
int[] arr = new int[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
arr[i] = (int) (Math.random() * maxValue) + 1;
}
return arr;
}
// 为了测试
public static void printArray(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
// 为了测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
int maxLen = 10;
int maxValue = 20;
int testTime = 1000000;
System.out.println("测试开始");
for (int i = 0; i < testTime; i++) {
int[] arr = randomArray(maxLen, maxValue);
int aim = (int) (Math.random() * maxValue);
int ans1 = coinsWay(arr, aim);
int ans2 = dp1(arr, aim);
int ans3 = dp2(arr, aim);
if (ans1 != ans2 || ans1 != ans3) {
System.out.println("Oops!");
printArray(arr);
System.out.println(aim);
System.out.println(ans1);
System.out.println(ans2);
System.out.println(ans3);
break;
}
}
System.out.println("测试结束");
}
}四 arr是货币数组,其中的值都是正数。再给定一个正数aim。
4.1 描述
arr是货币数组,其中的值都是正数。再给定一个正数aim。
每个值都认为是一张货币,
认为值相同的货币没有任何不同,
返回组成aim的方法数
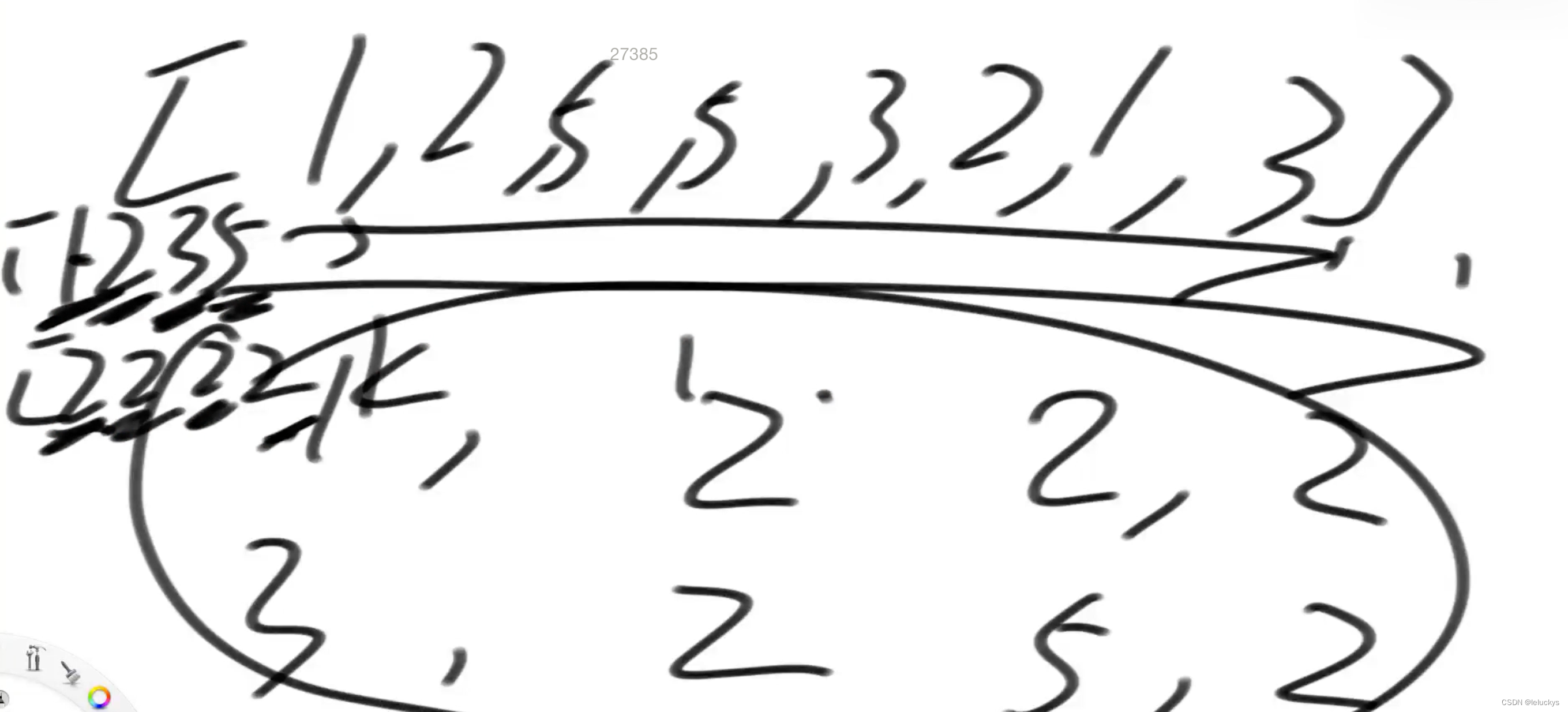
例如:arr = {1,2,1,1,2,1,2},aim = 4
方法:1+1+1+1、1+1+2、2+2
一共就3种方法,所以返回3
4.2 分析
每一种的面值模型张数是限制的,如下去重之后的每一种面值和每种面值的张数
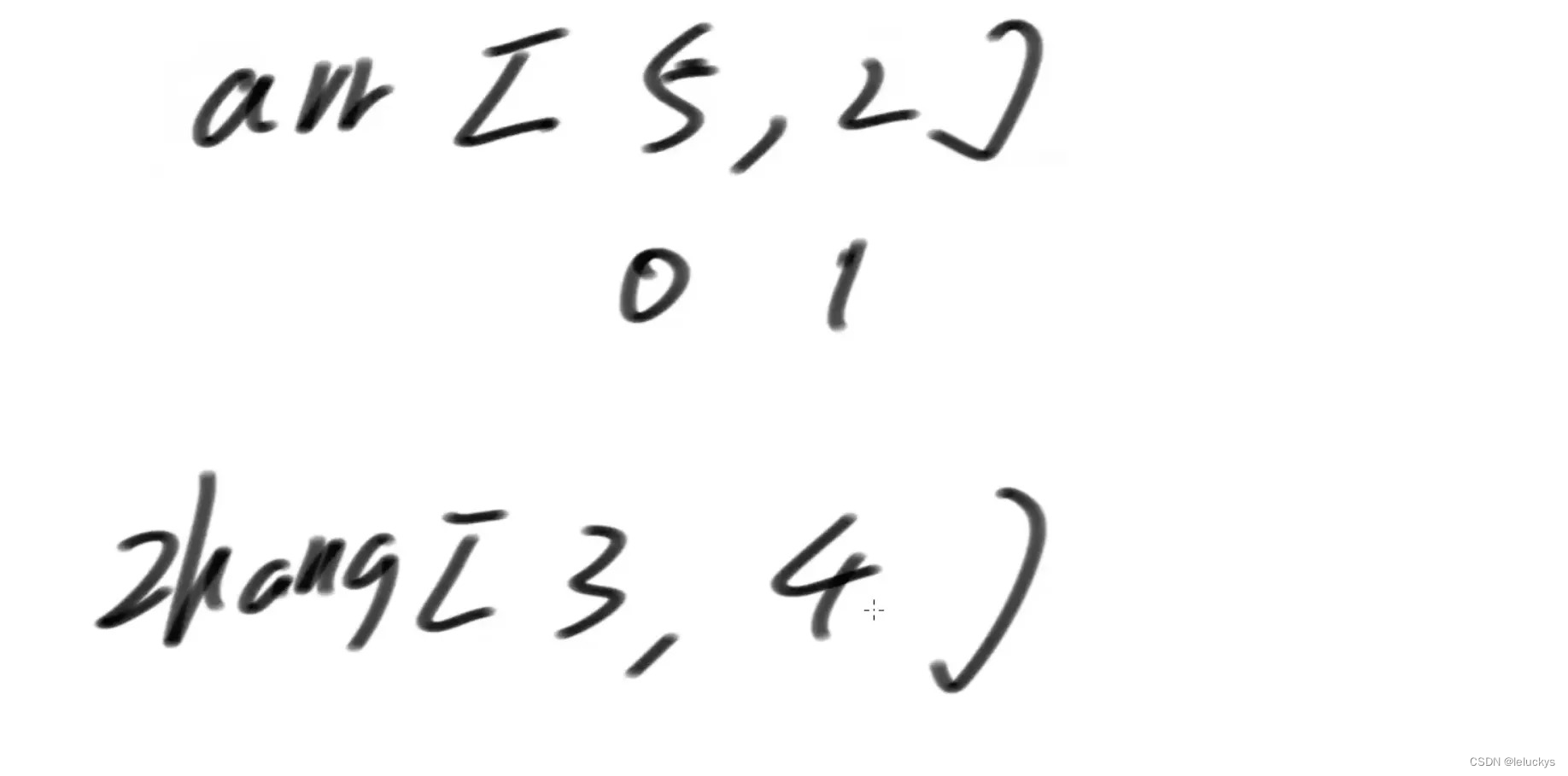
4.3 代码
java
package class21;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map.Entry;public class Code04_CoinsWaySameValueSamePapper {
public static class Info {
public int[] coins; public int[] zhangs; public Info(int[] c, int[] z) {
coins = c; zhangs = z; }
}
public static Info getInfo(int[] arr) {
HashMap<Integer, Integer> counts = new HashMap<>(); for (int value : arr) {
if (!counts.containsKey(value)) {
counts.put(value, 1); } else {
counts.put(value, counts.get(value) + 1); }
}
int N = counts.size(); int[] coins = new int[N]; int[] zhangs = new int[N]; int index = 0; for (Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : counts.entrySet()) {
coins[index] = entry.getKey(); zhangs[index++] = entry.getValue(); }
return new Info(coins, zhangs); }
public static int coinsWay(int[] arr, int aim) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0 || aim < 0) {
return 0; }
Info info = getInfo(arr); return process(info.coins, info.zhangs, 0, aim); }
// coins 面值数组,正数且去重 // zhangs 每种面值对应的张数 public static int process(int[] coins, int[] zhangs, int index, int rest) {
if (index == coins.length) {
return rest == 0 ? 1 : 0; }
int ways = 0; for (int zhang = 0; zhang * coins[index] <= rest && zhang <= zhangs[index]; zhang++) {
ways += process(coins, zhangs, index + 1, rest - (zhang * coins[index])); }
return ways; }
public static int dp1(int[] arr, int aim) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0 || aim < 0) {
return 0; }
Info info = getInfo(arr); int[] coins = info.coins; int[] zhangs = info.zhangs; int N = coins.length; int[][] dp = new int[N + 1][aim + 1]; dp[N][0] = 1; for (int index = N - 1; index >= 0; index--) {
for (int rest = 0; rest <= aim; rest++) {
int ways = 0; for (int zhang = 0; zhang * coins[index] <= rest && zhang <= zhangs[index]; zhang++) {
ways += dp[index + 1][rest - (zhang * coins[index])]; }
dp[index][rest] = ways; }
}
return dp[0][aim]; }
public static int dp2(int[] arr, int aim) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0 || aim < 0) {
return 0; }
Info info = getInfo(arr); int[] coins = info.coins; int[] zhangs = info.zhangs; int N = coins.length; int[][] dp = new int[N + 1][aim + 1]; dp[N][0] = 1; for (int index = N - 1; index >= 0; index--) {
for (int rest = 0; rest <= aim; rest++) {
dp[index][rest] = dp[index + 1][rest]; if (rest - coins[index] >= 0) {
dp[index][rest] += dp[index][rest - coins[index]]; }
if (rest - coins[index] * (zhangs[index] + 1) >= 0) {
dp[index][rest] -= dp[index + 1][rest - coins[index] * (zhangs[index] + 1)]; }
}
}
return dp[0][aim]; }
// 为了测试 public static int[] randomArray(int maxLen, int maxValue) {
int N = (int) (Math.random() * maxLen); int[] arr = new int[N]; for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
arr[i] = (int) (Math.random() * maxValue) + 1; }
return arr; }
// 为了测试 public static void printArray(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " "); }
System.out.println(); }
// 为了测试 public static void main(String[] args) {
int maxLen = 10; int maxValue = 20; int testTime = 1000000; System.out.println("测试开始"); for (int i = 0; i < testTime; i++) {
int[] arr = randomArray(maxLen, maxValue); int aim = (int) (Math.random() * maxValue); int ans1 = coinsWay(arr, aim); int ans2 = dp1(arr, aim); int ans3 = dp2(arr, aim); if (ans1 != ans2 || ans1 != ans3) {
System.out.println("Oops!"); printArray(arr); System.out.println(aim); System.out.println(ans1); System.out.println(ans2); System.out.println(ans3); break; }
}
System.out.println("测试结束"); }
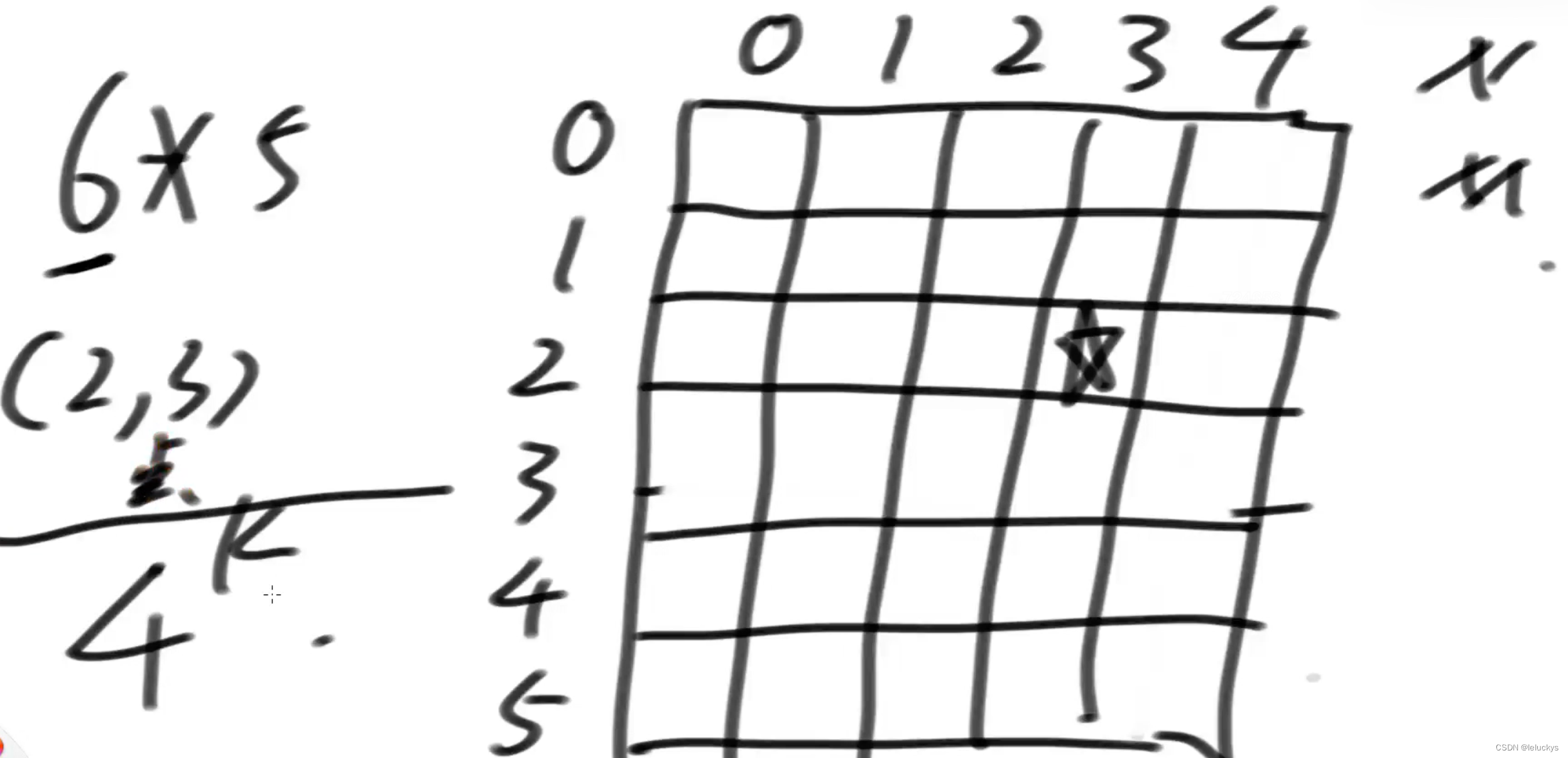
}六 给定5个参数,N,M,row,col,k
6.1 定5个参数,N,M,row,col,k
表示在NM的区域上,醉汉Bob初始在(row,col)位置Bob一共要迈出k步,且每步都会等概率向上下左右四个方向走一个单位任何时候Bob只要离开NM的区域,就直接死亡
返回k步之后,Bob还在N*M的区域的概率
6.2 分析
6.3 代码
java
public static double livePosibility1(int row, int col, int k, int N, int M) {
return (double) process(row, col, k, N, M) / Math.pow(4, k);
}
// 目前在row,col位置,还有rest步要走,走完了如果还在棋盘中就获得1个生存点,返回总的生存点数
public static long process(int row, int col, int rest, int N, int M) {
if (row < 0 || row == N || col < 0 || col == M) {
return 0;
}
// 还在棋盘中!
if (rest == 0) {
return 1;
}
// 还在棋盘中!还有步数要走
long up = process(row - 1, col, rest - 1, N, M);
long down = process(row + 1, col, rest - 1, N, M);
long left = process(row, col - 1, rest - 1, N, M);
long right = process(row, col + 1, rest - 1, N, M);
return up + down + left + right;
}6.4 动态规划分析 再看一下
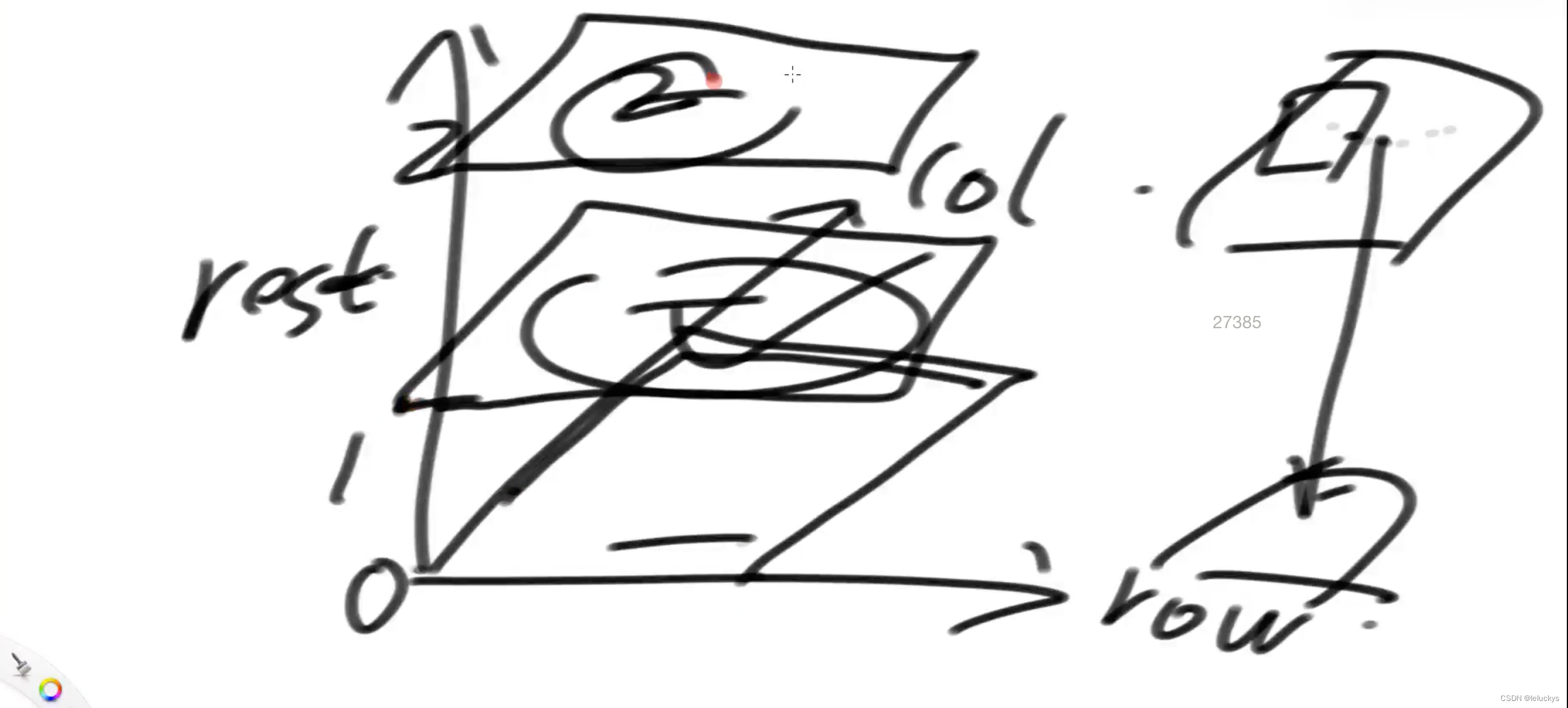
6.5 动态规划代码
java
public static double livePosibility2(int row, int col, int k, int N, int M) {
long[][][] dp = new long[N][M][k + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
dp[i][j][0] = 1;
}
}
for (int rest = 1; rest <= k; rest++) {
for (int r = 0; r < N; r++) {
for (int c = 0; c < M; c++) {
dp[r][c][rest] = pick(dp, N, M, r - 1, c, rest - 1);
dp[r][c][rest] += pick(dp, N, M, r + 1, c, rest - 1);
dp[r][c][rest] += pick(dp, N, M, r, c - 1, rest - 1);
dp[r][c][rest] += pick(dp, N, M, r, c + 1, rest - 1);
}
}
}
return (double) dp[row][col][k] / Math.pow(4, k);
}
public static long pick(long[][][] dp, int N, int M, int r, int c, int rest) {
if (r < 0 || r == N || c < 0 || c == M) {
return 0;
}
return dp[r][c][rest];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(livePosibility1(6, 6, 10, 50, 50));
System.out.println(livePosibility2(6, 6, 10, 50, 50));
}七 动态规划总结
记忆话搜索 暴力方法画一个表出来,不关心谁先依赖谁后依赖,没算过就去算,算过了就去拿值
严格表结构 严格的整理好表依赖关系 从表的简单位置填到复杂位置 比记忆话搜索进一步梳理了表额依赖关系,从简单到复杂去填