1 PWM 简介







2 F28335的ePWM介绍









2.1 时基模块TB


(1)时基模块的功能

(2)时基模块的关键信号和寄存器
给出时基模块内部结构图来了解里面的关键信号和寄存器,时基模块内部结构图如下所示:



(3)计算ePWM 周期和频率

1、向上-向下计数模式(先递增后递减)




2、向上计数模式(递增)
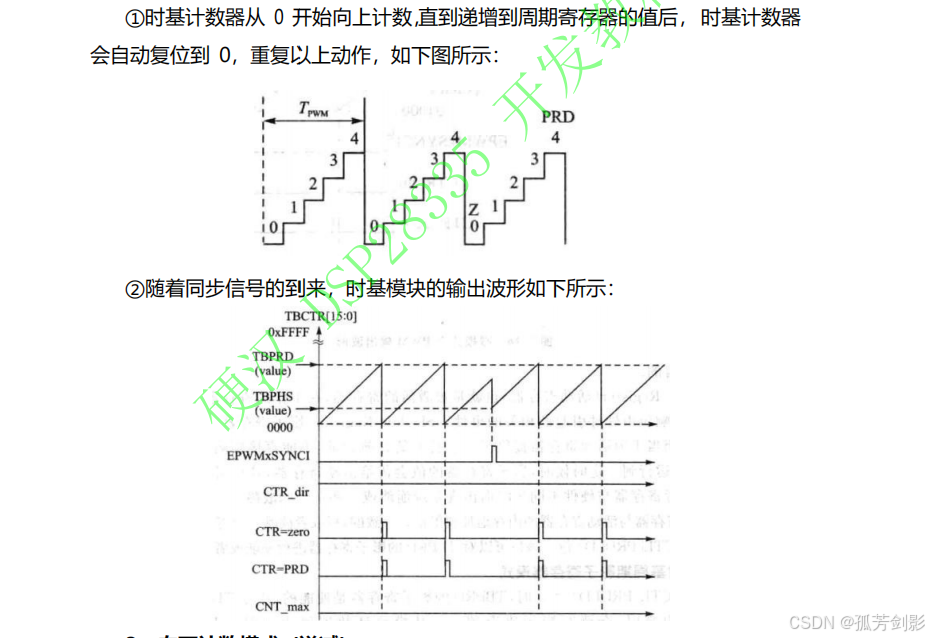
3、向下计数模式(递减)

(4)影子寄存器


2.2 计数比较模块CC


(1)计数器比较模块 CC 的功能

(2)计数器比较模块 CC 的关键信号与寄存器








2.3 动作限定模块AQ
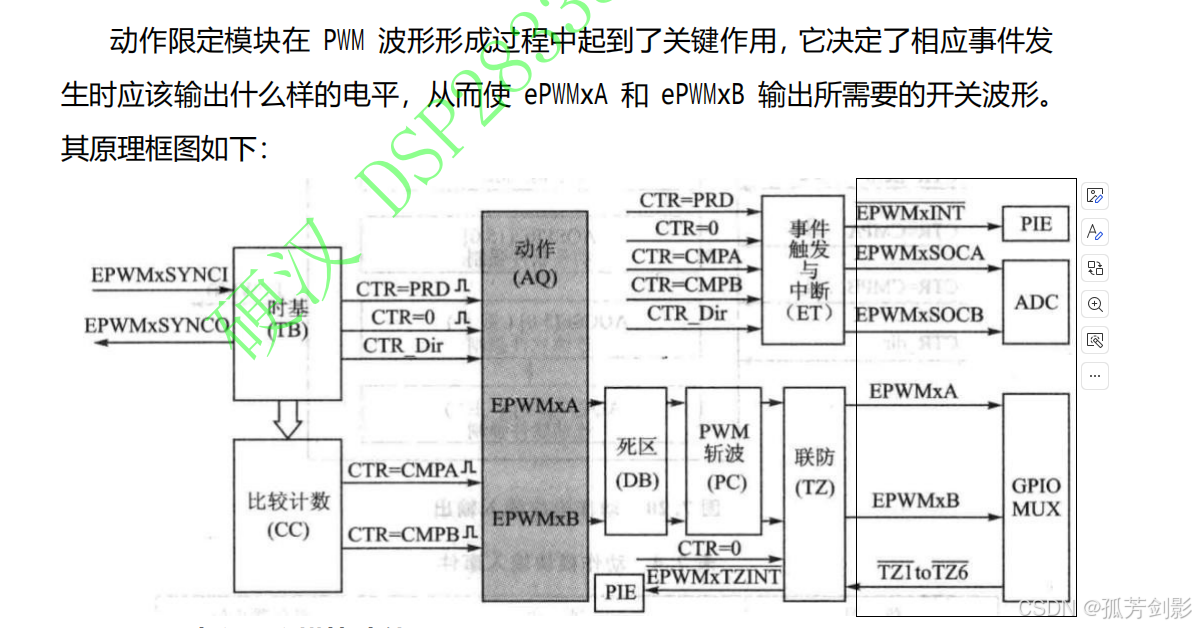
(1)动作限定模块功能

(2)动作限定模块关键信号与寄存器






(3) 动作限定模块事件优先级


最高同样是软件强制,最低是计数器等于周期寄存器的值匹配事件。
(4)动作限定模块一般配置条件下的输出波形


注意:
①PWM 周期=(TBPRD+1)*T(TBCLK)
②CMPA 决定 ePWMxA 的占空比,CMPB 决定 ePWMxB 占空比。
下面是该输出波形相关配置代码:
c
EPwm6Regs.TBPRD = tbprd;//设定 PWM 周期为 tbprd+1 个 TBCLK 时钟周期
EPwm6Regs.CMPA.half.CMPA = 350;//比较器 A 的值为 350
EPwm6Regs.CMPB = 200;//比较器 B 的值为 200
EPwm6Regs.TBPHS.half.TBPHS = 0;//相位寄存器清零
EPwm6Regs.TBCTR = 0x0000;//时基计数器清零
EPwm6Regs.TBCTL.bit.CTRMODE = TB_COUNT_UP;//设定为增计数模式
EPwm6Regs.TBCTL.bit.PHSEN = TB_DISABLE;//禁止相位控制
EPwm6Regs.TBCTL.bit.PRDLD = TB_SHADOW;//TBPRD 寄存器采用影子寄存器模式
EPwm1Regs.TBCTL.bit.SYNCOSEL = TB_SYNC_DISABLE;//禁止同步信号
EPwm6Regs.TBCTL.bit.HSPCLKDIV=TB_DIV1;//设定 TBCLK=SYSCLK 时基时钟=系统时钟
EPwm6Regs.TBCTL.bit.CLKDIV=TB_DIV1;
EPwm6Regs.CMPCTL.bit.SHDWAMODE = CC_SHADOW;//设定 CMPA 为影子寄存器 模式
EPwm6Regs.CMPCTL.bit.SHDWBMODE = CC_SHADOW;
EPwm6Regs.CMPCTL.bit.LOADAMODE = CC_CTR_ZERO;//在 CTR=Zero 时装载
EPwm6Regs.CMPCTL.bit.LOADBMODE = CC_CTR_ZERO;
EPwm6Regs.AQCTLA.bit.ZRO = AQ_SET;//CTR=ZERO 时,将 ePWM6A 置高
EPwm6Regs.AQCTLA.bit.CAU = AQ_CLEAR;//CTR=CAU 时,将 ePWM6A 置低
EPwm6Regs.AQCTLB.bit.ZRO = AQ_SET;//CTR=ZERO 时,将 ePWM6B 置高
EPwm6Regs.AQCTLB.bit.CBU = AQ_CLEAR;//CTR=CAU 时,将 ePWM6B 置低
EPwm6Regs.CMPA.half.CMPA = Duty1A;//调整 ePWM6A 的占空比
EPwm6Regs.CMPB = Duty1B;//调整 ePWM6B 的占空比








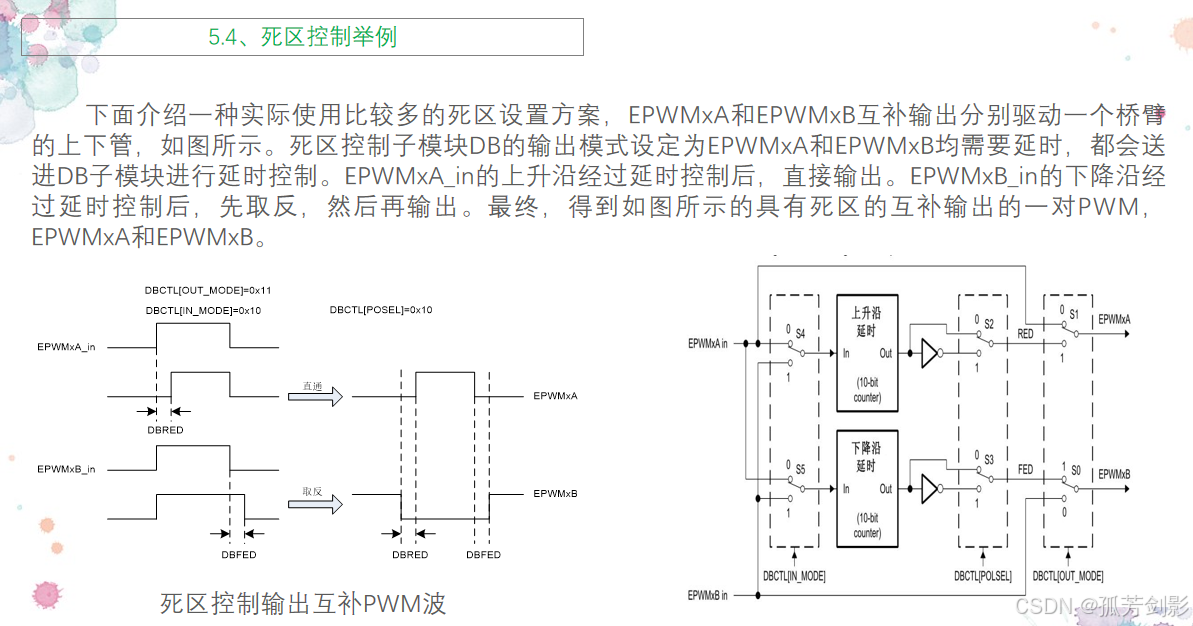
2.4 死区控制模块DB
ePWM中的死区控制子模块DB就是用来严格地控制死区产生的边沿和极性。死区控制子模块在整个ePWM模块中的位置如图所示。

(1)为什么要产生死区



(2)死区控制模块的作用
F28335 的死区模块主要作用就是让两个互补的对称的 PWM 波形中,上升沿的

(3)死区控制模块的特点




(4)举例
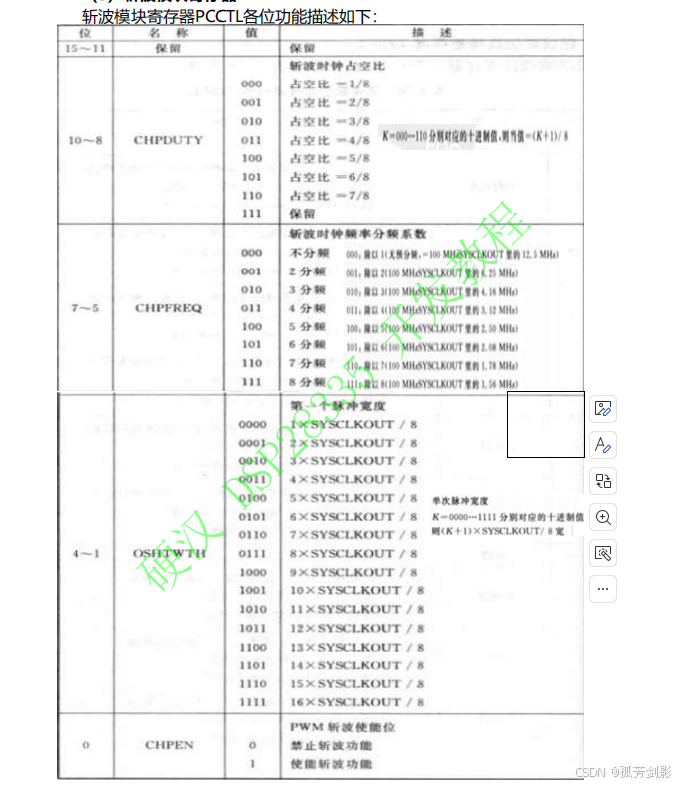
2.5 PWM 斩波模块PC
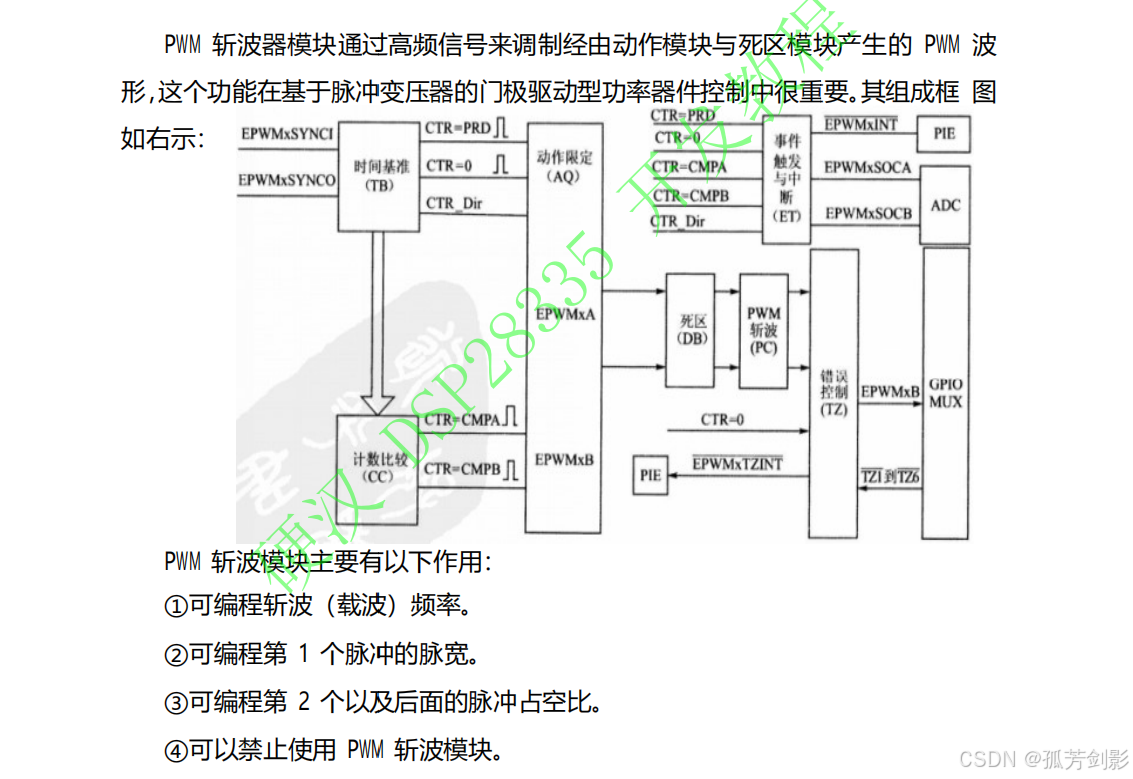
在使用ePWM模块的过程中如果无须用到此功能,可通过相关寄存器完全屏蔽该子模块,从而使PWM 脉冲直接通过。
(1)PWM 斩波模块的特点
如果信号不需要通过斩波控制子模块而直接输出,只需将PCCTL[CHPEN]置0就可以。若将PCCTL[CHPEN]置1,则斩波功能使能,PWM信号将经过高频载波信号调制后再输出。



(2)单次脉冲
原先PWM高电平的地方变成了高频载波信号,把每一个周期内的第一个载波脉冲称为首次脉冲(one shot)。首次脉冲的宽度是可编程的,可以使得第一个脉冲携带较大的能量,从而保证功率器件能够可靠开通,而其余脉冲用来维持功率器件的持续开通与关断。



2.6 错误联防模块 TZ
每个 ePWM 模块都与 GPIO 多路复用引脚中的 6 个 TZn(TZ1-TZ6)信号脚连接。
这些信号脚用来响应外部错误或外部触发条件,当错误发生时,PWM 模块可以通 过
编程来响应这些问题。错误联防模块的位置如下图所示:

(1)错误联防模块的主要作用如下:

(2)故障捕获子模块内部逻辑图
通过选择寄存器TZSEL,每个ePWM模块都可以使用或者忽略6路故障触发信号中的任何一路,如果某个ePWM不使用故障保护的功能,也就是忽略了所有的故障触发信号,那么这个ePWM模块的PWM信号不受故障保护,将直接输出。如果为某个ePWM模块选择了故障触发信号输入引脚,该引脚平时是高电平状态,如果通过电路的设计,外部一旦出现故障,将该故障触发信号输入引脚的电平置为低电平,则故障捕获子模块捕获到故障信号,然后根据控制寄存器TZCTL的设置来完成相应的动作,可以将相应的EPWMxA引脚和EPWMxB引脚强制为低电平、高电平或者高阻态输出。
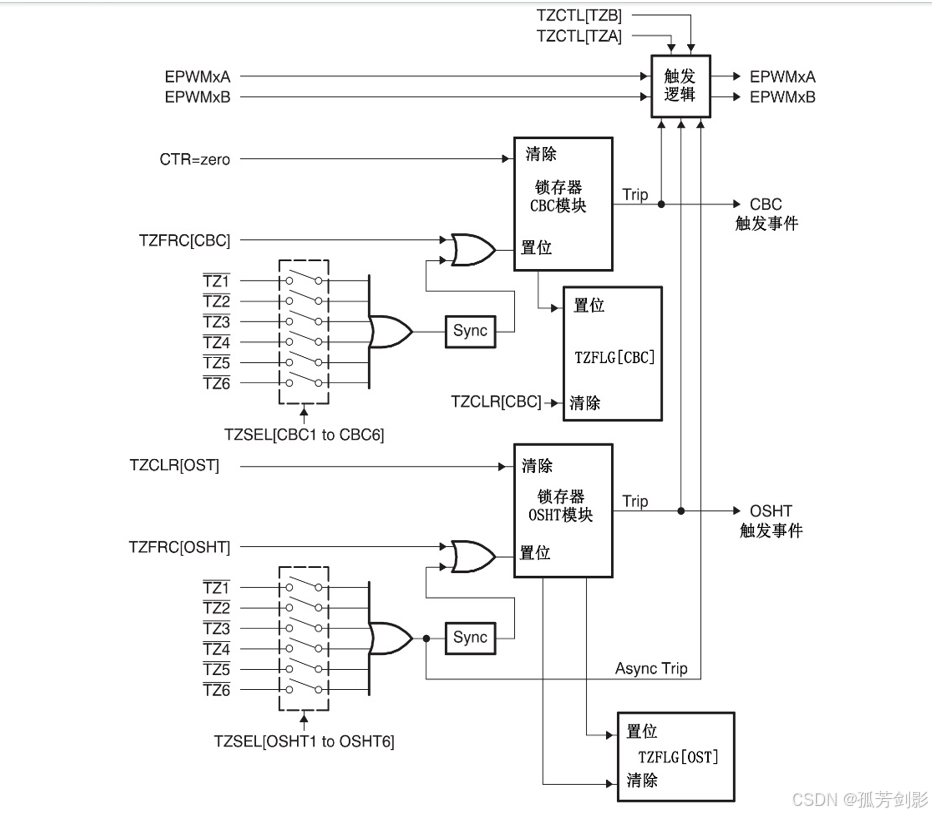
(3)错误联防模块的操作




2.7 事件触发模块
事件触发子模块(ET)用来处理时间基准计数器、比较功能子模块所产生的事件,从而向CPU发出中断请求或产生ADC启动信号SOCA或SOCB。










2.8 PWM模块相关寄存器
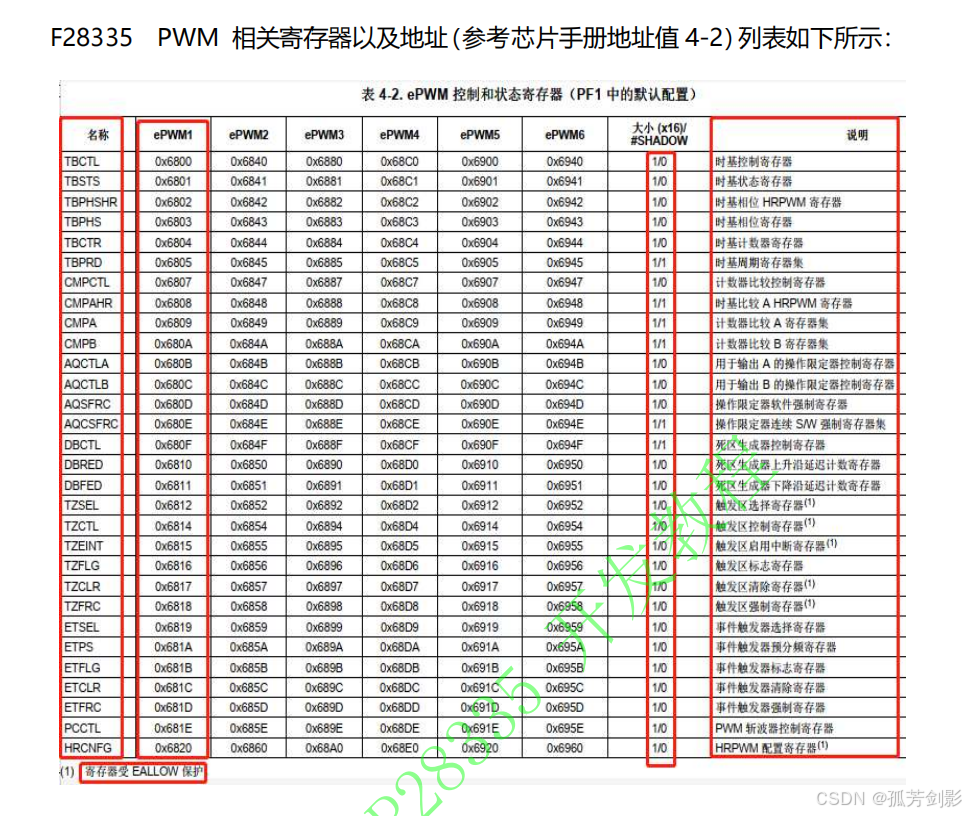
(1)时基模块相关寄存器




(2)计数比较模块寄存器


(3)动作模块寄存器





(4)死区模块寄存器


(5)斩波模块寄存器
(6)错误联防模块寄存器





(7)事件触发模块寄存器





3 PWM 输出配置步骤
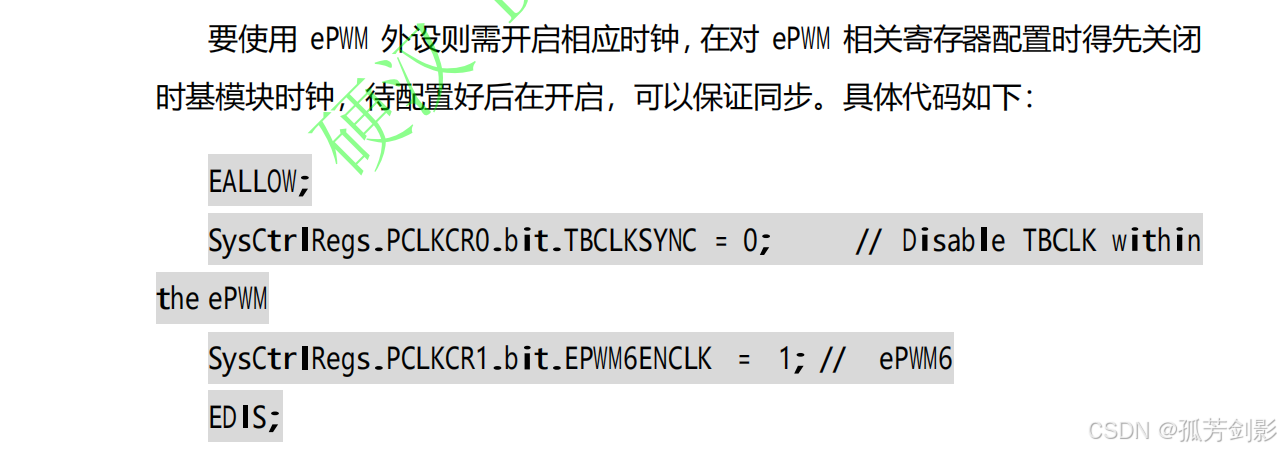
(1)使能 ePWM 外设时钟及使能时基模块时钟
(2)开启 ePWM 对应 GPIO 时钟及初始化配置
由于 PWM 输出通道是对应着 F28335 芯片的 IO 口,所以需要使能对应的端口 时钟,并将对应 IO 口配置为 ePWM 输出功能。初始化 ePWM GPIO 的函数 TI已经提供给我们了,直接调用即可。本章使用的是 ePWM6,调用的函数如下:
c
InitEPwm6Gpio();
//其内部具体实现代码如下:
void InitEPwm6Gpio(void)
{
EALLOW;
/* Enable internal pull-up for the selected pins */
// Pull-ups can be enabled or disabled by the user.
// This will enable the pullups for the specified pins.
// Comment out other unwanted lines. GpioCtrlRegs.GPAPUD.bit.GPIO10 = 0; // Enable pull-up on
GPIO10 (EPWM6A)
GpioCtrlRegs.GPAPUD.bit.GPIO11 = 0; // Enable pull-up on
GPIO11 (EPWM6B)
/* Configure ePWM-6 pins using GPIO regs*/
// This specifies which of the possible GPIO pins will be ePWM6 functional pins.
// Comment out other unwanted lines. EPWM6A
EPWM6B
GpioCtrlRegs.GPAMUX1.bit.GPIO10 = 1; // Configure GPIO10
as
GpioCtrlRegs.GPAMUX1.bit.GPIO11 = 1; // Configure GPIO11
as
EDIS;
}我们是使用 GPIO10、GPIO11 的 ePWM6A 和 ePWM6B 功能,即对这两个 IO 口初始化,使能上拉和 GPIO 外设复用功能。
(3)初始化时基模块,即配置 TB 相关寄存器值
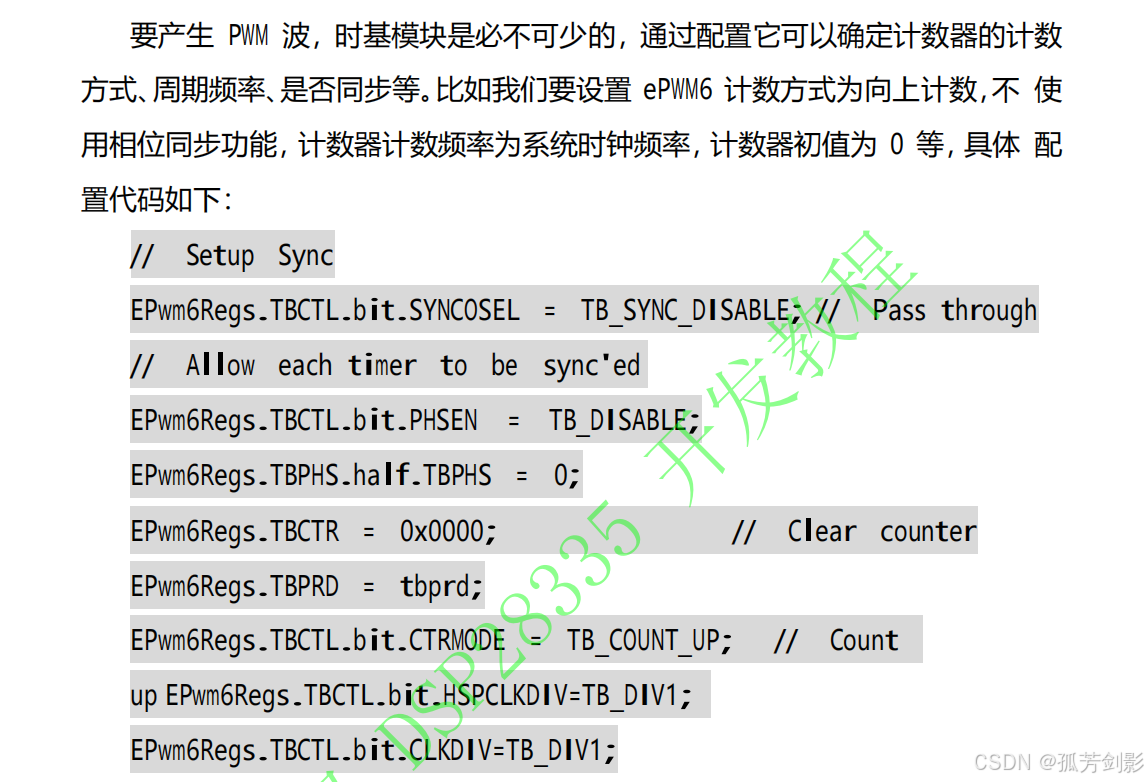
(4)初始化比较模块,即配置 CC 相关寄存器值

(5)初始化动作限定模块,即配置 AQ 相关寄存器值
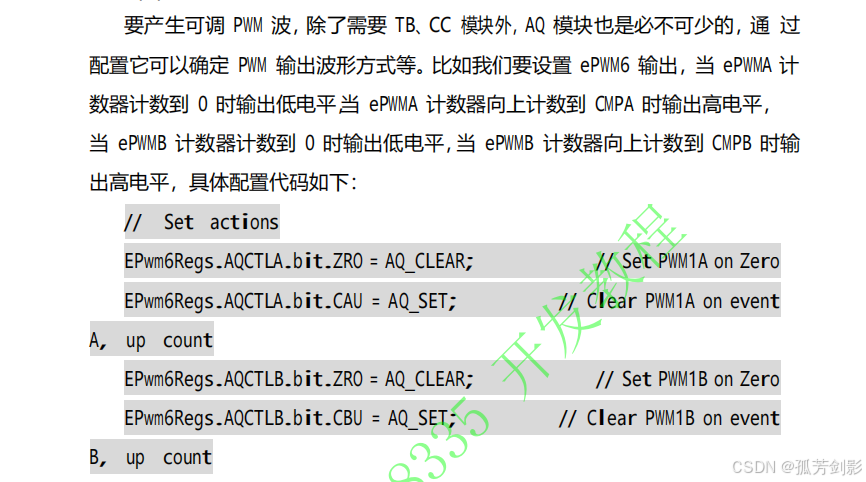
(6)初始化事件触发模块,即配置 ET 相关寄存器值
当需要事件触发输出控制,就需要对 ET 相关寄存器配置。比如计数器计数 到 0 时,同时使能事件触发中断,每发生一次触发事件就输出 PWM。相关配置代 码如下:
c
EPwm6Regs.ETSEL.bit.INTSEL = ET_CTR_ZERO; // Select INT on Zero event
EPwm6Regs.ETSEL.bit.INTEN = 1; // Enable INT
EPwm6Regs.ETPS.bit.INTPRD = ET_1ST; // Generate INT on 1stevent(7)初始化死区模块、斩波模块,即配置 DB、PC 相关寄存器值
如果不是特殊应用的话,一般不对死区模块和斩波模块配置,它们的应用方
法在前面各小节也介绍过,所以这里我们不作介绍。
(8)使能时基计数器时钟
将各模块寄存器配置好后,最后开启时基计数器时钟,完成这步操作,对应的IO口即可输出PWM波。开启时基计数器时钟如下:
c
EALLOW;
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR0.bit.TBCLKSYNC = 1; // Start all the
timers synced
EDIS;这里列举的是 ePWM6 的配置,至于其他 ePWM 配置都是一样,只需修改对应
的数字即可。里面涉及到的相关寄存器在前面已做介绍,大家可以用到哪个就查
询哪个,不需要死记硬背。
4 软件设计

4.1 ePWM6 初始化函数
要使用 F28335 的 ePWM6 输出功能,我们必须先对它进行配置。Epwm6 初始化
代码如下:
c
void EPWM6_Init(Uint16 tbprd)
{
EALLOW;
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR0.bit.TBCLKSYNC = 0; // Disable TBCLK within
the ePWM
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR1.bit.EPWM6ENCLK = 1; // ePWM6
EDIS;
InitEPwm6Gpio();
// Setup Sync
EPwm6Regs.TBCTL.bit.SYNCOSEL = TB_SYNC_DISABLE; // Pass through
// Allow each timer to be sync'ed
EPwm6Regs.TBCTL.bit.PHSEN = TB_DISABLE;
EPwm6Regs.TBPHS.half.TBPHS = 0;
EPwm6Regs.TBCTR = 0x0000; // Clear counter
EPwm6Regs.TBPRD = tbprd;
EPwm6Regs.TBCTL.bit.CTRMODE = TB_COUNT_UP; // Count up
EPwm6Regs.TBCTL.bit.HSPCLKDIV=TB_DIV1;
EPwm6Regs.TBCTL.bit.CLKDIV=TB_DIV1;
// Setup shadow register load on ZERO
EPwm6Regs.CMPCTL.bit.SHDWAMODE = CC_SHADOW;
EPwm6Regs.CMPCTL.bit.SHDWBMODE = CC_SHADOW;
EPwm6Regs.CMPCTL.bit.LOADAMODE = CC_CTR_ZERO;
EPwm6Regs.CMPCTL.bit.LOADBMODE = CC_CTR_ZERO;
// Set Compare values
EPwm6Regs.CMPA.half.CMPA = 0; // Set compare A value
EPwm6Regs.CMPB = 0; // Set Compare B value Zero
// Set actions
EPwm6Regs.AQCTLA.bit.ZRO = AQ_CLEAR; // Set PWM1A on
EPwm6Regs.AQCTLA.bit.CAU = AQ_SET; // Clear PWM1A on event A, up count
EPwm6Regs.AQCTLB.bit.ZRO = AQ_CLEAR; // Set PWM1B on Zero
EPwm6Regs.AQCTLB.bit.CBU = AQ_SET; // Clear PWM1B on event B, up count
EPwm6Regs.ETSEL.bit.INTSEL = ET_CTR_ZERO; // Select INT on Zero event
EPwm6Regs.ETSEL.bit.INTEN = 1; // Enable INT
EPwm6Regs.ETPS.bit.INTPRD = ET_1ST; // Generate INT on 1st event
EALLOW;
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR0.bit.TBCLKSYNC = 1; // Start all the
timers synced
EDIS;
}该函数实现了对 ePWM6 的初始化配置,内部实现过程是按照上一节介绍 ePWM
操作步骤完成,函数的入口带有一个参数 tbprd,通过该参数可修改 ePWM 的频
率。
4.2 主函数
编写好 PWM 初始化函数后,接下来就可以编写主函数了,代码如下:
c
#include "DSP2833x_Device.h" // DSP2833x Headerfile Include File
#include "DSP2833x_Examples.h" // DSP2833x Examples Include File
#include "leds.h" #include "time.h" #include "epwm.h"
/****************************************************************
***************
* 函 数 名 : main
* 函数功能 : 主函数
* 输 入 : 无
* 输 出 : 无
*****************************************************************
**************/
void main()
{
int i=0;
unsigned char fx=0;
InitSysCtrl();
InitPieCtrl();
IER = 0x0000;
IFR = 0x0000;
InitPieVectTable();
// LED_Init();
EPWM6_Init(500);
while(1)
{
if(fx==0)
{
i++;
if(i==300)
{
fx=1;
}
}
else
{
i--;
if(i==0)
{
fx=0;
}
}
EPwm6A_SetCompare(i); //i 值最大可以取 499,因为 ARR 最大值是 499.
EPwm6B_SetCompare(300-i); //i 值最大可以取 499,因为 ARR 大值是499.
DELAY_US(10*1000);
}
}主函数实现的功能很简单,首先初始化系统时钟、PIE 中断相关寄存器及中 断
向量表,本套教程所有有关中断代码都采用这种设置,后面就不做重复。再对 使用
到的硬件端口时钟和 IO 口初始化,然后调用我们前面编写的 ePWM6 的初始 化
函数,这里我们设定时基周期寄存器值为 500,计数器计数频率和系统时钟频 率
一致,定时周期即为 3.3us,频率即为 303KHz。最后进入 while 循环语句,
ePWM 开始工作,GPIO10、GPIO11 开始输出 PWM 波形,波形频率约为 303K,你 也
可以修改这个频率值,但是要注意,不能将频率设置过大,否则会看到波形占空比
不明显。通过变量 fx 控制 i 的方向,如果 fx=0,i 值累加, 否则递减,
然后将这个变化的 i 值传递给 EPwm6A_SetCompare 和EPwm6B_SetCompare 函数,
这

5 实验
(1)定时器中断


c
//###########################################################################
//
// FILE: Example_2833xEPwmTimerInt.c
//
// TITLE: DSP2833x ePWM Timer Interrupt example.
//
// ASSUMPTIONS:
//
// This program requires the DSP2833x header files.
//
// Other then boot mode configuration, no other hardware configuration
// is required.
//
// 根据在RAM中调试的需要,这个项目配置成"boot to SARAM".2833x引导模式
// 表如下显示. 常用的还有"boot to Flash"模式,当程序在RAM调试完善后就
// 可以将代码烧进Flash中并使用"boot to Flash"引导模式.
//
// $Boot_Table:
//
// GPIO87 GPIO86 GPIO85 GPIO84
// XA15 XA14 XA13 XA12
// PU PU PU PU
// ==========================================
// 1 1 1 1 Jump to Flash
// 1 1 1 0 SCI-A boot
// 1 1 0 1 SPI-A boot
// 1 1 0 0 I2C-A boot
// 1 0 1 1 eCAN-A boot
// 1 0 1 0 McBSP-A boot
// 1 0 0 1 Jump to XINTF x16
// 1 0 0 0 Jump to XINTF x32
// 0 1 1 1 Jump to OTP
// 0 1 1 0 Parallel GPIO I/O boot
// 0 1 0 1 Parallel XINTF boot
// 0 1 0 0 Jump to SARAM <- "boot to SARAM"
// 0 0 1 1 Branch to check boot mode
// 0 0 1 0 Boot to flash, bypass ADC cal
// 0 0 0 1 Boot to SARAM, bypass ADC cal
// 0 0 0 0 Boot to SCI-A, bypass ADC cal
// Boot_Table_End$
//
// 功能描述
//
// 本例配置ePWM定时器并且每次中断时相应计数变量增加一次
//
// 应用如下:
//
// 所有的ePWM都被初始化.注意28335有6个ePWM,但并不是所有的2833x系列
// 都有6个ePWM
//
// 所有的定时器都有相等的定时周期,所有的定时器同步
// 对于每个ePWM定时器遇到计数0匹配事件时都发生以下响应:
//
// ePWM1: 每1次0匹配事件发生一次中断
// ePWM2: 每2次0匹配事件发生一次中断
// ePWM3: 每3次0匹配事件发生一次中断
// ePWM4-ePWM6: 每1次0匹配事件发生一次中断
//
// Thus the Interrupt count for ePWM1, ePWM4-ePWM6 should be equal
// The interrupt count for ePWM2 should be about half that of ePWM1
// and the interrupt count for ePWM3 should be about 1/3 that of ePWM1
//
// Watch Variables:
// EPwm1TimerIntCount
// EPwm2TimerIntCount
// EPwm3TimerIntCount
// EPwm4TimerIntCount
// EPwm5TimerIntCount
// EPwm6TimerIntCount
#include "DSP2833x_Device.h" // DSP2833x Headerfile Include File
#include "DSP2833x_Examples.h" // DSP2833x Examples Include File
// Configure which ePWM timer interrupts are enabled at the PIE level:
// 1 = enabled, 0 = disabled
#define PWM1_INT_ENABLE 1
#define PWM2_INT_ENABLE 1
#define PWM3_INT_ENABLE 1
#define PWM4_INT_ENABLE 1
#define PWM5_INT_ENABLE 1
#define PWM6_INT_ENABLE 1
// Configure the period for each timer
#define PWM1_TIMER_TBPRD 0x1FFF
#define PWM2_TIMER_TBPRD 0x1FFF
#define PWM3_TIMER_TBPRD 0x1FFF
#define PWM4_TIMER_TBPRD 0x1FFF
#define PWM5_TIMER_TBPRD 0x1FFF
#define PWM6_TIMER_TBPRD 0x1FFF
// Prototype statements for functions found within this file.
interrupt void epwm1_timer_isr(void);
interrupt void epwm2_timer_isr(void);
interrupt void epwm3_timer_isr(void);
interrupt void epwm4_timer_isr(void);
interrupt void epwm5_timer_isr(void);
interrupt void epwm6_timer_isr(void);
void InitEPwmTimer(void);
// Global variables used in this example
Uint32 EPwm1TimerIntCount;
Uint32 EPwm2TimerIntCount;
Uint32 EPwm3TimerIntCount;
Uint32 EPwm4TimerIntCount;
Uint32 EPwm5TimerIntCount;
Uint32 EPwm6TimerIntCount;
void main(void)
{
int i;
// Step 1. Initialize System Control:
// PLL, WatchDog, enable Peripheral Clocks
// This example function is found in the DSP2833x_SysCtrl.c file.
InitSysCtrl();
// Step 2. Initalize GPIO:
// This example function is found in the DSP2833x_Gpio.c file and
// illustrates how to set the GPIO to it's default state.
// InitGpio(); // Skipped for this example
// Step 3. Clear all interrupts and initialize PIE vector table:
// Disable CPU interrupts
DINT;
// Initialize the PIE control registers to their default state.
// The default state is all PIE interrupts disabled and flags
// are cleared.
// This function is found in the DSP2833x_PieCtrl.c file.
InitPieCtrl();
// Disable CPU interrupts and clear all CPU interrupt flags:
IER = 0x0000;
IFR = 0x0000;
// Initialize the PIE vector table with pointers to the shell Interrupt
// Service Routines (ISR).
// This will populate the entire table, even if the interrupt
// is not used in this example. This is useful for debug purposes.
// The shell ISR routines are found in DSP2833x_DefaultIsr.c.
// This function is found in DSP2833x_PieVect.c.
InitPieVectTable();
// Interrupts that are used in this example are re-mapped to
// ISR functions found within this file.
EALLOW; // This is needed to write to EALLOW protected registers
PieVectTable.EPWM1_INT = &epwm1_timer_isr;
PieVectTable.EPWM2_INT = &epwm2_timer_isr;
PieVectTable.EPWM3_INT = &epwm3_timer_isr;
PieVectTable.EPWM4_INT = &epwm4_timer_isr;
PieVectTable.EPWM5_INT = &epwm5_timer_isr;
PieVectTable.EPWM6_INT = &epwm6_timer_isr;
EDIS; // This is needed to disable write to EALLOW protected registers
// Step 4. Initialize all the Device Peripherals:
// This function is found in DSP2833x_InitPeripherals.c
// InitPeripherals(); // Not required for this example
InitEPwmTimer(); // For this example, only initialize the ePWM Timers
// Step 5. User specific code, enable interrupts:
// Initalize counters:
EPwm1TimerIntCount = 0;
EPwm2TimerIntCount = 0;
EPwm3TimerIntCount = 0;
EPwm4TimerIntCount = 0;
EPwm5TimerIntCount = 0;
EPwm6TimerIntCount = 0;
// Enable CPU INT3 which is connected to EPWM1-6 INT:
IER |= M_INT3;
// Enable EPWM INTn in the PIE: Group 3 interrupt 1-6
PieCtrlRegs.PIEIER3.bit.INTx1 = PWM1_INT_ENABLE;
PieCtrlRegs.PIEIER3.bit.INTx2 = PWM2_INT_ENABLE;
PieCtrlRegs.PIEIER3.bit.INTx3 = PWM3_INT_ENABLE;
PieCtrlRegs.PIEIER3.bit.INTx4 = PWM4_INT_ENABLE;
PieCtrlRegs.PIEIER3.bit.INTx5 = PWM5_INT_ENABLE;
PieCtrlRegs.PIEIER3.bit.INTx6 = PWM6_INT_ENABLE;
// Enable global Interrupts and higher priority real-time debug events:
EINT; // Enable Global interrupt INTM
ERTM; // Enable Global realtime interrupt DBGM
// Step 6. IDLE loop. Just sit and loop forever (optional):
for(;;)
{
asm(" NOP");
for(i=1;i<=10;i++)
{}
}
}
void InitEPwmTimer()
{
EALLOW;
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR0.bit.TBCLKSYNC = 0; // Stop all the TB clocks
EDIS;
// Setup Sync
EPwm1Regs.TBCTL.bit.SYNCOSEL = TB_SYNC_IN; // Pass through
EPwm2Regs.TBCTL.bit.SYNCOSEL = TB_SYNC_IN; // Pass through
EPwm3Regs.TBCTL.bit.SYNCOSEL = TB_SYNC_IN; // Pass through
EPwm4Regs.TBCTL.bit.SYNCOSEL = TB_SYNC_IN; // Pass through
EPwm5Regs.TBCTL.bit.SYNCOSEL = TB_SYNC_IN; // Pass through
EPwm6Regs.TBCTL.bit.SYNCOSEL = TB_SYNC_IN; // Pass through
// Allow each timer to be sync'ed
EPwm1Regs.TBCTL.bit.PHSEN = TB_ENABLE;
EPwm2Regs.TBCTL.bit.PHSEN = TB_ENABLE;
EPwm3Regs.TBCTL.bit.PHSEN = TB_ENABLE;
EPwm4Regs.TBCTL.bit.PHSEN = TB_ENABLE;
EPwm5Regs.TBCTL.bit.PHSEN = TB_ENABLE;
EPwm6Regs.TBCTL.bit.PHSEN = TB_ENABLE;
EPwm1Regs.TBPHS.half.TBPHS = 100;
EPwm2Regs.TBPHS.half.TBPHS = 200;
EPwm3Regs.TBPHS.half.TBPHS = 300;
EPwm4Regs.TBPHS.half.TBPHS = 400;
EPwm5Regs.TBPHS.half.TBPHS = 500;
EPwm6Regs.TBPHS.half.TBPHS = 600;
EPwm1Regs.TBPRD = PWM1_TIMER_TBPRD;
EPwm1Regs.TBCTL.bit.CTRMODE = TB_COUNT_UP; // Count up
EPwm1Regs.ETSEL.bit.INTSEL = ET_CTR_ZERO; // Select INT on Zero event
EPwm1Regs.ETSEL.bit.INTEN = PWM1_INT_ENABLE; // Enable INT
EPwm1Regs.ETPS.bit.INTPRD = ET_1ST; // Generate INT on 1st event
EPwm2Regs.TBPRD = PWM2_TIMER_TBPRD;
EPwm2Regs.TBCTL.bit.CTRMODE = TB_COUNT_UP; // Count up
EPwm2Regs.ETSEL.bit.INTSEL = ET_CTR_ZERO; // Enable INT on Zero event
EPwm2Regs.ETSEL.bit.INTEN = PWM2_INT_ENABLE; // Enable INT
EPwm2Regs.ETPS.bit.INTPRD = ET_2ND; // Generate INT on 2nd event
EPwm3Regs.TBPRD = PWM3_TIMER_TBPRD;
EPwm3Regs.TBCTL.bit.CTRMODE = TB_COUNT_UP; // Count up
EPwm3Regs.ETSEL.bit.INTSEL = ET_CTR_ZERO; // Enable INT on Zero event
EPwm3Regs.ETSEL.bit.INTEN = PWM3_INT_ENABLE; // Enable INT
EPwm3Regs.ETPS.bit.INTPRD = ET_3RD; // Generate INT on 3rd event
EPwm4Regs.TBPRD = PWM4_TIMER_TBPRD;
EPwm4Regs.TBCTL.bit.CTRMODE = TB_COUNT_UP; // Count up
EPwm4Regs.ETSEL.bit.INTSEL = ET_CTR_ZERO; // Enable INT on Zero event
EPwm4Regs.ETSEL.bit.INTEN = PWM4_INT_ENABLE; // Enable INT
EPwm4Regs.ETPS.bit.INTPRD = ET_1ST; // Generate INT on 1st event
EPwm5Regs.TBPRD = PWM5_TIMER_TBPRD;
EPwm5Regs.TBCTL.bit.CTRMODE= TB_COUNT_UP; // Count up
EPwm5Regs.ETSEL.bit.INTSEL = ET_CTR_ZERO; // Enable INT on Zero event
EPwm5Regs.ETSEL.bit.INTEN = PWM5_INT_ENABLE; // Enable INT
EPwm5Regs.ETPS.bit.INTPRD = ET_1ST; // Generate INT on 1st event
EPwm6Regs.TBPRD = PWM6_TIMER_TBPRD;
EPwm6Regs.TBCTL.bit.CTRMODE = TB_COUNT_UP; // Count up
EPwm6Regs.ETSEL.bit.INTSEL = ET_CTR_ZERO; // Enable INT on Zero event
EPwm6Regs.ETSEL.bit.INTEN = PWM6_INT_ENABLE; // Enable INT
EPwm6Regs.ETPS.bit.INTPRD = ET_1ST; // Generate INT on 1st event
EALLOW;
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR0.bit.TBCLKSYNC = 1; // Start all the timers synced
EDIS;
}
// Interrupt routines uses in this example:
interrupt void epwm1_timer_isr(void)
{
EPwm1TimerIntCount++;
// Clear INT flag for this timer
EPwm1Regs.ETCLR.bit.INT = 1;
// Acknowledge this interrupt to receive more interrupts from group 3
PieCtrlRegs.PIEACK.all = PIEACK_GROUP3;
}
interrupt void epwm2_timer_isr(void)
{
EPwm2TimerIntCount++;
// Clear INT flag for this timer
EPwm2Regs.ETCLR.bit.INT = 1;
// Acknowledge this interrupt to receive more interrupts from group 3
PieCtrlRegs.PIEACK.all = PIEACK_GROUP3;
}
interrupt void epwm3_timer_isr(void)
{
EPwm3TimerIntCount++;
// Clear INT flag for this timer
EPwm3Regs.ETCLR.bit.INT = 1;
// Acknowledge this interrupt to receive more interrupts from group 3
PieCtrlRegs.PIEACK.all = PIEACK_GROUP3;
}
interrupt void epwm4_timer_isr(void)
{
EPwm4TimerIntCount++;
// Clear INT flag for this timer
EPwm4Regs.ETCLR.bit.INT = 1;
// Acknowledge this interrupt to receive more interrupts from group 3
PieCtrlRegs.PIEACK.all = PIEACK_GROUP3;
}
interrupt void epwm5_timer_isr(void)
{
EPwm5TimerIntCount++;
// Clear INT flag for this timer
EPwm5Regs.ETCLR.bit.INT = 1;
// Acknowledge this interrupt to receive more interrupts from group 3
PieCtrlRegs.PIEACK.all = PIEACK_GROUP3;
}
interrupt void epwm6_timer_isr(void)
{
EPwm6TimerIntCount++;
// Clear INT flag for this timer
EPwm6Regs.ETCLR.bit.INT = 1;
// Acknowledge this interrupt to receive more interrupts from group 3
PieCtrlRegs.PIEACK.all = PIEACK_GROUP3;
}
//===========================================================================
// No more.
//===========================================================================(2)动作限定模块增计数占空比模式



c
//###########################################################################
//
// 文件: Example_2833xEPwm3UpAQ.c
//
// 标题: 动作限定模块增计数模式
//
// ASSUMPTIONS:
//
// 此程序需要 DSP2833x头文件.
//
// 按以下描述用示波器观察 ePWM1 - ePWM3引脚
//
// EPWM1A定义在GPIO0上
// EPWM1B定义在GPIO1上
//
// EPWM2A定义在GPIO2上
// EPWM2B定义在GPIO3上
//
// EPWM3A定义在GPIO4上
// EPWM3B定义在GPIO5上
//
// 根据在RAM中调试的需要,这个项目配置成"boot to SARAM".2833x引导模式
// 表如下显示. 常用的还有"boot to Flash"模式,当程序在RAM调试完善后就
// 可以将代码烧进Flash中并使用"boot to Flash"引导模式.
//
// $Boot_Table:
//
// GPIO87 GPIO86 GPIO85 GPIO84
// XA15 XA14 XA13 XA12
// PU PU PU PU
// ==========================================
// 1 1 1 1 Jump to Flash
// 1 1 1 0 SCI-A boot
// 1 1 0 1 SPI-A boot
// 1 1 0 0 I2C-A boot
// 1 0 1 1 eCAN-A boot
// 1 0 1 0 McBSP-A boot
// 1 0 0 1 Jump to XINTF x16
// 1 0 0 0 Jump to XINTF x32
// 0 1 1 1 Jump to OTP
// 0 1 1 0 Parallel GPIO I/O boot
// 0 1 0 1 Parallel XINTF boot
// 0 1 0 0 Jump to SARAM <- "boot to SARAM"
// 0 0 1 1 Branch to check boot mode
// 0 0 1 0 Boot to flash, bypass ADC cal
// 0 0 0 1 Boot to SARAM, bypass ADC cal
// 0 0 0 0 Boot to SCI-A, bypass ADC cal
// Boot_Table_End$
//
// 描述:
//
// 本例配置ePWM1, ePWM2, ePWM3产生产生EPWMxA和EPWMxB波形
//
// 在ePWM中断子程序中,比较寄存器CMPA和CMPB的值被修改
//
// 本例时基时钟被配置为增计数模式
// 通过示波器观察EPWM1A/B, EPWM2A/B 和 EPWM3A/B波形
//
//###########################################################################
// 释放日期:2013.11.26
//###########################################################################
#include "DSP2833x_Device.h" // DSP2833x Headerfile Include File
#include "DSP2833x_Examples.h" // DSP2833x Examples Include File
typedef struct
{
volatile struct EPWM_REGS *EPwmRegHandle;
Uint16 EPwm_CMPA_Direction;
Uint16 EPwm_CMPB_Direction;
Uint16 EPwmTimerIntCount;
Uint16 EPwmMaxCMPA;
Uint16 EPwmMinCMPA;
Uint16 EPwmMaxCMPB;
Uint16 EPwmMinCMPB;
}EPWM_INFO;
// Prototype statements for functions found within this file.
void InitEPwm1Example(void);
void InitEPwm2Example(void);
void InitEPwm3Example(void);
interrupt void epwm1_isr(void);
interrupt void epwm2_isr(void);
interrupt void epwm3_isr(void);
void update_compare(EPWM_INFO*);
// Global variables used in this example
EPWM_INFO epwm1_info;
EPWM_INFO epwm2_info;
EPWM_INFO epwm3_info;
// Configure the period for each timer
#define EPWM1_TIMER_TBPRD 2000 // Period register
#define EPWM1_MAX_CMPA 1950
#define EPWM1_MIN_CMPA 50
#define EPWM1_MAX_CMPB 1950
#define EPWM1_MIN_CMPB 50
#define EPWM2_TIMER_TBPRD 2000 // Period register
#define EPWM2_MAX_CMPA 1950
#define EPWM2_MIN_CMPA 50
#define EPWM2_MAX_CMPB 1950
#define EPWM2_MIN_CMPB 50
#define EPWM3_TIMER_TBPRD 2000 // Period register
#define EPWM3_MAX_CMPA 950
#define EPWM3_MIN_CMPA 50
#define EPWM3_MAX_CMPB 1950
#define EPWM3_MIN_CMPB 1050
// To keep track of which way the compare value is moving
#define EPWM_CMP_UP 1
#define EPWM_CMP_DOWN 0
void main(void)
{
// Step 1. Initialize System Control:
// PLL, WatchDog, enable Peripheral Clocks
// This example function is found in the DSP2833x_SysCtrl.c file.
InitSysCtrl();
// Step 2. Initalize GPIO:
// This example function is found in the DSP2833x_Gpio.c file and
// illustrates how to set the GPIO to it's default state.
// InitGpio(); // Skipped for this example
// For this case just init GPIO pins for ePWM1, ePWM2, ePWM3
// These functions are in the DSP2833x_EPwm.c file
InitEPwm1Gpio();
InitEPwm2Gpio();
InitEPwm3Gpio();
// Step 3. Clear all interrupts and initialize PIE vector table:
// Disable CPU interrupts
DINT;
// Initialize the PIE control registers to their default state.
// The default state is all PIE interrupts disabled and flags
// are cleared.
// This function is found in the DSP2833x_PieCtrl.c file.
InitPieCtrl();
// Disable CPU interrupts and clear all CPU interrupt flags:
IER = 0x0000;
IFR = 0x0000;
// Initialize the PIE vector table with pointers to the shell Interrupt
// Service Routines (ISR).
// This will populate the entire table, even if the interrupt
// is not used in this example. This is useful for debug purposes.
// The shell ISR routines are found in DSP2833x_DefaultIsr.c.
// This function is found in DSP2833x_PieVect.c.
InitPieVectTable();
// Interrupts that are used in this example are re-mapped to
// ISR functions found within this file.
EALLOW; // This is needed to write to EALLOW protected registers
PieVectTable.EPWM1_INT = &epwm1_isr;
PieVectTable.EPWM2_INT = &epwm2_isr;
PieVectTable.EPWM3_INT = &epwm3_isr;
EDIS; // This is needed to disable write to EALLOW protected registers
// Step 4. Initialize all the Device Peripherals:
// This function is found in DSP2833x_InitPeripherals.c
// InitPeripherals(); // Not required for this example
// For this example, only initialize the ePWM
EALLOW;
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR0.bit.TBCLKSYNC = 0;
EDIS;
InitEPwm1Example();
InitEPwm2Example();
InitEPwm3Example();
EALLOW;
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR0.bit.TBCLKSYNC = 1;
EDIS;
// Step 5. User specific code, enable interrupts:
// Enable CPU INT3 which is connected to EPWM1-3 INT:
IER |= M_INT3;
// Enable EPWM INTn in the PIE: Group 3 interrupt 1-3
PieCtrlRegs.PIEIER3.bit.INTx1 = 1;
PieCtrlRegs.PIEIER3.bit.INTx2 = 1;
PieCtrlRegs.PIEIER3.bit.INTx3 = 1;
// Enable global Interrupts and higher priority real-time debug events:
EINT; // Enable Global interrupt INTM
ERTM; // Enable Global realtime interrupt DBGM
// Step 6. IDLE loop. Just sit and loop forever (optional):
for(;;)
{
asm(" NOP");
}
}
interrupt void epwm1_isr(void)
{
// Update the CMPA and CMPB values
update_compare(&epwm1_info);
// Clear INT flag for this timer
EPwm1Regs.ETCLR.bit.INT = 1;
// Acknowledge this interrupt to receive more interrupts from group 3
PieCtrlRegs.PIEACK.all = PIEACK_GROUP3;
}
interrupt void epwm2_isr(void)
{
// Update the CMPA and CMPB values
update_compare(&epwm2_info);
// Clear INT flag for this timer
EPwm2Regs.ETCLR.bit.INT = 1;
// Acknowledge this interrupt to receive more interrupts from group 3
PieCtrlRegs.PIEACK.all = PIEACK_GROUP3;
}
interrupt void epwm3_isr(void)
{
// Update the CMPA and CMPB values
update_compare(&epwm3_info);
// Clear INT flag for this timer
EPwm3Regs.ETCLR.bit.INT = 1;
// Acknowledge this interrupt to receive more interrupts from group 3
PieCtrlRegs.PIEACK.all = PIEACK_GROUP3;
}
void InitEPwm1Example()
{
// Setup TBCLK
EPwm1Regs.TBCTL.bit.CTRMODE = TB_COUNT_UP; // Count up
EPwm1Regs.TBPRD = EPWM1_TIMER_TBPRD; // Set timer period
EPwm1Regs.TBCTL.bit.PHSEN = TB_DISABLE; // Disable phase loading
EPwm1Regs.TBPHS.half.TBPHS = 0x0000; // Phase is 0
EPwm1Regs.TBCTR = 0x0000; // Clear counter
EPwm1Regs.TBCTL.bit.HSPCLKDIV = TB_DIV2; // Clock ratio to SYSCLKOUT
EPwm1Regs.TBCTL.bit.CLKDIV = TB_DIV2;
// Setup shadow register load on ZERO
EPwm1Regs.CMPCTL.bit.SHDWAMODE = CC_SHADOW;
EPwm1Regs.CMPCTL.bit.SHDWBMODE = CC_SHADOW;
EPwm1Regs.CMPCTL.bit.LOADAMODE = CC_CTR_ZERO;
EPwm1Regs.CMPCTL.bit.LOADBMODE = CC_CTR_ZERO;
// Set Compare values
EPwm1Regs.CMPA.half.CMPA = EPWM1_MIN_CMPA; // Set compare A value
EPwm1Regs.CMPB = EPWM1_MIN_CMPB; // Set Compare B value
// Set actions
EPwm1Regs.AQCTLA.bit.ZRO = AQ_SET; // Set PWM1A on Zero
EPwm1Regs.AQCTLA.bit.CAU = AQ_CLEAR; // Clear PWM1A on event A, upcount
EPwm1Regs.AQCTLB.bit.ZRO = AQ_SET; // Set PWM1B on Zero
EPwm1Regs.AQCTLB.bit.CBU = AQ_CLEAR; // Clear PWM1B on event B, upcount
// Interrupt where we will change the Compare Values
EPwm1Regs.ETSEL.bit.INTSEL = ET_CTR_ZERO; // Select INT on Zero event
EPwm1Regs.ETSEL.bit.INTEN = 1; // Enable INT
EPwm1Regs.ETPS.bit.INTPRD = ET_3RD; // Generate INT on 3rd event
// Information this example uses to keep track
// of the direction the CMPA/CMPB values are
// moving, the min and max allowed values and
// a pointer to the correct ePWM registers
epwm1_info.EPwm_CMPA_Direction = EPWM_CMP_UP; // Start by increasing CMPA & CMPB
epwm1_info.EPwm_CMPB_Direction = EPWM_CMP_UP;
epwm1_info.EPwmTimerIntCount = 0; // Zero the interrupt counter
epwm1_info.EPwmRegHandle = &EPwm1Regs; // Set the pointer to the ePWM module
epwm1_info.EPwmMaxCMPA = EPWM1_MAX_CMPA; // Setup min/max CMPA/CMPB values
epwm1_info.EPwmMinCMPA = EPWM1_MIN_CMPA;
epwm1_info.EPwmMaxCMPB = EPWM1_MAX_CMPB;
epwm1_info.EPwmMinCMPB = EPWM1_MIN_CMPB;
}
void InitEPwm2Example()
{
// Setup TBCLK
EPwm2Regs.TBCTL.bit.CTRMODE = TB_COUNT_UP; // Count up
EPwm2Regs.TBPRD = EPWM2_TIMER_TBPRD; // Set timer period
EPwm2Regs.TBCTL.bit.PHSEN = TB_DISABLE; // Disable phase loading
EPwm2Regs.TBPHS.half.TBPHS = 0x0000; // Phase is 0
EPwm2Regs.TBCTR = 0x0000; // Clear counter
EPwm2Regs.TBCTL.bit.HSPCLKDIV = TB_DIV2; // Clock ratio to SYSCLKOUT
EPwm2Regs.TBCTL.bit.CLKDIV = TB_DIV2;
// Setup shadow register load on ZERO
EPwm2Regs.CMPCTL.bit.SHDWAMODE = CC_SHADOW;
EPwm2Regs.CMPCTL.bit.SHDWBMODE = CC_SHADOW;
EPwm2Regs.CMPCTL.bit.LOADAMODE = CC_CTR_ZERO;
EPwm2Regs.CMPCTL.bit.LOADBMODE = CC_CTR_ZERO;
// Set Compare values
EPwm2Regs.CMPA.half.CMPA = EPWM2_MIN_CMPA; // Set compare A value
EPwm2Regs.CMPB = EPWM2_MAX_CMPB; // Set Compare B value
// Set actions
EPwm2Regs.AQCTLA.bit.PRD = AQ_CLEAR; // Clear PWM2A on Period
EPwm2Regs.AQCTLA.bit.CAU = AQ_SET; // Set PWM2A on event A, up count
EPwm2Regs.AQCTLB.bit.PRD = AQ_CLEAR; // Clear PWM2B on Period
EPwm2Regs.AQCTLB.bit.CBU = AQ_SET; // Set PWM2B on event B, up count
// Interrupt where we will change the Compare Values
EPwm2Regs.ETSEL.bit.INTSEL = ET_CTR_ZERO; // Select INT on Zero event
EPwm2Regs.ETSEL.bit.INTEN = 1; // Enable INT
EPwm2Regs.ETPS.bit.INTPRD = ET_3RD; // Generate INT on 3rd event
// Information this example uses to keep track
// of the direction the CMPA/CMPB values are
// moving, the min and max allowed values and
// a pointer to the correct ePWM registers
epwm2_info.EPwm_CMPA_Direction = EPWM_CMP_UP; // Start by increasing CMPA
epwm2_info.EPwm_CMPB_Direction = EPWM_CMP_DOWN; // and decreasing CMPB
epwm2_info.EPwmTimerIntCount = 0; // Zero the interrupt counter
epwm2_info.EPwmRegHandle = &EPwm2Regs; // Set the pointer to the ePWM module
epwm2_info.EPwmMaxCMPA = EPWM2_MAX_CMPA; // Setup min/max CMPA/CMPB values
epwm2_info.EPwmMinCMPA = EPWM2_MIN_CMPA;
epwm2_info.EPwmMaxCMPB = EPWM2_MAX_CMPB;
epwm2_info.EPwmMinCMPB = EPWM2_MIN_CMPB;
}
void InitEPwm3Example(void)
{
// Setup TBCLK
EPwm3Regs.TBCTL.bit.CTRMODE = TB_COUNT_UP; // Count up
EPwm3Regs.TBPRD = EPWM3_TIMER_TBPRD; // Set timer period
EPwm3Regs.TBCTL.bit.PHSEN = TB_DISABLE; // Disable phase loading
EPwm3Regs.TBPHS.half.TBPHS = 0x0000; // Phase is 0
EPwm3Regs.TBCTR = 0x0000; // Clear counter
EPwm3Regs.TBCTL.bit.HSPCLKDIV = TB_DIV1; // Clock ratio to SYSCLKOUT
EPwm3Regs.TBCTL.bit.CLKDIV = TB_DIV1;
// Setup shadow register load on ZERO
EPwm3Regs.CMPCTL.bit.SHDWAMODE = CC_SHADOW;
EPwm3Regs.CMPCTL.bit.SHDWBMODE = CC_SHADOW;
EPwm3Regs.CMPCTL.bit.LOADAMODE = CC_CTR_ZERO;
EPwm3Regs.CMPCTL.bit.LOADBMODE = CC_CTR_ZERO;
// Set Compare values
EPwm3Regs.CMPA.half.CMPA = EPWM3_MIN_CMPA; // Set compare A value
EPwm3Regs.CMPB = EPWM3_MAX_CMPB; // Set Compare B value
// Set Actions
EPwm3Regs.AQCTLA.bit.CAU = AQ_SET; // Set PWM3A on event B, up count
EPwm3Regs.AQCTLA.bit.CBU = AQ_CLEAR; // Clear PWM3A on event B, up count
EPwm3Regs.AQCTLB.bit.ZRO = AQ_TOGGLE; // Toggle EPWM3B on Zero
// Interrupt where we will change the Compare Values
EPwm3Regs.ETSEL.bit.INTSEL = ET_CTR_ZERO; // Select INT on Zero event
EPwm3Regs.ETSEL.bit.INTEN = 1; // Enable INT
EPwm3Regs.ETPS.bit.INTPRD = ET_3RD; // Generate INT on 3rd event
// Start by increasing the compare A and decreasing compare B
epwm3_info.EPwm_CMPA_Direction = EPWM_CMP_UP;
epwm3_info.EPwm_CMPB_Direction = EPWM_CMP_DOWN;
// Start the cout at 0
epwm3_info.EPwmTimerIntCount = 0;
epwm3_info.EPwmRegHandle = &EPwm3Regs;
epwm3_info.EPwmMaxCMPA = EPWM3_MAX_CMPA;
epwm3_info.EPwmMinCMPA = EPWM3_MIN_CMPA;
epwm3_info.EPwmMaxCMPB = EPWM3_MAX_CMPB;
epwm3_info.EPwmMinCMPB = EPWM3_MIN_CMPB;
}
void update_compare(EPWM_INFO *epwm_info)
{
// Every 10'th interrupt, change the CMPA/CMPB values
if(epwm_info->EPwmTimerIntCount == 10)
{
epwm_info->EPwmTimerIntCount = 0;
// If we were increasing CMPA, check to see if
// we reached the max value. If not, increase CMPA
// else, change directions and decrease CMPA
if(epwm_info->EPwm_CMPA_Direction == EPWM_CMP_UP)
{
if(epwm_info->EPwmRegHandle->CMPA.half.CMPA < epwm_info->EPwmMaxCMPA)
{
epwm_info->EPwmRegHandle->CMPA.half.CMPA++;
}
else
{
epwm_info->EPwm_CMPA_Direction = EPWM_CMP_DOWN;
epwm_info->EPwmRegHandle->CMPA.half.CMPA--;
}
}
// If we were decreasing CMPA, check to see if
// we reached the min value. If not, decrease CMPA
// else, change directions and increase CMPA
else
{
if(epwm_info->EPwmRegHandle->CMPA.half.CMPA == epwm_info->EPwmMinCMPA)
{
epwm_info->EPwm_CMPA_Direction = EPWM_CMP_UP;
epwm_info->EPwmRegHandle->CMPA.half.CMPA++;
}
else
{
epwm_info->EPwmRegHandle->CMPA.half.CMPA--;
}
}
// If we were increasing CMPB, check to see if
// we reached the max value. If not, increase CMPB
// else, change directions and decrease CMPB
if(epwm_info->EPwm_CMPB_Direction == EPWM_CMP_UP)
{
if(epwm_info->EPwmRegHandle->CMPB < epwm_info->EPwmMaxCMPB)
{
epwm_info->EPwmRegHandle->CMPB++;
}
else
{
epwm_info->EPwm_CMPB_Direction = EPWM_CMP_DOWN;
epwm_info->EPwmRegHandle->CMPB--;
}
}
// If we were decreasing CMPB, check to see if
// we reached the min value. If not, decrease CMPB
// else, change directions and increase CMPB
else
{
if(epwm_info->EPwmRegHandle->CMPB == epwm_info->EPwmMinCMPB)
{
epwm_info->EPwm_CMPB_Direction = EPWM_CMP_UP;
epwm_info->EPwmRegHandle->CMPB++;
}
else
{
epwm_info->EPwmRegHandle->CMPB--;
}
}
}
else
{
epwm_info->EPwmTimerIntCount++;
}
return;
}
//===========================================================================
// No more.
//===========================================================================(3)动作限定模块 - 使用增/减计数模式



c
//###########################################################################
//
// 文件名: Example_2833xEPwmUpDownAQ.c
//
// 标题: 动作限定模块 - 使用增/减计数模式
//
//
// 此程序需要 DSP2833x头文件.
//
// 按以下描述用示波器观察 ePWM1 - ePWM3引脚
//
// EPWM1A定义在GPIO0上
// EPWM1B定义在GPIO1上
//
// EPWM2A定义在GPIO2上
// EPWM2B定义在GPIO3上
//
// EPWM3A定义在GPIO4上
// EPWM3B定义在GPIO5上
//
// 根据在RAM中调试的需要,这个项目配置成"boot to SARAM".2833x引导模式
// 表如下显示. 常用的还有"boot to Flash"模式,当程序在RAM调试完善后就
// 可以将代码烧进Flash中并使用"boot to Flash"引导模式.
//
// $Boot_Table:
//
// GPIO87 GPIO86 GPIO85 GPIO84
// XA15 XA14 XA13 XA12
// PU PU PU PU
// ==========================================
// 1 1 1 1 Jump to Flash
// 1 1 1 0 SCI-A boot
// 1 1 0 1 SPI-A boot
// 1 1 0 0 I2C-A boot
// 1 0 1 1 eCAN-A boot
// 1 0 1 0 McBSP-A boot
// 1 0 0 1 Jump to XINTF x16
// 1 0 0 0 Jump to XINTF x32
// 0 1 1 1 Jump to OTP
// 0 1 1 0 Parallel GPIO I/O boot
// 0 1 0 1 Parallel XINTF boot
// 0 1 0 0 Jump to SARAM <- "boot to SARAM"
// 0 0 1 1 Branch to check boot mode
// 0 0 1 0 Boot to flash, bypass ADC cal
// 0 0 0 1 Boot to SARAM, bypass ADC cal
// 0 0 0 0 Boot to SCI-A, bypass ADC cal
// Boot_Table_End$
//
// 功能描述:
//
// 本例配置ePWM1, ePWM2, ePWM3产生产生EPWMxA和EPWMxB波形
//
// 在ePWM中断子程序中,比较寄存器CMPA和CMPB的值被修改
//
// 本例时基时钟被配置为增减计数模式
// 通过示波器观察EPWM1A/B, EPWM2A/B 和 EPWM3A/B波形
//
//
//###########################################################################
// 释放日期:2013.11.25
//###########################################################################
#include "DSP2833x_Device.h" // DSP2833x Headerfile Include File
#include "DSP2833x_Examples.h" // DSP2833x Examples Include File
typedef struct
{
volatile struct EPWM_REGS *EPwmRegHandle;
Uint16 EPwm_CMPA_Direction;
Uint16 EPwm_CMPB_Direction;
Uint16 EPwmTimerIntCount;
Uint16 EPwmMaxCMPA;
Uint16 EPwmMinCMPA;
Uint16 EPwmMaxCMPB;
Uint16 EPwmMinCMPB;
}EPWM_INFO;
// Prototype statements for functions found within this file.
void InitEPwm1Example(void);
void InitEPwm2Example(void);
void InitEPwm3Example(void);
interrupt void epwm1_isr(void);
interrupt void epwm2_isr(void);
interrupt void epwm3_isr(void);
void update_compare(EPWM_INFO*);
// Global variables used in this example
EPWM_INFO epwm1_info;
EPWM_INFO epwm2_info;
EPWM_INFO epwm3_info;
// Configure the period for each timer
#define EPWM1_TIMER_TBPRD 2000 // Period register
#define EPWM1_MAX_CMPA 1950
#define EPWM1_MIN_CMPA 50
#define EPWM1_MAX_CMPB 1950
#define EPWM1_MIN_CMPB 50
#define EPWM2_TIMER_TBPRD 2000 // Period register
#define EPWM2_MAX_CMPA 1950
#define EPWM2_MIN_CMPA 50
#define EPWM2_MAX_CMPB 1950
#define EPWM2_MIN_CMPB 50
#define EPWM3_TIMER_TBPRD 2000 // Period register
#define EPWM3_MAX_CMPA 950
#define EPWM3_MIN_CMPA 50
#define EPWM3_MAX_CMPB 1950
#define EPWM3_MIN_CMPB 1050
// To keep track of which way the compare value is moving
#define EPWM_CMP_UP 1
#define EPWM_CMP_DOWN 0
void main(void)
{
// Step 1. Initialize System Control:
// PLL, WatchDog, enable Peripheral Clocks
// This example function is found in the DSP2833x_SysCtrl.c file.
InitSysCtrl();
// Step 2. Initalize GPIO:
// This example function is found in the DSP2833x_Gpio.c file and
// illustrates how to set the GPIO to it's default state.
// InitGpio(); // Skipped for this example
// For this case just init GPIO pins for ePWM1, ePWM2, ePWM3
// These functions are in the DSP2833x_EPwm.c file
InitEPwm1Gpio();
InitEPwm2Gpio();
InitEPwm3Gpio();
// Step 3. Clear all interrupts and initialize PIE vector table:
// Disable CPU interrupts
DINT;
// Initialize the PIE control registers to their default state.
// The default state is all PIE interrupts disabled and flags
// are cleared.
// This function is found in the DSP2833x_PieCtrl.c file.
InitPieCtrl();
// Disable CPU interrupts and clear all CPU interrupt flags:
IER = 0x0000;
IFR = 0x0000;
// Initialize the PIE vector table with pointers to the shell Interrupt
// Service Routines (ISR).
// This will populate the entire table, even if the interrupt
// is not used in this example. This is useful for debug purposes.
// The shell ISR routines are found in DSP2833x_DefaultIsr.c.
// This function is found in DSP2833x_PieVect.c.
InitPieVectTable();
// Interrupts that are used in this example are re-mapped to
// ISR functions found within this file.
EALLOW; // This is needed to write to EALLOW protected registers
PieVectTable.EPWM1_INT = &epwm1_isr;
PieVectTable.EPWM2_INT = &epwm2_isr;
PieVectTable.EPWM3_INT = &epwm3_isr;
EDIS; // This is needed to disable write to EALLOW protected registers
// Step 4. Initialize all the Device Peripherals:
// This function is found in DSP2833x_InitPeripherals.c
// InitPeripherals(); // Not required for this example
// For this example, only initialize the ePWM
EALLOW;
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR0.bit.TBCLKSYNC = 0;
EDIS;
InitEPwm1Example();
InitEPwm2Example();
InitEPwm3Example();
EALLOW;
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR0.bit.TBCLKSYNC = 1;
EDIS;
// Step 5. User specific code, enable interrupts:
// Enable CPU INT3 which is connected to EPWM1-3 INT:
IER |= M_INT3;
// Enable EPWM INTn in the PIE: Group 3 interrupt 1-3
PieCtrlRegs.PIEIER3.bit.INTx1 = 1;
PieCtrlRegs.PIEIER3.bit.INTx2 = 1;
PieCtrlRegs.PIEIER3.bit.INTx3 = 1;
// Enable global Interrupts and higher priority real-time debug events:
EINT; // Enable Global interrupt INTM
ERTM; // Enable Global realtime interrupt DBGM
// Step 6. IDLE loop. Just sit and loop forever (optional):
for(;;)
{
asm(" NOP");
}
}
interrupt void epwm1_isr(void)
{
// Update the CMPA and CMPB values
update_compare(&epwm1_info);
// Clear INT flag for this timer
EPwm1Regs.ETCLR.bit.INT = 1;
// Acknowledge this interrupt to receive more interrupts from group 3
PieCtrlRegs.PIEACK.all = PIEACK_GROUP3;
}
interrupt void epwm2_isr(void)
{
// Update the CMPA and CMPB values
update_compare(&epwm2_info);
// Clear INT flag for this timer
EPwm2Regs.ETCLR.bit.INT = 1;
// Acknowledge this interrupt to receive more interrupts from group 3
PieCtrlRegs.PIEACK.all = PIEACK_GROUP3;
}
interrupt void epwm3_isr(void)
{
// Update the CMPA and CMPB values
update_compare(&epwm3_info);
// Clear INT flag for this timer
EPwm3Regs.ETCLR.bit.INT = 1;
// Acknowledge this interrupt to receive more interrupts from group 3
PieCtrlRegs.PIEACK.all = PIEACK_GROUP3;
}
void InitEPwm1Example()
{
// Setup TBCLK
EPwm1Regs.TBPRD = EPWM1_TIMER_TBPRD; // Set timer period 801 TBCLKs
EPwm1Regs.TBPHS.half.TBPHS = 0x0000; // Phase is 0
EPwm1Regs.TBCTR = 0x0000; // Clear counter
// Set Compare values
EPwm1Regs.CMPA.half.CMPA = EPWM1_MIN_CMPA; // Set compare A value
EPwm1Regs.CMPB = EPWM1_MAX_CMPB; // Set Compare B value
// Setup counter mode
EPwm1Regs.TBCTL.bit.CTRMODE = TB_COUNT_UPDOWN; // Count up
EPwm1Regs.TBCTL.bit.PHSEN = TB_DISABLE; // Disable phase loading
EPwm1Regs.TBCTL.bit.HSPCLKDIV = TB_DIV1; // Clock ratio to SYSCLKOUT
EPwm1Regs.TBCTL.bit.CLKDIV = TB_DIV1;
// Setup shadowing Load on Zero
EPwm1Regs.CMPCTL.bit.SHDWAMODE = CC_SHADOW;
EPwm1Regs.CMPCTL.bit.SHDWBMODE = CC_SHADOW;
EPwm1Regs.CMPCTL.bit.LOADAMODE = CC_CTR_ZERO;
EPwm1Regs.CMPCTL.bit.LOADBMODE = CC_CTR_ZERO;
// Set actions
EPwm1Regs.AQCTLA.bit.CAU = AQ_SET; // Set PWM1A on event A, up count
EPwm1Regs.AQCTLA.bit.CAD = AQ_CLEAR; // Clear PWM1A on event A, down count
EPwm1Regs.AQCTLB.bit.CBU = AQ_SET; // Set PWM1B on event B, up count
EPwm1Regs.AQCTLB.bit.CBD = AQ_CLEAR; // Clear PWM1B on event B, down count
// Interrupt where we will change the Compare Values
EPwm1Regs.ETSEL.bit.INTSEL = ET_CTR_ZERO; // Select INT on Zero event
EPwm1Regs.ETSEL.bit.INTEN = 1; // Enable INT
EPwm1Regs.ETPS.bit.INTPRD = ET_3RD; // Generate INT on 3rd event
// Information this example uses to keep track
// of the direction the CMPA/CMPB values are
// moving, the min and max allowed values and
// a pointer to the correct ePWM registers
epwm1_info.EPwm_CMPA_Direction = EPWM_CMP_UP; // Start by increasing CMPA &
epwm1_info.EPwm_CMPB_Direction = EPWM_CMP_DOWN; // decreasing CMPB
epwm1_info.EPwmTimerIntCount = 0; // Zero the interrupt counter
epwm1_info.EPwmRegHandle = &EPwm1Regs; // Set the pointer to the ePWM module
epwm1_info.EPwmMaxCMPA = EPWM1_MAX_CMPA; // Setup min/max CMPA/CMPB values
epwm1_info.EPwmMinCMPA = EPWM1_MIN_CMPA;
epwm1_info.EPwmMaxCMPB = EPWM1_MAX_CMPB;
epwm1_info.EPwmMinCMPB = EPWM1_MIN_CMPB;
}
void InitEPwm2Example()
{
// Setup TBCLK
EPwm2Regs.TBPRD = EPWM2_TIMER_TBPRD; // Set timer period 801 TBCLKs
EPwm2Regs.TBPHS.half.TBPHS = 0x0000; // Phase is 0
EPwm2Regs.TBCTR = 0x0000; // Clear counter
// Set Compare values
EPwm2Regs.CMPA.half.CMPA = EPWM2_MIN_CMPA; // Set compare A value
EPwm2Regs.CMPB = EPWM2_MIN_CMPB; // Set Compare B value
// Setup counter mode
EPwm2Regs.TBCTL.bit.CTRMODE = TB_COUNT_UPDOWN; // Count up
EPwm2Regs.TBCTL.bit.PHSEN = TB_DISABLE; // Disable phase loading
EPwm2Regs.TBCTL.bit.HSPCLKDIV = TB_DIV1; // Clock ratio to SYSCLKOUT
EPwm2Regs.TBCTL.bit.CLKDIV = TB_DIV1;
// Setup shadowing
EPwm2Regs.CMPCTL.bit.SHDWAMODE = CC_SHADOW;
EPwm2Regs.CMPCTL.bit.SHDWBMODE = CC_SHADOW;
EPwm2Regs.CMPCTL.bit.LOADAMODE = CC_CTR_ZERO; // Load on Zero
EPwm2Regs.CMPCTL.bit.LOADBMODE = CC_CTR_ZERO;
// Set actions
EPwm2Regs.AQCTLA.bit.CAU = AQ_SET; // Set PWM2A on event A, up count
EPwm2Regs.AQCTLA.bit.CBD = AQ_CLEAR; // Clear PWM2A on event B, down count
EPwm2Regs.AQCTLB.bit.ZRO = AQ_CLEAR; // Clear PWM2B on zero
EPwm2Regs.AQCTLB.bit.PRD = AQ_SET ; // Set PWM2B on period
// Interrupt where we will change the Compare Values
EPwm2Regs.ETSEL.bit.INTSEL = ET_CTR_ZERO; // Select INT on Zero event
EPwm2Regs.ETSEL.bit.INTEN = 1; // Enable INT
EPwm2Regs.ETPS.bit.INTPRD = ET_3RD; // Generate INT on 3rd event
// Information this example uses to keep track
// of the direction the CMPA/CMPB values are
// moving, the min and max allowed values and
// a pointer to the correct ePWM registers
epwm2_info.EPwm_CMPA_Direction = EPWM_CMP_UP; // Start by increasing CMPA &
epwm2_info.EPwm_CMPB_Direction = EPWM_CMP_UP; // increasing CMPB
epwm2_info.EPwmTimerIntCount = 0; // Zero the interrupt counter
epwm2_info.EPwmRegHandle = &EPwm2Regs; // Set the pointer to the ePWM module
epwm2_info.EPwmMaxCMPA = EPWM2_MAX_CMPA; // Setup min/max CMPA/CMPB values
epwm2_info.EPwmMinCMPA = EPWM2_MIN_CMPA;
epwm2_info.EPwmMaxCMPB = EPWM2_MAX_CMPB;
epwm2_info.EPwmMinCMPB = EPWM2_MIN_CMPB;
}
void InitEPwm3Example(void)
{
// Setup TBCLK
EPwm3Regs.TBCTL.bit.CTRMODE = TB_COUNT_UPDOWN;// Count up/down
EPwm3Regs.TBPRD = EPWM3_TIMER_TBPRD; // Set timer period
EPwm3Regs.TBCTL.bit.PHSEN = TB_DISABLE; // Disable phase loading
EPwm3Regs.TBPHS.half.TBPHS = 0x0000; // Phase is 0
EPwm3Regs.TBCTR = 0x0000; // Clear counter
EPwm3Regs.TBCTL.bit.HSPCLKDIV = TB_DIV1; // Clock ratio to SYSCLKOUT
EPwm3Regs.TBCTL.bit.CLKDIV = TB_DIV1;
// Setup shadow register load on ZERO
EPwm3Regs.CMPCTL.bit.SHDWAMODE = CC_SHADOW;
EPwm3Regs.CMPCTL.bit.SHDWBMODE = CC_SHADOW;
EPwm3Regs.CMPCTL.bit.LOADAMODE = CC_CTR_ZERO;
EPwm3Regs.CMPCTL.bit.LOADBMODE = CC_CTR_ZERO;
// Set Compare values
EPwm3Regs.CMPA.half.CMPA = EPWM3_MIN_CMPA; // Set compare A value
EPwm3Regs.CMPB = EPWM3_MAX_CMPB; // Set Compare B value
// Set Actions
EPwm3Regs.AQCTLA.bit.PRD = AQ_SET; // Set PWM3A on period
EPwm3Regs.AQCTLA.bit.CBD = AQ_CLEAR; // Clear PWM3A on event B, down count
EPwm3Regs.AQCTLB.bit.PRD = AQ_CLEAR; // Clear PWM3A on period
EPwm3Regs.AQCTLB.bit.CAU = AQ_SET; // Set PWM3A on event A, up count
// Interrupt where we will change the Compare Values
EPwm3Regs.ETSEL.bit.INTSEL = ET_CTR_ZERO; // Select INT on Zero event
EPwm3Regs.ETSEL.bit.INTEN = 1; // Enable INT
EPwm3Regs.ETPS.bit.INTPRD = ET_3RD; // Generate INT on 3rd event
// Information this example uses to keep track
// of the direction the CMPA/CMPB values are
// moving, the min and max allowed values and
// a pointer to the correct ePWM registers
epwm3_info.EPwm_CMPA_Direction = EPWM_CMP_UP; // Start by increasing CMPA &
epwm3_info.EPwm_CMPB_Direction = EPWM_CMP_DOWN; // decreasing CMPB
epwm3_info.EPwmTimerIntCount = 0; // Zero the interrupt counter
epwm3_info.EPwmRegHandle = &EPwm3Regs; // Set the pointer to the ePWM module
epwm3_info.EPwmMaxCMPA = EPWM3_MAX_CMPA; // Setup min/max CMPA/CMPB values
epwm3_info.EPwmMinCMPA = EPWM3_MIN_CMPA;
epwm3_info.EPwmMaxCMPB = EPWM3_MAX_CMPB;
epwm3_info.EPwmMinCMPB = EPWM3_MIN_CMPB;
}
void update_compare(EPWM_INFO *epwm_info)
{
// Every 10'th interrupt, change the CMPA/CMPB values
if(epwm_info->EPwmTimerIntCount == 10)
{
epwm_info->EPwmTimerIntCount = 0;
// If we were increasing CMPA, check to see if
// we reached the max value. If not, increase CMPA
// else, change directions and decrease CMPA
if(epwm_info->EPwm_CMPA_Direction == EPWM_CMP_UP)
{
if(epwm_info->EPwmRegHandle->CMPA.half.CMPA < epwm_info->EPwmMaxCMPA)
{
epwm_info->EPwmRegHandle->CMPA.half.CMPA++;
}
else
{
epwm_info->EPwm_CMPA_Direction = EPWM_CMP_DOWN;
epwm_info->EPwmRegHandle->CMPA.half.CMPA--;
}
}
// If we were decreasing CMPA, check to see if
// we reached the min value. If not, decrease CMPA
// else, change directions and increase CMPA
else
{
if(epwm_info->EPwmRegHandle->CMPA.half.CMPA == epwm_info->EPwmMinCMPA)
{
epwm_info->EPwm_CMPA_Direction = EPWM_CMP_UP;
epwm_info->EPwmRegHandle->CMPA.half.CMPA++;
}
else
{
epwm_info->EPwmRegHandle->CMPA.half.CMPA--;
}
}
// If we were increasing CMPB, check to see if
// we reached the max value. If not, increase CMPB
// else, change directions and decrease CMPB
if(epwm_info->EPwm_CMPB_Direction == EPWM_CMP_UP)
{
if(epwm_info->EPwmRegHandle->CMPB < epwm_info->EPwmMaxCMPB)
{
epwm_info->EPwmRegHandle->CMPB++;
}
else
{
epwm_info->EPwm_CMPB_Direction = EPWM_CMP_DOWN;
epwm_info->EPwmRegHandle->CMPB--;
}
}
// If we were decreasing CMPB, check to see if
// we reached the min value. If not, decrease CMPB
// else, change directions and increase CMPB
else
{
if(epwm_info->EPwmRegHandle->CMPB == epwm_info->EPwmMinCMPB)
{
epwm_info->EPwm_CMPB_Direction = EPWM_CMP_UP;
epwm_info->EPwmRegHandle->CMPB++;
}
else
{
epwm_info->EPwmRegHandle->CMPB--;
}
}
}
else
{
epwm_info->EPwmTimerIntCount++;
}
return;
}
//===========================================================================
// No more.
//===========================================================================(4)检查PWM的死区产生





c
//###########################################################################
//
// 文件名: Example_2833xEpwmDeadBand.c
//
// 标题: 检查PWM的死区产生
//
// ASSUMPTIONS:
//
// 此程序需要 DSP2833x头文件.
//
// 按以下描述用示波器观察 ePWM1 - ePWM3引脚
//
// EPWM1A定义在GPIO0上
// EPWM1B定义在GPIO1上
//
// EPWM2A定义在GPIO2上
// EPWM2B定义在GPIO3上
//
// EPWM3A定义在GPIO4上
// EPWM3B定义在GPIO5上
//
// 根据在RAM中调试的需要,这个项目配置成"boot to SARAM".2833x引导模式
// 表如下显示. 常用的还有"boot to Flash"模式,当程序在RAM调试完善后就
// 可以将代码烧进Flash中并使用"boot to Flash"引导模式.
//
// $Boot_Table:
//
// GPIO87 GPIO86 GPIO85 GPIO84
// XA15 XA14 XA13 XA12
// PU PU PU PU
// ==========================================
// 1 1 1 1 Jump to Flash
// 1 1 1 0 SCI-A boot
// 1 1 0 1 SPI-A boot
// 1 1 0 0 I2C-A boot
// 1 0 1 1 eCAN-A boot
// 1 0 1 0 McBSP-A boot
// 1 0 0 1 Jump to XINTF x16
// 1 0 0 0 Jump to XINTF x32
// 0 1 1 1 Jump to OTP
// 0 1 1 0 Parallel GPIO I/O boot
// 0 1 0 1 Parallel XINTF boot
// 0 1 0 0 Jump to SARAM <- "boot to SARAM"
// 0 0 1 1 Branch to check boot mode
// 0 0 1 0 Boot to flash, bypass ADC cal
// 0 0 0 1 Boot to SARAM, bypass ADC cal
// 0 0 0 0 Boot to SCI-A, bypass ADC cal
// Boot_Table_End$
//
// 功能描述:
//
// 本例配置ePWM1, ePWM2 and ePWM3为:
// - 增减计数模式
// - 带死区
//
// 3个例子的配置如下:
// * ePWM1:低电平有效(AL)
// * ePWM2:低电平有效,互补输出(ALC)
// * ePWM3:高电平有效,互补输出(AHC)
//
// 每个ePWM配置为3次0匹配事件产生1次中断,在中断子程序中
// 修改死区延迟寄存器的值 0 <= DB <= DB_MAX,然后输出PWM的
// 死区会在0与最大值之间变化
//
//
// 通过示波器观察EPWM1A/B, EPWM2A/B and EPWM3A/B 波形
//
//###########################################################################
// 释放日期:2013.11.25
//###########################################################################
#include "DSP2833x_Device.h" // DSP2833x Headerfile Include File
#include "DSP2833x_Examples.h" // DSP2833x Examples Include File
// Prototype statements for functions found within this file.
void InitEPwm1Example(void);
void InitEPwm2Example(void);
void InitEPwm3Example(void);
interrupt void epwm1_isr(void);
interrupt void epwm2_isr(void);
interrupt void epwm3_isr(void);
// Global variables used in this example
Uint32 EPwm1TimerIntCount;
Uint32 EPwm2TimerIntCount;
Uint32 EPwm3TimerIntCount;
Uint16 EPwm1_DB_Direction;
Uint16 EPwm2_DB_Direction;
Uint16 EPwm3_DB_Direction;
// Maximum Dead Band values
#define EPWM1_MAX_DB 0x03FF
#define EPWM2_MAX_DB 0x03FF
#define EPWM3_MAX_DB 0x03FF
#define EPWM1_MIN_DB 0
#define EPWM2_MIN_DB 0
#define EPWM3_MIN_DB 0
// To keep track of which way the Dead Band is moving
#define DB_UP 1
#define DB_DOWN 0
void main(void)
{
// Step 1. Initialize System Control:
// PLL, WatchDog, enable Peripheral Clocks
// This example function is found in the DSP2833x_SysCtrl.c file.
InitSysCtrl();
// Step 2. Initalize GPIO:
// This example function is found in the DSP2833x_Gpio.c file and
// illustrates how to set the GPIO to it's default state.
// InitGpio(); // Skipped for this example
// For this case just init GPIO pins for ePWM1, ePWM2, ePWM3
// These functions are in the DSP2833x_EPwm.c file
InitEPwm1Gpio();
InitEPwm2Gpio();
InitEPwm3Gpio();
// Step 3. Clear all interrupts and initialize PIE vector table:
// Disable CPU interrupts
DINT;
// Initialize the PIE control registers to their default state.
// The default state is all PIE interrupts disabled and flags
// are cleared.
// This function is found in the DSP2833x_PieCtrl.c file.
InitPieCtrl();
// Disable CPU interrupts and clear all CPU interrupt flags:
IER = 0x0000;
IFR = 0x0000;
// Initialize the PIE vector table with pointers to the shell Interrupt
// Service Routines (ISR).
// This will populate the entire table, even if the interrupt
// is not used in this example. This is useful for debug purposes.
// The shell ISR routines are found in DSP2833x_DefaultIsr.c.
// This function is found in DSP2833x_PieVect.c.
InitPieVectTable();
// Interrupts that are used in this example are re-mapped to
// ISR functions found within this file.
EALLOW; // This is needed to write to EALLOW protected registers
PieVectTable.EPWM1_INT = &epwm1_isr;
PieVectTable.EPWM2_INT = &epwm2_isr;
PieVectTable.EPWM3_INT = &epwm3_isr;
EDIS; // This is needed to disable write to EALLOW protected registers
// Step 4. Initialize all the Device Peripherals:
// This function is found in DSP2833x_InitPeripherals.c
// InitPeripherals(); // Not required for this example
EALLOW;
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR0.bit.TBCLKSYNC = 0;
EDIS;
InitEPwm1Example();
InitEPwm2Example();
InitEPwm3Example();
EALLOW;
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR0.bit.TBCLKSYNC = 1;
EDIS;
// Step 5. User specific code, enable interrupts
// Initalize counters:
EPwm1TimerIntCount = 0;
EPwm2TimerIntCount = 0;
EPwm3TimerIntCount = 0;
// Enable CPU INT3 which is connected to EPWM1-3 INT:
IER |= M_INT3;
// Enable EPWM INTn in the PIE: Group 3 interrupt 1-3
PieCtrlRegs.PIEIER3.bit.INTx1 = 1;
PieCtrlRegs.PIEIER3.bit.INTx2 = 1;
PieCtrlRegs.PIEIER3.bit.INTx3 = 1;
// Enable global Interrupts and higher priority real-time debug events:
EINT; // Enable Global interrupt INTM
ERTM; // Enable Global realtime interrupt DBGM
// Step 6. IDLE loop. Just sit and loop forever (optional):
for(;;)
{
asm(" NOP");
}
}
interrupt void epwm1_isr(void)
{
if(EPwm1_DB_Direction == DB_UP)
{
if(EPwm1Regs.DBFED < EPWM1_MAX_DB)
{
EPwm1Regs.DBFED++;
EPwm1Regs.DBRED++;
}
else
{
EPwm1_DB_Direction = DB_DOWN;
EPwm1Regs.DBFED--;
EPwm1Regs.DBRED--;
}
}
else
{
if(EPwm1Regs.DBFED == EPWM1_MIN_DB)
{
EPwm1_DB_Direction = DB_UP;
EPwm1Regs.DBFED++;
EPwm1Regs.DBRED++;
}
else
{
EPwm1Regs.DBFED--;
EPwm1Regs.DBRED--;
}
}
EPwm1TimerIntCount++;
// Clear INT flag for this timer
EPwm1Regs.ETCLR.bit.INT = 1;
// Acknowledge this interrupt to receive more interrupts from group 3
PieCtrlRegs.PIEACK.all = PIEACK_GROUP3;
}
interrupt void epwm2_isr(void)
{
if(EPwm2_DB_Direction == DB_UP)
{
if(EPwm2Regs.DBFED < EPWM2_MAX_DB)
{
EPwm2Regs.DBFED++;
EPwm2Regs.DBRED++;
}
else
{
EPwm2_DB_Direction = DB_DOWN;
EPwm2Regs.DBFED--;
EPwm2Regs.DBRED--;
}
}
else
{
if(EPwm2Regs.DBFED == EPWM2_MIN_DB)
{
EPwm2_DB_Direction = DB_UP;
EPwm2Regs.DBFED++;
EPwm2Regs.DBRED++;
}
else
{
EPwm2Regs.DBFED--;
EPwm2Regs.DBRED--;
}
}
EPwm2TimerIntCount++;
// Clear INT flag for this timer
EPwm2Regs.ETCLR.bit.INT = 1;
// Acknowledge this interrupt to receive more interrupts from group 3
PieCtrlRegs.PIEACK.all = PIEACK_GROUP3;
}
interrupt void epwm3_isr(void)
{
if(EPwm3_DB_Direction == DB_UP)
{
if(EPwm3Regs.DBFED < EPWM3_MAX_DB)
{
EPwm3Regs.DBFED++;
EPwm3Regs.DBRED++;
}
else
{
EPwm3_DB_Direction = DB_DOWN;
EPwm3Regs.DBFED--;
EPwm3Regs.DBRED--;
}
}
else
{
if(EPwm3Regs.DBFED == EPWM3_MIN_DB)
{
EPwm3_DB_Direction = DB_UP;
EPwm3Regs.DBFED++;
EPwm3Regs.DBRED++;
}
else
{
EPwm3Regs.DBFED--;
EPwm3Regs.DBRED--;
}
}
EPwm3TimerIntCount++;
// Clear INT flag for this timer
EPwm3Regs.ETCLR.bit.INT = 1;
// Acknowledge this interrupt to receive more interrupts from group 3
PieCtrlRegs.PIEACK.all = PIEACK_GROUP3;
}
void InitEPwm1Example()
{
EPwm1Regs.TBPRD = 6000; // Set timer period
EPwm1Regs.TBPHS.half.TBPHS = 0x0000; // Phase is 0
EPwm1Regs.TBCTR = 0x0000; // Clear counter
// Setup TBCLK
EPwm1Regs.TBCTL.bit.CTRMODE = TB_COUNT_UPDOWN; // Count up
EPwm1Regs.TBCTL.bit.PHSEN = TB_DISABLE; // Disable phase loading
EPwm1Regs.TBCTL.bit.HSPCLKDIV = TB_DIV4; // Clock ratio to SYSCLKOUT
EPwm1Regs.TBCTL.bit.CLKDIV = TB_DIV4;
EPwm1Regs.CMPCTL.bit.SHDWAMODE = CC_SHADOW; // Load registers every ZERO
EPwm1Regs.CMPCTL.bit.SHDWBMODE = CC_SHADOW;
EPwm1Regs.CMPCTL.bit.LOADAMODE = CC_CTR_ZERO;
EPwm1Regs.CMPCTL.bit.LOADBMODE = CC_CTR_ZERO;
// Setup compare
EPwm1Regs.CMPA.half.CMPA = 3000;
// Set actions
EPwm1Regs.AQCTLA.bit.CAU = AQ_SET; // Set PWM1A on Zero
EPwm1Regs.AQCTLA.bit.CAD = AQ_CLEAR;
EPwm1Regs.AQCTLB.bit.CAU = AQ_CLEAR; // Set PWM1A on Zero
EPwm1Regs.AQCTLB.bit.CAD = AQ_SET;
// Active Low PWMs - Setup Deadband
EPwm1Regs.DBCTL.bit.OUT_MODE = DB_FULL_ENABLE;
EPwm1Regs.DBCTL.bit.POLSEL = DB_ACTV_LO;
EPwm1Regs.DBCTL.bit.IN_MODE = DBA_ALL;
EPwm1Regs.DBRED = EPWM1_MIN_DB;
EPwm1Regs.DBFED = EPWM1_MIN_DB;
EPwm1_DB_Direction = DB_UP;
// Interrupt where we will change the Deadband
EPwm1Regs.ETSEL.bit.INTSEL = ET_CTR_ZERO; // Select INT on Zero event
EPwm1Regs.ETSEL.bit.INTEN = 1; // Enable INT
EPwm1Regs.ETPS.bit.INTPRD = ET_3RD; // Generate INT on 3rd event
}
void InitEPwm2Example()
{
EPwm2Regs.TBPRD = 6000; // Set timer period
EPwm2Regs.TBPHS.half.TBPHS = 0x0000; // Phase is 0
EPwm2Regs.TBCTR = 0x0000; // Clear counter
// Setup TBCLK
EPwm2Regs.TBCTL.bit.CTRMODE = TB_COUNT_UPDOWN; // Count up
EPwm2Regs.TBCTL.bit.PHSEN = TB_DISABLE; // Disable phase loading
EPwm2Regs.TBCTL.bit.HSPCLKDIV = TB_DIV4; // Clock ratio to SYSCLKOUT
EPwm2Regs.TBCTL.bit.CLKDIV = TB_DIV4; // Slow just to observe on the scope
// Setup compare
EPwm2Regs.CMPA.half.CMPA = 3000;
// Set actions
EPwm2Regs.AQCTLA.bit.CAU = AQ_SET; // Set PWM2A on Zero
EPwm2Regs.AQCTLA.bit.CAD = AQ_CLEAR;
EPwm2Regs.AQCTLB.bit.CAU = AQ_CLEAR; // Set PWM2A on Zero
EPwm2Regs.AQCTLB.bit.CAD = AQ_SET;
// Active Low complementary PWMs - setup the deadband
EPwm2Regs.DBCTL.bit.OUT_MODE = DB_FULL_ENABLE;
EPwm2Regs.DBCTL.bit.POLSEL = DB_ACTV_LOC;
EPwm2Regs.DBCTL.bit.IN_MODE = DBA_ALL;
EPwm2Regs.DBRED = EPWM2_MIN_DB;
EPwm2Regs.DBFED = EPWM2_MIN_DB;
EPwm2_DB_Direction = DB_UP;
// Interrupt where we will modify the deadband
EPwm2Regs.ETSEL.bit.INTSEL = ET_CTR_ZERO; // Select INT on Zero event
EPwm2Regs.ETSEL.bit.INTEN = 1; // Enable INT
EPwm2Regs.ETPS.bit.INTPRD = ET_3RD; // Generate INT on 3rd event
}
void InitEPwm3Example()
{
EPwm3Regs.TBPRD = 6000; // Set timer period
EPwm3Regs.TBPHS.half.TBPHS = 0x0000; // Phase is 0
EPwm3Regs.TBCTR = 0x0000; // Clear counter
// Setup TBCLK
EPwm3Regs.TBCTL.bit.CTRMODE = TB_COUNT_UPDOWN; // Count up
EPwm3Regs.TBCTL.bit.PHSEN = TB_DISABLE; // Disable phase loading
EPwm3Regs.TBCTL.bit.HSPCLKDIV = TB_DIV4; // Clock ratio to SYSCLKOUT
EPwm3Regs.TBCTL.bit.CLKDIV = TB_DIV4; // Slow so we can observe on the scope
// Setup compare
EPwm3Regs.CMPA.half.CMPA = 3000;
// Set actions
EPwm3Regs.AQCTLA.bit.CAU = AQ_SET; // Set PWM3A on Zero
EPwm3Regs.AQCTLA.bit.CAD = AQ_CLEAR;
EPwm3Regs.AQCTLB.bit.CAU = AQ_CLEAR; // Set PWM3A on Zero
EPwm3Regs.AQCTLB.bit.CAD = AQ_SET;
// Active high complementary PWMs - Setup the deadband
EPwm3Regs.DBCTL.bit.OUT_MODE = DB_FULL_ENABLE;
EPwm3Regs.DBCTL.bit.POLSEL = DB_ACTV_HIC;
EPwm3Regs.DBCTL.bit.IN_MODE = DBA_ALL;
EPwm3Regs.DBRED = EPWM3_MIN_DB;
EPwm3Regs.DBFED = EPWM3_MIN_DB;
EPwm3_DB_Direction = DB_UP;
// Interrupt where we will change the deadband
EPwm3Regs.ETSEL.bit.INTSEL = ET_CTR_ZERO; // Select INT on Zero event
EPwm3Regs.ETSEL.bit.INTEN = 1; // Enable INT
EPwm3Regs.ETPS.bit.INTPRD = ET_3RD; // Generate INT on 3rd event
}
//===========================================================================
// No more.
//===========================================================================(5)PWM 错误控制模块测试




c
//###########################################################################
//
// 文件名: Example_2833xEpwmTripZone.c
//
// 标题: PWM错误控制模块测试
//
// ASSUMPTIONS:
//
// 此程序需要 DSP2833x头文件.
//
// 初始化TZ1 (GPIO12) and TZ2 (GPIO13)为高
//
// 在测试期间, 观察按键SW1(TZ1)和SW2(TZ2)对ePWM1、ePWM2输出的影响
//
// EPWM1A对应引脚GPIO0
// EPWM1B对应引脚GPIO1
// EPWM2A对应引脚GPIO2
// EPWM2B对应引脚GPIO3
//
// 当单次触发后ePWM1立即响应
//
// 周期触发时ePWM2将响应,一旦TZ1和TZ2变为高电平后,
// ePWM2引脚状态立即被清除
//
//
// 根据在RAM中调试的需要,这个项目配置成"boot to SARAM".2833x引导模式
// 表如下显示. 常用的还有"boot to Flash"模式,当程序在RAM调试完善后就
// 可以将代码烧进Flash中并使用"boot to Flash"引导模式.
//
// $Boot_Table:
//
// GPIO87 GPIO86 GPIO85 GPIO84
// XA15 XA14 XA13 XA12
// PU PU PU PU
// ==========================================
// 1 1 1 1 Jump to Flash
// 1 1 1 0 SCI-A boot
// 1 1 0 1 SPI-A boot
// 1 1 0 0 I2C-A boot
// 1 0 1 1 eCAN-A boot
// 1 0 1 0 McBSP-A boot
// 1 0 0 1 Jump to XINTF x16
// 1 0 0 0 Jump to XINTF x32
// 0 1 1 1 Jump to OTP
// 0 1 1 0 Parallel GPIO I/O boot
// 0 1 0 1 Parallel XINTF boot
// 0 1 0 0 Jump to SARAM <- "boot to SARAM"
// 0 0 1 1 Branch to check boot mode
// 0 0 1 0 Boot to flash, bypass ADC cal
// 0 0 0 1 Boot to SARAM, bypass ADC cal
// 0 0 0 0 Boot to SCI-A, bypass ADC cal
// Boot_Table_End$
//
// 功能描述:
//
// 本例配置ePWM1 和 ePWM2
//
// 2个例子如下:
// * ePWM1使用TZ1 和TZ2 作为单次触发源
// * ePWM2 使用 TZ1 和 TZ2 作为周期触发源
//
//
// 通过示波器观察EPWM1A/B, EPWM2A/B波形,
// 可以发现按键SW1(TZ1)和SW2(TZ2)对EPWM1A/B, EPWM2A/B波形的影响
//
// 当按下按键SW1(TZ1)或SW2(TZ2)后EPWM1A变为高电平、EPWM1B变为低电平
// 松开按键后,输出波形不变;
// 当按下按键SW1(TZ1)或SW2(TZ2)后EPWM2A变为高电平、EPWM2B变为低电平
// 松开按键后,输出波形恢复之前的PWM波形
//
//###########################################################################
// 释放日期:2013.11.26
//###########################################################################
#include "DSP2833x_Device.h" // DSP2833x Headerfile Include File
#include "DSP2833x_Examples.h" // DSP2833x Examples Include File
// Prototype statements for functions found within this file.
void InitEPwm1Example(void);
void InitEPwm2Example(void);
interrupt void epwm1_tzint_isr(void);
interrupt void epwm2_tzint_isr(void);
// Global variables used in this example
Uint32 EPwm1TZIntCount;
Uint32 EPwm2TZIntCount;
void main(void)
{
// Step 1. Initialize System Control:
// PLL, WatchDog, enable Peripheral Clocks
// This example function is found in the DSP2833x_SysCtrl.c file.
InitSysCtrl();
// Step 2. Initalize GPIO:
// This example function is found in the DSP2833x_Gpio.c file and
// illustrates how to set the GPIO to it's default state.
// InitGpio(); // Skipped for this example
// For this case just init GPIO pins for ePWM1, ePWM2, and TZ pins
InitEPwm1Gpio();
InitEPwm2Gpio();
InitTzGpio();
// Step 3. Clear all interrupts and initialize PIE vector table:
// Disable CPU interrupts
DINT;
// Initialize the PIE control registers to their default state.
// The default state is all PIE interrupts disabled and flags
// are cleared.
// This function is found in the DSP2833x_PieCtrl.c file.
InitPieCtrl();
// Disable CPU interrupts and clear all CPU interrupt flags:
IER = 0x0000;
IFR = 0x0000;
// Initialize the PIE vector table with pointers to the shell Interrupt
// Service Routines (ISR).
// This will populate the entire table, even if the interrupt
// is not used in this example. This is useful for debug purposes.
// The shell ISR routines are found in DSP2833x_DefaultIsr.c.
// This function is found in DSP2833x_PieVect.c.
InitPieVectTable();
// Interrupts that are used in this example are re-mapped to
// ISR functions found within this file.
EALLOW; // This is needed to write to EALLOW protected registers
PieVectTable.EPWM1_TZINT = &epwm1_tzint_isr;
PieVectTable.EPWM2_TZINT = &epwm2_tzint_isr;
EDIS; // This is needed to disable write to EALLOW protected registers
// Step 4. Initialize all the Device Peripherals:
// This function is found in DSP2833x_InitPeripherals.c
// InitPeripherals(); // Not required for this example
EALLOW;
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR0.bit.TBCLKSYNC = 0;
EDIS;
InitEPwm1Example();
InitEPwm2Example();
EALLOW;
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR0.bit.TBCLKSYNC = 1;
EDIS;
// Step 5. User specific code, enable interrupts
// Initalize counters:
EPwm1TZIntCount = 0;
EPwm2TZIntCount = 0;
// Enable CPU INT3 which is connected to EPWM1-3 INT:
IER |= M_INT2;
// Enable EPWM INTn in the PIE: Group 2 interrupt 1-3
PieCtrlRegs.PIEIER2.bit.INTx1 = 1;
PieCtrlRegs.PIEIER2.bit.INTx2 = 1;
// Enable global Interrupts and higher priority real-time debug events:
EINT; // Enable Global interrupt INTM
ERTM; // Enable Global realtime interrupt DBGM
// Step 6. IDLE loop. Just sit and loop forever (optional):
for(;;)
{
asm(" NOP");
}
}
interrupt void epwm1_tzint_isr(void)
{
EPwm1TZIntCount++;
// Leave these flags set so we only take this
// interrupt once
//
// EALLOW;
// EPwm1Regs.TZCLR.bit.OST = 1;
// EPwm1Regs.TZCLR.bit.INT = 1;
// EDIS;
// Acknowledge this interrupt to receive more interrupts from group 2
PieCtrlRegs.PIEACK.all = PIEACK_GROUP2;
}
interrupt void epwm2_tzint_isr(void)
{
EPwm2TZIntCount++;
// Clear the flags - we will continue to take
// this interrupt until the TZ pin goes high
//
EALLOW;
EPwm2Regs.TZCLR.bit.CBC = 1;
EPwm2Regs.TZCLR.bit.INT = 1;
EDIS;
// Acknowledge this interrupt to receive more interrupts from group 2
PieCtrlRegs.PIEACK.all = PIEACK_GROUP2;
}
void InitEPwm1Example()
{
// Enable TZ1 and TZ2 as one shot trip sources
EALLOW;
EPwm1Regs.TZSEL.bit.OSHT1 = 1;
EPwm1Regs.TZSEL.bit.OSHT2 = 1;
// What do we want the TZ1 and TZ2 to do?
EPwm1Regs.TZCTL.bit.TZA = TZ_FORCE_HI;
EPwm1Regs.TZCTL.bit.TZB = TZ_FORCE_LO;
// Enable TZ interrupt
EPwm1Regs.TZEINT.bit.OST = 1;
EDIS;
EPwm1Regs.TBPRD = 6000; // Set timer period
EPwm1Regs.TBPHS.half.TBPHS = 0x0000; // Phase is 0
EPwm1Regs.TBCTR = 0x0000; // Clear counter
// Setup TBCLK
EPwm1Regs.TBCTL.bit.CTRMODE = TB_COUNT_UPDOWN; // Count up
EPwm1Regs.TBCTL.bit.PHSEN = TB_DISABLE; // Disable phase loading
EPwm1Regs.TBCTL.bit.HSPCLKDIV = TB_DIV4; // Clock ratio to SYSCLKOUT
EPwm1Regs.TBCTL.bit.CLKDIV = TB_DIV4;
EPwm1Regs.CMPCTL.bit.SHDWAMODE = CC_SHADOW; // Load registers every ZERO
EPwm1Regs.CMPCTL.bit.SHDWBMODE = CC_SHADOW;
EPwm1Regs.CMPCTL.bit.LOADAMODE = CC_CTR_ZERO;
EPwm1Regs.CMPCTL.bit.LOADBMODE = CC_CTR_ZERO;
// Setup compare
EPwm1Regs.CMPA.half.CMPA = 3000;
// Set actions
EPwm1Regs.AQCTLA.bit.CAU = AQ_SET; // Set PWM1A on Zero
EPwm1Regs.AQCTLA.bit.CAD = AQ_CLEAR;
EPwm1Regs.AQCTLB.bit.CAU = AQ_CLEAR; // Set PWM1A on Zero
EPwm1Regs.AQCTLB.bit.CAD = AQ_SET;
}
void InitEPwm2Example()
{
// Enable TZ1 and TZ2 as one cycle-by-cycle trip sources
EALLOW;
EPwm2Regs.TZSEL.bit.CBC1 = 1;
EPwm2Regs.TZSEL.bit.CBC2 = 1;
// What do we want the TZ1 and TZ2 to do?
EPwm2Regs.TZCTL.bit.TZA = TZ_FORCE_HI;
EPwm2Regs.TZCTL.bit.TZB = TZ_FORCE_LO;
// Enable TZ interrupt
EPwm2Regs.TZEINT.bit.CBC = 1;
EDIS;
EPwm2Regs.TBPRD = 6000; // Set timer period
EPwm2Regs.TBPHS.half.TBPHS = 0x0000; // Phase is 0
EPwm2Regs.TBCTR = 0x0000; // Clear counter
// Setup TBCLK
EPwm2Regs.TBCTL.bit.CTRMODE = TB_COUNT_UPDOWN; // Count up
EPwm2Regs.TBCTL.bit.PHSEN = TB_DISABLE; // Disable phase loading
EPwm2Regs.TBCTL.bit.HSPCLKDIV = TB_DIV4; // Clock ratio to SYSCLKOUT
EPwm2Regs.TBCTL.bit.CLKDIV = TB_DIV4; // Slow just to observe on the scope
// Setup compare
EPwm2Regs.CMPA.half.CMPA = 3000;
// Set actions
EPwm2Regs.AQCTLA.bit.CAU = AQ_SET; // Set PWM2A on Zero
EPwm2Regs.AQCTLA.bit.CAD = AQ_CLEAR;
EPwm2Regs.AQCTLB.bit.CAU = AQ_CLEAR; // Set PWM2A on Zero
EPwm2Regs.AQCTLB.bit.CAD = AQ_SET;
}
//===========================================================================
// No more.
//===========================================================================