文章目录
- [1. 计算设备:GPU/CPU](#1. 计算设备:GPU/CPU)
- [2. Tensor的GPU计算](#2. Tensor的GPU计算)
- [3. 模型的GPU计算](#3. 模型的GPU计算)
对复杂的神经网络和大规模的数据来说,使用CPU来计算可能不够高效。这里,我们将介绍如何使用单块NVIDIA GPU来计算。
首先,需要确保已经安装好了PyTorch GPU版本,具体操作步骤可以参考博客:Ubuntu 22.04安装cuda及Pytorch教程。
查看显卡占用情况:
bash
nvidia-smi每隔2s刷新一次显卡占用情况:
python
watch -n 2 nvidia-smi输出如下:
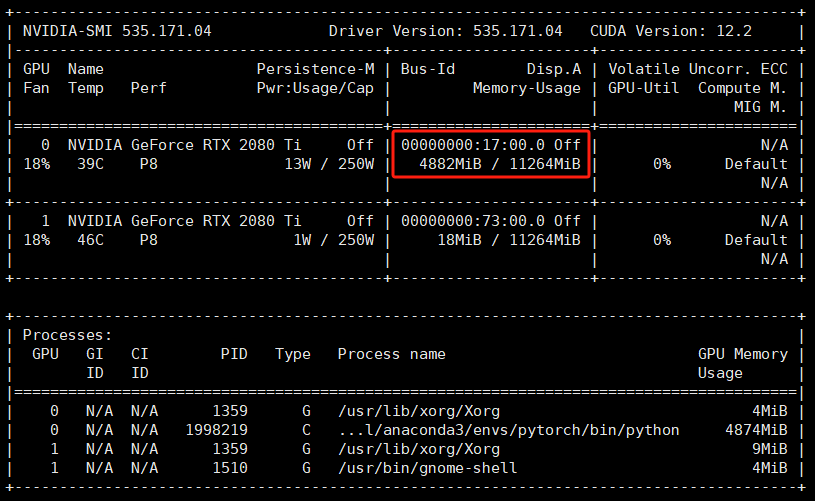
可以看到我这里只有两块 NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2080,单块显卡有11G的显存。
1. 计算设备:GPU/CPU
PyTorch可以指定用来存储和计算的设备,如使用内存的CPU或者使用显存的GPU。默认情况下,PyTorch会将数据创建在内存,然后利用CPU来计算。
- 查看GPU是否可用:
python
torch.cuda.is_available() # 输出 True- 查看GPU数量:
python
torch.cuda.device_count() # 输出 2- 查看当前GPU索引号,索引号从0开始:
python
torch.cuda.current_device() # 输出 0- 根据索引号查看GPU名字:
python
torch.cuda.get_device_name(0) # 输出 'GeForce RTX 2080'2. Tensor的GPU计算
默认情况下,Tensor会被存在内存上(即CPU中)。因此,之前我们每次打印Tensor的时候看不到GPU相关标识。
python
x = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3])
x输出:
python
tensor([1, 2, 3])1. 使用.cuda()可以将CPU上的Tensor转换(复制)到GPU上:
如果有多块GPU,我们用.cuda(i)来表示第 i i i 块GPU及相应的显存( i i i从0开始)且cuda(0)和cuda()等价。
python
x = x.cuda(0)
x输出:
python
tensor([1, 2, 3], device='cuda:0')2. 通过Tensor的device属性来查看该Tensor所在的设备:
python
x.device输出:
python
device(type='cuda', index=0)3. 创建Tensor时指定设备:
我们也可以直接在创建Tensor时就指定设备。
python
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
x = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3], device=device)
# or
x = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3]).to(device)
x输出:
python
tensor([1, 2, 3], device='cuda:0')4. 如果对在GPU上的数据进行运算,那么结果还是存放在GPU上。
python
y = x**2
y输出:
python
tensor([1, 4, 9], device='cuda:0')5. GPU与CPU无法混用。
需要注意的是,存储在不同位置中的数据是不可以直接进行计算的。即存放在CPU上的数据不可以直接与存放在GPU上的数据进行运算,位于不同GPU上的数据也是不能直接进行计算的。
python
z = y + x.cpu()会报错:
python
RuntimeError: Expected object of type torch.cuda.LongTensor but found type torch.LongTensor for argument #3 'other'3. 模型的GPU计算
同Tensor类似,PyTorch模型也可以通过.cuda转换到GPU上。我们可以通过检查模型的参数的device属性来查看存放模型的设备。
python
net = nn.Linear(3, 1)
list(net.parameters())[0].device输出:
python
device(type='cpu')可见模型在CPU上。
1. 将模型转换到GPU上:
python
net.cuda()
list(net.parameters())[0].device输出:
python
device(type='cuda', index=0)2. 模型输入的Tensor和模型需在同一设备上。
同样的,我么需要保证模型输入的Tensor和模型都在同一设备上,否则会报错。
这里,我们给出两种将Tensor和模型转换到GPU设备上的写法:
python
import torch
x = torch.rand(2, 3)
net = nn.Linear(3, 1)- 写法1:基于 cuda() 函数
python
x = x.cuda()
net = net.cuda()
net(x)- 写法2:基于 to(device) 函数 (推荐)
python
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
x = x.to(device)
net = net.to(device)
net(x)to(device) 这种写法可以自动化获取设备(CPU或GPU),并将Tensor和Model自动转化到设备上,在实际使用过程中更为常见。
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')自动获取设备。x = x.to(device)基于to()函数将张量数据转换到GPU设备上。net = net.to(device)基于to()函数将模型转换到GPU设备上。
输出:
python
tensor([[-0.5800],
[-0.2995]], device='cuda:0', grad_fn=<ThAddmmBackward>)