版本一
代码实现
java
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class CacheExample01 {
private final static HashMap<String, Integer> cache = new HashMap<>();
public static Integer check(String userId) throws InterruptedException {
Integer result = cache.get(userId);
//未查到结果则保存到缓存中,缓存中有则直接返回
if (result == null) {
result = computer(userId);
cache.put(userId, result);
}
return result;
}
private static Integer computer(String userId) throws InterruptedException {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);//模拟查询数据库耗时
return new Integer(userId);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//模拟实际查询
System.out.println("第一次查询:" + check("1314"));
System.out.println("第二次查询:" + check("1314"));
//结果为:
//第一次查询:1314
//第二次查询:1314
//其中第一次查询耗时>5s, 第二次查询耗时<1s;
}
}特点
- 代码复用性差,缓存计算与业务耦合
- 线程不安全,并发情况下会导致意外错误
版本二 用装饰者模式解耦
计算接口
Computable.java文件
java
package computable;
/*有一个计算函数computer, 用来代表耗时计算,每个计算器
都要实现这个接口,这样就可以无入侵实现缓存功能
*/
public interface Computable<A, V> {
V compute(A arg) throws Exception;
}具体耗时查询实现
ExpensiveFunciton.java文件
java
package computable;
public class ExpensiveFunciton implements Computable<String, Integer>{
@Override
public Integer compute(String arg) throws Exception {
System.out.println("进入耗时缓存");
Thread.sleep(5000);
return Integer.valueOf(arg);
}
}缓存
java
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import computable.Computable;
import computable.ExpensiveFunciton;
public class CacheExample02<A, V> implements Computable<A, V> {
private final Map<A, V> cache = new HashMap<>();
private final Computable<A, V> c;
private CacheExample02(Computable<A, V> c) {
this.c = c;
}
@Override
public synchronized V compute(A args) throws Exception {
V result = cache.get(args);
if (result == null) {
result = c.compute(args);
cache.put(args, result);
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
CacheExample02<String, Integer> example = new CacheExample02<>(new ExpensiveFunciton());
Integer result = example.compute("1314");
System.out.println("第一次结算结果:" + result);
result = example.compute("1314");
System.out.println("第二次计算结果:" + result);
/*结果为:
进入耗时缓存
第一次查询结果:1314
第二次查询结果:1314
*/
}
}特点
- 解决了缓存计算与业务耦合的问题,实现了无侵入式的计算接口
- 无法并行计算,效率低
版本三 ConcurrentHashMap保证线程安全
代码实现
用ConcurrentHashMap替代版本二的HashMap即可
java
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import computable.Computable;
import computable.ExpensiveFunciton;
public class CacheExample02<A, V> implements Computable<A, V> {
private final Map<A, V> cache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private final Computable<A, V> c;
private CacheExample02(Computable<A, V> c) {
this.c = c;
}
@Override
public V compute(A args) throws Exception {
V result = cache.get(args);
if (result == null) {
result = c.compute(args);
cache.put(args, result);
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
CacheExample02<String, Integer> example = new CacheExample02<>(new ExpensiveFunciton());
Integer result = example.compute("1314");
System.out.println("第一次结算结果:" + result);
result = example.compute("1314");
System.out.println("第二次计算结果:" + result);
}
}特点
- 用ConcurrentHashMap替代了HashMap,实现了线程安全
- 在计算完成前,多个要求计算相同值的请求到来,会导致计算多遍,导致低性能

版本四 用Future解决重复计算问题
代码实现
java
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;
import computable.Computable;
import computable.ExpensiveFunciton;
public class CacheExample03<A, V> implements Computable<A, V> {
private final Map<A, Future<V>> cache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private final Computable<A, V> c;
private CacheExample03(Computable<A, V> c) {
this.c = c;
}
@Override
public V compute(A arg) throws Exception {
Future<V> f = cache.get(arg);
if (f == null) {
Callable<V> callable = new Callable<V>() {
@Override
public V call() throws Exception {
return c.compute(arg);
}
};
FutureTask<V> ft = new FutureTask<>(callable);
f = ft;
cache.put(arg, ft);
ft.run();
}
return f.get();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
CacheExample03<String, Integer> example = new CacheExample03<>(new ExpensiveFunciton());
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Integer result = example.compute("1314");
System.out.println("第一次计算结果:" + result);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Integer result = example.compute("6666");
System.out.println("第二次计算结果:" + result);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Integer result = example.compute("1314");
System.out.println("第三次计算结果:" + result);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Integer result = example.compute("1314");
System.out.println("第四次计算结果:" + result);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
}
}代码结果为:

结果分析
需要注意的是,如果把计算值从"1314", "6666", "1314", "1314"全部改成"1314"的话,代码结果如下

或

但是当相同请求结果上升到六个甚至更多时,也只会有2-3个线程进入耗时缓存

证明了这个方法能解决大部分的重复计算问题,不能完全解决。因为在多个相同请求值同时进入时,在第一个请求还未达到 cache.put(arg, ft);这条代码时,其它线程仍会重复计算。
注意 :
如果线程的创建用的是Lambda 表达式,会导致进入耗时缓存略多于使用匿名内部类 Runnable 来创建线程,因为Lambda表达式性能略优于使用匿名内部类 Runnable。
使用Lambda表达式结果如下:

特点
- 解决了大部分的重复计算问题,但仍然存在小概率的重复计算情况

版本五 用原子组合操作解决小部分重复操作问题
代码实现
java
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;
import computable.Computable;
import computable.ExpensiveFunciton;
public class CacheExample02<A, V> implements Computable<A, V> {
private final Map<A, Future<V>> cache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private final Computable<A, V> c;
private CacheExample02(Computable<A, V> c) {
this.c = c;
}
@Override
public V compute(A arg) throws Exception {
Future<V> f = cache.get(arg);
if (f == null) {
Callable<V> callable = new Callable<V>() {
@Override
public V call() throws Exception {
return c.compute(arg);
}
};
FutureTask<V> ft = new FutureTask<>(callable);
f = cache.putIfAbsent(arg, ft);
if (f == null) {
f = ft;
ft.run();
}
}
return f.get();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
CacheExample02<String, Integer> example = new CacheExample02<>(new ExpensiveFunciton());
new Thread(() -> {
try {
Integer result = example.compute("1314");
System.out.println("第一次计算结果:" + result);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
Integer result = example.compute("1314");
System.out.println("第二次计算结果:" + result);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
Integer result = example.compute("1314");
System.out.println("第三次计算结果:" + result);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch blocks
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
Integer result = example.compute("1314");
System.out.println("第四次计算结果:" + result);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch blocks
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
Integer result = example.compute("1314");
System.out.println("第五次计算结果:" + result);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch blocks
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
Integer result = example.compute("1314");
System.out.println("第六次计算结果:" + result);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch blocks
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
Integer result = example.compute("1314");
System.out.println("第七次计算结果:" + result);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
Integer result = example.compute("1314");
System.out.println("第八次计算结果:" + result);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
Integer result = example.compute("1314");
System.out.println("第九次计算结果:" + result);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
Integer result = example.compute("1314");
System.out.println("第十次计算结果:" + result);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
}
}结果分析
代码结果 :

可以看到在多个线程同时请求相同值时,也只有一个线程进入了耗时计算(在多次重复实验后也是如此)
特点
- 完全解决了重复计算的问题,使得不同线程在执行的同时避免了重复计算的消耗,大大提升了性能
- 未考虑在业务中计算出错时的错误处理以及缓存污染问题
版本六 处理缓存污染以及错误处理
代码实现
MayfailFunction.java文件
主要用于模拟业务中可能出现的计算错误
java
package computable;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class MayfailFunction implements Computable<String, Integer>{
@Override
public Integer compute(String arg) throws Exception{
double random = Math.random();
if (random < 0.5) {
throw new IOException("计算出错");
}
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
return Integer.valueOf(arg);
}
}主要实现文件
java
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.CancellationException;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;
import computable.Computable;
import computable.ExpensiveFunciton;
import computable.MayfailFunction;
public class CacheExample04<A, V> implements Computable<A, V> {
private final Map<A, Future<V>> cache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private final Computable<A, V> c;
private CacheExample04(Computable<A, V> c) {
this.c = c;
}
@Override
public V compute(A arg) throws InterruptedException, CancellationException {
//具体计算部分用while(true)包裹起来,是为了在计算出错后能自动重复计算直至计算成功
while (true) {
Future<V> f = cache.get(arg);
if (f == null) {
Callable<V> callable = new Callable<V>() {
@Override
public V call() throws Exception {
return c.compute(arg);
}
};
FutureTask<V> ft = new FutureTask<>(callable);
f = cache.putIfAbsent(arg, ft);
if (f == null) {
f = ft;
ft.run();
}
}
try {
return f.get();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
cache.remove(arg);//在出现错误的时候将计算出错的值从缓存池中移除,避免缓存池的污染
throw e;
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
cache.remove(arg);
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (CancellationException e) {
cache.remove(arg);
throw e;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
CacheExample04<String, Integer> example = new CacheExample04<>(new MayfailFunction());
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Integer result = example.compute("1314");
System.out.println("第一次计算结果:" + result);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Integer result = example.compute("1314");
System.out.println("第二次计算结果:" + result);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Integer result = example.compute("1314");
System.out.println("第三次计算结果:" + result);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Integer result = example.compute("1314");
System.out.println("第四次计算结果:" + result);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Integer result = example.compute("1314");
System.out.println("第五次计算结果:" + result);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Integer result = example.compute("1314");
System.out.println("第六次计算结果:" + result);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
}
}结果分析
代码结果 :

成功地实现了在计算出错的情况下,仍然能自动重复计算直到计算成功,并且及时将计算出错的值从缓存中去除。
注意 :
如果在捕获错误时缺少cache.remove(arg);(即不及时将计算错误的值从缓存池中去除)会导致缓存池污染,导致相同请求值返回错误的值(在该代码中体现为一直出现计算错误并且不会停止)。
错误结果如下:

出现无止境的"计算出错"的报错
版本七 ScheduledExecutorService实现缓存过期
代码实现
java
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.CancellationException;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import computable.Computable;
import computable.ExpensiveFunciton;
import computable.MayfailFunction;
public class CacheExample05<A, V> implements Computable<A, V> {
private final Map<A, Future<V>> cache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private final Computable<A, V> c;
private CacheExample05(Computable<A, V> c) {
this.c = c;
}
@Override
public V compute(A arg) throws InterruptedException, CancellationException {
while (true) {
Future<V> f = cache.get(arg);
if (f == null) {
Callable<V> callable = new Callable<V>() {
@Override
public V call() throws Exception {
return c.compute(arg);
}
};
FutureTask<V> ft = new FutureTask<>(callable);
f = cache.putIfAbsent(arg, ft);
if (f == null) {
f = ft;
ft.run();
}
}
try {
return f.get();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
cache.remove(arg);
throw e;
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
cache.remove(arg);
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (CancellationException e) {
cache.remove(arg);
throw e;
}
}
}
private final static ScheduledExecutorService executor = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(6);
public V compute(A arg, long expireTime) throws CancellationException, InterruptedException {
if (expireTime > 0) {
executor.schedule(() -> {
expire(arg);
}, expireTime, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
};
return compute(arg);
}
public synchronized void expire(A key) {
Future<V> f = cache.get(key);
if (f != null) {
if (!f.isDone()) {
f.cancel(true);
System.out.println("任务被取消了");
}
System.out.println("过期时间到,缓存被清除");
cache.remove(key);
}
}
//随机赋予缓存失效时间,避免同时失效导致线程长时间阻塞
public V computeRandomExpire(A arg) throws CancellationException, InterruptedException {
long randomExpireTime = (long) Math.random() * 1000;
return compute(arg, randomExpireTime);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
CacheExample05<String, Integer> example = new CacheExample05<>(new MayfailFunction());
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Integer result = example.computeRandomExpire("1314");
System.out.println("第一次计算结果:" + result);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
Thread.sleep(10000);
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Integer result = example.computeRandomExpire("1314");
System.out.println("第二次计算结果:" + result);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Integer result = example.computeRandomExpire("1314");
System.out.println("第三次计算结果:" + result);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Integer result = example.computeRandomExpire("1314");
System.out.println("第四次计算结果:" + result);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Integer result = example.computeRandomExpire("1314");
System.out.println("第五次计算结果:" + result);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Integer result = example.computeRandomExpire("1314");
System.out.println("第六次计算结果:" + result);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
}
}特点:
- 实现了随机缓存过期失效功能
缓存项目性能测试
线程池压力测试
部分工具类用法功能:
-
isShutdown():
这个方法用来检查线程池是否已经被关闭。如果线程池已经调用了 shutdown() 方法,那么 isShutdown() 会返回 true。
shutdown() 方法会启动线程池的关闭过程,它会停止接收新的任务,并且会等待所有已提交的任务完成执行后关闭线程池。
-
isTerminated():
这个方法用来检查所有任务是否都已完成执行。如果线程池已经调用了 shutdown() 方法,并且所有提交的任务都已经执行完毕,那么isTerminated() 会返回 true。
isTerminated() 通常与 awaitTermination()方法一起使用,awaitTermination() 会阻塞当前线程直到所有任务执行完成或者超时。
简而言之,isShutdown() 表示线程池是否已经开始关闭过程,而 isTerminated() 表示线程池是否已经完全关闭,即所有任务都已执行完毕。在使用线程池时,通常先调用 shutdown() 方法来开始关闭过程,然后通过 isTerminated() 或 awaitTermination() 来检查关闭过程是否完成。
代码实现
创建含大量线程的线程池执行缓存的过程
java
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.CancellationException;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;
import computable.Computable;
import computable.ExpensiveFunciton;
public class CacheExample06<A, V> implements Computable<A, V> {
private final Map<A, Future<V>> cache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private final Computable<A, V> c;
private CacheExample06(Computable<A, V> c) {
this.c = c;
}
@Override
public V compute(A arg) throws InterruptedException, CancellationException {
while (true) {
Future<V> f = cache.get(arg);
if (f == null) {
Callable<V> callable = new Callable<V>() {
@Override
public V call() throws Exception {
return c.compute(arg);
}
};
FutureTask<V> ft = new FutureTask<>(callable);
f = cache.putIfAbsent(arg, ft);
if (f == null) {
f = ft;
ft.run();
}
}
try {
return f.get();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
cache.remove(arg);
throw e;
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
cache.remove(arg);
} catch (CancellationException e) {
cache.remove(arg);
throw e;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
CacheExample06<String, Integer> example = new CacheExample06<>(new ExpensiveFunciton());
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(6000);
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 6000; i ++ ) {
executor.submit(() -> {
Integer result = null;
try {
result = example.compute("1314");
} catch (CancellationException | InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("result:" + result);
});
};
executor.shutdown();
while (!executor.isTerminated()) {
}
System.out.println("总耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime));
}
}结果分析
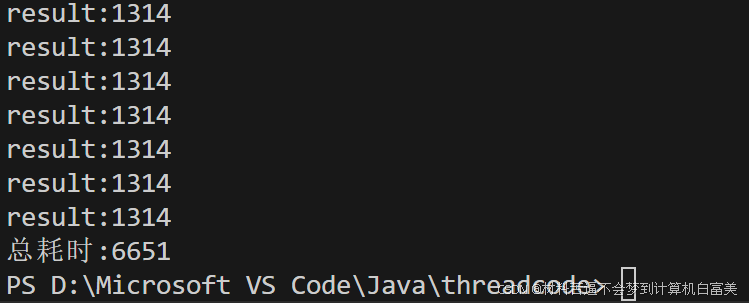
第一次缓存耗时5s + 后续从缓存中获取结果1.651s = 总耗时6651ms
存在问题
大量请求实际上不是同时到达,而是先后到达,导致给缓存池造成的压力较小,无法真正体现缓存池在多线程并发访问下的性能
CountDownLatch压力测试
使用CountDownLatch工具类来真正实现大量线程在同一时间下的并发访问,能给予缓存池更大的压力
工具类用法
- 计数器操作
countDown():每次调用这个方法,计数器的值就会减1。当计数器的值达到0时,CountDownLatch 就会"开启",所有等待在 await() 方法上的线程将继续执行。
getCount():返回当前计数器的值。 - 等待
await():当前线程会在这里阻塞,直到 CountDownLatch 被"开启"(即计数器的值达到0)。如果 CountDownLatch 没有被开启,await() 方法会无限期地等待。
await(long timeout, TimeUnit unit):与 await() 类似,但是它允许你设置一个超时时间。如果在指定的时间内计数器的值没有达到0,线程将不再阻塞,并返回一个布尔值,表示是否在超时前计数器已经达到0。
代码实现
java
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.CancellationException;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;
import computable.Computable;
import computable.ExpensiveFunciton;
public class CacheExample06<A, V> implements Computable<A, V> {
private final Map<A, Future<V>> cache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private final Computable<A, V> c;
private CacheExample06(Computable<A, V> c) {
this.c = c;
}
private final static CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(1);
private static CacheExample06<String, Integer> example = new CacheExample06<>(new ExpensiveFunciton());
@Override
public V compute(A arg) throws InterruptedException, CancellationException {
while (true) {
Future<V> f = cache.get(arg);
if (f == null) {
Callable<V> callable = new Callable<V>() {
@Override
public V call() throws Exception {
return c.compute(arg);
}
};
FutureTask<V> ft = new FutureTask<>(callable);
f = cache.putIfAbsent(arg, ft);
if (f == null) {
f = ft;
ft.run();
}
}
try {
return f.get();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
cache.remove(arg);
throw e;
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
cache.remove(arg);
} catch (CancellationException e) {
cache.remove(arg);
throw e;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(100);
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i ++ ) {
executor.submit(() -> {
Integer result = null;
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "被阻塞");
latch.await();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "开始运行");
result = example.compute("1314");
} catch (CancellationException | InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("result:" + result);
});
};
executor.shutdown();
Thread.sleep(5000);//保证所有线程都被阻塞后再统一放行
latch.countDown();
while (!executor.isTerminated()) {
}
System.out.println("总耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime));
}
}结果分析
部分截图,总的来说线程1 - 100先被阻塞,后统一被放行

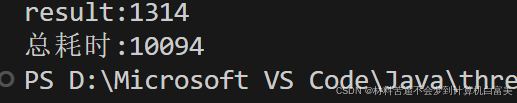
主线程sleep(5000) + 缓存计算5s + 剩余线程读取缓存94ms = 总耗时10094ms