目录
前言
本篇内容将会介绍用算法对好评差评进行分类,并对某评论是好评还是差评进行合理预测
一、获取数据并保存
1.获取好评数据
python
import requests
import time
import re
from lxml import etree
head = {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/128.0.0.0 Safari/537.36 Edg/128.0.0.0"
}
def pa():
for j in range(1, 200):
time.sleep(3)
url = f"https://review.suning.com/cluster_cmmdty_review/cluster-38249278-000000012389328846-0000000000-{j}-good.htm?originalCmmdtyType=general&safp=d488778a.10004.loverRight.166"
response = requests.get(url, headers=head)
sn_text = response.text
tree = etree.HTML(sn_text)
li_list = tree.xpath("//div[@class='rv-target-item']/div")
sn_coments = []
for i in li_list:
sn_coment = ''.join(i.xpath(".//p[@class='body-content']/text()")) # xpath返回的是列表
sn_coment = re.match(r".*[\u4e00-\u9fff]*.*?", sn_coment.strip()).group()
sn_coments.append(sn_coment)
print(sn_coment)
sngood.write(sn_coment + '\n')
# print(sn_coments)
if __name__ == '__main__':
sngood = open('sngood.txt', 'w', encoding='utf8')
pa()
sngood.close()好评数据:
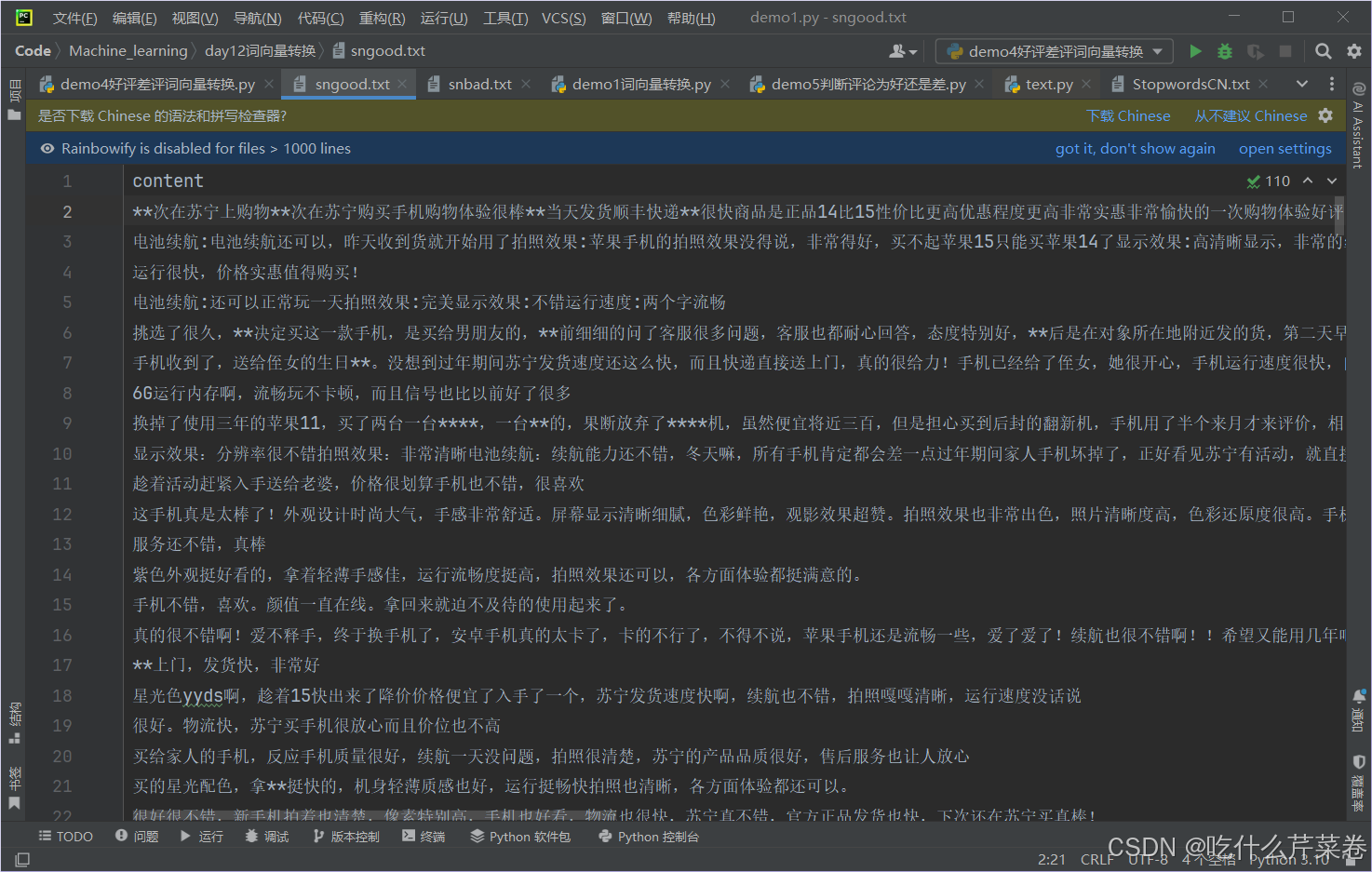
2.获取差评数据
python
import requests
import time
import re
from lxml import etree
head = {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/128.0.0.0 Safari/537.36 Edg/128.0.0.0"
}
def pa():
for j in range(1, 3):
time.sleep(3)
url = f"https://review.suning.com/cluster_cmmdty_review/cluster-38249278-000000012389328846-0000000000-{j}-bad.htm?originalCmmdtyType=general&safp=d488778a.10004.loverRight.166&safpn=10009"
response = requests.get(url, headers=head)
sn_text = response.text
tree = etree.HTML(sn_text)
li_list = tree.xpath("//div[@class='rv-target-item']/div")
sn_coments = []
for i in li_list:
sn_coment = ''.join(i.xpath(".//p[@class='body-content']/text()")) # xpath返回的是列表
sn_coment = re.match(r".*[\u4e00-\u9fff]*.*?", sn_coment.strip()).group()
sn_coments.append(sn_coment)
print(sn_coment)
snbad.write(sn_coment + '\n')
# print(sn_coments)
if __name__ == '__main__':
snbad = open('snbad.txt', 'w', encoding='utf8')
pa()
snbad.close()差评数据:
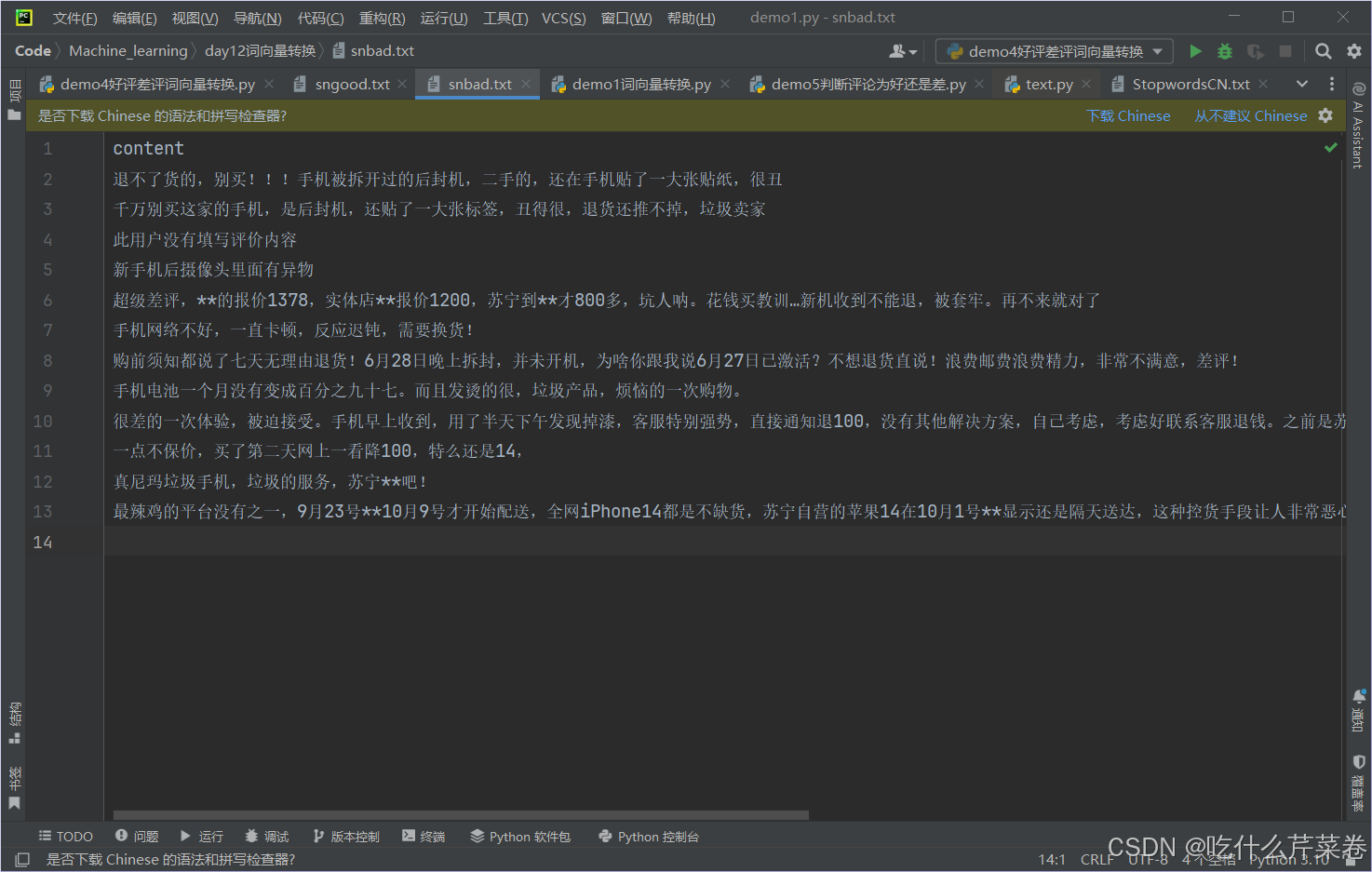
二、处理数据并建立模型实现目标
1.处理数据
1.读取数据
python
import pandas as pd
cp_content = pd.read_csv('snbad.txt', encoding='utf8', sep='\t')
hp_content = pd.read_csv('sngood.txt', encoding='utf8', sep='\t')2.使用jieba库对好评差评进行分词
python
"""
对差评分词
"""
import jieba
cp_segments = []
contents = cp_content['content'].values.tolist() # 将评论转换到列表内
for content in contents:
results = jieba.lcut(content) # 对每条评论进行分词
if len(results) > 1:
cp_segments.append(results)
cp_fc_results = pd.DataFrame({'content': cp_segments})
cp_fc_results.to_excel('snbad.xlsx', index=False)
"""
对好评分词
"""
hp_segments = []
contents = hp_content['content'].values.tolist() # 将评论转换到列表内
for content in contents:
results = jieba.lcut(content) # 对每条评论进行分词
if len(results) > 1:
hp_segments.append(results)
hp_fc_results = pd.DataFrame({'content': hp_segments})
hp_fc_results.to_excel('sngood.xlsx', index=False)3.去除停用词
python
# 导入停词库
stopwords = pd.read_csv('StopwordsCN.txt', encoding='utf8', engine='python', index_col=False)
# 定义去除停用词函数
def drop_stopwords(contents, stopwords):
segments_clean = []
for content in contents:
line_clean = []
for word in content:
if word in stopwords:
continue
line_clean.append(word)
segments_clean.append(line_clean) # 每一个字符串代表每条评论去除停用词之后的词
return segments_clean
# 调用去除停用词函数
stopwords = stopwords['stopword'].tolist() # list类型 / stopwords['stopword'].values ndarray类型
contents = cp_fc_results['content'].tolist()
cp_fc_contents_clean_s = drop_stopwords(contents, stopwords)
contents = hp_fc_results['content'].tolist()
hp_fc_contents_clean_s = drop_stopwords(contents, stopwords)2.建立模型
1.将处理之后的数据转换成词向量
- 注意!!! 要使用训练集的数据去建立词库
python
"""
朴素贝叶斯分类
"""
'''给每个数据添加数字标签'''
cp_train = pd.DataFrame({'segments_clean': cp_fc_contents_clean_s, 'label': 1})
hp_train = pd.DataFrame({'segments_clean': hp_fc_contents_clean_s, 'label': 0})
pj_train = pd.concat([cp_train, hp_train]) # 上下相连
pj_train.to_excel('pj_train.xlsx', index=False)
'''数据切分'''
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = \
train_test_split(pj_train['segments_clean'].values, pj_train['label'].values, random_state=0)
# values 可加可不加 作用是将pj_train['segments_clean']获取到的series对象转换成numpy数组
# pj_train['segments_clean'].values 将该列所有值按顺序取出来,不带索引 取出来之后自动加上索引 x_train 也是随机取值 不带索引 取出来之后自动加上索引
'''将所有词转换成词向量'''
words = []
for index in range(len(x_train)):
words.append(' '.join(x_train[index]))
# print(words)
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
vec = CountVectorizer(max_features=4000, lowercase=False, ngram_range=(1, 1))
# lowercase参数的功能:把所有的词是是否需要转换为小写。False。
vec.fit(words) # 传入训练集的所有文字, 根据文字构建词汇表2.训练模型并预测
- 应将原数据用transform转换成词向量矩阵之后再带入模型进行训练以及预测
python
'''导入朴素贝叶斯分类器'''
from sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB
x_train = vec.transform(words)
classifier = MultinomialNB(alpha=0.1)
classifier.fit(x_train, y_train)
train_predict = classifier.predict(x_train)
# 训练集预测得分
from sklearn import metrics
print(metrics.classification_report(y_train, train_predict))
# 测试集数据进行分析
test_words = []
for line_index in range(len(x_test)):
test_words.append(' '.join(x_test[line_index]))
x_test = vec.transform(test_words)
test_predict = classifier.predict(x_test)
print(metrics.classification_report(y_test, test_predict))
print(test_predict)输出结果:
python
precision recall f1-score support
0 1.00 0.98 0.99 1163
1 0.21 1.00 0.35 7
accuracy 0.98 1170
macro avg 0.61 0.99 0.67 1170
weighted avg 1.00 0.98 0.98 1170
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.99 0.99 0.99 386
1 0.50 0.60 0.55 5
accuracy 0.99 391
macro avg 0.75 0.80 0.77 391
weighted avg 0.99 0.99 0.99 391
[0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]三、对某评论是好评还是差评进行合理预测
- 对评论进行分词
- 去除停用词
- 转换成词向量矩阵
- 进行预测
python
"""单条评论判断"""
def text(comment):
# 1.分词
a = jieba.lcut(comment)
# 2.去除停用词
b = []
for i in a:
if i not in stopwords and len(i.strip()) > 0:
b.append(i)
c = []
c.append(' '.join(b[:])) # 将多个字符串连接并放到列表里
# 3.转换成词向量矩阵
c_train = vec.transform(c)
# 4.进行预测
c_pr = classifier.predict(c_train)
return c_pr
comment1 = '这个玩意真好,我很喜欢'
comment2 = '这个玩意太垃圾了'
print(text(comment1))
print(text(comment2))输出:
- 分类正确
python
[0]
[1]总结
将这个模型训练出来,有自动化评论分类 、改进客户服务和个性化推荐等作用。