WXinlong/SOLO:用于实例分割的 SOLO 和 SOLOv2,ECCV 2020 和 NeurIPS 2020。 (github.com)
1.MaskFormer
1.1 环境配置 Ubuntu20.04+cuda11.1
conda create --name mask2former python=3.8 -y
conda activate mask2former
conda install pytorch==1.9.0 torchvision==0.10.0 cudatoolkit=11.1 -c pytorch -c nvidia
pip install -U opencv-python
git clone git@github.com:facebookresearch/detectron2.git
上面这个git不好用的话就手动下载这个代码
cd detectron2
pip install -e .
pip install git+https://github.com/cocodataset/panopticapi.git
cd ..
git clone git@github.com:facebookresearch/Mask2Former.git
同理,可以手动下载这个源码
cd Mask2Former
pip install -r requirements.txt
cd mask2former/modeling/pixel_decoder/ops
sh make.sh
上述内容就是完整的配置环境的过程
1.2 数据集预处理
1.2.1 划分为训练集和验证集
import os
import json
import shutil
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# 文件夹路径
img_folder = '/hy-tmp/pic'
mask_folder = '/hy-tmp/cv2_mask'
output_dir = '/hy-tmp/output'
# 创建输出文件夹
train_img_folder = os.path.join(output_dir, 'train2017')
train_mask_folder = os.path.join(output_dir, 'train2017_masks')
val_img_folder = os.path.join(output_dir, 'val2017')
val_mask_folder = os.path.join(output_dir, 'val2017_masks')
os.makedirs(train_img_folder, exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(train_mask_folder, exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(val_img_folder, exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(val_mask_folder, exist_ok=True)
# 读取所有图像文件名
img_files = [f for f in os.listdir(img_folder) if os.path.isfile(os.path.join(img_folder, f))]
# 使用 train_test_split 划分数据集
train_files, val_files = train_test_split(img_files, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
# 复制文件到相应的文件夹
for img_filename in train_files:
img_name, img_ext = os.path.splitext(img_filename)
shutil.copy(os.path.join(img_folder, img_filename), os.path.join(train_img_folder, img_filename))
shutil.copy(os.path.join(mask_folder, img_name + '.png'), os.path.join(train_mask_folder, img_name + '.png'))
for img_filename in val_files:
img_name, img_ext = os.path.splitext(img_filename)
shutil.copy(os.path.join(img_folder, img_filename), os.path.join(val_img_folder, img_filename))
shutil.copy(os.path.join(mask_folder, img_name + '.png'), os.path.join(val_mask_folder, img_name + '.png'))
print("Dataset split completed.")1.2.2 转换为json格式
import os
import json
import cv2
import numpy as np
from pycocotools import mask as coco_mask
from PIL import Image
# 文件夹路径
img_folder = '/hy-tmp/pic'
mask_folder = '/hy-tmp/cv2_mask'
output_dir = '/hy-tmp/1'
train_img_folder = '/hy-tmp/output/train2017'
train_mask_folder = '/hy-tmp/output/train2017_masks'
val_img_folder = '/hy-tmp/output/val2017'
val_mask_folder = '/hy-tmp/output/val2017_masks'
# 初始化 COCO 格式字典
def init_coco_format():
return {
"images": [],
"annotations": [],
"categories": [{"id": 1, "name": "object", "supercategory": "object"}]
}
def create_annotations(img_folder, mask_folder, output_json_path):
coco_format = init_coco_format()
annotation_id = 1
image_id = 1
for img_filename in os.listdir(img_folder):
img_name, img_ext = os.path.splitext(img_filename)
img_path = os.path.join(img_folder, img_filename)
mask_path = os.path.join(mask_folder, img_name + '.png')
if not os.path.exists(mask_path):
continue
# 读取图像
img = Image.open(img_path)
width, height = img.size
# 生成图像信息
image_info = {
"id": image_id,
"file_name": img_filename,
"width": width,
"height": height
}
coco_format["images"].append(image_info)
# 读取掩码
mask = Image.open(mask_path)
mask = np.array(mask)
# 寻找掩码的边界框
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(mask, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
for contour in contours:
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(contour)
bbox = [x, y, w, h]
# 生成掩码的二进制格式
binary_mask = np.zeros((height, width), dtype=np.uint8)
cv2.drawContours(binary_mask, [contour], -1, 1, -1)
encoded_mask = coco_mask.encode(np.asfortranarray(binary_mask))
# 将 RLE 编码转换为可序列化的格式
rle = {
'counts': encoded_mask['counts'].decode('utf-8'), # 转换为字符串
'size': encoded_mask['size']
}
annotation = {
"id": annotation_id,
"image_id": image_id,
"category_id": 1,
"segmentation": rle,
"area": float(coco_mask.area(encoded_mask)),
"bbox": bbox,
"iscrowd": 0
}
coco_format["annotations"].append(annotation)
annotation_id += 1
image_id += 1
# 保存到JSON文件
with open(output_json_path, 'w') as f:
json.dump(coco_format, f)
print(f"COCO format annotation file created at {output_json_path}.")
# 创建注释文件
create_annotations(train_img_folder, train_mask_folder, os.path.join(output_dir, 'annotations/instances_train2017.json'))
create_annotations(val_img_folder, val_mask_folder, os.path.join(output_dir, 'annotations/instances_val2017.json'))1.2.3 实例分割数据集
import os
import json
import cv2
import numpy as np
from pycocotools import mask as coco_mask
from PIL import Image
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import shutil
# 文件夹路径
img_folder = '/hy-tmp/pic'
mask_folder = '/hy-tmp/cv2_mask'
output_dir = '/hy-tmp/json'
# 创建输出文件夹
train_img_folder = os.path.join(output_dir, 'train2017')
train_mask_folder = os.path.join(output_dir, 'train2017_masks')
val_img_folder = os.path.join(output_dir, 'val2017')
val_mask_folder = os.path.join(output_dir, 'val2017_masks')
os.makedirs(train_img_folder, exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(train_mask_folder, exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(val_img_folder, exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(val_mask_folder, exist_ok=True)
# 读取所有图像文件名
img_files = [f for f in os.listdir(img_folder) if os.path.isfile(os.path.join(img_folder, f))]
# 使用 train_test_split 划分数据集
train_files, val_files = train_test_split(img_files, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
# 复制文件到相应的文件夹
for img_filename in train_files:
img_name, img_ext = os.path.splitext(img_filename)
shutil.copy(os.path.join(img_folder, img_filename), os.path.join(train_img_folder, img_filename))
shutil.copy(os.path.join(mask_folder, img_name + '.png'), os.path.join(train_mask_folder, img_name + '.png'))
for img_filename in val_files:
img_name, img_ext = os.path.splitext(img_filename)
shutil.copy(os.path.join(img_folder, img_filename), os.path.join(val_img_folder, img_filename))
shutil.copy(os.path.join(mask_folder, img_name + '.png'), os.path.join(val_mask_folder, img_name + '.png'))
print("Dataset split completed.")
# 初始化 COCO 格式字典
def init_coco_format():
return {
"images": [],
"annotations": [],
"categories": [{"id": 1, "name": "object", "supercategory": "object"}]
}
def create_instance_annotations(img_folder, mask_folder, output_json_path):
coco_format = init_coco_format()
annotation_id = 1
image_id = 1
for img_filename in os.listdir(img_folder):
img_name, img_ext = os.path.splitext(img_filename)
img_path = os.path.join(img_folder, img_filename)
mask_path = os.path.join(mask_folder, img_name + '.png')
if not os.path.exists(mask_path):
continue
# 读取图像
img = Image.open(img_path)
width, height = img.size
# 生成图像信息
image_info = {
"id": image_id,
"file_name": img_filename,
"width": width,
"height": height
}
coco_format["images"].append(image_info)
# 读取掩码
mask = Image.open(mask_path)
mask = np.array(mask)
# 寻找掩码的边界框
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(mask, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
for contour in contours:
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(contour)
bbox = [x, y, w, h]
# 生成掩码的二进制格式
binary_mask = np.zeros((height, width), dtype=np.uint8)
cv2.drawContours(binary_mask, [contour], -1, 1, -1)
encoded_mask = coco_mask.encode(np.asfortranarray(binary_mask))
# 将 RLE 编码转换为可序列化的格式
rle = {
'counts': encoded_mask['counts'].decode('utf-8'), # 转换为字符串
'size': encoded_mask['size']
}
annotation = {
"id": annotation_id,
"image_id": image_id,
"category_id": 1,
"segmentation": rle,
"area": float(coco_mask.area(encoded_mask)),
"bbox": bbox,
"iscrowd": 0
}
coco_format["annotations"].append(annotation)
annotation_id += 1
image_id += 1
# 保存到JSON文件
with open(output_json_path, 'w') as f:
json.dump(coco_format, f)
print(f"COCO format instance annotation file created at {output_json_path}.")
# 创建实例分割注释文件
create_instance_annotations(train_img_folder, train_mask_folder, os.path.join(output_dir, 'annotations/instances_train2017.json'))
create_instance_annotations(val_img_folder, val_mask_folder, os.path.join(output_dir, 'annotations/instances_val2017.json'))1.2.4 全景分割数据集
import os
import json
import cv2
import numpy as np
from pycocotools import mask as coco_mask
from PIL import Image
# 初始化 COCO 格式字典
def init_coco_format():
return {
"images": [],
"annotations": [],
"categories": [{"id": 1, "name": "object", "supercategory": "object"}],
"licenses": [],
"info": {
"year": 2023,
"version": "1.0",
"description": "COCO Panoptic Dataset",
"contributor": "",
"url": "",
"date_created": "2023-01-01"
}
}
def create_panoptic_annotations(img_folder, mask_folder, output_json_path):
coco_format = init_coco_format()
panoptic_annotations = []
annotation_id = 1
image_id = 1
for img_filename in os.listdir(img_folder):
img_name, img_ext = os.path.splitext(img_filename)
img_path = os.path.join(img_folder, img_filename)
mask_path = os.path.join(mask_folder, img_name + '.png')
if not os.path.exists(mask_path):
continue
# 读取图像
img = Image.open(img_path)
width, height = img.size
# 生成图像信息
image_info = {
"id": image_id,
"file_name": img_filename,
"width": width,
"height": height
}
coco_format["images"].append(image_info)
# 读取掩码
mask = Image.open(mask_path)
mask = np.array(mask)
# 生成全景注释信息
panoptic_annotation = {
"image_id": image_id,
"file_name": img_filename.replace('.jpg', '.png'),
"segments_info": []
}
# 寻找掩码的边界框
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(mask, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
for contour in contours:
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(contour)
bbox = [x, y, w, h]
# 生成掩码的二进制格式
binary_mask = np.zeros((height, width), dtype=np.uint8)
cv2.drawContours(binary_mask, [contour], -1, 1, -1)
encoded_mask = coco_mask.encode(np.asfortranarray(binary_mask))
# 将 RLE 编码转换为可序列化的格式
rle = {
'counts': encoded_mask['counts'].decode('utf-8'), # 转换为字符串
'size': encoded_mask['size']
}
segment_info = {
"id": annotation_id,
"category_id": 1,
"iscrowd": 0,
"bbox": bbox,
"area": float(coco_mask.area(encoded_mask)),
"segmentation": rle
}
panoptic_annotation["segments_info"].append(segment_info)
annotation_id += 1
panoptic_annotations.append(panoptic_annotation)
image_id += 1
# 保存到JSON文件
os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(output_json_path), exist_ok=True)
with open(output_json_path, 'w') as f:
json.dump({
"images": coco_format["images"],
"annotations": panoptic_annotations,
"categories": coco_format["categories"],
"licenses": coco_format["licenses"],
"info": coco_format["info"]
}, f)
print(f"COCO format panoptic annotation file created at {output_json_path}.")
# 创建全景注释文件
create_panoptic_annotations(train_img_folder, train_mask_folder, os.path.join(output_dir, 'annotations/panoptic_train2017.json'))
create_panoptic_annotations(val_img_folder, val_mask_folder, os.path.join(output_dir, 'annotations/panoptic_val2017.json'))1.2.5 全景分割数据集找到对应的图片(.png格式)
import json
import os
import shutil
# 定义文件路径
json_path = 'path/to/panoptic_train2017.json'
img_dir = 'path/to/img'
output_dir = 'path/to/output_folder'
# 如果输出文件夹不存在,则创建
if not os.path.exists(output_dir):
os.makedirs(output_dir)
# 加载 JSON 文件
with open(json_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
data = json.load(f)
# 假设 JSON 文件中有一个键 "images",其中包含每个图像的相关信息
image_info_list = data.get('images', [])
# 遍历每个图像信息并复制对应的图片到输出文件夹
for image_info in image_info_list:
# 假设每个图像信息包含 "file_name" 键
file_name = image_info.get('file_name')
if file_name:
# 构建原始图片路径
img_path = os.path.join(img_dir, file_name)
# 构建目标图片路径
output_path = os.path.join(output_dir, file_name)
# 检查文件是否存在并复制
if os.path.isfile(img_path):
shutil.copy(img_path, output_path)
print(f"图片 {file_name} 已复制到 {output_path}")
else:
print(f"图片 {file_name} 不存在于路径 {img_path}")
else:
print("图像信息中缺少 'file_name' 键")1.3训练过程
单卡训练太慢了,需要好几天,选择多卡训练
单卡训练的代码
python train_net.py \
--config-file configs/coco/panoptic-segmentation/maskformer2_R50_bs16_50ep.yaml \
--num-gpus 1 SOLVER.IMS_PER_BATCH 2 SOLVER.BASE_LR 0.00025下图为正式运行的过程

多卡训练的代码
遇到的小插曲
报错
TypeError: init() got an unexpected keyword argument 'dtype'
修改events.py文件以及
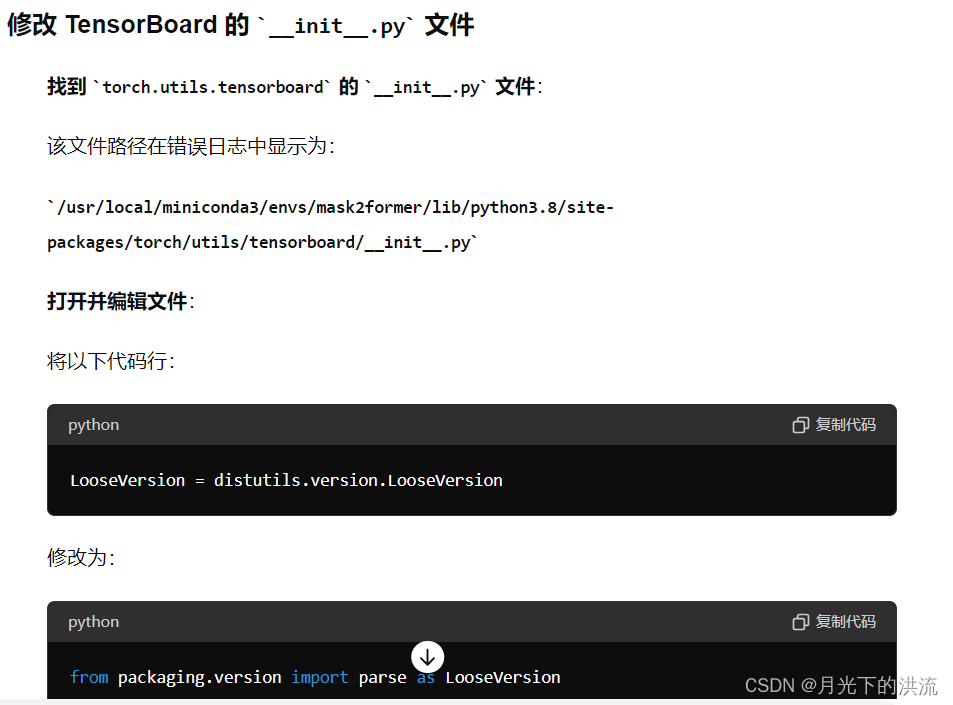
from packaging.version import parse as LooseVersion1.4测试过程
2. SOLOV2
2.1 环境配置
2.1.1选择pytorch版本
torch 1.5.0+cu101 pypi_0 pypi
2.1.2 编译
git clone https://github.com/WXinlong/SOLO.git
cd SOLO
pip install -r requirements/build.txt
pip install "git+https://github.com/cocodataset/cocoapi.git#subdirectory=PythonAPI"
pip install -v -e . # or "python setup.py develop"
2.2 数据集预处理
将数据集转换为coco数据集格式
2.2.1 把img以及对应的mask转换为train_2017.json以及val_2017.json格式
代码如下
import os
import json
import cv2
import numpy as np
from pycocotools import mask as coco_mask
from PIL import Image
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# 文件夹路径
img_folder = '/hy-tmp/pic'
mask_folder = '/hy-tmp/cv2_mask'
output_train_json_path = '/hy-tmp/coco/annotations/instances_train2017.json'
output_val_json_path = '/hy-tmp/coco/annotations/instances_val2017.json'
# 初始化 COCO 格式字典
def init_coco_format():
return {
"images": [],
"annotations": [],
"categories": [{"id": 1, "name": "object", "supercategory": "object"}]
}
# 读取文件名
img_files = [f for f in os.listdir(img_folder) if os.path.isfile(os.path.join(img_folder, f))]
train_files, val_files = train_test_split(img_files, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
def create_annotations(files, coco_format, start_image_id=1, start_annotation_id=1):
image_id = start_image_id
annotation_id = start_annotation_id
for img_filename in files:
img_name, img_ext = os.path.splitext(img_filename)
img_path = os.path.join(img_folder, img_filename)
mask_path = os.path.join(mask_folder, img_name + '.png') # 假设掩码是 .png 格式
if not os.path.exists(mask_path):
continue
# 读取图像
img = Image.open(img_path)
width, height = img.size
# 生成图像信息
image_info = {
"id": image_id,
"file_name": img_filename,
"width": width,
"height": height
}
coco_format["images"].append(image_info)
# 读取掩码
mask = Image.open(mask_path)
mask = np.array(mask)
# 寻找掩码的边界框
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(mask, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
for contour in contours:
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(contour)
bbox = [x, y, w, h]
# 生成掩码的二进制格式
binary_mask = np.zeros((height, width), dtype=np.uint8)
cv2.drawContours(binary_mask, [contour], -1, 1, -1)
encoded_mask = coco_mask.encode(np.asfortranarray(binary_mask))
# 将 RLE 编码转换为可序列化的格式
rle = {
'counts': encoded_mask['counts'].decode('utf-8'), # 转换为字符串
'size': encoded_mask['size']
}
annotation = {
"id": annotation_id,
"image_id": image_id,
"category_id": 1,
"segmentation": rle,
"area": float(coco_mask.area(encoded_mask)),
"bbox": bbox,
"iscrowd": 0
}
coco_format["annotations"].append(annotation)
annotation_id += 1
image_id += 1
return coco_format, image_id, annotation_id
# 初始化 COCO 格式字典
coco_train_format = init_coco_format()
coco_val_format = init_coco_format()
# 创建训练集注释
coco_train_format, train_image_id, train_annotation_id = create_annotations(train_files, coco_train_format)
# 创建验证集注释
coco_val_format, _, _ = create_annotations(val_files, coco_val_format, start_image_id=train_image_id, start_annotation_id=train_annotation_id)
# 保存训练集注释到JSON文件
with open(output_train_json_path, 'w') as f:
json.dump(coco_train_format, f)
# 保存验证集注释到JSON文件
with open(output_val_json_path, 'w') as f:
json.dump(coco_val_format, f)
print("COCO format annotation files created.")2.2.2 把数据集划分为train和val
import os
import json
import shutil
# 文件夹路径
img_folder = '/hy-tmp/pic'
val_img_folder = '/hy-tmp/coco/train2017'
val_json_path = '/hy-tmp/coco/annotations/instances_train2017.json'
# 创建 val2017 文件夹,如果不存在
os.makedirs(val_img_folder, exist_ok=True)
# 读取 val2017.json 文件
with open(val_json_path, 'r') as f:
val_data = json.load(f)
# 获取 val2017.json 中所有图片文件名
val_img_files = [img_info['file_name'] for img_info in val_data['images']]
# 复制图片到 val2017 文件夹
for img_filename in val_img_files:
src_path = os.path.join(img_folder, img_filename)
dst_path = os.path.join(val_img_folder, img_filename)
if os.path.exists(src_path):
shutil.copy2(src_path, dst_path)
print(f"Copied: {src_path} to {dst_path}")
else:
print(f"File not found: {src_path}")
print("All val2017 images have been copied.")2.2.3 如果img和mask不是成对数据
首先运行下面的代码,然后在运行2.2.1以及2.2.2
import os
# 文件夹路径
img_folder = '/hy-tmp/pic'
mask_folder = '/hy-tmp/cv2_mask'
# 获取文件夹中所有文件名(不包括扩展名)
img_files = {os.path.splitext(f)[0] for f in os.listdir(img_folder) if os.path.isfile(os.path.join(img_folder, f))}
mask_files = {os.path.splitext(f)[0] for f in os.listdir(mask_folder) if os.path.isfile(os.path.join(mask_folder, f))}
# 找出在img文件夹中但不在mask文件夹中的文件
img_files_to_delete = img_files - mask_files
# 找出在mask文件夹中但不在img文件夹中的文件
mask_files_to_delete = mask_files - img_files
# 删除img文件夹中的不对应文件
for file in img_files_to_delete:
file_path = os.path.join(img_folder, file + '.jpg') # 假设文件扩展名是.jpg,根据实际情况修改
if os.path.exists(file_path):
os.remove(file_path)
print(f"Deleted from img: {file_path}")
# 删除mask文件夹中的不对应文件
for file in mask_files_to_delete:
file_path = os.path.join(mask_folder, file + '.png') # 假设文件扩展名是.png,根据实际情况修改
if os.path.exists(file_path):
os.remove(file_path)
print(f"Deleted from mask: {file_path}")
print("Deletion completed.")2.3 使用单卡进行训练
python tools/train.py configs/solov2/solov2_r50_fpn_8gpu_1x.py 成功运行界面如下图所示,目前官方给的epoch是12个,未修改

2.4 使用单卡进行测试
python tools/test_ins.py configs/solov2/solov2_r50_fpn_8gpu_1x.py /hy-tmp/SOLO/work_dirs/solov2_release_r50_fpn_8gpu_1x/latest.pth --show --out results_solo.pkl --eval segm结果如下图
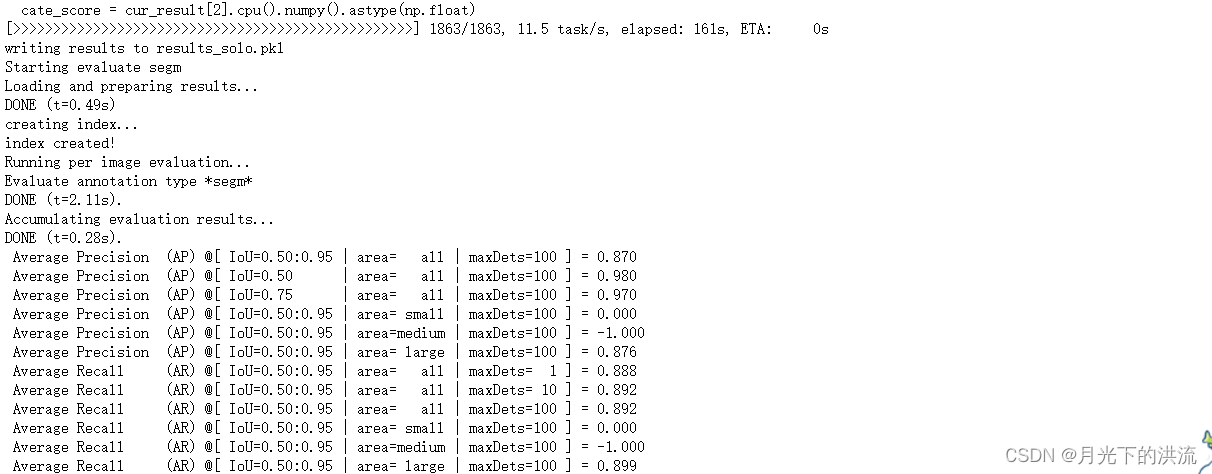
2.5 使用单卡进行可视化
python tools/test_ins_vis.py configs/solov2/solov2_r50_fpn_8gpu_1x.py /hy-tmp/SOLO/work_dirs/solov2_release_r50_fpn_8gpu_1x/latest.pth --show --save_dir work_dirs/vis_solo结果在work_dirs/vis_solo文件夹下面