这篇七个点:1 环境搭建, 2 JSX, 3 组件,4 数据流,5 生命周期,6 React与DOM,7 实例
1 环境搭建
1.1 引用React CDN
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<script src="https://cdn.staticfile.org/react/16.4.0/umd/react.development.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.staticfile.org/react-dom/16.4.0/umd/react-dom.development.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.staticfile.org/babel-standalone/6.26.0/babel.min.js"></script>
<div id="example"></div>
<script type="text/babel">
ReactDOM.render(
<h1>bolala</h1>,
document.getElementById('example')
)
</script>
</body>
</html>1.2 利用create-react-app脚手架
npm install -g cnpm --registry=https://registry.npm.taobao.org//使用淘宝镜像
npm config set registry https://registry.npm.taobao.org
set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned //执行本地脚本
A
cnpm install -g create-react-app//安装脚手架
create-react-app my-app //创建文件
cd my-app/
npm start//配置完成2 JSX
2.1 JSX为什么出现
React中创建虚拟元素分为:DOM元素和组件元素,分别对应原生元素与自定义元素。
-
DOM元素
<button class="btn">bolala</button>
<script> var btn = { type: 'button', props: { className: 'btn', children: { type: 'b', props: { children: "bolala"} } } }; </script>
这样就在JS中创建了DOM的虚拟元素。
-
组件元素
let Button=({color,test})=>{
return {
type: 'button',
props: {
className:btn-${color}, children: {//模板字符串用反引号
type: 'b',
props: {
children: test}
}
}
};
};
封装的button元素,这种表达层层嵌套后会很复杂,JSX语法就产生了:
2.2 JSX基础语法
2.2.1 XML语法
<script type="text/babel">
const Title=()=>(
<h3>child</h3>
);
const List=()=>(
<div>
<Title />
<ul>
<li>1</li>
<li>2</li>
<li>3</li>
</ul>
</div>
);
ReactDOM.render(
<List/>,
document.getElementById('example')
)
</script>注意点:
- 定义标签时,只允许被一个标签包裹!
- 标签一定要闭合。
2.2.2 元素类型
在JSX中,小写首字母对应DOM元素,组件元素对应大写首字母。
JSX还可以通过命名空间的方式使用组件元素。
要注意的是,在一个组件的子元素位置使用注释要用{}包起来。
2.2.3 元素属性
在JSX中,DOM元素和组件元素都有属性,DOM属性是标准规范属性,class改为className;for改为htmlFor,其他不变。
组件元素的属性是自定义属性,为实现组件所需要的参数。在写自定义属性时,要由标准写法改成小驼峰写法。
属性值要使用表达式,可以 用{}替换"";
3 组件
3.1 组件的演变
3.2 React组件的构建
React组件由三部分组成:属性(props),状态(state)以及生命周期方法。
React组件可以接收参数,也可能有自身状态。一旦接收到的参数或自身状态改变,组件就会执行相应的生命周期方法,最后渲染。
-
组件的构造方法。
<script type="text/babel"> var Bolala=React.createClass({ render:function () { return (
三种方法:1 React.createClass 最新版本已经放弃{this.props.name}
) } }); ReactDOM.render( <Bolala name="bolala"/>, document.getElementById('example') ) </script>
2 ES6 classes方法
import React,{Component} from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
class Button extends Component{
constructor(props){
super(props);
}
static defaultProps={
name:"默认"
};
render(){
return (
<button>{this.props.name}</button>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(
<Button name={'bolala'}/>,
document.getElementById('root')
);
文件结构.png
3 无状态函数
function Bottom(props) {
const sayHi=()=>{
console.log(`Hello ${props.name}`);
};
return(
<div>
<h1>{props.name}</h1>
<button onClick={sayHi}>显示</button>
</div>
)
}
ReactDOM.render(
<Bottom name={'bolala'}/>,
document.getElementById('root')
);无状态组件只传入props和context两个参数,不存在state,也没有生命周期方法,组件本身就是render方法。
4 数据流
state与props是最重要的概念,如果顶层组件初始化props,React会向下遍历整个组件树,重新渲染。state只关心每个组件自己内部的状态。
4.1 state
一般优先使用Redux,它自身也能管理组件的内部状态。
当使用setState方法时,该组件会尝试重新渲染。
class Counter extends Component{
constructor(props){
super(props);
this.state={count:2};
this.handleClick= this.handleClick.bind(this);
}
handleClick(){
this.setState({
count:this.state.count+1
})
}
render(){
return (
<div>
<p>{this.state.count}</p>
<button onClick={this.handleClick}>增加</button>
</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(
<Counter/>,
document.getElementById('root')
);注意setState是一个异步方法,一个生命周期的所有setState方法会合并操作。
4.2 props
React的单向数据流,主要流动管道就是props,组件的props一定来自于默认属性或通过父组件传递。
React通过defaultProps静态变量的方式来定义。
class SayName extends Component{
constructor(props){super(props);this.state={};}
static defaultProps={
name:"bolala"
};
render(){
return (
<div>{this.props.name}</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(
<SayName name="hashiqi"/>,
document.getElementById('root')
);React.PropTypes 在 React v15.5 版本后已经移到了 prop-types 库。
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/prop-types/15.6.1/prop-types.js"></script>
class MyTitle extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<h1>Hello, {this.props.title}</h1>
);
}
}
MyTitle.propTypes = {
title: PropTypes.string
};
ReactDOM.render(
<MyTitle title={title} />,
document.getElementById('example')
);5 生命周期
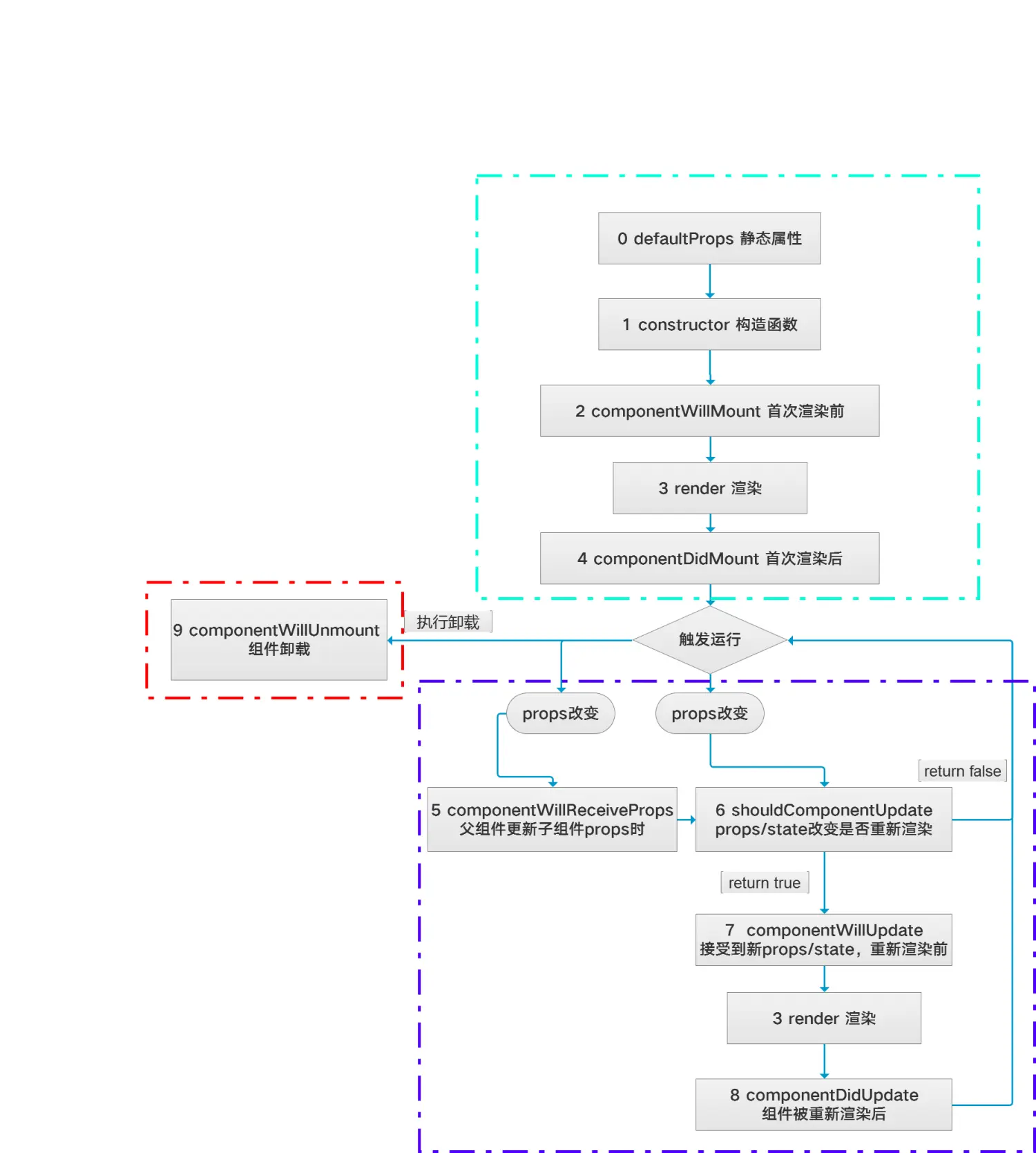
React生命周期分成三类:挂载,更新,卸载
5.1 组件挂载期
class App extends Component{
constructor(props){
super(props);this.state={};
console.log("1 构造函数和state")
}
static defaultProps={
name:"bolala"
};
componentWillMount(){
console.log("2 首次渲染前");
};
render(){
console.log("3 渲染");
return (
<div>{this.props.name}</div>
)
}
componentDidMount(){
console.log("4 render渲染后");
}
}
ReactDOM.render(
<App name="hashiqi"/>,
document.getElementById('root')
);5.2 组件更新期
class APPFather extends Component{
constructor(props){
super(props);this.state={};
this.update=this.update.bind(this);
}
update(){
this.setState({
name:"Vue"
})
}
render(){
return (
<div>
<App name1={this.state.name}/>
<button onClick={this.update}>修改</button>
</div>
)
}
}
class App extends Component{
constructor(props){
super(props);this.state={};
console.log("1 构造函数和state")
}
componentWillMount(){
console.log("2 首次渲染前");
};
render(){
console.log("3 渲染");
return (
<div>{this.props.name1?this.props.name1:"bolala"}</div>
)
}
componentDidMount(){
console.log("4 render渲染后");
}
componentWillReceiveProps(){
console.log("5 父组件更新子组件props时");
}
shouldComponentUpdate(){
console.log("6 props/state改变是否重新渲染");
return true;
}
componentWillUpdate(){
console.log("7 接受到新props/state,重新渲染前");
}
componentDidUpdate(){
console.log("8 组件被重新渲染后");
}
// 执行的顺序是:1,2,3,4,5,6,7,3,8
}
ReactDOM.render(
<APPFather/>,
document.getElementById('root')
);5.3 组件卸载期
componentWillUnmount() {
console.log('Component WILL UNMOUNT!')
}
index.png
6 React与DOM
6.1 ReactDOM
-
findDOMNode
组件的生命周期中,真正被添加DOM中的方法是componentDidMount和componentDidUpdate,ReactDOM。findDOMNode可以获取到真正的DOM元素。class SayName extends Component{
constructor(props){super(props);this.state={};}
static defaultProps={
name:"bolala"
};
componentDidMount(){
console.log(ReactDOM.findDOMNode(this));
//返回真实的DOM
}
render(){
return (
)
}
} -
render
参数1:组件,参数2:DOM元素,参数3:装载完毕执行的回调函数ReactDOM.render(
<SayName />,
document.getElementById('root'),
function () {
console.log("加载完毕");
}
);
6.2 refs
利用render可以得到组件的实例,但是在组件内部JSX并不会反悔一个组件的实例,refs就是为此出现的。refs组件被调用时会新建一个该组件的实例,而refs就会指向这个实例。
class Refs extends Component{
constructor(props){
super(props);this.state={};
this.handle=this.handle.bind(this)
}
handle(){
this.refs.name.focus();
console.log(this.refs.name);//获得dom元素
}
render(){
return (
<div>
<input type="text" ref="name"/>
<input
type="button"
value="点击"
onClick={this.handle}
/>
</div>
)
}
}对于DOM操作,不仅可以使用findDOMNode获取该组件DOM,还可以使用refs获取内部的DOM。
要获取一个React组件的引用,即可以使用this来获取当前react组件, 也可以使用refs获取子组件的引用。
class Clild extends Component{
constructor(props){
super(props);this.state={};
}
render(){
return(
<div>
<h1>标题</h1>
<h1>bolalalala</h1>
</div>
)
}
}
class Refs extends Component{
constructor(props){
super(props);this.state={};
this.handle=this.handle.bind(this)
}
handle(){
this.refs.name.focus();
console.log(this.refs.name);//获取input元素
console.log(this.refs.title);//这个是实例
console.log(ReactDOM.findDOMNode(this.refs.title));
//这个是子组件的DOM
console.log(ReactDOM.findDOMNode(this));
//这个是整个组件的DOM
}
render(){
return (
<div>
<Clild ref="title"/>
<input type="text" ref="name"/>
<input
type="button"
value="点击"
onClick={this.handle}
/>
</div>
)
}
}值得注意的是,findDOMNode和refs都无法用于无状态组建中,无状态组件挂载时只是方法调用,没有新建实例
7 实例
略
最后编辑于:2024-11-17 10:28:03
© 著作权归作者所有,转载或内容合作请联系作者

喜欢的朋友记得点赞、收藏、关注哦!!!