任务描述
"数据生产"的程序启动后,会持续向callLog.csv文件中写入模拟的通话记录。接下来,我们需要将这些实时的数据通过Flume采集到Kafka集群中,然后提供给HBase消费。
Flume :是Cloudera提供的一个高可用的,高可靠的,分布式的海量日志采集、聚合和传输的系统,Flume支持在日志系统中定制各类数据发送方,用于收集数据;同时,Flume提供对数据进行简单处理,并写到各种数据接受方(可定制)的能力。适合下游数据消费者不多的情况,适合数据安全性要求不高的操作,适合与Hadoop生态圈对接的操作。
Kafka :由Apache软件基金会开发的一个开源流处理平台。Kafka是一种高吞吐量的分布式发布订阅消息系统,它可以处理消费者规模的网站中的所有动作流数据。适合下游数据消费者较多的情况,适合数据安全性要求较高的操作。
在这里采用一种常见的组合模型:线上数据----Flume----Kafka----HBase(HDFS)。
任务指导
"数据生产"的程序启动后,会持续向callLog.csv文件中写入模拟的通话记录。接下来将这些实时的数据通过Flume采集到Kafka集群中,然后消费Kafka中的数据并存储到HBase中。
"数据采集/消费/存储"模块的流程图:

思路: 数据采集
-
启动ZooKeeper和Kafka集群;
-
创建Kafka主题;
-
配置Flume,监控日志文件或目录;
-
启动Flume收集数据发送到Kafka;
-
运行在"生产数据"小节中创建的日志生产脚本;
-
启动Kafka控制台消费者,用于测试对Kafka数据的消费;
-
编写Kafka的消费者代码,将Kafka中的数据存储到HBase中涉及的类:
1))HBaseConsumer消费Kafka中的数据存储到HBase
2)PropertiesUtil提取项目所需参数的辅助类
3)HBaseUtil封装HBase的DDL操作
4)HBaseDAO执行HBase具体执行DDL操作
5)ConnectionInstance与HBase建立连接
任务实现
1、启动ZooKeeper和Kafka集群
确定在master1、slave1、slave2启动ZooKeeper集群,如未启动通过以下命令启动:
[root@master1 ~]# zkServer.sh start
[root@slave1 ~]# zkServer.sh start
[root@slave2 ~]# zkServer.sh start确定Kafka在master1已启动,如未启动通过以下命令启动:
[root@master1 ~]# kafka-server-start.sh -daemon $KAFKA_HOME/config/server.properties2、创建Kafka主题:
[root@master1 ~]# kafka-topics.sh --create --zookeeper master1:2181,slave1:2181,slave2:2181 --replication-factor 1 --partitions 4 --topic calllog查看创建的Kafka主题:
[root@master1 ~]# kafka-topics.sh --describe --zookeeper slave1:2181,slave2:2181,slave3:21813、配置Flume监控数据传送至Kafka主题
在master1进入Flume配置目录新建kafka-conf.properties文件
[root@master1 ~]# cd $FLUME_HOME/conf
[root@master1 conf]# touch kafka-conf.properties 编辑kafka-conf.properties文件,配置内容如下:
exec-memory-kafka.sources = exec-source
exec-memory-kafka.channels = memory-channel
exec-memory-kafka.sinks = kafka-sink
exec-memory-kafka.sources.exec-source.type=exec
exec-memory-kafka.sources.exec-source.command=tail -F /opt/app/callLog.csv
exec-memory-kafka.sources.exec-source.channels=memory-channel
exec-memory-kafka.channels.memory-channel.type=memory
exec-memory-kafka.channels.memory-channel.capacity=10000
exec-memory-kafka.channels.memory-channel.transactionCapacity=100
exec-memory-kafka.sinks.kafka-sink.type= org.apache.flume.sink.kafka.KafkaSink
exec-memory-kafka.sinks.kafka-sink.brokerList=master1:9092
exec-memory-kafka.sinks.kafka-sink.topic=calllog
exec-memory-kafka.sinks.kafka-sink.serializer.class=kafka.serializer.StringEncoder
exec-memory-kafka.sinks.kafka-sink.channel=memory-channel4、启动Flume收集数据后发送至Kafka
[root@master1 conf]# cd $FLUME_HOME
[root@master1 apache-flume-1.9.0-bin]# flume-ng agent -c ./conf/ -f ./conf/kafka-conf.properties -n exec-memory-kafka -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console5、运行在任务15创建的日志生产脚本
[root@master1 ~]# cd /opt/app/
[root@master1 app]# nohup sh productlog.sh &6、启动Kafka控制台消费者,测试Flume信息的输入:
[root@slave1 ~]# kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server master1:9092 --from-beginning --topic calllog7、接下来编写操作HBase代码,用于消费Kafka数据,并将数据实时存储在HBase中,思路如下:
a) 编写Kafka消费者,读取Kafka集群中缓存的信息,并打印到控制台;
b) 如果读取Kafka中的数据可以打印到控制台,那么就可以编写调用HBase API的方法,将从Kafka中读取出来的数据写入到HBase;
c) 编写一些通用类,用于封装HBase操作的一些通用方法。
- 创建新的Maven项目
参考任务"数据生产"创建Maven项目ct_consumer
pom.xml文件配置:
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.qst </groupId>
<artifactId>ct_consumer</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.kafka</groupId>
<artifactId>kafka-clients</artifactId>
<version>2.4.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hbase</groupId>
<artifactId>hbase-client</artifactId>
<version>2.3.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hbase</groupId>
<artifactId>hbase</artifactId>
<version>2.3.5</version>
<type>pom</type>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hbase</groupId>
<artifactId>hbase-server</artifactId>
<version>2.3.5</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.12.4</version>
<configuration>
<skipTests>true</skipTests>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>如图为项目创建对应的包和类

-
HBaseConsumer类:主要用于消费Kafka中缓存的数据,然后调用HBase API持久化数据,将数据保存到HBase
package kafka;
import hbase.HBaseDAO;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.ConsumerRecord;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.ConsumerRecords;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.KafkaConsumer;
import utils.PropertiesUtil;import java.util.Arrays;
public class HBaseConsumer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
KafkaConsumer<String, String> kafkaConsumer = new KafkaConsumer<String, String>(PropertiesUtil.properties);
kafkaConsumer.subscribe(Arrays.asList(PropertiesUtil.getProperty("kafka.topics")));HBaseDAO hd = new HBaseDAO(); while(true){ ConsumerRecords<String, String> records = kafkaConsumer.poll(100); for(ConsumerRecord<String, String> cr : records){ String oriValue = cr.value(); System.out.println(oriValue); hd.put(oriValue); } } }}
-
PropertiesUtil类:以解耦合的方式,从文件中读取项目所需的参数,方便进行配置
package utils;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Properties;public class PropertiesUtil {
public static Properties properties = null;static{ InputStream is = ClassLoader.getSystemResourceAsStream("hbase_consumer.properties"); properties = new Properties(); try { properties.load(is); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static String getProperty(String key){ return properties.getProperty(key); }}
在resources目录下创建hbase_consumer.properties文件,并配置如下
# 设置kafka的brokerlist
bootstrap.servers=master1:9092
# 设置消费者所属的消费组
group.id=hbase_consumer_group
# 设置是否自动确认offset
enable.auto.commit=true
# 自动确认offset的时间间隔
auto.commit.interval.ms=30000
# 设置key,value的反序列化类的全名
key.deserializer=org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer
value.deserializer=org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer
# 以下为自定义属性设置
# 设置本次消费的主题
kafka.topics=calllog
# 设置HBase的一些变量
hbase.zookeeper.quorum=slave1:2181,slave2:2181,slave3:2181
hbase.calllog.regions=3
hbase.calllog.namespace=ns_ct
hbase.calllog.tablename=ns_ct:calllog
hbase.regions.count=3在resources目录下创建log4j.properties文件,并配置如下
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
# or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
# distributed with this work for additional information
# regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
# to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
# "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
# with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
# Define some default values that can be overridden by system properties
hbase.root.logger=INFO,console
hbase.security.logger=INFO,console
hbase.log.dir=.
hbase.log.file=hbase.log
# Define the root logger to the system property "hbase.root.logger".
log4j.rootLogger=${hbase.root.logger}
# Logging Threshold
log4j.threshold=ALL
#
# Daily Rolling File Appender
#
log4j.appender.DRFA=org.apache.log4j.DailyRollingFileAppender
log4j.appender.DRFA.File=${hbase.log.dir}/${hbase.log.file}
# Rollver at midnight
log4j.appender.DRFA.DatePattern=.yyyy-MM-dd
# 30-day backup
#log4j.appender.DRFA.MaxBackupIndex=30
log4j.appender.DRFA.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
# Pattern format: Date LogLevel LoggerName LogMessage
log4j.appender.DRFA.layout.ConversionPattern=%d{ISO8601} %-5p [%t] %c{2}: %m%n
# Rolling File Appender properties
hbase.log.maxfilesize=256MB
hbase.log.maxbackupindex=20
# Rolling File Appender
log4j.appender.RFA=org.apache.log4j.RollingFileAppender
log4j.appender.RFA.File=${hbase.log.dir}/${hbase.log.file}
log4j.appender.RFA.MaxFileSize=${hbase.log.maxfilesize}
log4j.appender.RFA.MaxBackupIndex=${hbase.log.maxbackupindex}
log4j.appender.RFA.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.RFA.layout.ConversionPattern=%d{ISO8601} %-5p [%t] %c{2}: %m%n
#
# Security audit appender
#
hbase.security.log.file=SecurityAuth.audit
hbase.security.log.maxfilesize=256MB
hbase.security.log.maxbackupindex=20
log4j.appender.RFAS=org.apache.log4j.RollingFileAppender
log4j.appender.RFAS.File=${hbase.log.dir}/${hbase.security.log.file}
log4j.appender.RFAS.MaxFileSize=${hbase.security.log.maxfilesize}
log4j.appender.RFAS.MaxBackupIndex=${hbase.security.log.maxbackupindex}
log4j.appender.RFAS.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.RFAS.layout.ConversionPattern=%d{ISO8601} %p %c: %m%n
log4j.category.SecurityLogger=${hbase.security.logger}
log4j.additivity.SecurityLogger=false
#log4j.logger.SecurityLogger.org.apache.hadoop.hbase.security.access.AccessController=TRACE
#log4j.logger.SecurityLogger.org.apache.hadoop.hbase.security.visibility.VisibilityController=TRACE
#
# Null Appender
#
log4j.appender.NullAppender=org.apache.log4j.varia.NullAppender
#
# console
# Add "console" to rootlogger above if you want to use this
#
log4j.appender.console=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.console.target=System.err
log4j.appender.console.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.console.layout.ConversionPattern=%d{ISO8601} %-5p [%t] %c{2}: %m%n
log4j.appender.asyncconsole=org.apache.hadoop.hbase.AsyncConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.asyncconsole.target=System.err
# Custom Logging levels
log4j.logger.org.apache.zookeeper=INFO
#log4j.logger.org.apache.hadoop.fs.FSNamesystem=DEBUG
log4j.logger.org.apache.hadoop.hbase=INFO
# Make these two classes INFO-level. Make them DEBUG to see more zk debug.
log4j.logger.org.apache.hadoop.hbase.zookeeper.ZKUtil=INFO
log4j.logger.org.apache.hadoop.hbase.zookeeper.ZooKeeperWatcher=INFO
#log4j.logger.org.apache.hadoop.dfs=DEBUG
# Set this class to log INFO only otherwise its OTT
# Enable this to get detailed connection error/retry logging.
# log4j.logger.org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.HConnectionManager$HConnectionImplementation=TRACE
# Uncomment this line to enable tracing on _every_ RPC call (this can be a lot of output)
#log4j.logger.org.apache.hadoop.ipc.HBaseServer.trace=DEBUG
# Uncomment the below if you want to remove logging of client region caching'
# and scan of hbase:meta messages
# log4j.logger.org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.HConnectionManager$HConnectionImplementation=INFO
# log4j.logger.org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.MetaScanner=INFO
# Prevent metrics subsystem start/stop messages (HBASE-17722)
log4j.logger.org.apache.hadoop.metrics2.impl.MetricsConfig=WARN
log4j.logger.org.apache.hadoop.metrics2.impl.MetricsSinkAdapter=WARN
log4j.logger.org.apache.hadoop.metrics2.impl.MetricsSystemImpl=WARN-
HBaseUtil类:主要用于封装HBase的常用DDL操作,如:创建命名空间、创建表等
package utils;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.HColumnDescriptor;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.HTableDescriptor;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.NamespaceDescriptor;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.TableName;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Admin;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Connection;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.ConnectionFactory;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.util.Bytes;import java.io.IOException;
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.TreeSet;public class HBaseUtil {
/**
* 判断表是否存在
* @param conf HBaseConfiguration
* @param tableName
* @return
*/
public static boolean isExistTable(Configuration conf, String tableName) throws IOException {
Connection connection = ConnectionFactory.createConnection(conf);
Admin admin = connection.getAdmin();
boolean result = admin.tableExists(TableName.valueOf(tableName));admin.close(); connection.close(); return result; } /** * 初始化命名空间 * @param conf * @param namespace */ public static void initNamespace(Configuration conf, String namespace) throws IOException { Connection connection = ConnectionFactory.createConnection(conf); Admin admin = connection.getAdmin(); NamespaceDescriptor nd = NamespaceDescriptor .create(namespace) .addConfiguration("CREATE_TIME", String.valueOf(System.currentTimeMillis())) .addConfiguration("AUTHOR", "Zhang San") .build(); admin.createNamespace(nd); admin.close(); connection.close(); } /** * 创建表:协处理器 * @param conf * @param tableName * @param columnFamily * @throws IOException */ public static void createTable(Configuration conf, String tableName, int regions, String... columnFamily) throws IOException { Connection connection = ConnectionFactory.createConnection(conf); Admin admin = connection.getAdmin(); if(isExistTable(conf, tableName)) return; HTableDescriptor htd = new HTableDescriptor(TableName.valueOf(tableName)); for(String cf: columnFamily){ htd.addFamily(new HColumnDescriptor(cf)); } htd.addCoprocessor("hbase.CalleeWriteObserver"); admin.createTable(htd, genSplitKeys(regions)); admin.close(); connection.close(); } private static byte[][] genSplitKeys(int regions){ //定义一个存放分区键的数组 String[] keys = new String[regions]; //目前推算,region个数不会超过2位数,所以region分区键格式化为两位数字所代表的字符串 DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("00"); for(int i = 0; i < regions; i ++){ keys[i] = df.format(i) + "|"; } byte[][] splitKeys = new byte[regions][]; //生成byte[][]类型的分区键的时候,一定要保证分区键是有序的 TreeSet<byte[]> treeSet = new TreeSet<byte[]>(Bytes.BYTES_COMPARATOR); for(int i = 0; i < regions; i++){ treeSet.add(Bytes.toBytes(keys[i])); } Iterator<byte[]> splitKeysIterator = treeSet.iterator(); int index = 0; while(splitKeysIterator.hasNext()){ byte[] b = splitKeysIterator.next(); splitKeys[index ++] = b; } return splitKeys; } /** * 生成rowkey * regionCode_call1_buildTime_call2_flag_duration * @return */ public static String genRowKey(String regionCode, String call1, String buildTime, String call2, String flag, String duration){ StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); sb.append(regionCode + "_") .append(call1 + "_") .append(buildTime + "_") .append(call2 + "_") .append(flag + "_") .append(duration); return sb.toString(); } /** * 手机号:15837312345 * 通话建立时间:2023-01-10 11:20:30 -> 20170110112030 * @param call1 * @param buildTime * @param regions * @return */ public static String genRegionCode(String call1, String buildTime, int regions){ int len = call1.length(); //取出后4位号码 String lastPhone = call1.substring(len - 4); //取出年月 String ym = buildTime .replaceAll("-", "") .replaceAll(":", "") .replaceAll(" ", "") .substring(0, 6); //离散操作1 Integer x = Integer.valueOf(lastPhone) ^ Integer.valueOf(ym); //离散操作2 int y = x.hashCode(); //生成分区号 int regionCode = y % regions; //格式化分区号 DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("00"); return df.format(regionCode); }}
上面代码中的HBase协处理器"htd.addCoprocessor("hbase.CalleeWriteObserver");",具体代码在下面步骤中给出。
-
HBaseDAO类:主要用于执行具体的DML操作,如保存数据、查询数据、Rowkey生成规则等
package hbase;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.HBaseConfiguration;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.TableName;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.*;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.util.Bytes;
import utils.ConnectionInstance;
import utils.HBaseUtil;
import utils.PropertiesUtil;import java.io.IOException;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;public class HBaseDAO {
private int regions;
private String namespace;
private String tableName;
public static final Configuration conf;
private HTable table;
private Connection connection;
private SimpleDateFormat sdf1 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
private SimpleDateFormat sdf2 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMddHHmmss");private List<Put> cacheList = new ArrayList<Put>(); static { conf = HBaseConfiguration.create(); String zookeeperQuorum = PropertiesUtil.getProperty("hbase.zookeeper.quorum"); conf.set("hbase.zookeeper.quorum", zookeeperQuorum); } public HBaseDAO() { try { regions = Integer.valueOf(PropertiesUtil.getProperty("hbase.calllog.regions")); namespace = PropertiesUtil.getProperty("hbase.calllog.namespace"); tableName = PropertiesUtil.getProperty("hbase.calllog.tablename"); if (!HBaseUtil.isExistTable(conf, tableName)) { HBaseUtil.initNamespace(conf, namespace); HBaseUtil.createTable(conf, tableName, regions, "f1", "f2"); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * ori数据样式: 18576581848,17269452013,2017-08-14 13:38:31,1761 * rowkey样式:01_18576581848_20170814133831_17269452013_1_1761 * HBase表的列:call1 call2 build_time build_time_ts flag duration * @param ori */ public void put(String ori) { try { if(cacheList.size() == 0){ connection = ConnectionInstance.getConnection(conf); table = (HTable) connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(tableName));// table.setAutoFlushTo(false);
// table.setWriteBufferSize(2 * 1024 * 1024);
}String[] splitOri = ori.split(","); String caller = splitOri[0]; String callee = splitOri[1]; String buildTime = splitOri[2]; String duration = splitOri[3]; String regionCode = HBaseUtil.genRegionCode(caller, buildTime, regions); String buildTimeReplace = sdf2.format(sdf1.parse(buildTime)); String buildTimeTs = String.valueOf(sdf1.parse(buildTime).getTime()); //生成rowkey String rowkey = HBaseUtil.genRowKey(regionCode, caller, buildTimeReplace, callee, "1", duration); //向表中插入该条数据 Put put = new Put(Bytes.toBytes(rowkey)); put.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("f1"), Bytes.toBytes("call1"), Bytes.toBytes(caller)); put.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("f1"), Bytes.toBytes("call2"), Bytes.toBytes(callee)); put.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("f1"), Bytes.toBytes("build_time"), Bytes.toBytes(buildTime)); put.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("f1"), Bytes.toBytes("build_time_ts"), Bytes.toBytes(buildTimeTs)); put.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("f1"), Bytes.toBytes("flag"), Bytes.toBytes("1")); put.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("f1"), Bytes.toBytes("duration"), Bytes.toBytes(duration)); cacheList.add(put); if(cacheList.size() >= 30){ table.put(cacheList); table.close(); cacheList.clear(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ParseException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }}
6)ConnectionInstance类:主要负责建立HBase连接
package utils;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Connection;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.ConnectionFactory;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ConnectionInstance {
private static Connection conn;
public static synchronized Connection getConnection(Configuration conf) {
try {
if(conn == null || conn.isClosed()){
conn = ConnectionFactory.createConnection(conf);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return conn;
}
}7)优化HBase数据存储方案,编写协处理器
在使用HBase查询数据时,尽量使用RowKey去定位数据,而非使用ColumnValueFilter或者SingleColumnValueFilter,因为在数据量较大的情况下Filter如果涉及到全表扫描时,效率是非常低的,所以在范围查询时尽量不要使用Filter,而是使用RowKey。
在项目中为了能够让数据尽量离散化,从而避免数据倾斜的发生,我们指定了若干的分区键,为了能让数据根据行键尽可能的分散到各分区当中,在这里行键的生成规则为:regionCode_call1_buildTime_call2_flag_duration,其中regionCode是分区号决定了数据会落入哪一个分区,也决定了是否会发生数据倾斜,regionCode的生成是使用第一个手机号(call1)的后4位和通话时间(年/月)经过两次离散操作,然后再和分区数取余生成的,这样就能保证每个月的通话记录都保存在同一个分区中。
在执行HBase数据查询,设置查询范围时,实际上regionCode生成规则是通过第一个手机号和通话时间(年/月)生成的,所以如果一个人在一个月内如果只接电话,而没有打电话的话,实际上是查不到通话记录的。解决这个问题的方法很多,现在用的比较多的方式是:以存储换效率,也就是说为了保证查询效率可以牺牲一定的存储空间。具体的做法是:将一条记录的第一个号码(call1)和第二个号码(call2)换一个位置,再次插入到数据表中,这样一条记录就会变成两条记录,即一条主叫记录和一条被叫记录。
我们可以在插入数据时,同时插入两条数据。在这里我们也可以使用协处理器为完成,即:当插入一条主叫记录时,会触发协处理器同时插入一条被叫记录。使用协处理器的目的一是可以启动两个线程来完成数据插入工作,第二、也可以让代码更加解耦、更清晰,方便管理。
在上面 步骤的HBaseUtil代码中 添加了协处理器。
- 什么是协处理器;
- 协处理器的特性;
- 协处理器的应用场景;
- 协处理器的分类;
- 怎么使用协处理器。
思路:
- 编写协处理器,用于协助处理HBase的相关操作,如增删改查等;
- 当一条主叫日志成功插入后,在协处理器中,将该日志切换为被叫视角再次插入一次,放到与主叫日志不同的列族中;
- 在创建HBase表时,为该表设置协处理器("htd.addCoprocessor("hbase.CalleeWriteObserver");");
- 上传协处理器的jar包到HDFS;
- 在HBase命令行中设置表的协处理器。
新建协处理器类:CalleeWriteObserver,并重写postPut方法,该方法会在数据成功插入之后被回调:
package hbase;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.CoprocessorEnvironment;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.TableName;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Durability;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Put;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Table;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.coprocessor.ObserverContext;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.coprocessor.RegionCoprocessor;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.coprocessor.RegionCoprocessorEnvironment;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.coprocessor.RegionObserver;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.util.Bytes;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.wal.WALEdit;
import utils.HBaseUtil;
import utils.PropertiesUtil;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Optional;
public class CalleeWriteObserver implements RegionObserver, RegionCoprocessor {
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMddHHmmss");
private RegionCoprocessorEnvironment env = null;
@Override
public Optional<RegionObserver> getRegionObserver() {
// Extremely important to be sure that the coprocessor is invoked as a RegionObserver
return Optional.of(this);
}
@Override
public void start(CoprocessorEnvironment e) throws IOException {
env = (RegionCoprocessorEnvironment) e;
}
@Override
public void stop(CoprocessorEnvironment e) throws IOException {
// nothing to do here
}
@Override
public void prePut(final ObserverContext<RegionCoprocessorEnvironment> e,
final Put put, final WALEdit edit, final Durability durability)
throws IOException {
//1、获取你想要操作的目标表的名称
// String targetTableName = PropertiesUtil.getProperty("hbase.calllog.tablename");
String targetTableName = "ns_ct:calllog";
//2、获取当前成功Put了数据的表(不一定是我们当前业务想要操作的表)
String currentTableName = e.getEnvironment().getRegionInfo().getTable().getNameAsString();
if(!targetTableName.equals(currentTableName)) return;
//01_18047140826_20180110154530_17864211243_1_0360
String oriRowKey = Bytes.toString(put.getRow());
String[] splitOriRowKey = oriRowKey.split("_");
String oldFlag = splitOriRowKey[4];
//如果当前插入的是被叫数据,则直接返回(因为默认提供的数据全部为主叫数据)
if(oldFlag.equals("0")) return;
// int regions = Integer.valueOf(PropertiesUtil.getProperty("hbase.calllog.regions"));
int regions = 3;
String caller = splitOriRowKey[1];
String callee = splitOriRowKey[3];
String buildTime = splitOriRowKey[2];
String flag = "0";
String duration = splitOriRowKey[5];
String regionCode = HBaseUtil.genRegionCode(callee, buildTime, regions);
String calleeRowKey = HBaseUtil.genRowKey(regionCode, callee, buildTime, caller, flag, duration);
//生成时间戳
String buildTimeTs = "";
try {
buildTimeTs = String.valueOf(sdf.parse(buildTime).getTime());
} catch (ParseException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
// call1 call2 build_time build_time_ts
Put calleePut = new Put(Bytes.toBytes(calleeRowKey));
calleePut.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("f2"), Bytes.toBytes("call1"), Bytes.toBytes(callee));
calleePut.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("f2"), Bytes.toBytes("call2"), Bytes.toBytes(caller));
calleePut.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("f2"),Bytes.toBytes("build_time"), Bytes.toBytes(buildTime));
calleePut.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("f2"), Bytes.toBytes("flag"), Bytes.toBytes(flag));
calleePut.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("f2"), Bytes.toBytes("duration"), Bytes.toBytes(duration));
calleePut.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("f2"),Bytes.toBytes("build_time_ts"),Bytes.toBytes(buildTimeTs));
Bytes.toBytes(100L);
// Table table = e.getEnvironment().getTable(TableName.valueOf(targetTableName));
Table table = e.getEnvironment().getConnection().getTable(TableName.valueOf(targetTableName));
table.put(calleePut);
table.close();
}
}- 运行测试
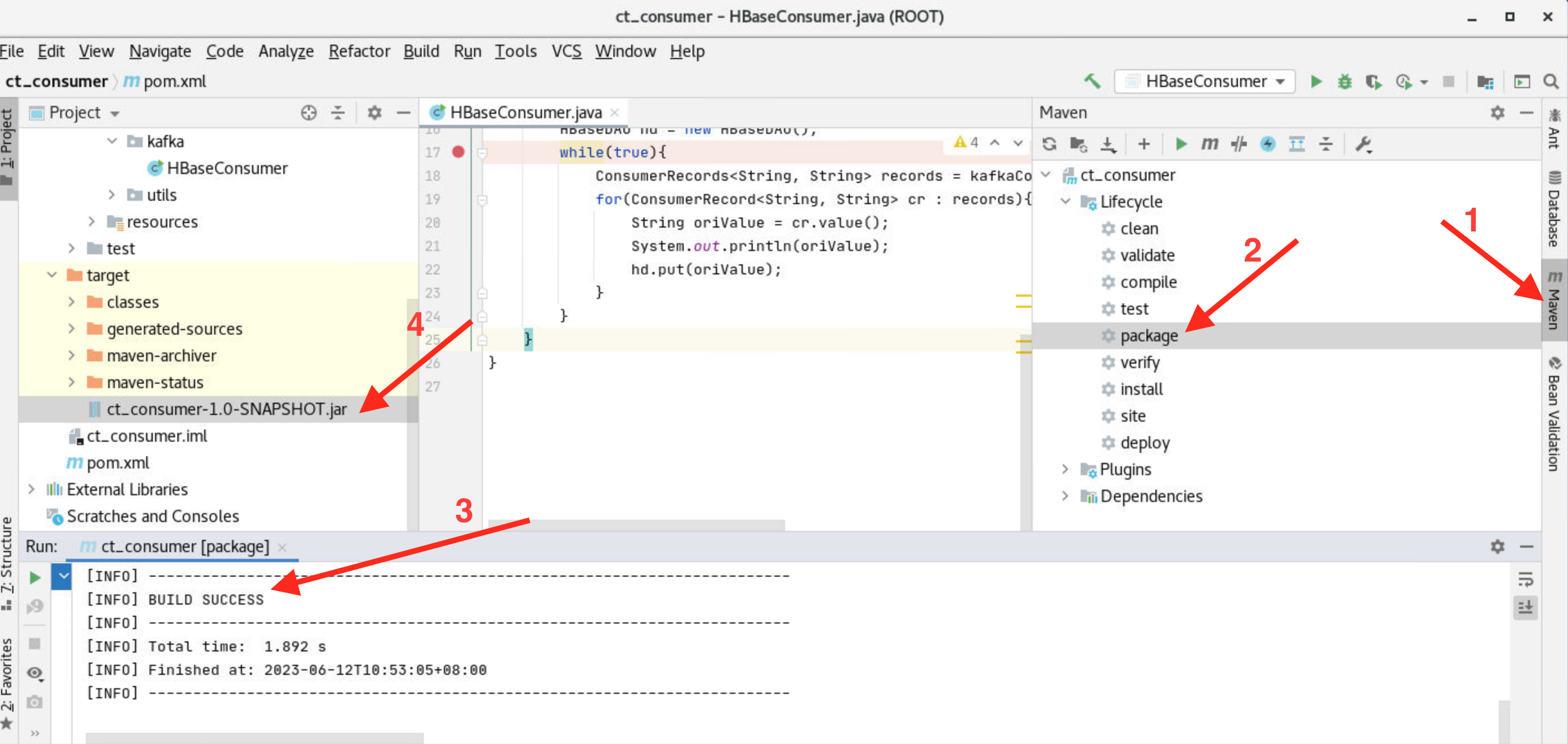
a) 在项目中选择右侧的Maven标签,双击Lifecycle->package对项目进行打包,当现实"BUILD SUCESS"后,在项目的target文件下将会生成ct_consumer-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar文件
b) 在HBase表中应用协处理器
将jar包上传到HDFS中(供协处理器使用),执行以下代码:(jar包在ct_consumer项目所在的target目录中,请根据真实情况进入项目目录,此处jar默认在/root/IdeaProjects/ct_consumer/target目录中)
[root@master1 ~]# cd /root/IdeaProjects/ct_consumer/target
[root@master1 target]# hdfs dfs -mkdir -p /hbase/coprocessor/
[root@master1 target]# hdfs dfs -put ct_consumer-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar /hbase/coprocessor/启动HBase,如未启动【master1】使用如下命令启动:
[root@master1 ~]# start-hbase.sh进入HBase命令行将协处理器应用到表,执行【hbase shell】进入HBase命令行,在命令行中执行以下代码:
hbase(main):001:0> disable 'ns_ct:calllog'
hbase(main):002:0> alter 'ns_ct:calllog', METHOD => 'table_att', 'coprocessor'=>'/hbase/coprocessor/ct_consumer-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar|hbase.CalleeWriteObserver|100'
hbase(main):003:0> enable 'ns_ct:calllog'
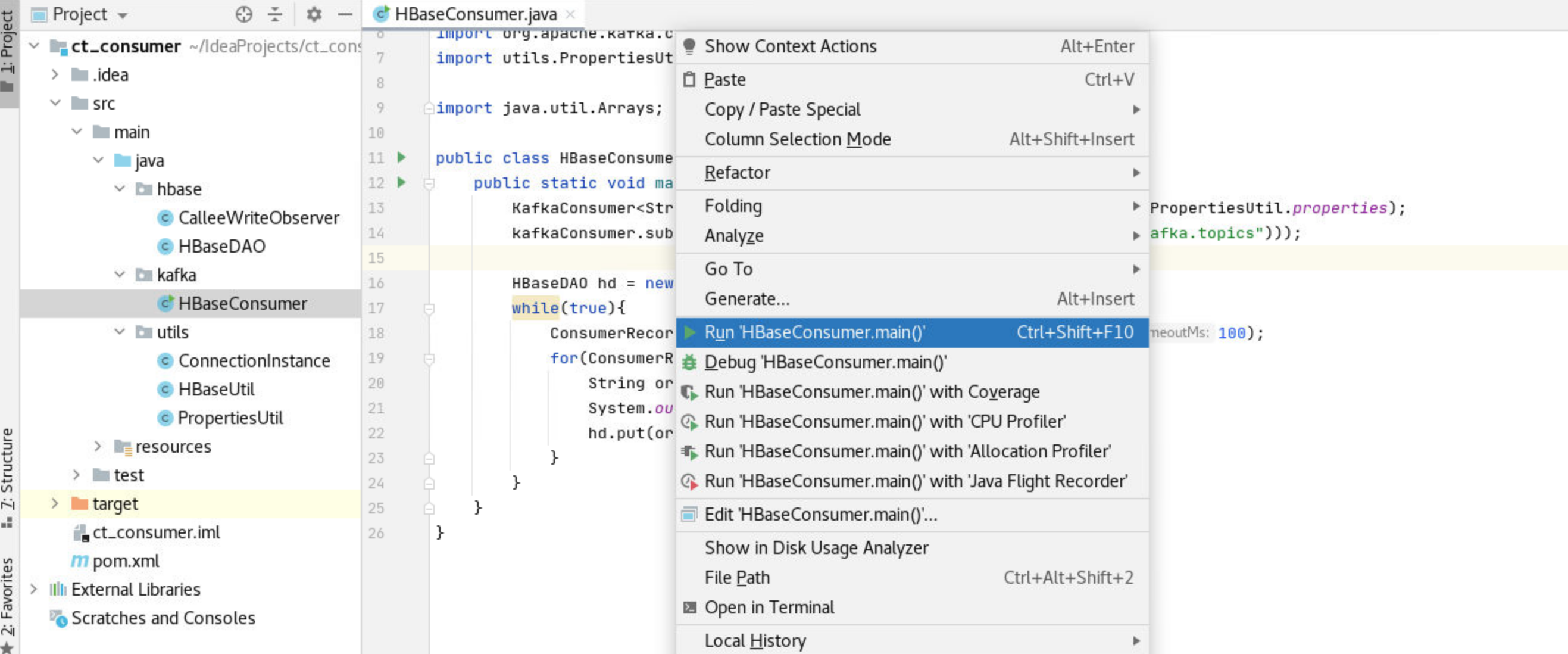
hbase(main):003:0> quit运行HBaseConsumerl类测试
进入HBase观察【ns_ct:calllog】表的数据
hbase(main):001:0> scan 'ns_ct:calllog',{STARTROW=> '0' , LIMIT => 10}或者通过count命令查看当前表的总记录数量
hbase(main):002:0> count 'ns_ct:calllog'如回显所示,在程序运行一定时间后,总记录条数为6720(建议运行一段时间程序以便在"数据展示"任务重得到更好的展示效果)
hbase(main):003:0> count 'ns_ct:calllog'
Current count: 1000, row: 00_16264433631_20171024123701_17269452013_1_1179
Current count: 2000, row: 00_18576581848_20170704010025_15542823911_1_0229
Current count: 3000, row: 01_15978226424_20170731100126_18468618874_1_0795
Current count: 4000, row: 01_18468618874_20171122084724_13980337439_0_0176
Current count: 5000, row: 02_15714728273_20170420175940_17005930322_1_1437
Current count: 6000, row: 02_17526304161_20170714141822_17078388295_1_0325
6720 row(s)
Took 0.6766 seconds
=> 6720