407. Trapping Rain Water II
Given an m x n integer matrix heightMap representing the height of each unit cell in a 2D elevation map, return the volume of water it can trap after raining.
Example 1:
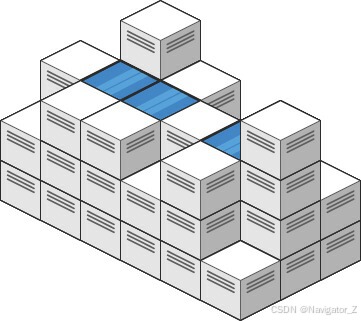
Input: heightMap = [[1,4,3,1,3,2],[3,2,1,3,2,4],[2,3,3,2,3,1]]
Output: 4
Explanation: After the rain, water is trapped between the blocks.We have two small ponds 1 and 3 units trapped.
The total volume of water trapped is 4.
Example 2:
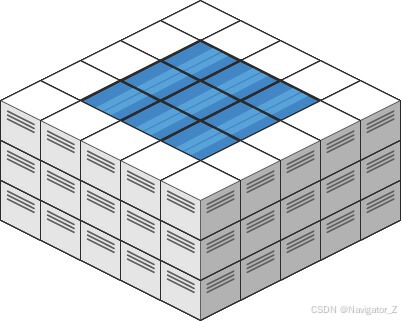
Input: heightMap = [[3,3,3,3,3],[3,2,2,2,3],[3,2,1,2,3],[3,2,2,2,3],[3,3,3,3,3]]
Output: 10
Constraints:
- m == heightMap.length
- n == heightMap[i].length
- 1 <= m, n <= 200
- 0 < = h e i g h t M a p [ i ] [ j ] < = 2 ∗ 1 0 4 0 <= heightMap[i][j] <= 2 * 10^4 0<=heightMap[i][j]<=2∗104
From: LeetCode
Link: 407. Trapping Rain Water II
Solution:
Ideas:
1. Dynamic Min-Heap Implementation:
- A MinHeap structure is created to manage the elements in the heap. It includes functions for initializing the heap, inserting elements, and extracting the minimum element.
- The capacity of the heap is doubled whenever it is full, avoiding the issues of insufficient space.
2. Element Structure:
- The Element structure is used to store the coordinates and height of each cell.
3. Boundary Processing:
- The code ensures boundary cells are added to the heap correctly and avoids overwriting memory by properly managing the heap size.
4. Clean-up:
- Proper memory deallocation is done to avoid memory leaks.
Code:
c
typedef struct {
int x, y;
int height;
} Element;
typedef struct {
Element *elements;
int size;
int capacity;
} MinHeap;
void initMinHeap(MinHeap *heap, int capacity) {
heap->elements = (Element *)malloc(sizeof(Element) * capacity);
heap->size = 0;
heap->capacity = capacity;
}
void swap(Element *a, Element *b) {
Element temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
void insertMinHeap(MinHeap *heap, Element element) {
if (heap->size == heap->capacity) {
heap->capacity *= 2;
heap->elements = (Element *)realloc(heap->elements, sizeof(Element) * heap->capacity);
}
heap->elements[heap->size] = element;
int i = heap->size++;
while (i > 0) {
int parent = (i - 1) / 2;
if (heap->elements[i].height < heap->elements[parent].height) {
swap(&heap->elements[i], &heap->elements[parent]);
i = parent;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
Element extractMin(MinHeap *heap) {
Element minElement = heap->elements[0];
heap->elements[0] = heap->elements[--heap->size];
int i = 0;
while (true) {
int left = 2 * i + 1;
int right = 2 * i + 2;
int smallest = i;
if (left < heap->size && heap->elements[left].height < heap->elements[smallest].height) {
smallest = left;
}
if (right < heap->size && heap->elements[right].height < heap->elements[smallest].height) {
smallest = right;
}
if (smallest == i) {
break;
}
swap(&heap->elements[i], &heap->elements[smallest]);
i = smallest;
}
return minElement;
}
bool isInBounds(int x, int y, int m, int n) {
return x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n;
}
int trapRainWater(int** heightMap, int heightMapSize, int* heightMapColSize) {
if (heightMapSize == 0 || *heightMapColSize == 0) {
return 0;
}
int m = heightMapSize;
int n = *heightMapColSize;
int totalWater = 0;
bool **visited = (bool **)malloc(m * sizeof(bool *));
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
visited[i] = (bool *)malloc(n * sizeof(bool));
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
visited[i][j] = false;
}
}
MinHeap heap;
initMinHeap(&heap, m * n);
// Add all boundary cells to the min-heap
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
visited[i][0] = true;
visited[i][n - 1] = true;
insertMinHeap(&heap, (Element){i, 0, heightMap[i][0]});
insertMinHeap(&heap, (Element){i, n - 1, heightMap[i][n - 1]});
}
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
visited[0][j] = true;
visited[m - 1][j] = true;
insertMinHeap(&heap, (Element){0, j, heightMap[0][j]});
insertMinHeap(&heap, (Element){m - 1, j, heightMap[m - 1][j]});
}
int directions[4][2] = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}};
// Process the heap
while (heap.size > 0) {
Element current = extractMin(&heap);
int x = current.x;
int y = current.y;
int currentHeight = current.height;
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
int nx = x + directions[j][0];
int ny = y + directions[j][1];
if (isInBounds(nx, ny, m, n) && !visited[nx][ny]) {
visited[nx][ny] = true;
// Calculate the water that can be trapped
if (currentHeight > heightMap[nx][ny]) {
totalWater += currentHeight - heightMap[nx][ny];
}
// Add the neighbor to the heap with the maximum height
insertMinHeap(&heap, (Element){nx, ny, heightMap[nx][ny] > currentHeight ? heightMap[nx][ny] : currentHeight});
}
}
}
// Clean up
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
free(visited[i]);
}
free(visited);
free(heap.elements);
return totalWater;
}