为了测试GPU函数的耗时,可以使用 CUDA 提供的计时功能:cudaEventCreate , cudaEventRecord , 和 cudaEventElapsedTime。这些函数可以帮助你测量某个 CUDA 操作(如设置设备)所花费的时间。
一、记录耗时案例
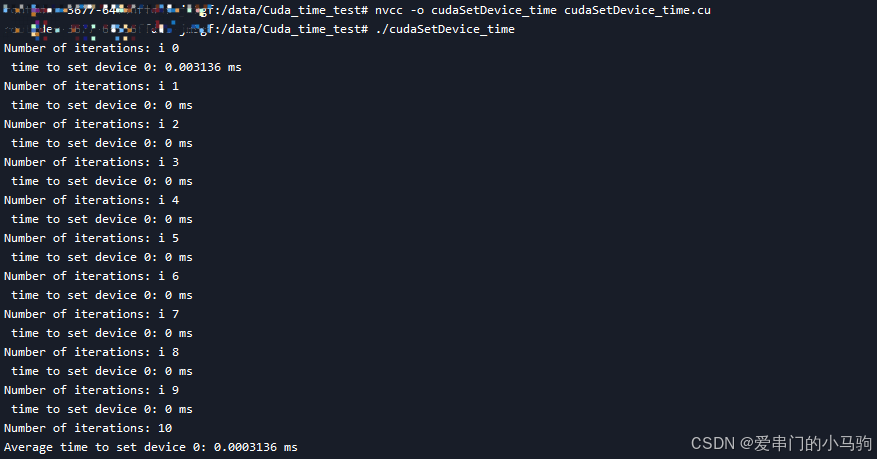
以下是一个示例程序,它测量调用 cudaSetDevice 所花费的时间:
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
__global__ void dummyKernel() {
// Dummy kernel to ensure CUDA context is initialized
}
int main() {
// CUDA device IDs
int device1 = 0;
int numIterations = 10; // Number of times to call cudaSetDevice
// Create CUDA events
cudaEvent_t start, stop;
cudaEventCreate(&start);
cudaEventCreate(&stop);
// Vector to store elapsed times
std::vector<float> elapsedTimes(numIterations);
// Set initial device (optional, but ensures a known starting state)
cudaSetDevice(device1);
// Measure time for multiple cudaSetDevice calls
for (int i = 0; i < numIterations; ++i) {
// Record the start event
cudaEventRecord(start, 0);
// Set the device (this is the operation we are timing)
cudaSetDevice(device1);
// Record the stop event
cudaEventRecord(stop, 0);
// Measure the elapsed time between the start and stop events
cudaEventElapsedTime(&elapsedTimes[i], start, stop);
// Output results
std::cout << "Number of iterations: i " << i << std::endl;
std::cout << " time to set device " << device1 << ": " << elapsedTimes[i] << " ms" << std::endl;
}
// Calculate statistics (e.g., average time)
float totalTime = 0.0f;
for (float time : elapsedTimes) {
totalTime += time;
}
float averageTime = totalTime / numIterations;
// Output results
std::cout << "Number of iterations: " << numIterations << std::endl;
std::cout << "Average time to set device " << device1 << ": " << averageTime << " ms" << std::endl;
// Optionally, run a dummy kernel to ensure CUDA is initialized and ready
dummyKernel<<<1, 1>>>();
cudaDeviceSynchronize();
// Clean up
cudaEventDestroy(start);
cudaEventDestroy(stop);
return 0;
}二、编译和运行
2.1 编译 : 使用 nvcc 编译这个 CUDA 程序。(上面程序文件铭为test_cudaSetDevice_multiple.cu)
bash
nvcc -o test_cudaSetDevice_multiple test_cudaSetDevice_multiple.cu2.2 运行: ,然后运行生成的可执行文件。
bash
./test_cudaSetDevice_multiple哈哈哈,就得到运行结果啦!