
1.copy()

2.replace()
3.replace_if()

cpp
class MyCompare
{
public:
bool operator()(const int val)
{
return val > 5;
}
};
void MyPrint(int val)
{
cout << val << " ";
}
void test01()
{
vector<int> v1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
}
cout << "替换前:" << endl;
for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), MyPrint);
cout << endl;
replace_if(v1.begin(), v1.end(), MyCompare(), 30);//将大于五的数全都替换为30
cout << "替换后:" << endl;
for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), MyPrint);
cout << endl;
}4.swap()

5.算术生成算法

5.1accumulate()

返回的是value+区间和
5.2fill()
向区间填充value值

cpp
void MyPrint(int val)
{
cout << val << " ";
}
void test01()
{
vector<int> v1;
v1.resize(10);
fill(v1.begin(), v1.end(), 100);//将v1全部填充100
for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), MyPrint);
}6.常用集合算法

6.1set_intersection()//交集
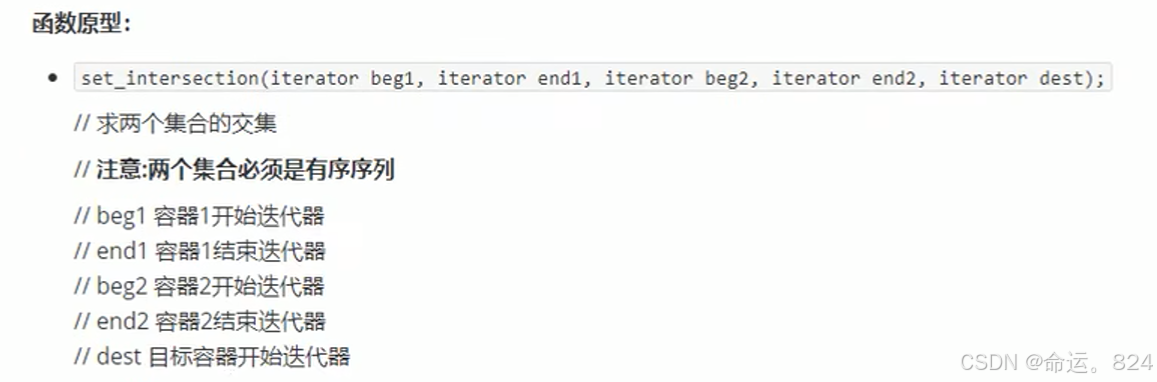
cpp
void MyPrint(int val)
{
cout << val << " ";
}
void test01()
{
vector<int> v1;
vector<int> v2;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
v2.push_back(i + 5);
}
for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), MyPrint);
cout << endl;//0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), MyPrint);
cout << endl;//5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
vector<int> v3;
v3.resize(min(v1.size(), v2.size()));
auto it=set_intersection(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), v3.begin());//返回交集最后一个元素的地址
for_each(v3.begin(),it, MyPrint);//5 6 7 8 9
cout << endl;
}6.2set_union()//并集
v3.resize(v1.size()+v2.size());
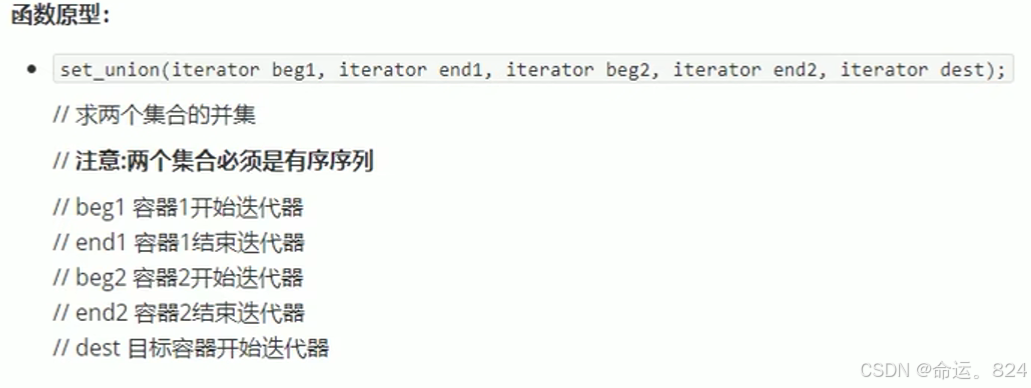
6.3set_difference()//差集
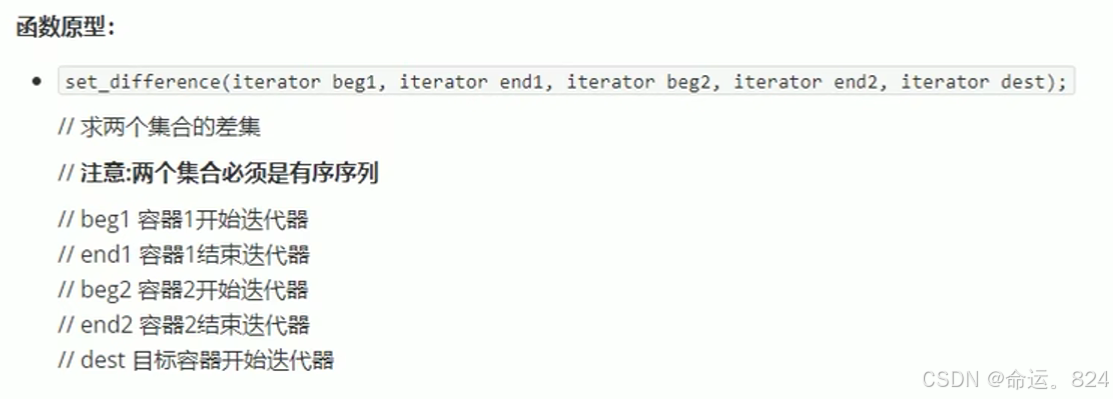
cpp
void MyPrint(int val)
{
cout << val << " ";
}
void test01()
{
vector<int> v1;
vector<int> v2;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
v2.push_back(i + 5);
}
for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), MyPrint);
cout << endl;//0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), MyPrint);
cout << endl;//5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
vector<int> v3;
v3.resize(v1.size());
cout << "v1-v2" << endl;//v1-v2
auto it=set_difference(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), v3.begin());//返回交集最后一个元素的地址
for_each(v3.begin(),it, MyPrint);
cout << endl;
v3.resize(v2.size());
cout << "v2-v1" << endl;//v2-v1
it = set_difference(v2.begin(), v2.end(), v1.begin(), v1.end(), v3.begin());//返回交集最后一个元素的地址
for_each(v3.begin(), it, MyPrint);
cout << endl;
}