非线性规划,一般用matlab调用cplex和gurobi了,但这两个一般用于线性规划和二次规划
线性规划LP,二次规划(quadratic programming),如果要求更一般的非线性规划IPOT是个很好的选择,求解器很多,根据情况自己选择
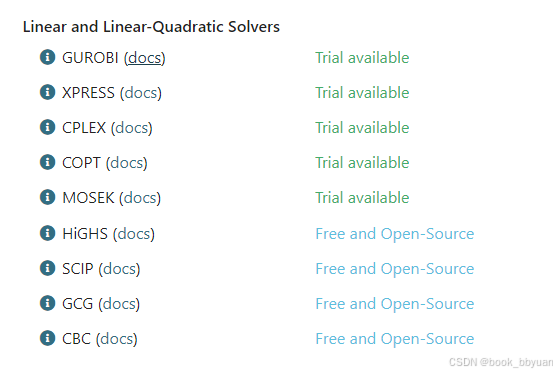
非线性
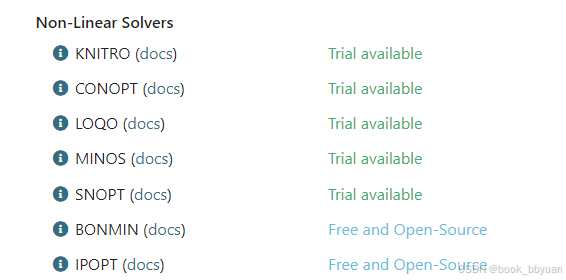
具体的,这篇文章介绍的很清楚了https://blog.csdn.net/mpt0816/article/details/127638557
我这里就是再选择一个问题进行求解
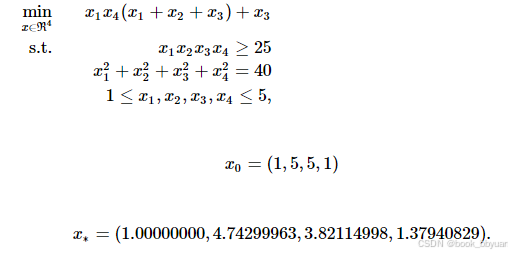
ipopt的可执行程序下载下来, Releases · coin-or/Ipopt · GitHub
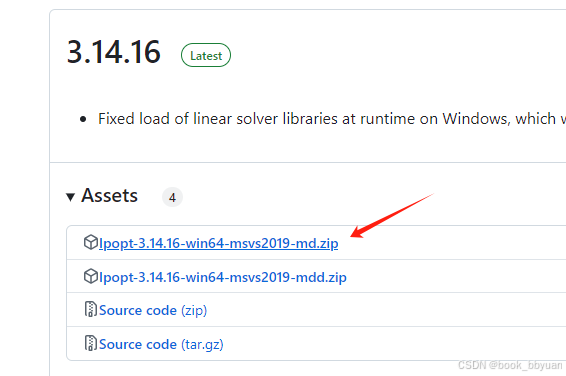
建立一个vs2022的工程,把include加到目录里面,把lib库都加进去,同样dll也准备好
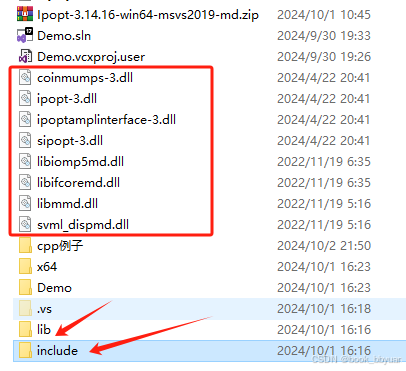
就这一个主文件放入工程
编译运行即可
四个自变量,两个约束
eval_f: 计算目标函数值,即需要最小化的目标。
eval_grad_f: 计算目标函数的梯度。分别是4个偏导数
eval_g: 计算约束条件的值。 n 是变量个数,m是约束条件个数,g是具体的约束函数
eval_jac_g: 计算约束条件的雅可比矩阵(两个约束条件的一阶偏导数)
eval_h: 计算目标函数和约束条件的二阶导数(即Hessian矩阵,二阶偏导数)。
现在使用matlab符号函数把 涉及到 用的 梯度、黑森矩阵都求一下
%
clear all
close all
clc
% 使用符号函数进行 求解梯度,黑森矩阵
syms f g1 g2
syms x1 x2 x3 x4
% 定义目标函数
f = x1 * x4 * (x1 + x2 + x3) + x3;
% 定义约束函数
g1 = x1 * x2 * x3 * x4;
g2 = x1^2 + x2^2 + x3^2 + x4^2;
% 计算目标函数的梯度和 Hessian
grad_f = gradient(f, [x1, x2, x3, x4]);
hess_f = hessian(f, [x1, x2, x3, x4]);
% 计算约束函数 g1 的梯度和 Hessian
grad_g1 = gradient(g1, [x1, x2, x3, x4]);
hess_g1 = hessian(g1, [x1, x2, x3, x4]);
% 计算约束函数 g2 的梯度和 Hessian
grad_g2 = gradient(g2, [x1, x2, x3, x4]);
hess_g2 = hessian(g2, [x1, x2, x3, x4]);得到如下结果:
目标函数 f 的梯度:
x1*x4 + x4*(x1 + x2 + x3)
x1*x4
x1*x4 + 1
x1*(x1 + x2 + x3)
目标函数 f 的 Hessian:
2\*x4, x4, x4, 2\*x1 + x2 + x3
x4, 0, 0, x1
x4, 0, 0, x1
2\*x1 + x2 + x3, x1, x1, 0
约束函数 g1 的梯度:
x2*x3*x4
x1*x3*x4
x1*x2*x4
x1*x2*x3
约束函数 g2 的梯度:
2*x1
2*x2
2*x3
2*x4
从g1 g2看出来
nele_jac = 8; 8个非零,两个约束条件,4个变量
nele_hess = 10; 4*5/2=10,看其中一个hess矩阵的上三角阵
约束函数 g1 的 Hessian:
0, x3\*x4, x2\*x4, x2\*x3
x3\*x4, 0, x1\*x4, x1\*x3
x2\*x4, x1\*x4, 0, x1\*x2
x2\*x3, x1\*x3, x1\*x2, 0
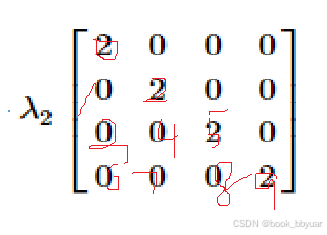
约束函数 g2 的 Hessian:
2, 0, 0, 0
0, 2, 0, 0
0, 0, 2, 0
0, 0, 0, 2
要替换的部分
1、eval_f 中 目标函数
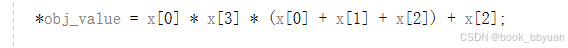
2、eval_grad_f 中的梯度
grad_f[0] = x[0] * x[3] + x[3] * (x[0] + x[1] + x[2]);
grad_f[1] = x[0] * x[3];
grad_f[2] = x[0] * x[3] + 1;
grad_f[3] = x[0] * (x[0] + x[1] + x[2]);
3、eval_g 约束条件
g[0] = x[0] * x[1] * x[2] * x[3] + my_data->g_offset[0];
g[1] = x[0] * x[0] + x[1] * x[1] + x[2] * x[2] + x[3] * x[3] + my_data->g_offset[1];
4、eval_jac_g 约束函数的jacobi矩阵
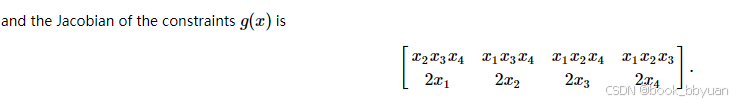
if中 (8个),位置是
00 01 02 03
10 11 12 13,
else 中
g1梯度,g2梯度

5、eval_h 黑森矩阵
固定抄写,4是变量个数
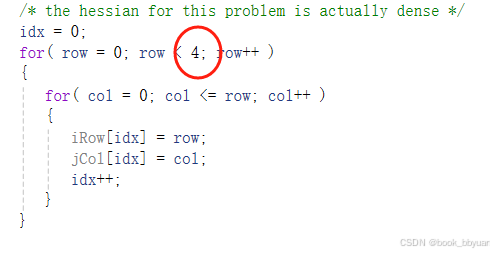
目标的黑森矩阵,注意走位,注意骚走位,注意下三角阵骚走位


约束的黑森
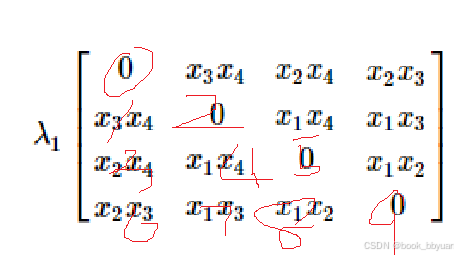
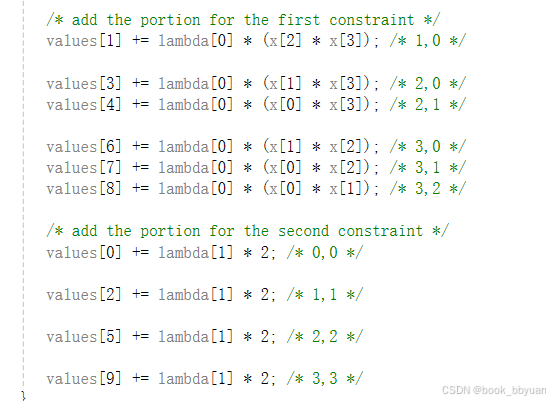
6、主函数
初始值和 上下限
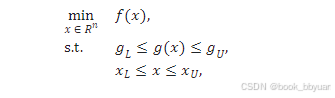

约束条件的jacobi矩阵和hess矩阵的非零元素

8个=2*自变量个数
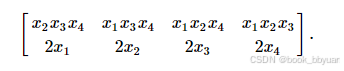
10个=自变量个数*(自变量个数+1)/2
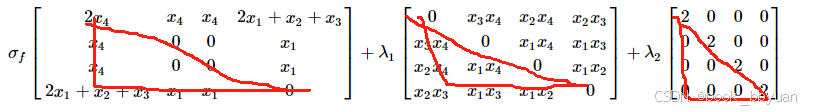
初始值

matlab符号函求解出来的各种算式写成c有点麻烦,我这边搞了一个函数可以很方便转c
Matlab
function f_str = changetoc(f)
syms x1 x2 x3 x4 %替换c语言风格
syms R %为了 R^2也能转
% f = x1^2 + x2^2 + x3^2 + x4^2; % 示例符号函数
% f = x1^2 + x2^2 + (x1 + x2)^2 + x3^2 + x4^2; % 示例符号函数,包含复杂表达式
% f = (r*sin(theta)*(3*cos(x1) - 4) + (x2*cos(theta)*(2*cos(x1) - 2))/n1 + (x2*sin(theta)*sin(x1))/n1)^2
% 将符号函数转换为字符串
f_str = char(f);
% 替换变量为 C 风格的数组索引 x[0], x[1], x[2], x[3]
f_str = regexprep(f_str, 'x1', 'x[0]');
f_str = regexprep(f_str, 'x2', 'x[1]');
f_str = regexprep(f_str, 'x3', 'x[2]');
f_str = regexprep(f_str, 'x4', 'x[3]');
% 定义一个集合(Cell数组)用于保存普通变量名
variables = {'x[0]','x[1]','x[2]','x[3]', 'R'};
%
% % 示例复杂表达式
% f = (r*sin(theta)*(3*cos(x1) - 4) + (x2*cos(theta)*(2*cos(x1) - 2))/n1 + (x2*sin(theta)*sin(x1))/n1)^2 - R^2 + ...
% (r*cos(theta) + r*sin(theta)*(6*x1 - 6*sin(x1)) + (x2*sin(theta)*(2*cos(x1) - 2))/n1 + ...
% (x2*cos(theta)*(3*x1 - 4*sin(x1)))/n1)^2;
% 将符号函数转换为字符串
% f_str = char(f);
% 1. 替换普通变量的平方为自乘形式
for i = 1:length(variables)
% 构建正则表达式,匹配形如 x1^2, x2^2 等
var_pattern = strcat(variables{i}, '^2');
% 构建替换字符串 (x1*x1), (x2*x2)
replacement = strcat('(', variables{i}, '*', variables{i}, ')');
% 进行替换
f_str = strrep(f_str, var_pattern, replacement);
end
% % 找到 x[i]^2 形式的幂运算,并替换为 (x[i]*x[i])
f_str = regexprep(f_str, '(\w+\[\d+\])\^2', '$1*$1');
% 2. 替换括号表达式的平方为自乘形式
% 匹配 (xxxx)^2,替换为 (xxxx)*(xxxx)
% f_str = regexprep(f_str, '\(([^\)]+)\)\^2', '($1)*($1)');
f_str = regexprep(f_str, '\((.*?)\)\^2', '($1)*($1)');
% 输出替换后的表达式
disp(f_str);
end