目录
一、带头双向循环链表接口实现
连接关系:
实现这个链表最重要的就是理清楚连接关系:这里我给出两个动图,模拟这个关系
插入: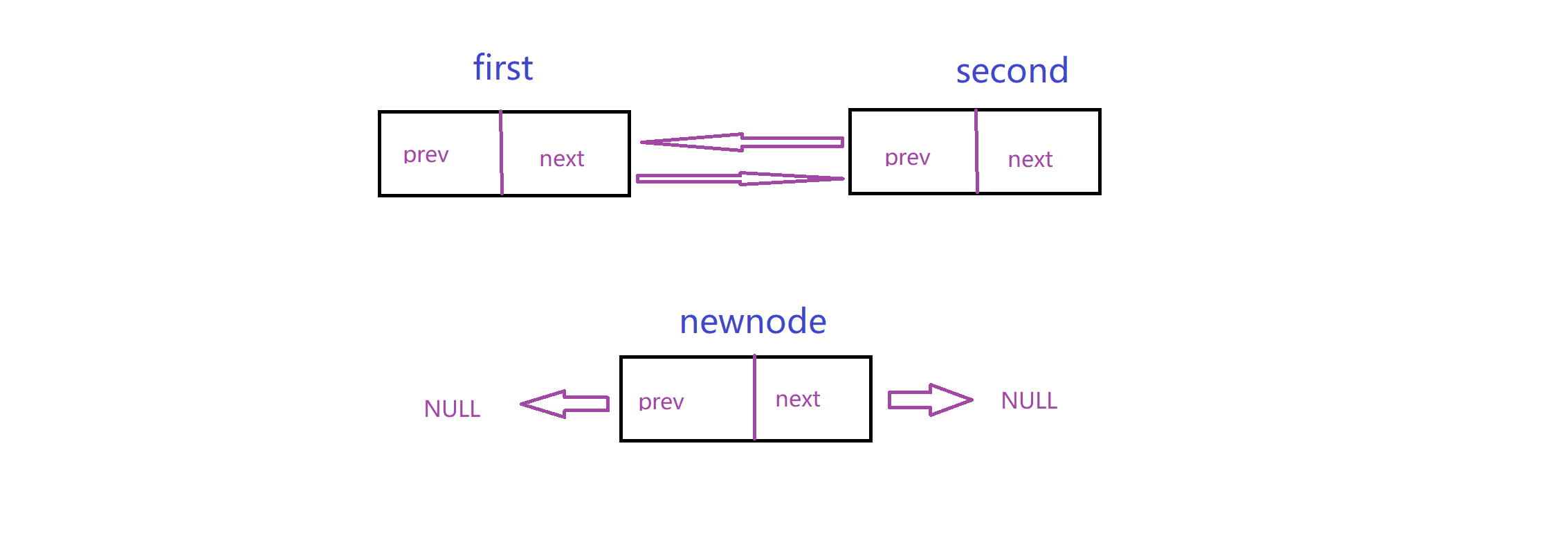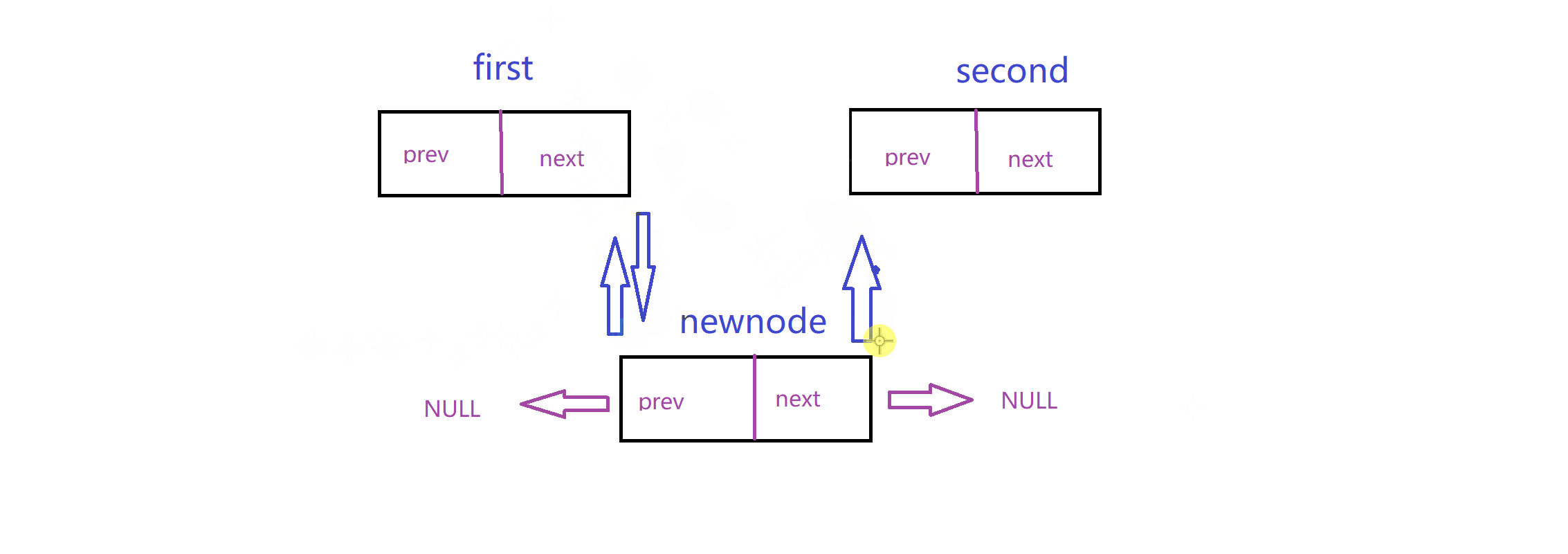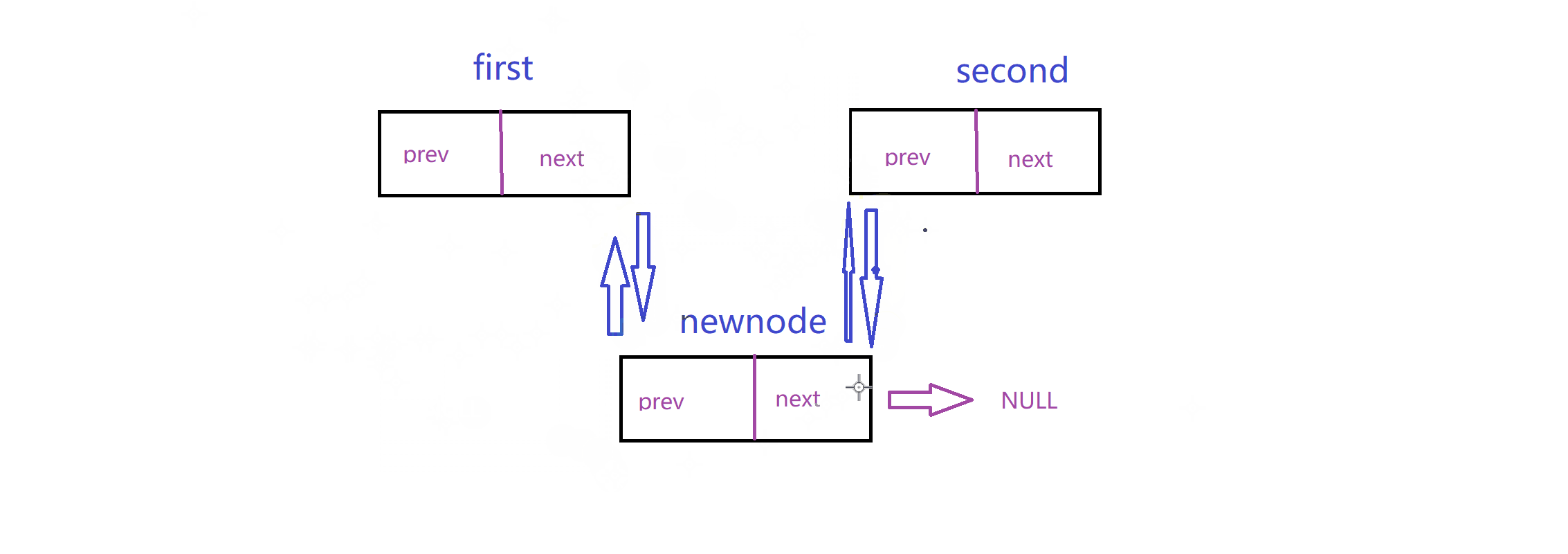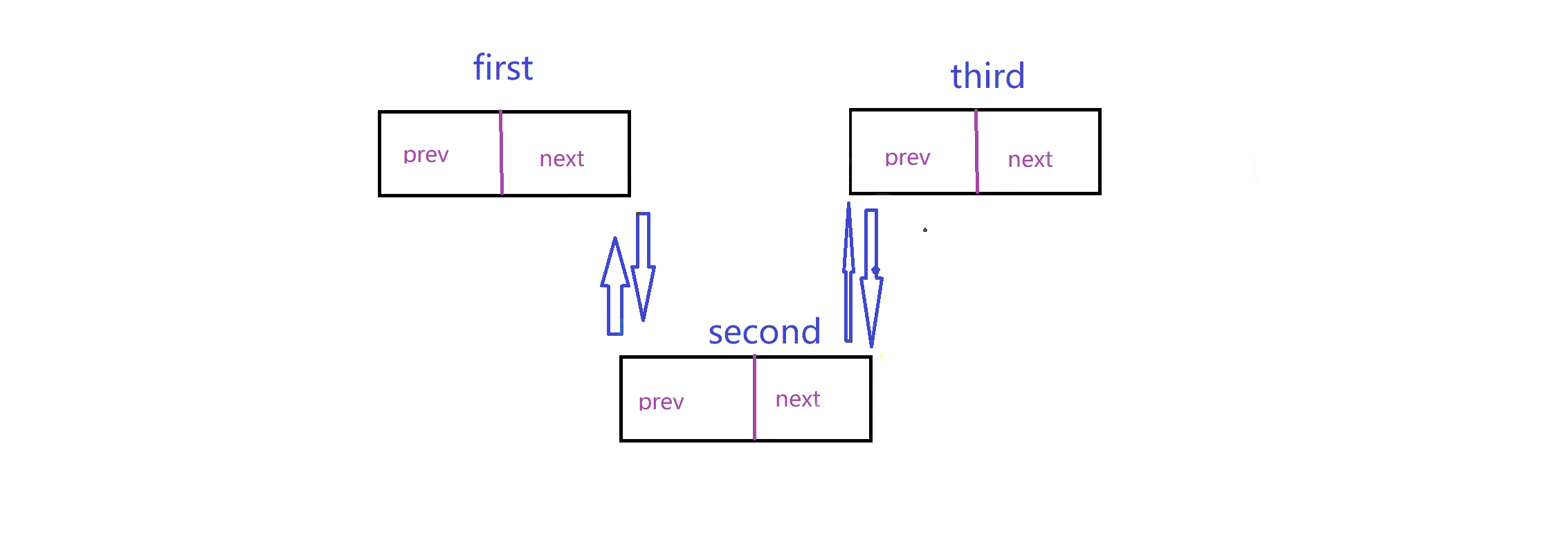
删除: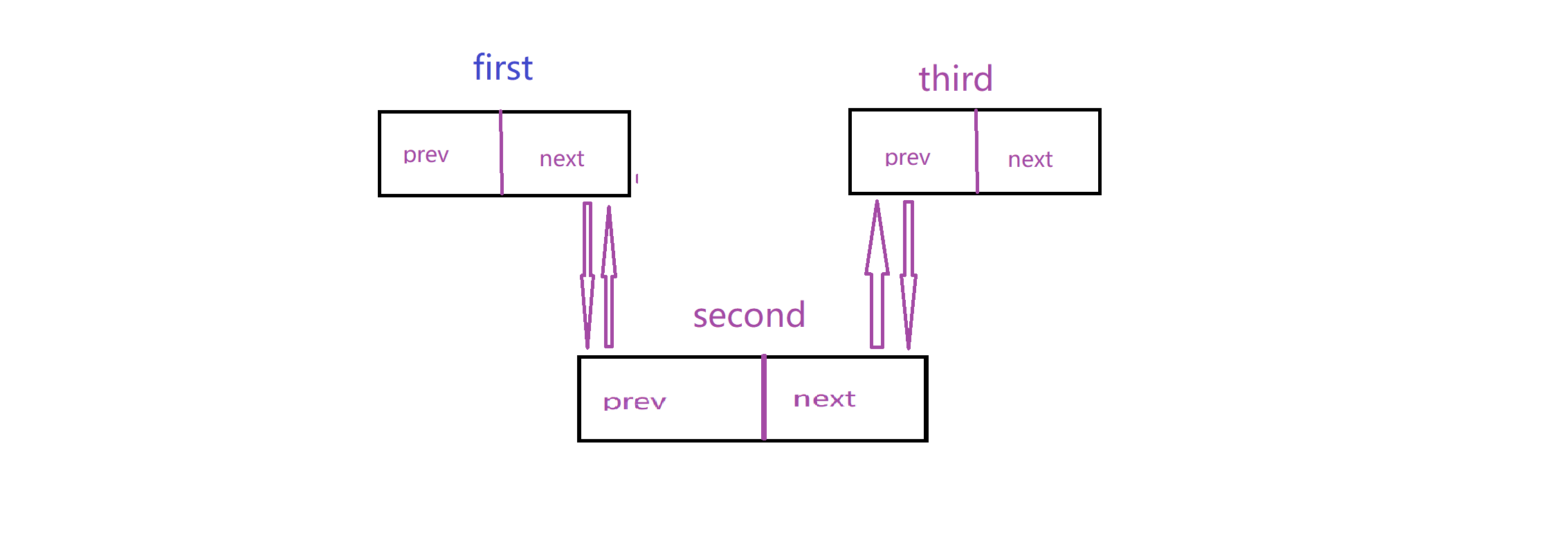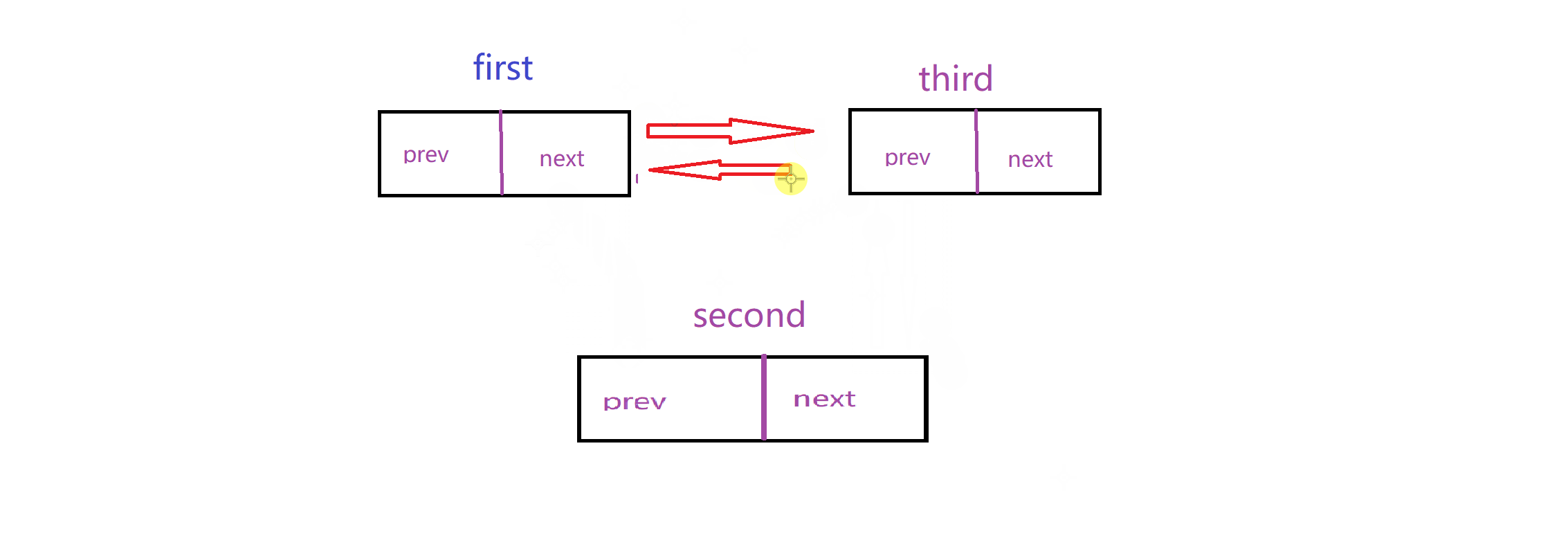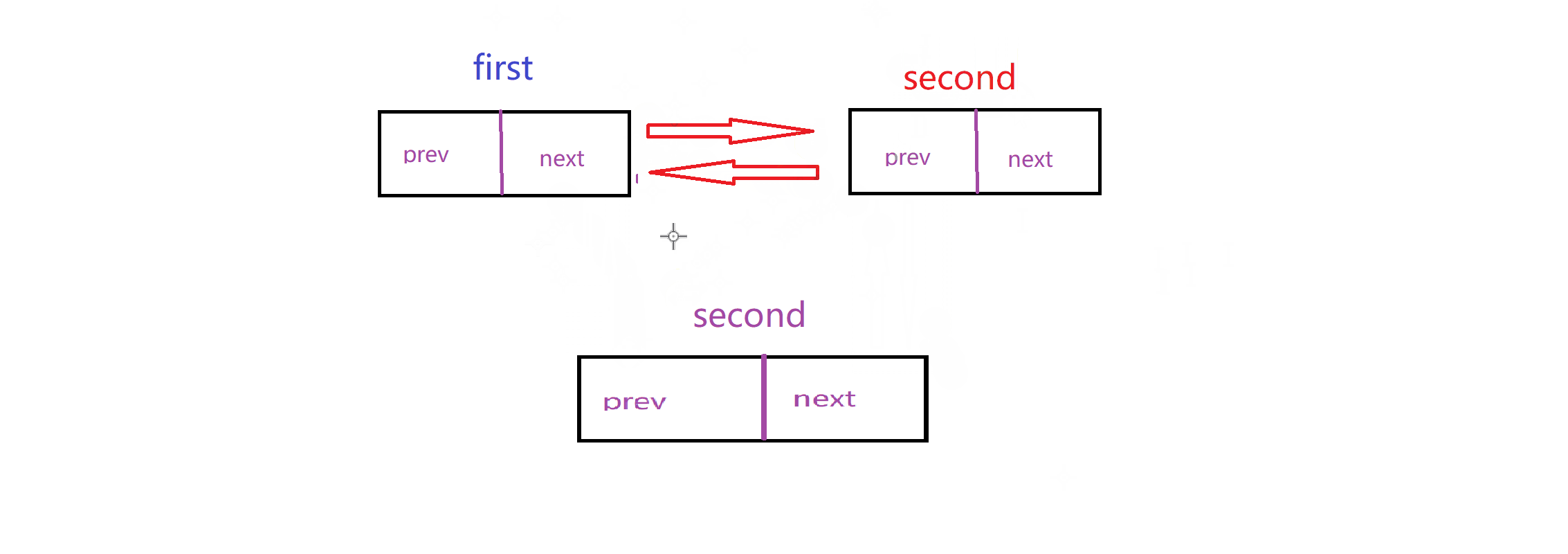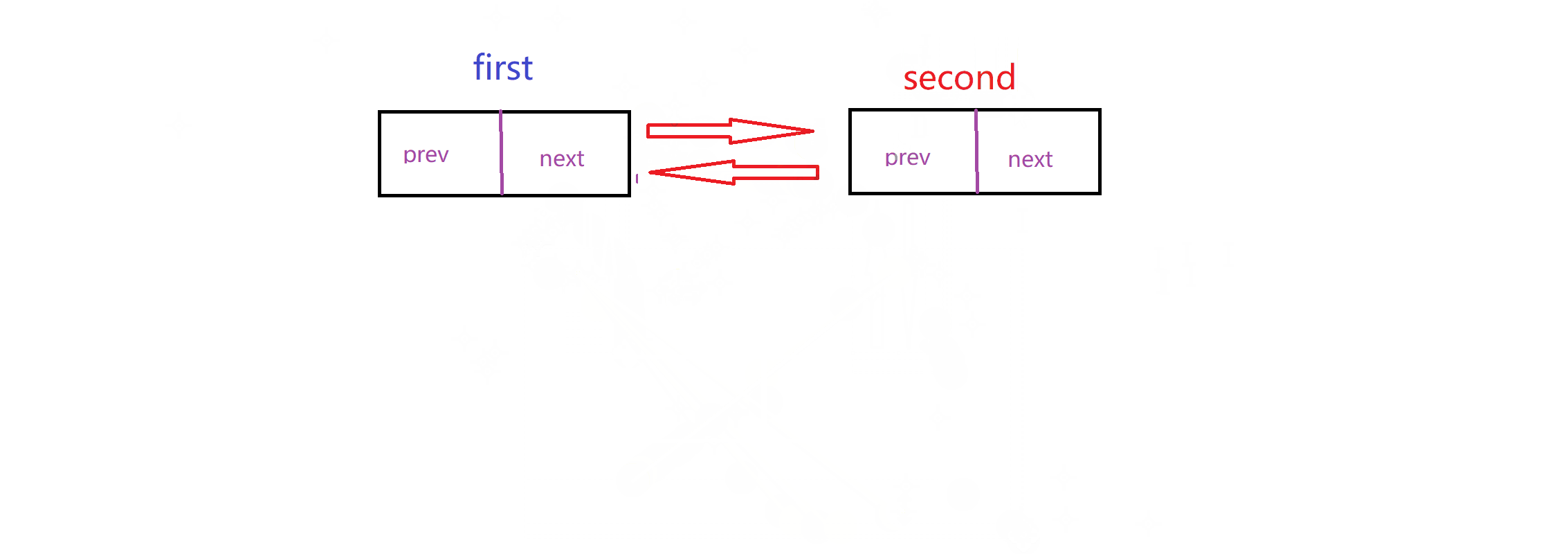
创建哨兵位(表头):
这里我们可以用两种方法,一种是采取二级指针的方法,另一种是直接创建一个表头,然后把表头地址返回去,这里我们采用第二种:
cpp
//创建新节点
ListNode* CreateNewNode(LTDataType x)
{
ListNode* newnode = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->_data = x;
newnode->_next = NULL;
newnode->_prev = NULL;
return newnode;
}
// 创建返回链表的头结点.
ListNode* ListCreate()
{
ListNode* head = CreateNewNode(-1);
head->_prev = head;
head->_next = head;
return head;
}头插------头删:
头插:
头插的时候,我们保存好链表第一个有效节点的地址,然后插入,记得把连接关系连接清楚
头删:
头删的时候,记得保存好,第二个节点的地址,记得把表头与第二节点的连接关系连接清楚
cpp
// 双向链表头插
void ListPushFront(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x)
{
assert(pHead);
ListNode* newnode = CreateNewNode(x);
ListNode* second = pHead->_next;
pHead->_next = newnode;
newnode->_prev = pHead;
newnode->_next = second;
second->_prev = newnode;
}
// 双向链表头删
void ListPopFront(ListNode* pHead)
{
assert(pHead);
assert(pHead->_next != pHead);
ListNode* first = pHead->_next;
ListNode* second = first->_next;
pHead->_next = second;
second->_prev = pHead;
free(first);
first = NULL;
}尾插------尾删:
尾插:
保存好当前尾节点的地址,注意搞清楚头节点,尾节点,新节点的连接关系
尾删:
保存好最后两个节点的位置,注意连接清楚头节点和倒数第二个节点
cpp
// 双向链表尾插
void ListPushBack(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x)
{
assert(pHead);
ListNode* newnode= CreateNewNode(x);
ListNode* tail = pHead->_prev;
newnode->_next = pHead;
newnode->_prev = tail;
tail->_next = newnode;
pHead->_prev = newnode;
}
// 双向链表尾删
void ListPopBack(ListNode* pHead)
{
assert(pHead);
assert(pHead->_next != pHead);
ListNode* tail = pHead->_prev;
ListNode* tailPrev = tail->_prev;
pHead->_prev = tailPrev;
tailPrev->_next = pHead;
free(tail);
tail = NULL;
}查找------打印:
注意:
循环从哨兵位的下一个节点开始,直到等于哨兵位结束
cpp
// 双向链表查找
ListNode* ListFind(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x)
{
assert(pHead);
ListNode* cur = pHead->_next;
while (cur != pHead)
{
if (cur->_data == x)
return cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
return NULL;
}
// 双向链表打印
void ListPrint(ListNode* pHead)
{
assert(pHead);
ListNode* cur = pHead->_next;
while (cur!=pHead)
{
printf("%d <-> ", cur->_data);
cur = cur->_next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}指定位置pos前插入,删除pos位置:
pos前插入:
保存好pos前一个位置的地址,连接清楚就行了
删除pos位置:
保存好pos前后的位置,连接清楚就行了
cpp
// 双向链表在pos的前面进行插入
void ListInsert(ListNode* pos, LTDataType x)
{
assert(pos);
ListNode* newnode = CreateNewNode(x);
ListNode* prev = pos->_prev;
prev->_next = newnode;
newnode->_prev = prev;
newnode->_next = pos;
pos->_prev = newnode;
}
// 双向链表删除pos位置的节点
void ListErase(ListNode* pos)
{
assert(pos);
ListNode* prev = pos->_prev;
ListNode* next = pos->_next;
prev->_next = next;
next->_prev = prev;
free(pos);
pos = NULL;
}链表销毁:
这一个要从哨兵位的下一个节点开始,循环直到不等于哨兵位结束:
cpp
// 双向链表销毁
void ListDestory(ListNode* pHead)
{
assert(pHead);
ListNode* cur = pHead->_next;
while (cur != pHead)
{
ListNode* next = cur->_next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
free(pHead);
}二、快速实现"链表"
学了带头双向循环链表之后,我们可以快速实现一个简单链表:
大多数接口其实都是不变的,但是有4个接口可以简化,那就是头插------头删------尾插------尾删;
这两个接口可以复用insert接口和erase接口:这四个接口连接关系是比较麻烦的,省去了这几个麻烦的,其他的接口就会很快写出来,大大节省了时间:
cpp
// 双向链表尾插
void ListPushBack(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x)
{
assert(pHead);
//ListNode* newnode= CreateNewNode(x);
//ListNode* tail = pHead->_prev;
//newnode->_next = pHead;
//newnode->_prev = tail;
//tail->_next = newnode;
//pHead->_prev = newnode;
ListInsert(pHead,x);
}
// 双向链表尾删
void ListPopBack(ListNode* pHead)
{
assert(pHead);
//assert(pHead->_next != pHead);
//ListNode* tail = pHead->_prev;
//ListNode* tailPrev = tail->_prev;
//pHead->_prev = tailPrev;
//tailPrev->_next = pHead;
//free(tail);
//tail = NULL;
ListErase(pHead->_prev);
}
// 双向链表头插
void ListPushFront(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x)
{
assert(pHead);
//ListNode* newnode = CreateNewNode(x);
//ListNode* second = pHead->_next;
//pHead->_next = newnode;
//newnode->_prev = pHead;
//newnode->_next = second;
//second->_prev = newnode;
ListInsert(pHead->_next, x);
}
// 双向链表头删
void ListPopFront(ListNode* pHead)
{
assert(pHead);
//assert(pHead->_next != pHead);
//ListNode* first = pHead->_next;
//ListNode* second = first->_next;
//pHead->_next = second;
//second->_prev = pHead;
//free(first);
//first = NULL;
ListErase(pHead->_next);
}三、链表和顺序表的区别:

顺序表空间连续支持下标访问使得我们在排序,访问等很多场景下都是很高效的
链表的合理利用空间使我们对空间的管理更合理
四、整体代码:
SList.h
cpp
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
// 带头+双向+循环链表增删查改实现
typedef int LTDataType;
typedef struct ListNode
{
LTDataType _data;
struct ListNode* _next;
struct ListNode* _prev;
}ListNode;
// 创建返回链表的头结点.
ListNode* ListCreate();
// 双向链表销毁
void ListDestory(ListNode* pHead);
// 双向链表打印
void ListPrint(ListNode* pHead);
// 双向链表尾插
void ListPushBack(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x);
// 双向链表尾删
void ListPopBack(ListNode* pHead);
// 双向链表头插
void ListPushFront(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x);
// 双向链表头删
void ListPopFront(ListNode* pHead);
// 双向链表查找
ListNode* ListFind(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x);
// 双向链表在pos的前面进行插入
void ListInsert(ListNode* pos, LTDataType x);
// 双向链表删除pos位置的节点
void ListErase(ListNode* pos);SList.c
cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"List.h"
//创建新节点
ListNode* CreateNewNode(LTDataType x)
{
ListNode* newnode = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->_data = x;
newnode->_next = NULL;
newnode->_prev = NULL;
return newnode;
}
// 创建返回链表的头结点.
ListNode* ListCreate()
{
ListNode* head = CreateNewNode(-1);
head->_prev = head;
head->_next = head;
return head;
}
// 双向链表销毁
void ListDestory(ListNode* pHead)
{
assert(pHead);
ListNode* cur = pHead->_next;
while (cur != pHead)
{
ListNode* next = cur->_next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
free(pHead);
}
// 双向链表打印
void ListPrint(ListNode* pHead)
{
assert(pHead);
ListNode* cur = pHead->_next;
while (cur!=pHead)
{
printf("%d <-> ", cur->_data);
cur = cur->_next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
// 双向链表尾插
void ListPushBack(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x)
{
assert(pHead);
//ListNode* newnode= CreateNewNode(x);
//ListNode* tail = pHead->_prev;
//newnode->_next = pHead;
//newnode->_prev = tail;
//tail->_next = newnode;
//pHead->_prev = newnode;
ListInsert(pHead,x);
}
// 双向链表尾删
void ListPopBack(ListNode* pHead)
{
assert(pHead);
//assert(pHead->_next != pHead);
//ListNode* tail = pHead->_prev;
//ListNode* tailPrev = tail->_prev;
//pHead->_prev = tailPrev;
//tailPrev->_next = pHead;
//free(tail);
//tail = NULL;
ListErase(pHead->_prev);
}
// 双向链表头插
void ListPushFront(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x)
{
assert(pHead);
//ListNode* newnode = CreateNewNode(x);
//ListNode* second = pHead->_next;
//pHead->_next = newnode;
//newnode->_prev = pHead;
//newnode->_next = second;
//second->_prev = newnode;
ListInsert(pHead->_next, x);
}
// 双向链表头删
void ListPopFront(ListNode* pHead)
{
assert(pHead);
//assert(pHead->_next != pHead);
//ListNode* first = pHead->_next;
//ListNode* second = first->_next;
//pHead->_next = second;
//second->_prev = pHead;
//free(first);
//first = NULL;
ListErase(pHead->_next);
}
// 双向链表查找
ListNode* ListFind(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x)
{
assert(pHead);
ListNode* cur = pHead->_next;
while (cur != pHead)
{
if (cur->_data == x)
return cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
return NULL;
}
// 双向链表在pos的前面进行插入
void ListInsert(ListNode* pos, LTDataType x)
{
assert(pos);
ListNode* newnode = CreateNewNode(x);
ListNode* prev = pos->_prev;
prev->_next = newnode;
newnode->_prev = prev;
newnode->_next = pos;
pos->_prev = newnode;
}
// 双向链表删除pos位置的节点
void ListErase(ListNode* pos)
{
assert(pos);
ListNode* prev = pos->_prev;
ListNode* next = pos->_next;
prev->_next = next;
next->_prev = prev;
free(pos);
pos = NULL;
}Test.c
cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"List.h"
void test()
{
ListNode* plist = ListCreate();
ListPushBack(plist,1);
ListPushBack(plist,2);
ListPushBack(plist,3);
ListPushBack(plist,4);
ListPushBack(plist,5);
ListPrint(plist);
ListPopBack(plist);
ListPopBack(plist);
ListPopBack(plist);
ListPrint(plist);
ListPushFront(plist,6);
ListPushFront(plist,7);
ListPushFront(plist,8);
ListPushFront(plist,9);
ListPushFront(plist,10);
ListPrint(plist);
ListPopFront(plist);
ListPopFront(plist);
ListPopFront(plist);
ListPrint(plist);
printf("%d\n", ListFind(plist, 6)->_data);
ListPrint(plist);
ListInsert(ListFind(plist,6), 99);
ListInsert(ListFind(plist,7), 88);
ListPrint(plist);
ListErase(ListFind(plist, 99));
ListErase(ListFind(plist, 88));
ListPrint(plist);
ListDestory(plist);
plist = NULL;
}
int main()
{
test();
return 0;
}