1.题目
https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
示例 1:
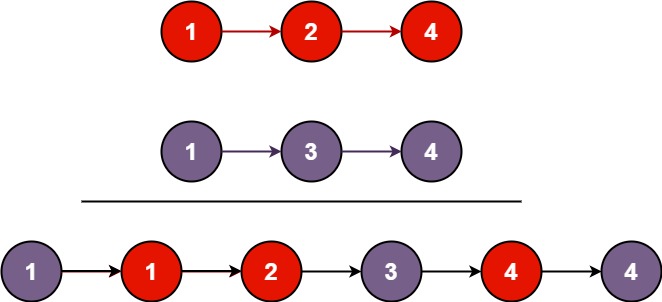
输入:l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4] 输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4]示例 2:
输入:l1 = [], l2 = [] 输出:[]示例 3:
输入:l1 = [], l2 = [0] 输出:[0]提示:
- 两个链表的节点数目范围是
[0, 50]-100 <= Node.val <= 100l1和l2均按 非递减顺序 排列- 代码模版
cpp/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * struct ListNode *next; * }; */ struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2) { }
2.自解
一个容易想到的解法:取小的尾插(开一个新的链表)
对于链表list1和list2,可以另外开一个新的链表,再将list1和list2的val复制进新链表的节点,最后返回新链表的头结点的地址即可
不加思索写出以下代码:
cpp
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2)
{
struct ListNode* cur1=list1;
struct ListNode* cur2=list2;
if (list1==NULL)
return list2;
if (list2==NULL)
return list1;
struct newListNode
{
int new_val;
struct ListNode* new_next;
};
struct newListNode* new_next=NULL;
struct newListNode* newhead=NULL;
struct newListNode* m_m_new=(struct newListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct newListNode));
newhead=m_m_new;
newhead->new_next=NULL;
struct newListNode* new_cur=newhead;
while(cur1!=NULL && cur2!=NULL)
{
if (cur1==NULL)
{
new_cur->new_val=cur2->val;
cur2=cur2->next;
//分配新结点的空间
struct newListNode* m_new=(struct newListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct newListNode));
new_cur->new_next=m_new;
new_cur=m_new;
continue;
}
if (cur2==NULL)
{
new_cur->new_val=cur1->val;
cur1=cur1->next;
struct newListNode* m_new=(struct newListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct newListNode));
new_cur->new_next=m_new;
new_cur=m_new;
continue;
}
if (cur1->val<=cur2->val)
{
new_cur->new_val=cur1->val;
cur1=cur1->next;
struct newListNode* m_new=(struct newListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct newListNode));
new_cur->new_next=m_new;
new_cur=m_new;
}
else
{
new_cur->new_val=cur2->val;
cur2=cur2->next;
//分配新结点的空间
struct newListNode* m_new=(struct newListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct newListNode));
new_cur->new_next=m_new;
new_cur=m_new;
}
}
new_cur->new_next=NULL;
new_cur=NULL;
return newhead;
}
运行时出现问题
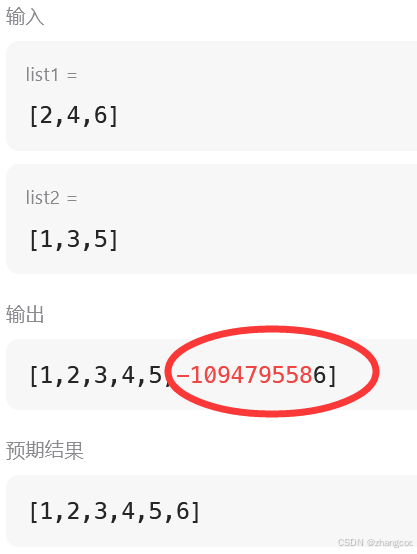
发现while循环的条件写错了!!
应该改成
cpp
while(!(cur1==NULL && cur2==NULL))完整代码
cpp
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2)
{
struct ListNode* cur1=list1;
struct ListNode* cur2=list2;
if (list1==NULL)
return list2;
if (list2==NULL)
return list1;
struct newListNode
{
int new_val;
struct ListNode* new_next;
};
struct newListNode* new_next=NULL;
struct newListNode* newhead=NULL;
struct newListNode* m_m_new=(struct newListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct newListNode));
newhead=m_m_new;
newhead->new_next=NULL;
struct newListNode* new_cur=newhead;
struct newListNode* before_new_cur=NULL;
while(!(cur1==NULL && cur2==NULL))
{
if (cur1==NULL)
{
new_cur->new_val=cur2->val;
cur2=cur2->next;
struct newListNode* m_new=(struct newListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct newListNode));
new_cur->new_next=m_new;
before_new_cur=new_cur;
new_cur=m_new;
new_cur->new_next=NULL;
continue;
}
if (cur2==NULL)
{
new_cur->new_val=cur1->val;
cur1=cur1->next;
struct newListNode* m_new=(struct newListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct newListNode));
new_cur->new_next=m_new;
before_new_cur=new_cur;
new_cur=m_new;
continue;
}
if (cur1->val<=cur2->val)
{
new_cur->new_val=cur1->val;
cur1=cur1->next;
struct newListNode* m_new=(struct newListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct newListNode));
new_cur->new_next=m_new;
new_cur=m_new;
}
else
{
new_cur->new_val=cur2->val;
cur2=cur2->next;
struct newListNode* m_new=(struct newListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct newListNode));
new_cur->new_next=m_new;
new_cur=m_new;
}
}
before_new_cur->new_next=NULL;
return newhead;
}
before_new_cur是当cur1===NULL或cur2==NULL,备份new_cur的前一个节点的地址
提交结果
3.其他解法
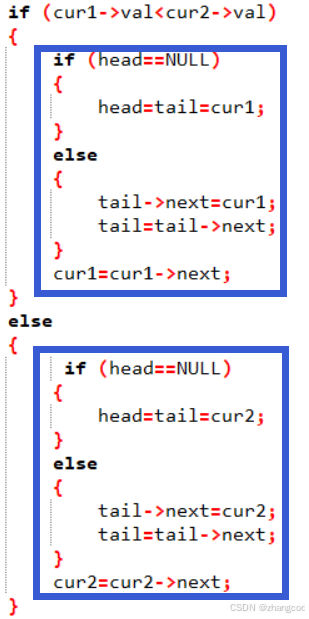
方法1:取小的尾插(不开新链表)
cpp
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2)
{
struct ListNode* cur1=list1;
struct ListNode* cur2=list2;
struct ListNode* head=NULL;
struct ListNode* tail=NULL;
if (list1==NULL)
return list2;
if (list2==NULL)
return list1;
while (cur1 && cur2)
{
if (cur1->val<cur2->val)
{
if (head==NULL)
{
head=tail=cur1;
}
else
{
tail->next=cur1;
tail=tail->next;
}
cur1=cur1->next;
}
else
{
if (head==NULL)
{
head=tail=cur2;
}
else
{
tail->next=cur2;
tail=tail->next;
}
cur2=cur2->next;
}
}
if(cur1)
tail->next=cur1;
if(cur2)
tail->next=cur2;
return head;
}分析
尾插要有尾指针tail(这样不用频繁找尾),同时要有指向头节点的指针head用于返回
cur1->val<cur2->val和cur1->val>=cur2->val操作方式是类似的