目录
[1. 日期+=天数](#1. 日期+=天数)
[2. 日期+天数](#2. 日期+天数)
[3. 日期-=天数](#3. 日期-=天数)
[3.1 日期-天数](#3.1 日期-天数)
[4. 比较运算符](#4. 比较运算符)
[5. 日期-日期](#5. 日期-日期)
[6. 代码汇总](#6. 代码汇总)
日期类实现
1. 日期+=天数
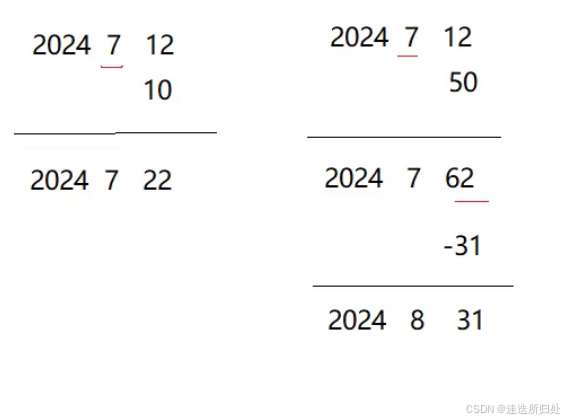
// d1 += 100
//+=可以改变d1,所以可以直接相加
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{
//如果天数小于0
if (day < 0)
{
return *this -= (-day);
}
//天数+天数
_day += day;
//当相加之后的天数大于当前月份的天数时进入循环
while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
//相加之后的天数减去当前月份的天数
_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
//月份++
++_month;
//当月份为13个月时
if (_month == 13)
{
//年++,月为1
_year++;
_month = 1;
}
}
return *this;
}2. 日期+天数
// d1 + 100
//+不能直接改变d1
Date Date::operator+(int day)
{
//所以可以使用拷贝构造来拷贝一份D1的值赋给tmp
Date tmp = *this;
//方法1:直接调用+=
tmp += day;
//方法2:原理和+=相同,只不过是多了一个tmp
/*tmp._day += day;
while (tmp._day > GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month))
{
tmp._day -= GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month);
++tmp._month;
if (tmp._month == 13)
{
tmp._year++;
tmp._month = 1;
}
}*/
return tmp;
}3. 日期-=天数
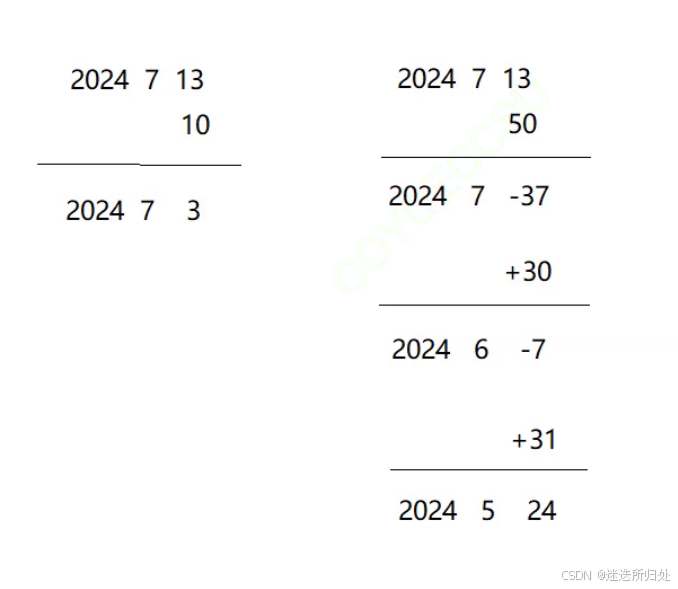
//d1 -= 100 日期-=天数
Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{
if (day < 0)
{
return *this += (-day);
}
//天数-天数
_day -= day;
//当天数小于0时进入循环
while (_day <= 0)
{
//借上一个月的天数
--_month;
//如果月份借完了,为0
if (_month == 0)
{
//那么就借上一年的12月
_month = 12;
--_year;
}
//把上个月借来的天数加上
_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
}
return *this;
}3.1 日期-天数
//d1 - 100 日期-天数
Date Date::operator-(int day) const
{
//逻辑和+相同
Date tmp = *this;
tmp -= day;
return tmp;
}4. 比较运算符
两个日期的大小比较
当同时实现了小于+等于 或者 大于+等于就可以使用 赋用 来实现其他的比较运算符,不光适用于日期类,还适合所有的类的比较运算符
/*当同时实现了小于+等于 或者 大于+等于
就可以使用 复用 来实现其他的比较运算符*/
//d1的参数为this指针,d1的参数为d
bool Date::operator<(const Date& d)
{
//如果年小于年
if (_year < d._year)
{
return true;
}//当年等于年时进入
else if (_year == d._year)
{
//如果月小于月
if (_month < d._month)
{
return true;
}//当月等于月时进入
else if (_month == d._month)
{
//比较天数大小
return _day < d._day;
}
}
//大于则返回false
return false;
}
bool Date::operator==(const Date& d)
{
return _year == d._year
&& _month == d._month
&& _day == d._day;
}5. 日期-日期

思路:先判断两个日期的大小,去小的那个日期,然后一直小的日期的++天数,直到小的日期与大的日期相等为止
//日期-日期
// d1 - d2
/*思路:先判断两个日期的大小,去小的那个日期,
然后一直小的日期的++天数,直到小的日期与大的日期相等为止*/
int Date::operator-(const Date& d) const
{
//假设第一个大第二个小,flag = 1
int flag = 1;
//d1=this d2=d
Date max = *this;
Date min = d;
//如果第一个小第二个大,flag = -1
if (*this < d)
{
max = d;
min = *this;
flag = -1;
}
//定义一个n统计min和max中间相差多少天数
int n = 0;
//不相等进入循环
while (min != max)
{
//前置++减少一点拷贝
++min;
//天数的差值
++n;
}
//天数的差值*flag
//当d1>d2,那么就为正数,d1<d2,则就为负数
return n * flag;
}6. 代码汇总
Date.h
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<assert.h>
//日期类只需要实现构造函数,其他的3个函数不需要实现
class Date
{
//友元函数声明
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d);
friend istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d);
public:
//检查日期
bool CheckDate() const;
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1);
//打印
void Print() const;
//打印
//void Print();
//默认是lnline
//monthDayArray:用来获取莫一年莫一个月的天数
int GetMonthDay(int year, int month)const
{
//月份天数以数组下标为判断,第一个-1下标为0
//把函数定义为静态,因为会频繁调用
static int monthDayArray[13] = { -1, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 };
//判断是不是闰年,如果是闰年那么2月就是29天
if (month == 2 && ((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0)))
{
return 29;
}
return monthDayArray[month];
}
bool operator<(const Date& d)const;
bool operator<=(const Date& d)const;
bool operator>(const Date& d)const;
bool operator>=(const Date& d)const;
bool operator==(const Date& d)const;
bool operator!=(const Date& d)const;
//d1 + 100 日期+天数
Date operator+(int day);
Date& operator+=(int day);
//d1 - 100 日期-天数
Date operator-(int day) const;
Date& operator-=(int day);
// d1++;
// d1.operator++(0);
Date operator++(int);
// ++d1;
// d1.operator++();
Date& operator++();
// d1--;
// d1.operator--(0);
Date operator--(int);
// --d1;
// d1.operator--();
Date& operator--();
// d1 - d2
int operator-(const Date& d) const;
//void operator<<(ostream& out);
Date* operator&()
{
//return this;
//return nullptr;
return (Date*)0x2673FF40;
}
const Date* operator&() const
{
//return this;
//return nullptr;
return (Date*)0x2673FE30;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d);
istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d);Date.cpp
#include"Date.h"
//检查日期
bool Date::CheckDate() const
{
if (_month < 1 || _month > 12
|| _day < 1 || _day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
return false;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
Date::Date(int year, int month, int day)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
if (!CheckDate())
{
cout << "非法日期:";
Print();
}
}
// void Date::Print(const Date* const this)
void Date::Print() const
{
//++_year;
cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;
}
// d1 += 100
//+=可以改变d1,所以可以直接相加
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{
//如果天数小于0
if (day < 0)
{
return *this -= (-day);
}
//天数+天数
_day += day;
//当相加之后的天数大于当前月份的天数时进入循环
while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
//相加之后的天数减去当前月份的天数
_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
//月份++
++_month;
//当月份为13个月时
if (_month == 13)
{
//年++,月为1
_year++;
_month = 1;
}
}
return *this;
}
// d1 + 100
//+不能直接改变d1
Date Date::operator+(int day)
{
//所以可以使用拷贝构造来拷贝一份D1的值赋给tmp
Date tmp = *this;
//方法1:直接调用+=
tmp += day;
//方法2:原理和+=相同,只不过是多了一个tmp
/*tmp._day += day;
while (tmp._day > GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month))
{
tmp._day -= GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month);
++tmp._month;
if (tmp._month == 13)
{
tmp._year++;
tmp._month = 1;
}
}*/
return tmp;
}
//d1 - 100 日期-天数
Date Date::operator-(int day) const
{
//逻辑和+相同
Date tmp = *this;
tmp -= day;
return tmp;
}
//d1 -= 100 日期-=天数
Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{
if (day < 0)
{
return *this += (-day);
}
//天数-天数
_day -= day;
//当天数小于0时进入循环
while (_day <= 0)
{
//借上一个月的天数
--_month;
//如果月份借完了,为0
if (_month == 0)
{
//那么就借上一年的12月
_month = 12;
--_year;
}
//把从上个月借来的天数加上
_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
}
return *this;
}
//比较运算符***********************
//两个日期比较大小
//d1的参数为this指针,d1的参数为d
bool Date::operator<(const Date& d)const
{
//如果年小于年
if (_year < d._year)
{
return true;
}//当年等于年时进入
else if (_year == d._year)
{
//如果月小于月
if (_month < d._month)
{
return true;
}//当月等于月时进入
else if (_month == d._month)
{
//比较天数大小
return _day < d._day;
}
}
//大于则返回false
return false;
}
bool Date::operator==(const Date& d)const
{
return _year == d._year
&& _month == d._month
&& _day == d._day;
}
/*当同时实现了小于+等于 或者 大于+等于
就可以使用 复用 来实现其他的比较运算符*/
bool Date::operator<=(const Date& d) const
{
return *this < d || *this == d;
}
bool Date::operator>(const Date& d) const
{
return !(*this <= d);
}
bool Date::operator>=(const Date& d) const
{
return !(*this < d);
}
bool Date::operator!=(const Date& d)const
{
return !(*this == d);
}
//日期的前置++ 与 后置++
// d1++;
// d1.operator++(0);
Date Date::operator++(int)
{
Date tmp = *this;
*this += 1;
return tmp;
}
// ++d1;
// d1.operator++();
Date& Date::operator++()
{
*this += 1;
return *this;
}
//日期-日期
// d1 - d2
/*思路:先判断两个日期的大小,去小的那个日期,
然后一直小的日期的++天数,直到小的日期与大的日期相等为止*/
int Date::operator-(const Date& d) const
{
//假设第一个大第二个小,flag = 1
int flag = 1;
//d1=this d2=d
Date max = *this;
Date min = d;
//如果第一个小第二个大,flag = -1
if (*this < d)
{
max = d;
min = *this;
flag = -1;
}
//定义一个n统计min和max中间相差多少天数
int n = 0;
//不相等进入循环
while (min != max)
{
//前置++减少一点拷贝
++min;
//天数的差值
++n;
}
//天数的差值*flag
//当d1>d2,那么就为正数,d1<d2,则就为负数
return n * flag;
}
//二元流插入
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d)
{
out << d._year << "年" << d._month << "月" << d._day << "日" << endl;
return out;
}
//流插入
istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d)
{
while (1)
{
cout << "请依次输入年月日:>";
in >> d._year >> d._month >> d._day;
if (!d.CheckDate())
{
cout << "输入日期非法:";
d.Print();
cout << "请重新输入!!!" << endl;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
return in;
}Test.cpp
#include"Date.h"
void TestDate1()
{
Date d1(2024, 7, 12);
Date d2 = d1 + 100;
//Date d3(d1 + 100);
d1.Print();
d2.Print();
//d1 += 100;
//d1.Print();
d1 += 30000;
d1.Print();
}
void TestDate2()
{
/*Date d1(2024, 7, 13);
d1 -= 30000;
d1.Print();*/
Date d1(2024, 7, 13);
Date ret1 = d1++;
ret1.Print();
d1.Print();
Date d2(2024, 7, 13);
Date ret2 = ++d2;
ret2.Print();
d2.Print();
}
void TestDate3()
{
Date d1(2024, 7, 12);
d1 += -100;
d1.Print();
d1 -= -100;
d1.Print();
}
void TestDate4()
{
Date d1(2034, 10, 1);
Date d2(2024, 6, 31);
cout << d1 - d2 << endl;
}
void TestDate5()
{
Date d1, d2;
cin >> d1 >> d2;
cout << d1 << d2;
cout << d1 - d2 << endl;
//cout << d1;
//operator<<(cout, d1);
//cout << d1 << d2;
// 倒反天罡
//d1 << cout;
//d1.operator<<(cout);
}
void TestDate6()
{
const Date d1(2024, 7, 13);
d1.Print();
Date d2(2024, 7, 13);
d2.Print();
cout << &d1 << endl;
cout << &d2 << endl;
}
//int main()
//{
// TestDate6();
//
// return 0;
//}
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class A
{
public:
//explicit A(int a = 0)
A(int a = 0)
{
_a1 = a;
}
A(const A& aa)
{
_a1 = aa._a1;
}
A(int a1, int a2)
:_a1(a1)
, _a2(a2)
{}
void Print() {
cout << _a1 << " " << _a2 << endl;
}
private:
int _a1;
int _a2;
};
class Stack
{
public:
void Push(const A& aa)
{
//...
}
private:
A _arr[10];
int _top;
};
int main()
{
A aa1(1);
aa1.Print();
// 隐式类型转换
// 2构造一个A的临时对象,再用这个临时对象拷贝构造aa2
// 编译器遇到连续构造+拷贝构造->优化为直接构造
A aa2 = 2;
aa2.Print();
A& raa1 = aa2;
const A& raa2 = 2;
int i = 1;
double d = i;
const double& rd = i;
Stack st;
A aa3(3);
st.Push(aa3);
st.Push(3);
// C++11
A aa5 = { 1, 1 };
const A& raa6 = { 2,2 };
st.Push(aa5);
st.Push({ 2,2 });
return 0;
}感谢观看~