数据集
正确选择数据集以对结果产生适当影响也是非常必要的。在此姿势检测中,模型在两个不同的数据集即COCO关键点数据集和MPII人类姿势数据集上进行了预训练。
1. COCO:COCO关键点数据集是一个多人2D姿势估计数据集,其中包含从Flickr收集的图像。迄今为止,COCO是最大的2D姿势估计数据集,并被视为测试2D姿势估计算法的基准。COCO模型有18种分类。COCO输出格式:鼻子--- 0,脖子---1,右肩---2,右肘---3,右手腕---4,左肩---5,左手肘---6,左手腕---7,右臀部---8,右膝盖---9,右脚踝---10,左臀部---11,左膝---12,左脚踝---13,右眼---14,左眼---15,右耳---16,左耳---17,背景---18
2. MPII:MPII人体姿势数据集是一个多人2D姿势估计数据集,包含从Youtube视频中收集的近500种不同的人类活动。MPII是第一个包含各种姿势范围的数据集,也是第一个在2014年发起2D姿势估计挑战的数据集。MPII模型输出15分。MPII输出格式:头---0,脖子---1,右肩---2,右肘---3,右腕---4,左肩---5,左肘---6,左腕---7,右臀部---8,右膝盖---9,右脚踝---10,左臀部---11,左膝盖---12,左脚踝---13,胸部---14,背景---15

这些点是在对数据集进行处理并通过卷积神经网络(CNN)进行全面训练时生成的。
具体步骤
步骤1:需求收集(模型权重)和负载网络
训练有素的模型需要加载到OpenCV中。这些模型在Caffe深度学习框架上进行了训练。Caffe模型包含两个文件,即.prototxt文件和.caffemodel文件。
- .prototxt文件指定了神经网络的体系结构。
- .caffemodel文件存储训练后的模型的权重。
然后我们将这两个文件加载到网络中。
|-----------|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| 1 2 3 4 5 | # Specify the paths for the 2 files protoFile ``= "pose/mpi/pose_deploy_linevec_faster_4_stages.prototxt" weightsFile ``= "pose/mpi/pose_iter_160000.caffemodel" # Read the network into Memory net ``= cv2.dnn.readNetFromCaffe(protoFile, weightsFile) |
步骤2:读取图像并准备输入网络
首先,我们需要使用blobFromImage函数将图像从OpenCV格式转换为Caffe blob格式,以便可以将其作为输入输入到网络。这些参数将在blobFromImage函数中提供。由于OpenCV和Caffe都使用BGR格式,因此无需交换R和B通道。
|-------------------|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | # Read image frame ``= cv2.imread(``"image.jpg"``) # Specify the input image dimensions inWidth ``= 368 inHeight ``= 368 # Prepare the frame to be fed to the network inpBlob ``= cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(frame, ``1.0 / 255``, (inWidth, inHeight), (``0``, ``0``, ``0``), swapRB``=``False``, crop``=``False``) # Set the prepared object as the input blob of the network net.setInput(inpBlob) |
步骤3:做出预测并解析关键点
一旦将图像传递到模型,就可以使用OpenCV中DNN类的正向方法进行预测,该方法通过网络进行正向传递,这只是说它正在进行预测的另一种方式。
|---|------------------------------|
| 1 | output ``= net.forward() |
输出为4D矩阵:
- 第一个维度是图片ID(如果您将多个图片传递到网络)。
- 第二个维度指示关键点的索引。该模型会生成置信度图(在图像上的概率分布,表示每个像素处关节位置的置信度)和所有已连接的零件亲和度图。对于COCO模型,它由57个部分组成-18个关键点置信度图+ 1个背景+ 19 * 2个部分亲和度图。同样,对于MPI,它会产生44点。我们将仅使用与关键点相对应的前几个点。
- 第三维是输出图的高度。
- 第四个维度是输出图的宽度。
然后,我们检查图像中是否存在每个关键点。我们通过找到关键点的置信度图的最大值来获得关键点的位置。我们还使用阈值来减少错误检测。
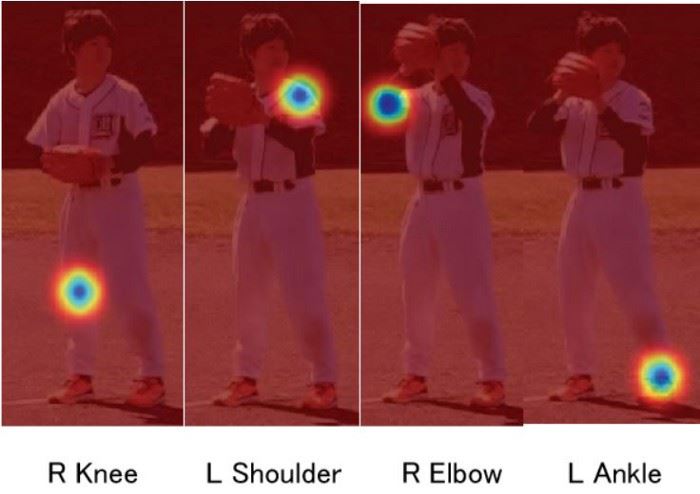

置信度图
一旦检测到关键点,我们便将其绘制在图像上。
|----------------------------------------------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 | H ``= out.shape[``2``] W ``= out.shape[``3``] # Empty list to store the detected keypoints points ``= [] for i ``in range``(``len``()): # confidence map of corresponding body's part. ``probMap ``= output[``0``, i, :, :] # Find global maxima of the probMap. ``minVal, prob, minLoc, point ``= cv2.minMaxLoc(probMap) # Scale the point to fit on the original image x ``= (frameWidth ``* point[``0``]) ``/ W y ``= (frameHeight ``* point[``1``]) ``/ H if prob > threshold : ``cv2.circle(frame, (``int``(x), ``int``(y)), ``15``, (``0``, ``255``, ``255``), thickness``=``-``1``, lineType``=``cv.FILLED) ``cv2.putText(frame, ``"{}"``.``format``(i), (``int``(x), ``int``(y)), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, ``1.4``, (``0``, ``0``, ``255``), ``3``, lineType``=``cv2.LINE_AA) # Add the point to the list if the probability is greater than the threshold ``points.append((``int``(x), ``int``(y))) else : ``points.append(``None``) cv2.imshow(``"Output-Keypoints"``,frame) cv2.waitKey(``0``) cv2.destroyAllWindows() |
步骤4:绘制骨架
由于我们已经绘制了关键点,因此我们现在只需将两对连接即可绘制骨架。
|-----------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| 1 2 3 4 5 | for pair ``in POSE_PAIRS: partA ``= pair[``0``] partB ``= pair[``1``] if points[partA] ``and points[partB]: cv2.line(frameCopy, points[partA], points[partB], (``0``, ``255``, ``0``), ``3``) |
结果
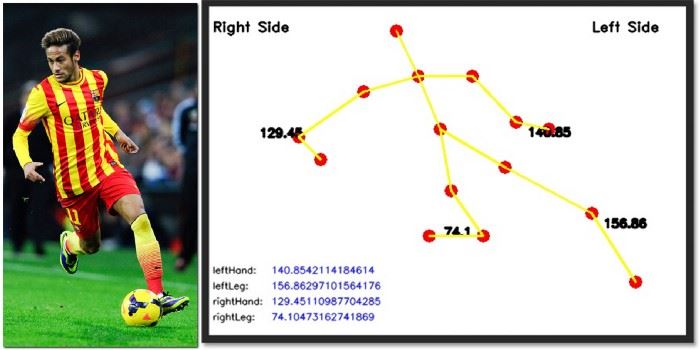
上面显示的输出向我们显示了运动员在特定时刻的准确姿势。下面是视频的检测结果。
【界面展示】
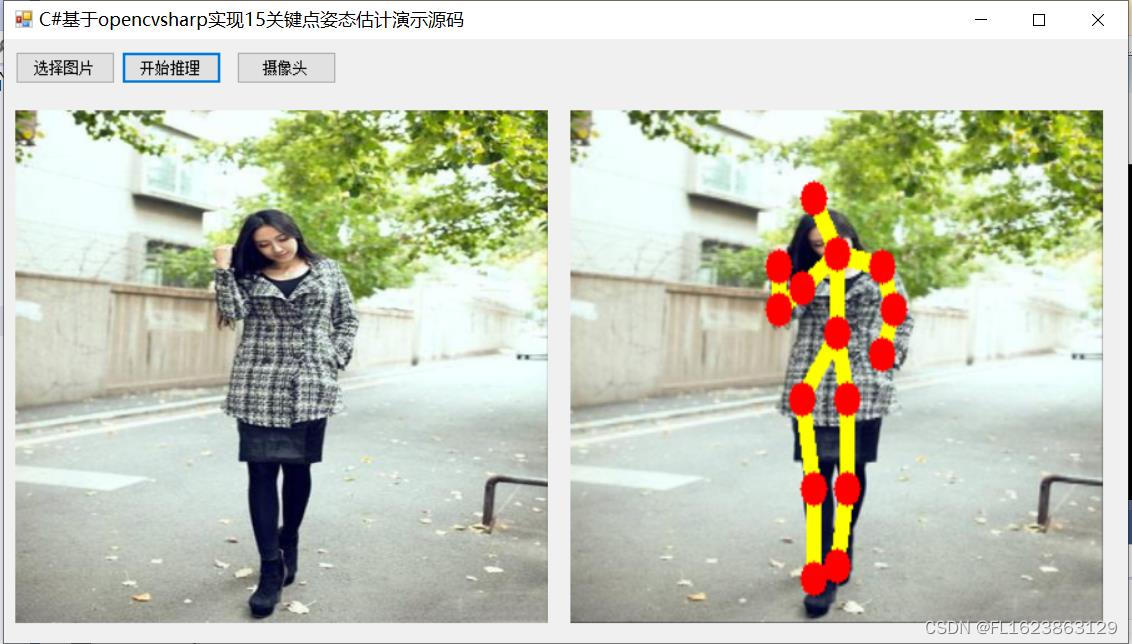
【效果演示】


【部分实现源码】
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using OpenCvSharp;
namespace FIRC
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
Mat src = new Mat();
PoseManager detector = new PoseManager(Application.StartupPath+ "\\weights\\pose_deploy_linevec_faster_4_stages.prototxt", Application.StartupPath + "\\weights\\pose_iter_160000.caffemodel");
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
OpenFileDialog openFileDialog = new OpenFileDialog();
openFileDialog.Filter = "图文件(*.*)|*.jpg;*.png;*.jpeg;*.bmp";
openFileDialog.RestoreDirectory = true;
openFileDialog.Multiselect = false;
if (openFileDialog.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
src = Cv2.ImRead(openFileDialog.FileName);
pictureBox1.Image = OpenCvSharp.Extensions.BitmapConverter.ToBitmap(src);
}
}
private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if(pictureBox1.Image==null)
{
return;
}
var resultMat = detector.Inference(src);
pictureBox2.Image= OpenCvSharp.Extensions.BitmapConverter.ToBitmap(resultMat); //Mat转Bitmap
}
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
private void button3_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
VideoCapture capture = new VideoCapture("test.mp4");
if (!capture.IsOpened())
{
Console.WriteLine("video not open!");
return;
}
Mat frame = new Mat();
var sw = new Stopwatch();
int fps = 0;
while (true)
{
capture.Read(frame);
if (frame.Empty())
{
Console.WriteLine("data is empty!");
break;
}
sw.Start();
var result = detector.Inference(frame);
sw.Stop();
fps = Convert.ToInt32(1 / sw.Elapsed.TotalSeconds);
sw.Reset();
Cv2.PutText(result, "FPS=" + fps, new OpenCvSharp.Point(30, 30), HersheyFonts.HersheyComplex, 1.0, new Scalar(255, 0, 0), 3);
//显示结果
Cv2.ImShow("Result", result);
int key = Cv2.WaitKey(10);
if (key == 27)
break;
}
capture.Release();
}
}
}【视频演示】
【测试环境】
vs2019
netframework4.7.2
opencvsharp4.8.0
【演示源码下载】
https://download.csdn.net/download/FL1623863129/89486922
【注意事项】
源码演示只支持单人姿态估计,不支持一个图片多人姿态估计,如果需要支持多人姿态估计可以先检测出人,然后截取出来进行单人估计即可