C. Tree Pruning
time limit per test: 3 seconds
memory limit per test: 256 megabytes
t+pazolite, ginkiha, Hommarju - Paved Garden
You are given a tree with n nodes, rooted at node 1. In this problem, a leaf is a non-root node with degree 1.
In one operation, you can remove a leaf and the edge adjacent to it (possibly, new leaves appear). What is the minimum number of operations that you have to perform to get a tree, also rooted at node 1, where all the leaves are at the same distance from the root?
Input
Each test contains multiple test cases. The first line contains the number of test cases t (1≤t≤10^4). The description of the test cases follows.
The first line of each test case contains a single integer n (3≤n≤5⋅10^5) --- the number of nodes.
Each of the next n−1 lines contains two integers u, v (1≤u,v≤n, u≠v), describing an edge that connects u and v. It is guaranteed that the given edges form a tree.
It is guaranteed that the sum of n over all test cases does not exceed 5⋅10^5.
Output
For each test case, output a single integer: the minimum number of operations needed to achieve your goal.
Example
Input
3
7
1 2
1 3
2 4
2 5
4 6
4 7
7
1 2
1 3
1 4
2 5
3 6
5 7
15
12 9
1 6
6 14
9 11
8 7
3 5
13 5
6 10
13 15
13 6
14 12
7 2
8 1
1 4
Output
2
2
5Note
In the first two examples, the tree is as follows:
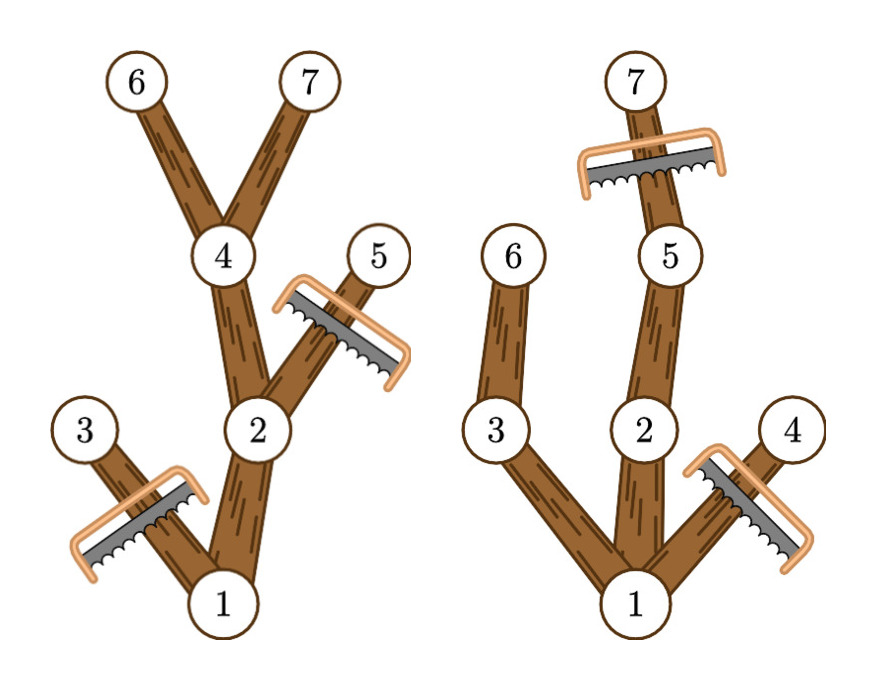
In the first example, by removing edges (1,3) and (2,5), the resulting tree has all leaves (nodes 6 and 7) at the same distance from the root (node 1), which is 3. The answer is 2, as it is the minimum number of edges that need to be removed to achieve the goal.
In the second example, removing edges (1,4) and (5,7) results in a tree where all leaves (nodes 4 and 5) are at the same distance from the root (node 1), which is 2.
【思路分析】
树上前后缀。删节点有两个case,case1:直接将所有长链删到某一长度;case2:存在若干短链需要全删,其它长链删到某一长度。显然我们不能简单推导保留链的长度是多少,因此从1到n枚举深度,维护每个节点的maxDeep,预处理树上前后缀即可。时间复杂度。
本题也可以采用重链剖分+维护更新来做,实现比较复杂,暂不讨论。
cpp
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define i64 long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 5e5 + 5;
vector<i64> G[N];
i64 mxd = LLONG_MIN / 2, suf[N], pre[N], mxDep[N];
void dfs(i64 i, i64 dep, i64 fa){
suf[dep]++;
mxDep[i] = dep;
if (G[i].size() == 1 && G[i][0] == fa) {
pre[dep]++;
mxd = max(dep, mxd);
return;
}
for (const auto &item: G[i]) {
if (item != fa) {
dfs(item, dep+1, i);
mxDep[i] = max(mxDep[item], mxDep[i]);
}
}
pre[mxDep[i]]++;
}
void solve() {
mxd = LLONG_MIN / 2;
i64 n;
cin>>n;
for (int i = 0; i < n + 2; ++i) {
pre[i] = 0;
suf[i] = 0;
mxDep[i] = 0;
G[i].clear();
}
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i) {
i64 u,v;
cin>>u>>v;
G[u].emplace_back(v);
G[v].emplace_back(u);
}
dfs(1,0,-1);
pre[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= mxd; ++i) {
pre[i] += pre[i - 1];
}
for (int i = mxd - 1; i >= 1; --i) {
suf[i] += suf[i + 1];
}
i64 res = LLONG_MAX / 2;
for (int i = mxd; i >= 1; --i) {
res = min(res, suf[i + 1] + pre[i - 1]);
}
cout<<res<<endl;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
int t = 1;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}