297. Serialize and Deserialize Binary Tree
Serialization is the process of converting a data structure or object into a sequence of bits so that it can be stored in a file or memory buffer, or transmitted across a network connection link to be reconstructed later in the same or another computer environment.
Design an algorithm to serialize and deserialize a binary tree. There is no restriction on how your serialization/deserialization algorithm should work. You just need to ensure that a binary tree can be serialized to a string and this string can be deserialized to the original tree structure.
Clarification: The input/output format is the same as how LeetCode serializes a binary tree. You do not necessarily need to follow this format, so please be creative and come up with different approaches yourself.
Example 1:
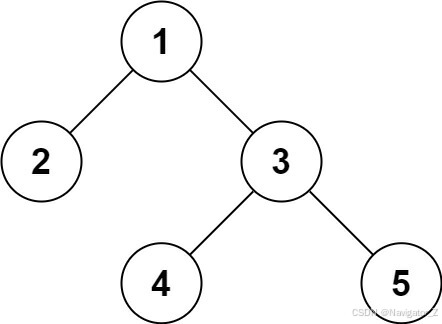
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,null,4,5]
Output: [1,2,3,null,null,4,5]
Example 2:
Input: root = []
Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [ 0 , 1 0 4 ] [0, 10^4] [0,104].
- -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
From: LeetCode
Link: 297. Serialize and Deserialize Binary Tree
Solution:
Ideas:
- Serialization:
- We traverse the tree in pre-order.
- Each node's value is appended to the buffer string.
- For NULL nodes, we append "#," to indicate an absence of a child.
- Deserialization:
- We parse the string token by token.
- If we encounter a "#", we return NULL for that node.
- Otherwise, we create a new node and recursively build its left and right children.
Code:
c
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
// Function to create a new tree node.
struct TreeNode* newNode(int val) {
struct TreeNode* node = (struct TreeNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode));
node->val = val;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
// Helper function for serialization.
void serializeHelper(struct TreeNode* root, char* buffer, int* index) {
if (root == NULL) {
strcpy(&buffer[*index], "#,");
*index += 2;
return;
}
int len = sprintf(&buffer[*index], "%d,", root->val);
*index += len;
serializeHelper(root->left, buffer, index);
serializeHelper(root->right, buffer, index);
}
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
char* serialize(struct TreeNode* root) {
// Allocate a buffer to store the serialized string.
// Size of 10000 * 6 is arbitrary, based on the problem constraints.
char* buffer = (char*)malloc(10000 * 6);
int index = 0;
serializeHelper(root, buffer, &index);
buffer[index] = '\0';
return buffer;
}
// Helper function for deserialization.
struct TreeNode* deserializeHelper(char** data) {
if (**data == '#') {
*data += 2; // Skip '#,'
return NULL;
}
int val = 0;
int sign = 1;
if (**data == '-') { // Check for negative numbers
sign = -1;
(*data)++;
}
while (**data != ',') {
val = val * 10 + (**data - '0');
(*data)++;
}
val *= sign;
(*data)++; // Skip ','
struct TreeNode* node = newNode(val);
node->left = deserializeHelper(data);
node->right = deserializeHelper(data);
return node;
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
struct TreeNode* deserialize(char* data) {
return deserializeHelper(&data);
}
// Your functions will be called as such:
// char* data = serialize(root);
// deserialize(data);