letcode 分类练习 110. 平衡二叉树 101. 对称二叉树 104.二叉树的最大深度 111.二叉树的最小深度
- [110. 平衡二叉树](#110. 平衡二叉树)
- [257. 二叉树的所有路径](#257. 二叉树的所有路径)
- [404. 左叶子之和](#404. 左叶子之和)
- [222. 完全二叉树的节点个数](#222. 完全二叉树的节点个数)
- 对称二叉树 104.二叉树的最大深度 111.二叉树的最小深度)
110. 平衡二叉树
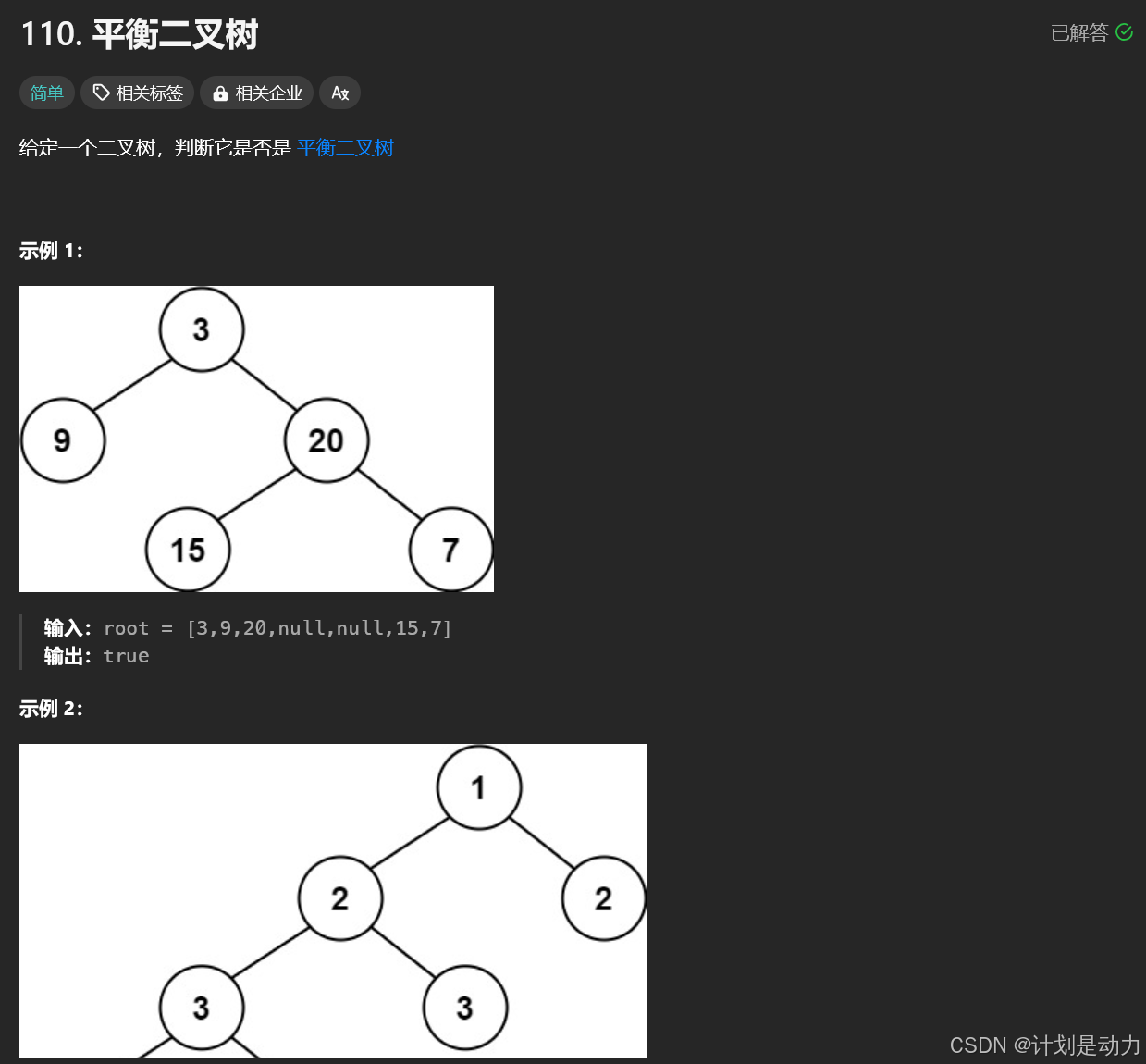
用递归的思路检查左子树和右子树的高度差绝对值是不是在1以内,为了方便同时获取左子树和右子树的高度,我们定义如果高度为-1表示该子树不满足平衡二叉树,如果不等于-1表示子树的高度
c
class Solution {
public:
int height(TreeNode* node){
if(!node) return 0;
int left_depth = height(node -> left);
int right_depth = height(node -> right);
if(left_depth == -1 || right_depth == -1 || abs(left_depth - right_depth) > 1)return -1;
else return max(left_depth, right_depth) + 1;
}
bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) {
return height(root) >= 0;
}
};257. 二叉树的所有路径
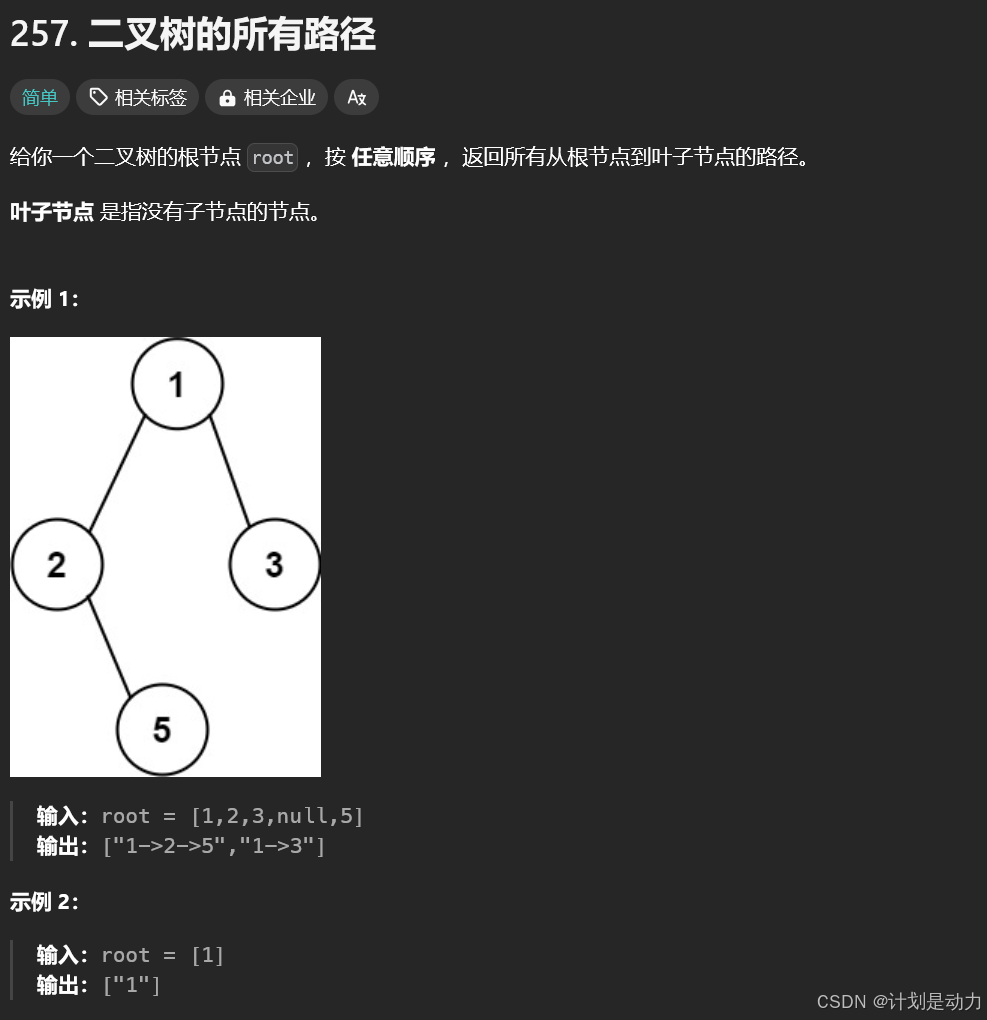
每个节点都对应唯一的从根节点出发的路径,只需要做一个遍历,如果它是叶子节点就记录路径即可
c
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> result;
void dfs(TreeNode* root, string s){
if(!root) return;
if(!root->left && !root->right)result.push_back(s);
if(root->left)dfs(root -> left, s + "->" + to_string(root -> left -> val));
if(root->right)dfs(root -> right, s + "->" + to_string(root -> right -> val));
}
vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root) return result;
if(!root -> left&& !root->right){result.push_back(to_string(root->val)); return result;}
dfs(root, to_string(root->val));
return result;
}
};404. 左叶子之和
 传参的时候可以告诉该节点是左孩子还是右孩子,再判断一下当前节点是不是叶子结点即可
传参的时候可以告诉该节点是左孩子还是右孩子,再判断一下当前节点是不是叶子结点即可
c
class Solution {
public:
int sum = 0;
void dfs(TreeNode* root, int flag){
if(!root) return;
if(!root -> left && !root -> right && flag == 0)sum+= root->val;
dfs(root->left, 0);
dfs(root ->right, 1);
}
int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root, -1);
return sum;
}
};222. 完全二叉树的节点个数
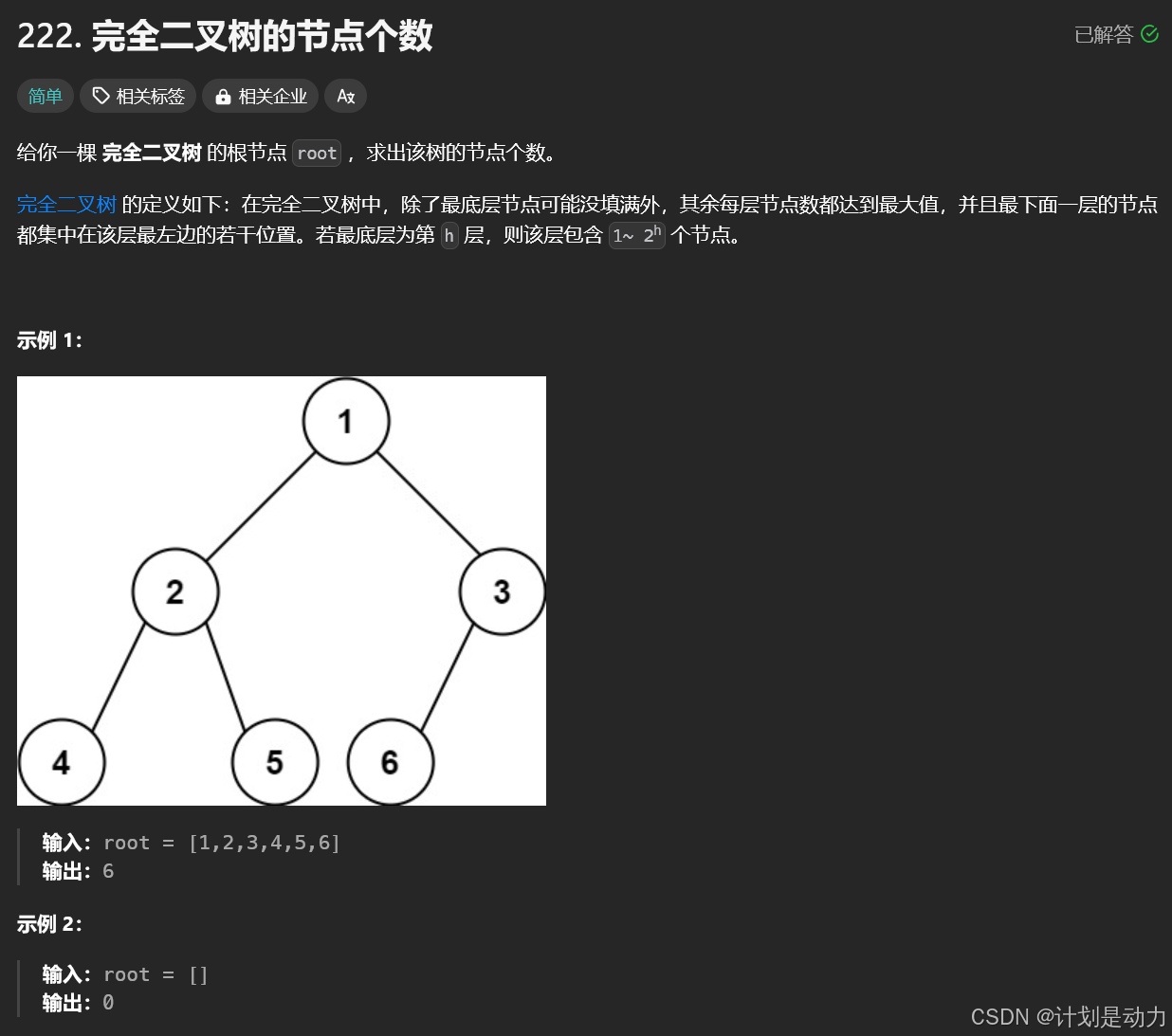
可以利用完全二叉树的性质解题
完全二叉树是一定要按照一层一层的顺序装填的,所以判断完全二叉树只需要一直向左和一直向右迭代,两边的深度一样即可,注意下面的不是完全二叉树:

c
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) return 0;
TreeNode* left = root->left;
TreeNode* right = root->right;
int leftDepth = 0, rightDepth = 0; // 这里初始为0是有目的的,为了下面求指数方便
while (left) { // 求左子树深度
left = left->left;
leftDepth++;
}
while (right) { // 求右子树深度
right = right->right;
rightDepth++;
}
if (leftDepth == rightDepth) {
return (2 << leftDepth) - 1; // 注意(2<<1) 相当于2^2,所以leftDepth初始为0
}
return countNodes(root->left) + countNodes(root->right) + 1;
}
};