
目录
[实现"head -n 文件名"命令的功能](#实现“head -n 文件名”命令的功能)
[编程实现"ls -l 文件名"功能](#编程实现“ls -l 文件名”功能)

stat函数
int stat(const char *path, struct stat *buf);
功能:获取文件属性
参数: path:文件路径名
buf:保存文件属性信息的结构体
返回值:成功:0
失败:-1
struct stat {
ino_t st_ino; /* inode号 ls -il */
mode_t st_mode; /* 文件类型和权限 */
nlink_t st_nlink; /* 硬链接数 */
uid_t st_uid; /* 用户ID */
gid_t st_gid; /* 组ID */
off_t st_size; /* 大小 */
time_t st_atime; /* 最后访问时间 */
time_t st_mtime; /* 最后修改时间 */
time_t st_ctime; /* 最后状态改变时间 */
};打印inode号,链接数,大小:
#include<stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
struct stat st;
if(stat("a.c",&st)<0)
{
perror("stat err");
return -1;
}
printf("inode:%lu nlink:%d size:%ld\n",st.st_ino,st.st_nlink,
st.st_size);
return 0;
}获取文件属性
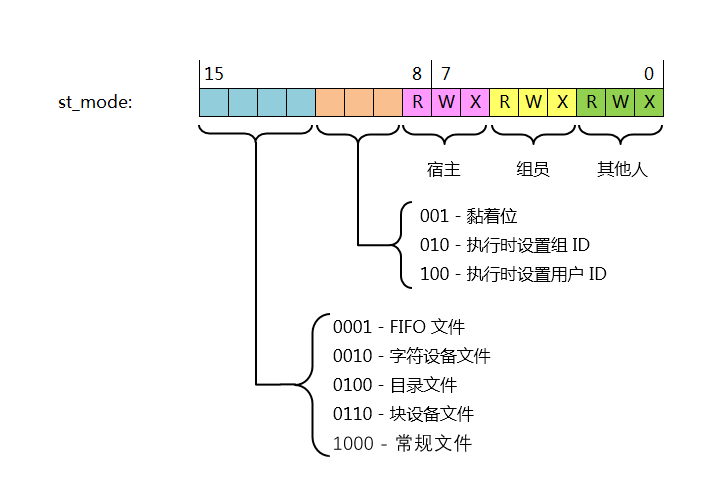
S_IFMT是一个掩码,它的值是0170000(注意这里用的是八进制前缀为0,二进制为0b1111000000000000), 可以用来过滤出四位表示的文件类型

例如:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
struct stat st;
if (stat(".", &st) < 0)
{
perror("stat err");
return -1;
}
printf("inode:%lu nlink:%d size:%ld\n", st.st_ino, st.st_nlink,
st.st_size);
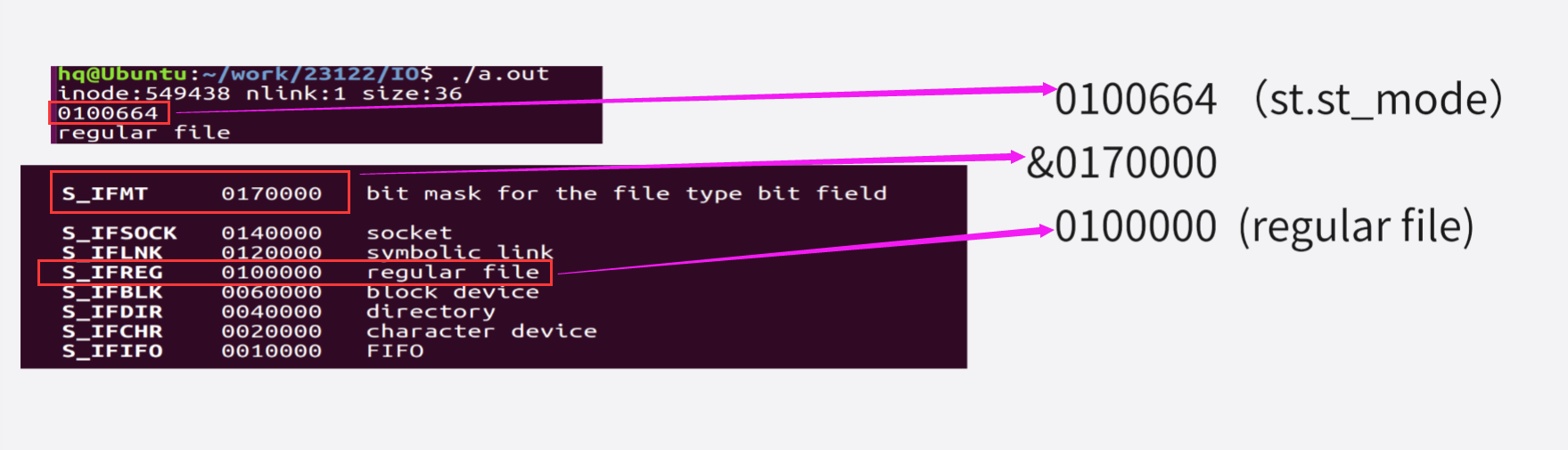
printf("%#o\n", st.st_mode);
//判断文件类型
if ((st.st_mode & __S_IFMT) == __S_IFREG)
printf("regular file\n");
else if ((st.st_mode & __S_IFMT) == __S_IFDIR)
printf("directory\n");
//或者用宏函数
if (S_ISREG(st.st_mode))
printf("-");
else if (S_ISDIR(st.st_mode))
printf("d");
return 0;
}获取文件权限
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
struct stat st;
if (stat(".", &st) < 0)
{
perror("stat err");
return -1;
}
printf("inode:%lu nlink:%d size:%ld\n", st.st_ino, st.st_nlink,
st.st_size);
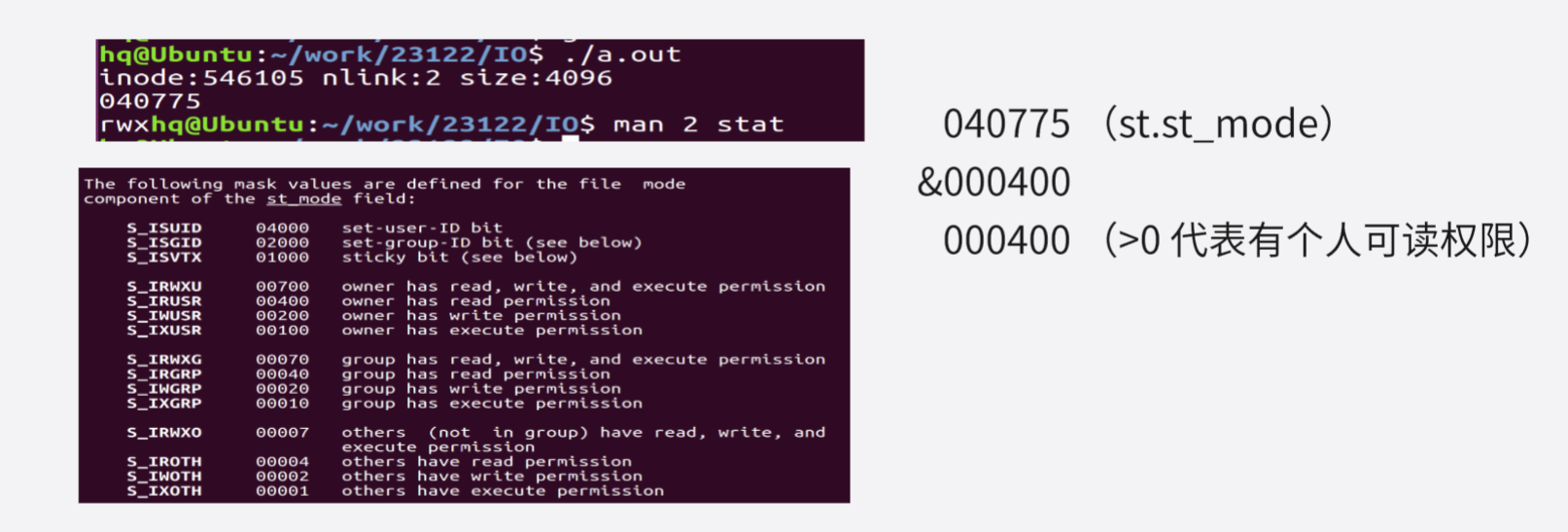
printf("%#o\n", st.st_mode);
//判断文件权限
//个人权限
if (st.st_mode & S_IRUSR)
putchar('r');
else
putchar('-');
if (st.st_mode & S_IWUSR)
putchar('w');
else
putchar('-');
if (st.st_mode & S_IXUSR)
putchar('x');
else
putchar('-');
return 0;
}实现"head -n 文件名"命令的功能
例:head -3 test.c -> ./a.out -3 test.c
atoi : "1234" -- 1234
思路:1. 打开文件 2. 获取到行数 3.循环读,读到内容判断\n则n++,打印。4. 直到n为行数则停止
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
FILE *fp;
int num, n = 0;
char buf[32] = "";
if (argc != 3)
{
printf("Usage: %s -n <file>\n", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
fp = fopen(argv[2], "r");
if (fp == NULL)
{
perror("fopen err");
return -1;
}
num = atoi(argv[1] + 1); //./a.out -3 a.c,+1是为了去掉-
if (num == 0) //判断-0的情况
return 0;
while (fgets(buf, 32, fp)) //或者fgets(buf,32,fp)!=NULL
{
//如果最后一个是换行则,行数加一。
if (buf[strlen(buf) - 1] == '\n')
n++;
//先打印,之后如果达到所记录行数则终止循环。
printf("%s", buf);
if (num == n)
break;
}
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}编程实现"ls -l 文件名"功能
getpwuid
getgrgid
localtime或ctime
ctime函数在C库中,头文件为<time.h>
函数原型:
char *ctime (const time_t *__timer)
作用:返回一个表示当地时间的字符串,当地时间是基于参数 timer
格式例如: Wed Aug 29 19:48:54 2018
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <pwd.h>
#include <grp.h>
#include <time.h>
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
struct stat st;
if (stat(argv[1], &st) < 0)
{
perror("stat err");
return -1;
}
//判断文件类型
switch (st.st_mode & S_IFMT)
{
case S_IFREG:
printf("-");
break;
case S_IFDIR:
printf("d");
break;
case S_IFCHR:
printf("c");
break;
case S_IFIFO:
printf("f");
break;
case S_IFLNK:
printf("l");
break;
case S_IFBLK:
printf("b");
break;
case S_IFSOCK:
printf("s");
break;
default:
printf("mode err\n");
break;
}
//判断文件权限
//个人权限
if (st.st_mode & S_IRUSR)
printf("r");
else
printf("-");
if (st.st_mode & S_IWUSR)
printf("w");
else
printf("-");
if ((st.st_mode & S_IXUSR))
printf("x");
else
printf("-");
//小组权限
if (st.st_mode & S_IRGRP)
printf("r");
else
printf("-");
if (st.st_mode & S_IWGRP)
printf("w");
else
printf("-");
if ((st.st_mode & S_IXGRP))
printf("x");
else
printf("-");
//其他人权限
if (st.st_mode & S_IROTH)
printf("r");
else
printf("-");
if (st.st_mode & S_IWOTH)
printf("w");
else
printf("-");
if ((st.st_mode & S_IXOTH))
printf("x");
else
printf("-");
//链接数
printf(" %d",st.st_nlink);
//用户名 用getpwuid函数
printf(" %s",getpwuid(st.st_uid)->pw_name);
//组名 用getgrgid函数
printf(" %s",getgrgid(st.st_gid)->gr_name);
//文件大小
printf(" %ld",st.st_size);
//最后修改时间
printf(" %.12s",ctime(&st.st_mtime)+4); //+4是为了跳过前4位(偏移4个地址), .12是为了只打印12个字符
//名字
printf(" %s\n",argv[1]);
return 0;
}stat/fstat/lstat的区别?
stat函数返回一个与此命名文件有关的信息结构
fstat函数获得已在描述符filedes上打开的文件的有关信息,也就是参数是文件描述符,其他与stat相同。
lstat函数类似于stat,但是当命名的文件是一个符号连接时,lstat返回该符号连接的有关信息,而不是由该符号连接引用的文件的信息.