目录
- [1- 思路](#1- 思路)
- [2- 实现](#2- 实现)
-
- [⭐94. 二叉树的中序遍历------题解思路](#⭐94. 二叉树的中序遍历——题解思路)
- [3- ACM实现](#3- ACM实现)
- 原题连接:94. 二叉树的中序遍历
1- 思路
栈-统一遍历
二叉树的处理遍历过程,主要分为两步
- 1- 访问节点
- 2- 处理节点
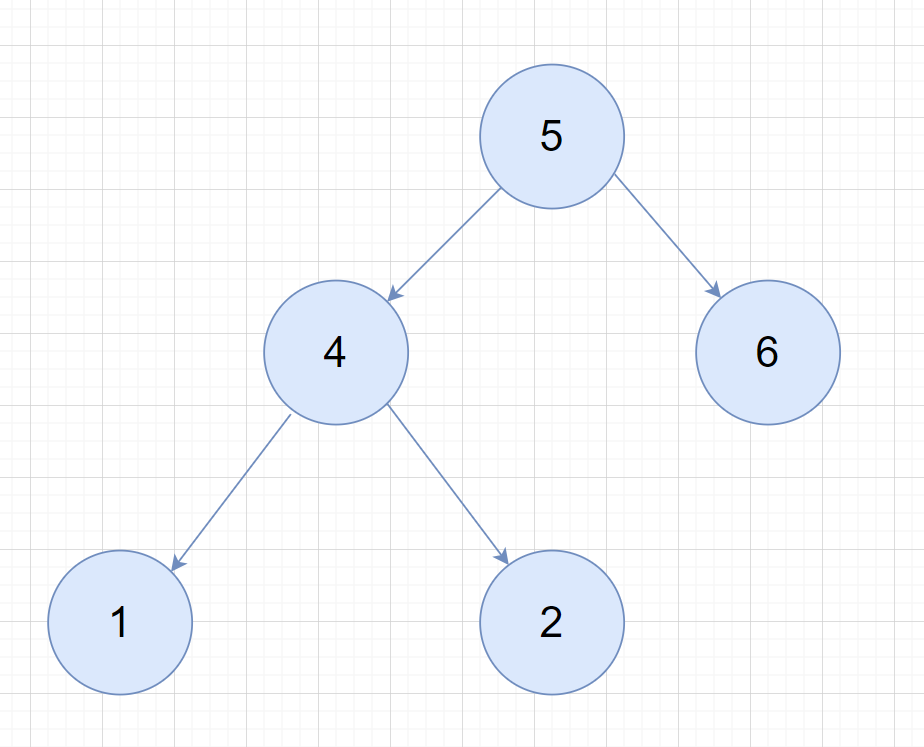
中序遍历
- 中序遍历的顺序是 ------> 左 中 右 ------> 给我们的又是根节点,需要从根节点开始访问
- 例如二叉树,可以看到从根节点
5开始访问,但不能先处理节点5- 先访问
5------>4------>1,其中1才是我们需要处理的结点。
- 先访问
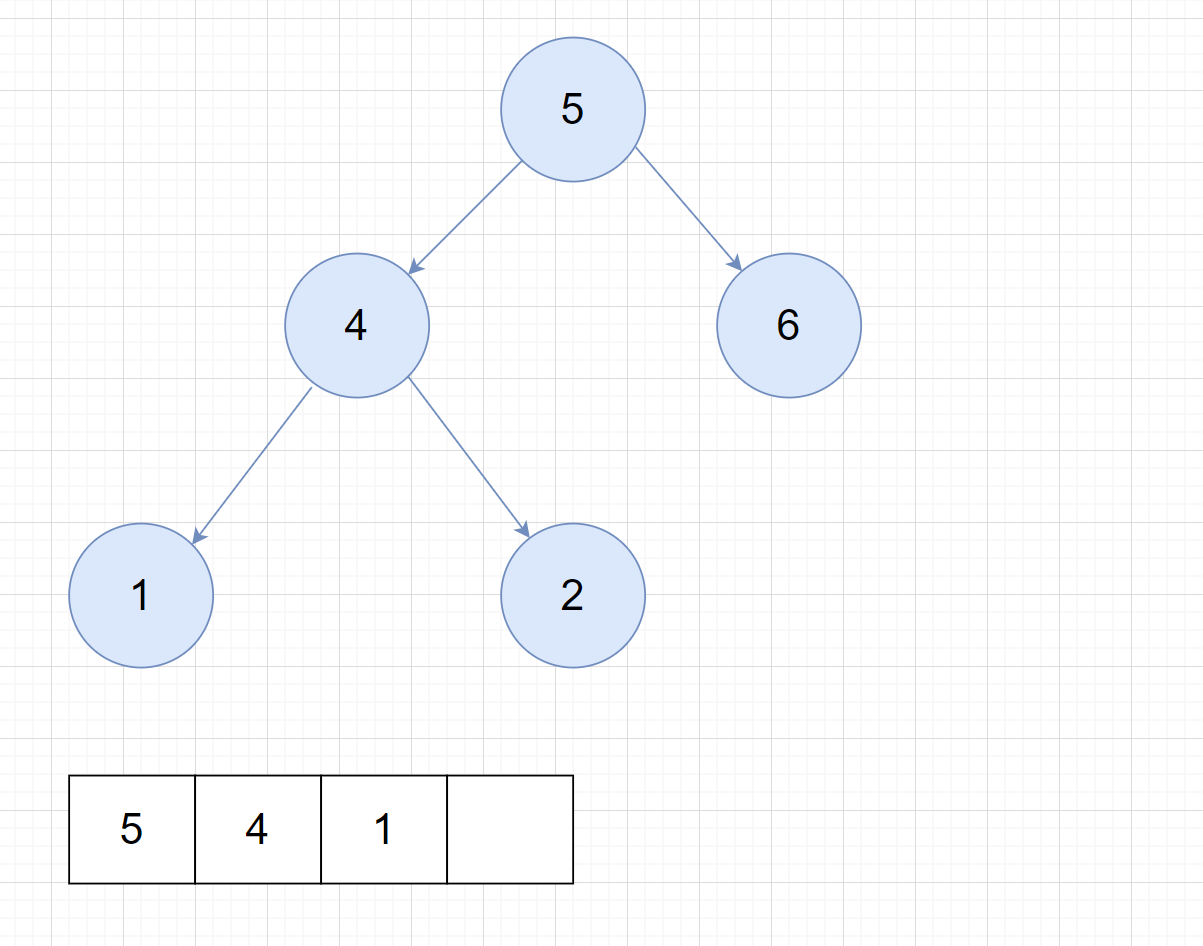
借助栈实现
- 使用一个指针,来遍历二叉树,访问节点后将其入栈
- 直到遍历到
null,比如指针到1的左节点此时是null了,就需要栈中弹出元素,处理第一个结点就是1,之后将1加入结果集
2- 实现
⭐94. 二叉树的中序遍历------题解思路

java
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> st = new Stack<>();
if(root==null){
return res;
}
// 指针
TreeNode cur = root;
while(cur!=null || !st.isEmpty()){
if(cur!=null){
st.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}else{
cur = st.pop();
res.add(cur.val);
cur = cur.right;
}
}
return res;
}
}3- ACM实现
java
public class inorderT {
public static class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {}
TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
public static TreeNode build(String str){
if(str == null || str.length()==0){
return null;
}
String input = str.replace("[","");
input = input.replace("]","");
String[] parts = input.split(",");
Integer[] nums = new Integer[parts.length];
for(int i = 0 ; i < parts.length;i++){
if(!parts[i].equals("null")){
nums[i] = Integer.parseInt(parts[i]);
}else{
nums[i] = null;
}
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(nums[0]);
queue.offer(root);
int index = 1;
while(!queue.isEmpty()&& index<parts.length){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if(index<nums.length && nums[index]!=null){
node.left = new TreeNode(nums[index]);
queue.offer(node.left);
}
index++;
if(index<nums.length && nums[index]!=null){
node.right = new TreeNode(nums[index]);
queue.offer(node.right);
}
index++;
}
return root;
}
public static List<Integer> inorderT(TreeNode root){
// 借助 栈 + 指针
TreeNode cur = root;
Stack<TreeNode> st = new Stack<>();
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(root==null){
return res;
}
// 遍历
while (cur!=null || !st.isEmpty()){
// 一直遍历
if(cur!=null){
st.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}else{
// 处理节点
cur = st.pop();
res.add(cur.val);
cur = cur.right;
}
}
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String input = sc.nextLine();
TreeNode root = build(input);
List<Integer> res = inorderT(root);
System.out.println(res.toString());
}
}