文章目录
一、前言
哎!只要是书上写的和经典设计模式不同,我就会很伤脑筋。😩
命令模式到底是干什么的?
答:命令的发送者和接收者完全解耦
简单来说:转换了调用主体,调用主体由原来的类,变成了命令类(或者调用命令类的类)为调用主体
相关代码可以在这里,如有帮助给个star!AidenYuanDev/design_patterns_in_modern_Cpp_20
二、分析 + 拆解
1、经典命令模式
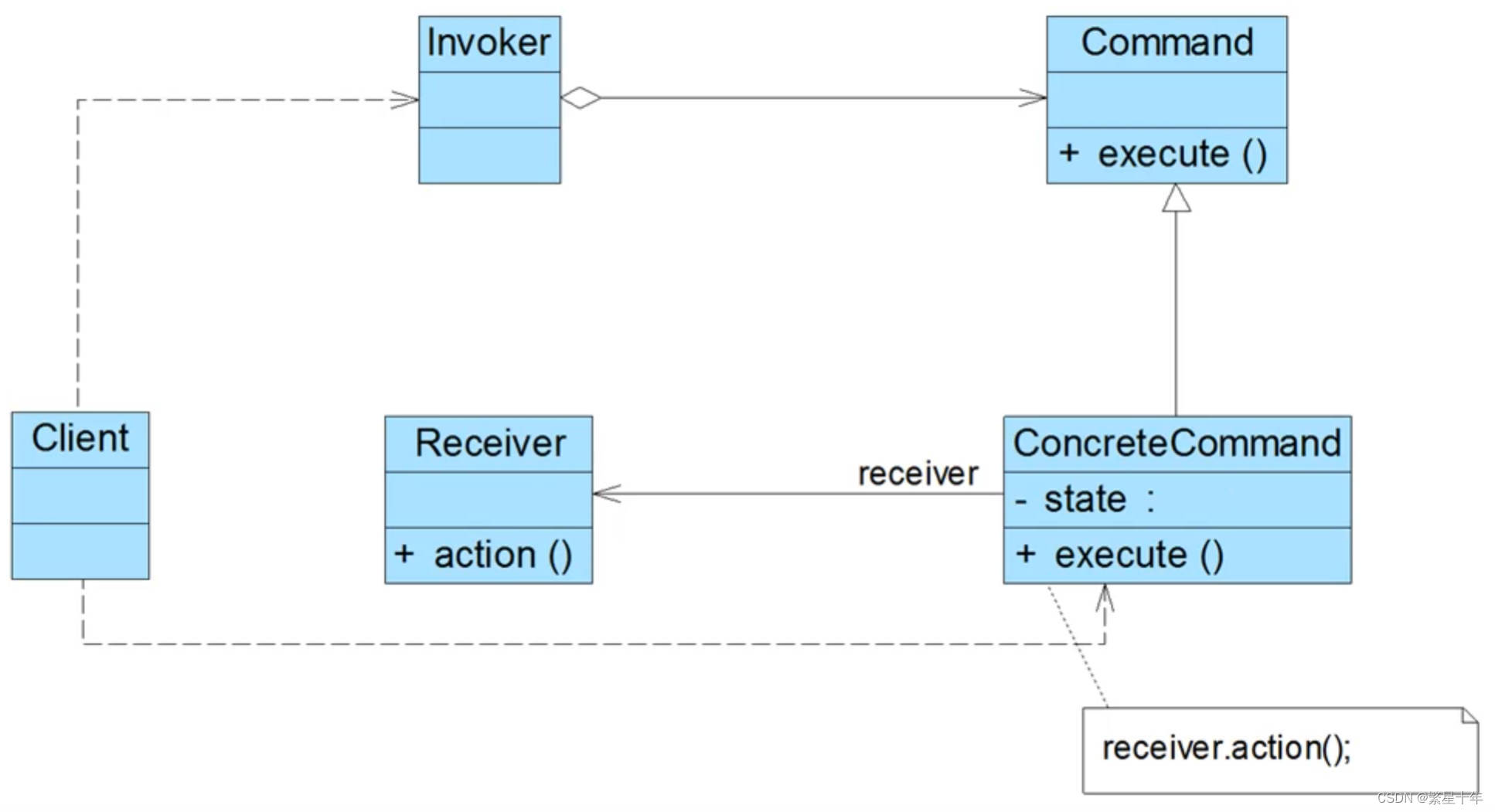
个人觉得太复杂,没有很直观的描述出命令模式的作用。
下面是我拆解的图
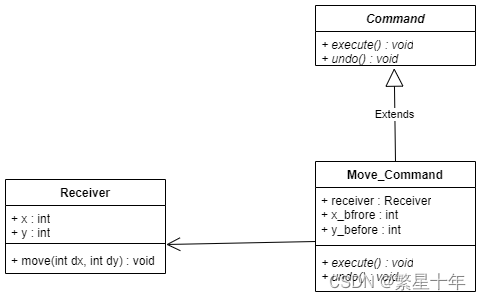
具体的成员变量可成员函数大家可以先不用看,现在你只要明白一个点就可以了------ Move_Command类组合了Receiver类,所以可以由 Move_Command随意调用move方法(即这就是我说的调用主体的改变)
2、撤销操作
也就是记录一下以前没执行的状态,再还原就行了。
3、关于Invoker类
Invoker类也就是命令的发送者。
举个例子:
对于游戏呢,就接收很多命令在Invoker类中,我们
用Invoker类依次发送 Command类就可以了。
三、实现
c
#include <iostream>
#include <iterator>
#include <memory>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class Receiver {
private:
int x;
int y;
public:
Receiver(int x, int y) : x(x), y(y) {}
void move(int dx, int dy) {
x += dx;
y += dy;
}
void show_pos() {
cout << "pos:" << endl;
cout << "x -->" << x << endl;
cout << "y ->>" << y << endl << endl;
}
int get_x() { return x; }
int get_y() { return y; }
};
class Command {
public:
virtual void excute() = 0;
virtual void undo() = 0;
};
class Move_Command :public Command {
private:
unique_ptr<Receiver>& receiver;
int x;
int y;
bool flag;
public:
Move_Command(unique_ptr<Receiver> &receiver, int x, int y) :
receiver(receiver), x(y), y(y), flag(false) {}
void excute() override {
receiver->move(x, y);
flag = true;
}
void undo() override {
if (flag) {
flag = false;
receiver->move(-x, -y);
}
}
};
class Invoke {
private:
vector<shared_ptr<Command>> commands;
public:
Invoke *push_command(shared_ptr<Command> command) {
commands.push_back(command);
return this;
}
void excute() {
for (auto it : commands) it->excute();
}
void undo() {
for (auto it = commands.rbegin(); it != commands.rend(); it++) (*it)->undo();
}
};
int main() {
auto invoke = make_unique<Invoke>();
auto receiver = make_unique<Receiver>(5, 6);
auto command_1 = make_shared<Move_Command>(receiver, 6, 6);
auto command_2 = make_shared<Move_Command>(receiver, 1, 6);
auto command_3 = make_shared<Move_Command>(receiver, 6, 5);
receiver->show_pos();
invoke->push_command(command_1)
->push_command(command_2)
->push_command(command_3)
->excute();
receiver->show_pos();
invoke->undo();
receiver->show_pos();
return 0;
}