类与对象
类的语法
案列:定时器
功能:
- 设置倒计时:分,秒
- tick() 走 1 秒
- 读取当前剩余:分,秒
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 定时器的定义
class Timer
{
public:
void set(int min,int sec);
void tick();
int get_min();
int get_sec();
private:
int min;
int sec;
};
// 定时器的实现
void Timer::set(int m, int s)
{
min = m;
sec = s;
}
// 走1秒
void Timer::tick()
{
if(sec>0){
sec--;
}else if(min>0){
min--;
sec = 59;
}
if(min==0 && sec==0)cout << "beep ... beep ... " <<endl;
}
// 读取时间
int Timer::get_min() { return min; }
int Timer::get_sec() { return sec; }
int main()
{
Timer a;
a.set(1,15);
a.tick();
cout << a.get_min() << "," << a.get_sec() <<
endl;
for(int i=0; i<80; i++) a.tick();
return 0;
}
对象初始化
如果不对对象进行初始化,则成员变量值不确定 初始化途径:
- 定义成员变量时给初始值 创建对象时,
- 用 { } 语法
- 构造函数(构造子)
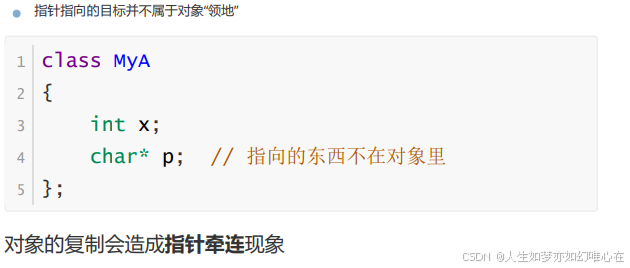
对象与指针
对象内部的指针
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class MyA
{
public:
void set(char* name, int age){
x = age;
p = new char [strlen(name)+1];
strcpy(p,name);
}
char* get_p(){
return p;
}
private:
int x;
char* p;
};
int main()
{
MyA a;
a.set("zhangsan",10);
MyA b=a;
b.set("zha",10);
cout << a.get_p() << endl;
return 0;
}

==内存泄漏==过程示例
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class MyA
{
public:
void set(char* name, int age){
x = age;
p = new char [strlen(name)+1];
strcpy(p,name);
}
private:
int x;
char* p;
};
int main()
{
MyA a;
a.set("zhangsan", 10);
cout << sizeof(MyA) << endl;
return 0;
}
修正:
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class MyA
{
public:
void set(char* name, int age){
x = age;
p = new char [strlen(name)+1];
strcpy(p,name);
}
void finish(){
delete [] p;
}
private:
int x;
char* p;
};
int main()
{
MyA a;
a.set("zhangsan", 10);
a.finish();
cout << sizeof(MyA) << endl;
return 0;
}
指向对象的指针
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class MyA
{
public:
void set(char* name, int age){
x = age;
p = new char [strlen(name)+1];
strcpy(p,name);
}
void finish(){
delete [] p;
}
private:
int x;
char* p;
};
int main()
{
MyA* p=new MyA();
p->set("zhangsan",10);
p[0].finish();
delete p;
return 0;
}
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class MyA
{
public:
void set(char* name, int age){
x = age;
p = new char [strlen(name)+1];
strcpy(p,name);
}
char* get_p(){
return p;
}
void finish(){
delete [] p;
}
private:
int x;
char* p;
};
int main()
{
MyA* p=new MyA();
p->set("zhangsan",10);
p[1].finish();
cout << p->get_p() << endl;
delete p;
return 0;
}

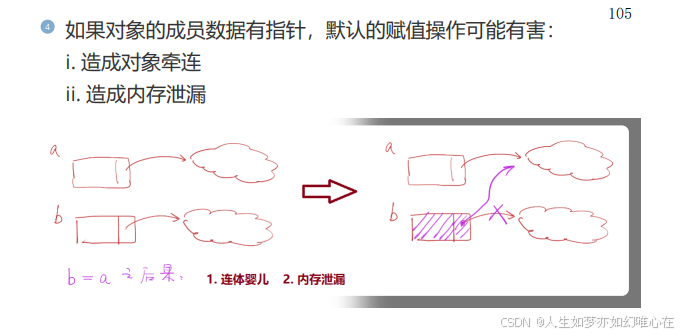
指针赋值与对象拷贝
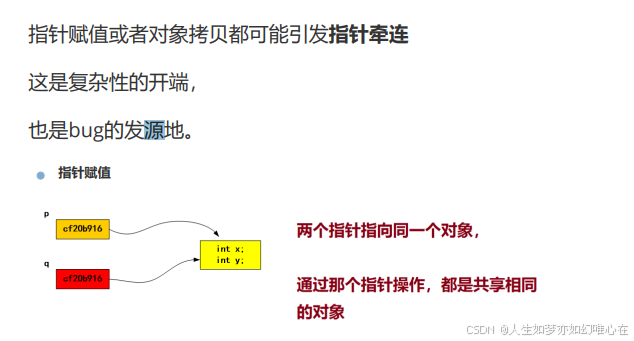

对象赋值(对象拷贝)




注意:
属性在public中能用{}初始化对象,在private中就用不了。
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class MyA{
public:
int x;
int y;
void show(){
printf("(%d,%d)\n", x, y);
}
};
int main()
{
MyA p={1,2};
MyA* b=new MyA{1,2};
return 0;
}MyA* p = new MyA{10,20}; 和 MyA p = {10,20}; 区别



浅拷贝与深拷贝
浅拷贝
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class LinkNode{
public:
int data;
LinkNode* next;
void add(LinkNode* it){
it->next = next;
next = it;
}
void clear(){
if(next==NULL) return;
next->clear();
delete next;
next = NULL;
}
void show(){
cout << data << " ";
if(next) next->show();
}
};
int main()
{
LinkNode a = {-1,NULL};
for(int i=9; i>=1; i--) a.add(new
LinkNode{i,NULL});
LinkNode b = a;
b.show();
cout << endl;
a.clear();
b.show(); cout << endl;
return 0;
}a调用clear方法,影响b的值。

深拷贝
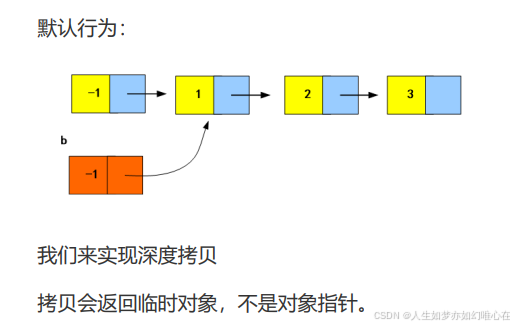
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class LinkNode{
public:
int data;
LinkNode* next;
void add(LinkNode* it){
it->next = next;
next = it;
}
void clear(){
if(next) next->clear();
delete next;
next = NULL;
}
void show(){
cout << data << " ";
if(next) next->show();
}
LinkNode copy(); // 深度拷贝
};
LinkNode LinkNode::copy()
{
LinkNode t = {data, NULL};
LinkNode* p = next;
LinkNode* q = &t;
while(p){
q->next = new LinkNode{p->data,NULL};
p = p->next;
q = q->next;
}
return t;
}
int main()
{
LinkNode a = {-1,NULL};
for(int i=9; i>=1; i--) a.add(new
LinkNode{i,NULL});
LinkNode b = a.copy();
b.show(); cout << endl;
a.clear();
b.show(); cout << endl;
return 0;
}
成员函数与this指针

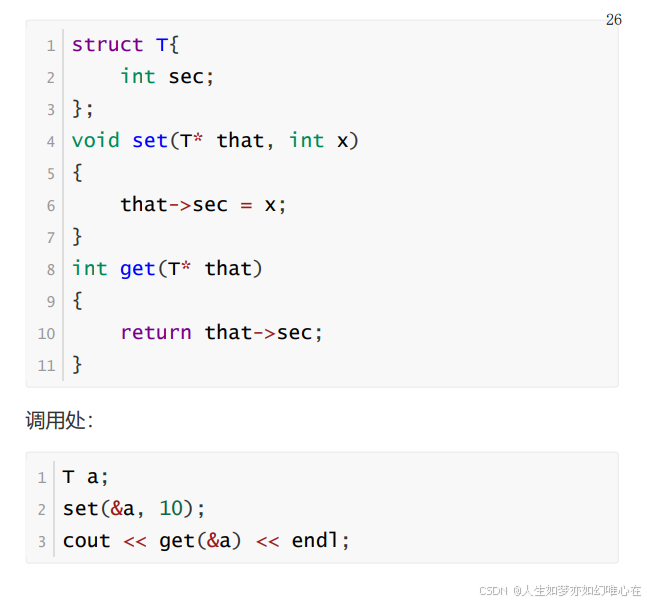


构造子与析构子

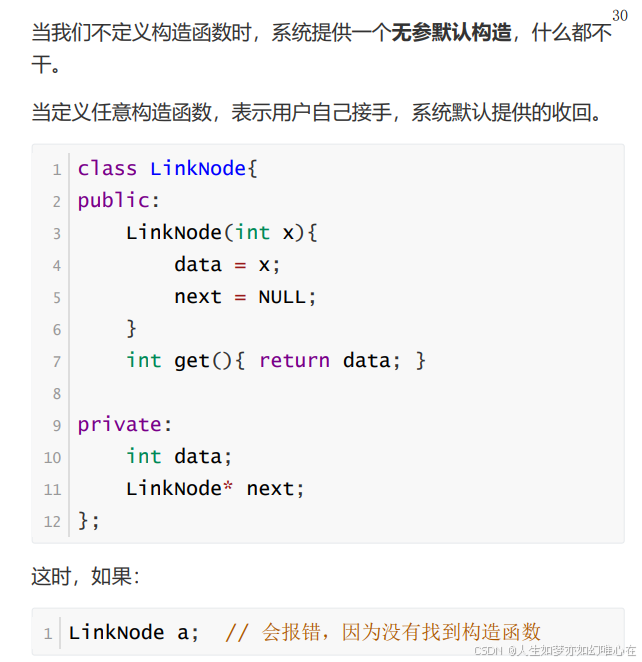

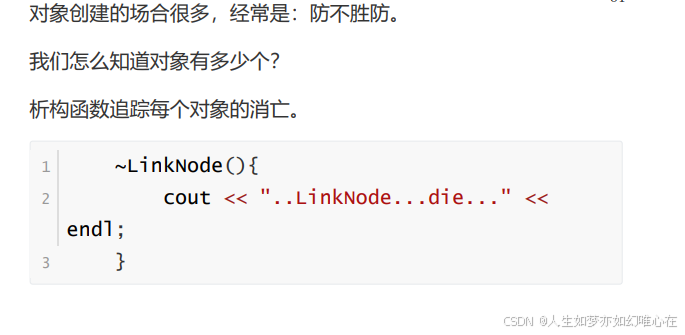

cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class LinkNode
{
public:
LinkNode(int x){
data = x;
next = NULL;
}
~LinkNode(){
cout << "destroy... " << endl;
if(next) delete next;
next = NULL;
}
LinkNode& add(int x){
LinkNode* p = new LinkNode(x);
p->next = next;
next = p;
return *p;
}
void show(){
LinkNode* p = this;
while(p){
cout << p->data << " ";
p = p->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
private:
int data;
LinkNode* next;
};
int main()
{
LinkNode head(-1);
head.add(1).add(2).add(3);
head.show();
return 0;
}
构造函数重载

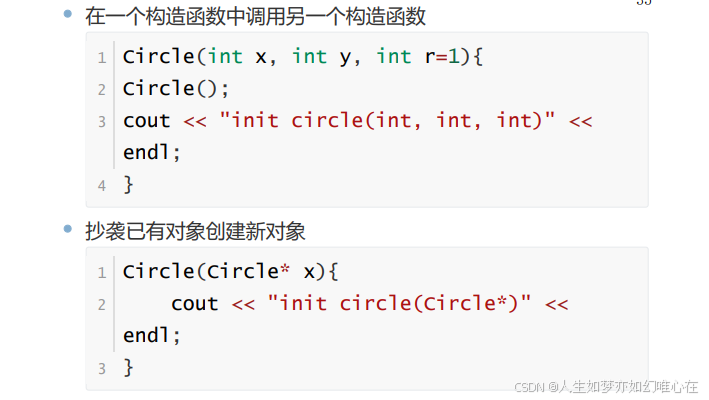
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class Circle{
public:
Circle(){
cout << "init Circle()" << endl;
}
Circle(int x, int y, int r=1){
cout << "init circle(int, int,int)" << endl;
}
private:
int x;
int y;
int r;
};
int main()
{
Circle a;
Circle b={1,2,3};
return 0;
}

cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class Point
{
public:
Point() {
cout << "init point()" << endl;
x = 0;
y = 0;
}
Point(int x, int y){
cout << "init point(x, y)" << endl;
this->x = x;
this->y = y;
}
void set(int x, int y){
this->x = x;
this->y = y;
}
int getx() { return x; }
int gety() { return y; }
private:
int x;
int y;
};
class Circle
{
public:
Circle(){
cout << "init circle()" << endl;
pt.set(0,0);
r = 1;
}
Circle(int r){
cout << "init circle(int)" << endl;
Circle();
this->r = r;
}
void show(){
printf("circle: (%d,%d)%d\n",pt.getx(),pt.gety(),r);
}
private:
Point pt; // 圆心
int r; // 半径
};
int main()
{
//Circle a; //此时,Point对象初始化几次?
Circle a(10); // Point对象初始化时机和次数?
//a.show();
return 0;
}
注意:会重复创建Point对象

cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class Point
{
public:
Point() {
cout << "init point()" << endl;
x = 0;
y = 0;
}
Point(int x, int y){
cout << "init point(x, y)" << endl;
this->x = x;
this->y = y;
}
void set(int x, int y){
this->x = x;
this->y = y;
}
int getx() { return x; }
int gety() { return y; }
private:
int x;
int y;
};
class Circle
{
public:
Circle():pt(1,1),r(10){
cout << "init circle()" << endl;
// pt.set(0,0);
// r = 1;
}
Circle(int r):Circle(){
cout << "init circle(int)" << endl;
//Circle();
this->r = r;
}
void show(){
printf("circle: (%d,%d)%d\n",pt.getx(),pt.gety(),r);
}
private:
Point pt; // 圆心
int r; // 半径
};
int main()
{
//Circle a; //此时,Point对象初始化几次?
Circle a(10); // Point对象初始化时机和次数?
//a.show();
return 0;
}对象的生存期
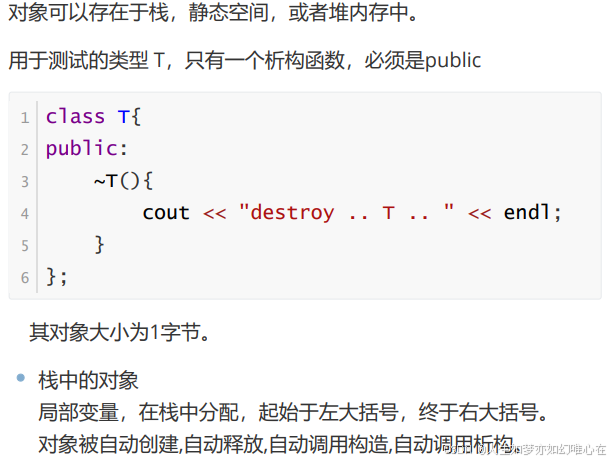




cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class T
{
public:
~T(){
cout << "destroy .. T .. " << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
T a; //不能T a();
cout << "end" <<endl;
return 0;
}
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class T
{
public:
~T(){
cout << "destroy .. T .. " << endl;
}
};
void f(T x){}
int main()
{
T a; //不能T a();
f(a);
return 0;
}
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class T
{
public:
~T(){
cout << "destroy .. T .. " << endl;
}
};
void f(T x){}
int main()
{
T{};//立即数
f(T{});
cout << "111" << endl;
return 0;
}
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class T
{
public:
~T(){
cout << "destroy .. T .. " << endl;
}
};
T f(T x){
return T{};
}
int main()
{
T a;
f(a);
return 0;
}
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class T
{
public:
~T(){
cout << "destroy .. T .. " << endl;
}
};
T f(T x){
return T{};
}
int main()
{
T* p=new T();//也可以用 T* p=new T{};
return 0;
}T* p=new T();和 T* p=new T{}; 区别


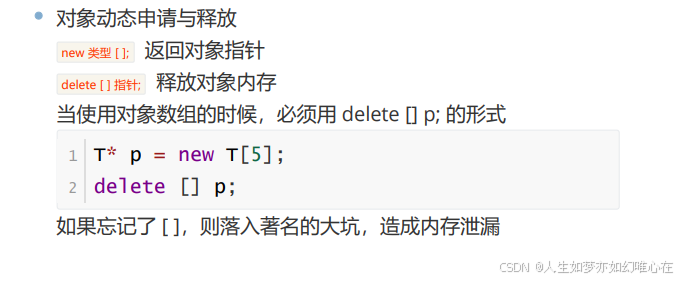
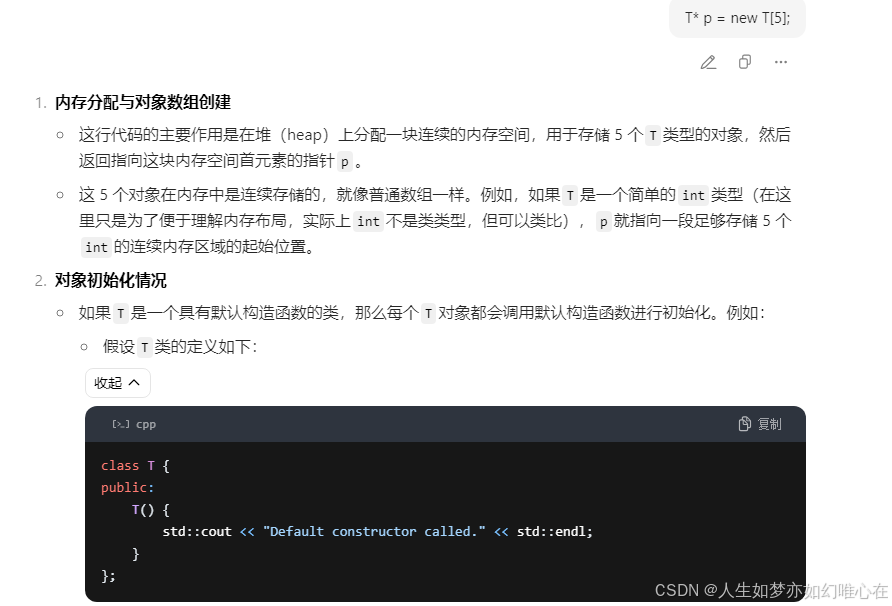
C++创建数组的方式:



对象的传递

cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class Cnt{
public:
Cnt(){ x = 0; }
~Cnt() { cout << "destroy .. counter ..." << x << endl; }
void inc() { x++; }
void dec() { x--; }
int get() { return x; }
private:
int x;
};
int main()
{
Cnt a;
a.inc();
a.inc();
cout << a.get() << endl;
return 0;
}


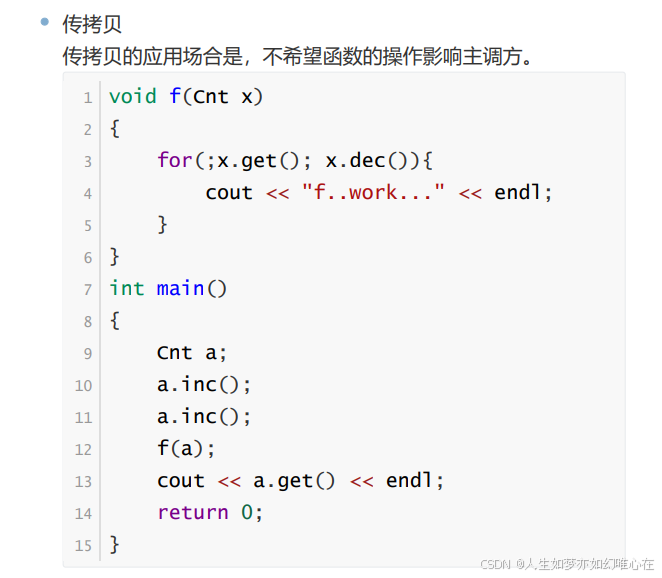
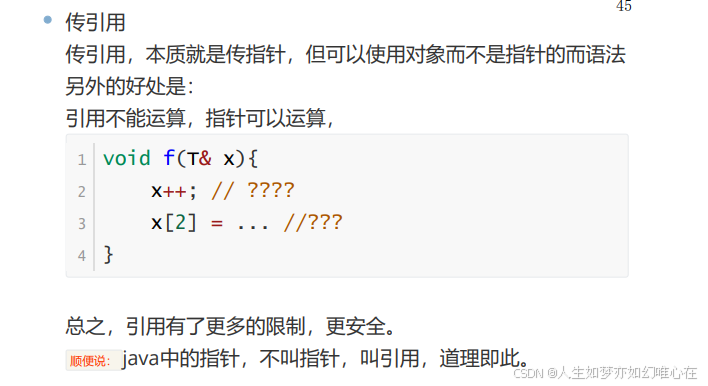
指针和引用的区别


引用不能运算,指针可以运算


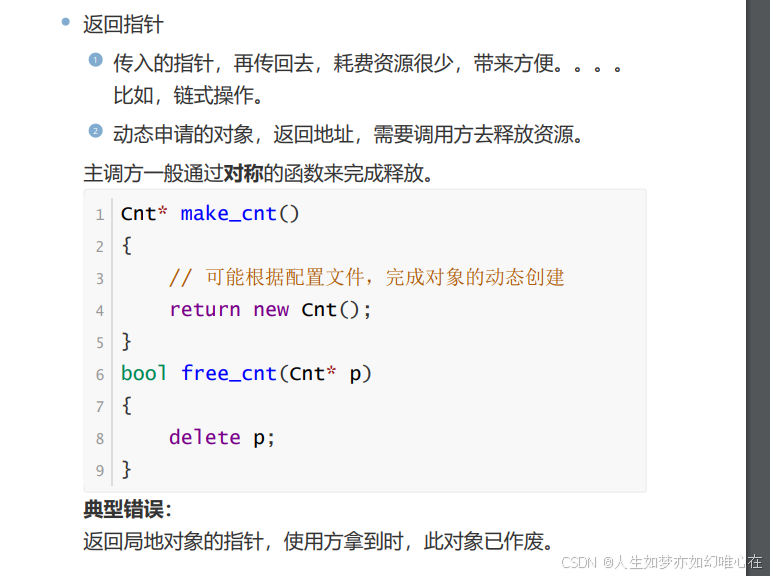

静态成员函数

静态成员函数的常见使用场景

cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class Cnt{
public:
Cnt(){
x = 0;
}
Cnt& inc(){ x++; return *this; }
Cnt& dec(){ x--; return *this; }
void show() { cout << x << endl; }
void add(Cnt& t){ // t 的值并入 我自己
x += t.x;
}
static Cnt add(Cnt& a, Cnt& b){ // a,b都不变,返回新的
Cnt t;
t.x = a.x + b.x;
return t;
}
private:
int x;
};
int main()
{
Cnt a;
a.inc().inc();
Cnt b;
b.inc();
a.add(b);
a.show();
//Cnt c=a.add(a,b); 看起来不简便
Cnt c=Cnt::add(a,b);
c.show();
return 0;
}



静态成员变量


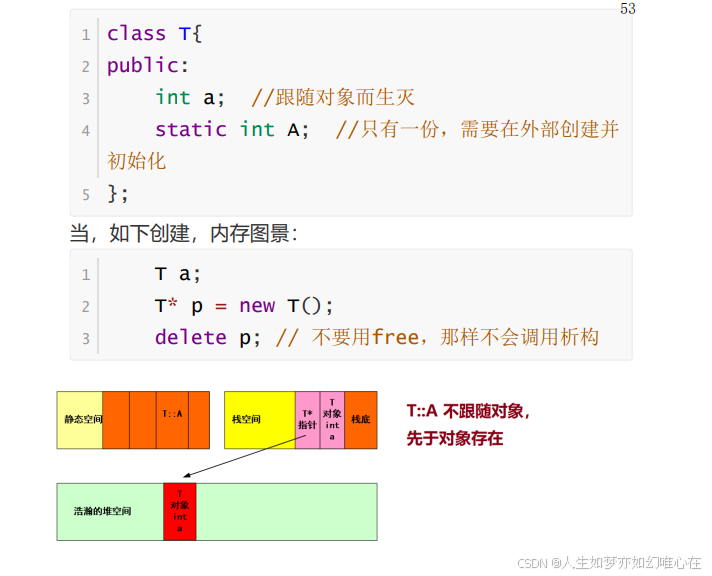

cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class T{
public:
T(){ A++; }
~T(){ A--; }
int x;
static int A;
};
int T::A=0;
int main()
{
T a;
T b;
cout << T::A << endl;
return 0;
}

cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class T{
public:
static T* get_instance(){
if(pObj==NULL) pObj = new T();
return pObj;
}
static void free(){
if(pObj){
delete pObj;
pObj = NULL;
}
}
private:
T(){}
~T(){}
static T* pObj;
};
T* T::pObj = NULL; // 不要忘记真正创建变量
int main()
{
T* p1 = T::get_instance();
T* p2 = T::get_instance();
cout << (p1 == p2) << endl;
return 0;
}
对象的状态

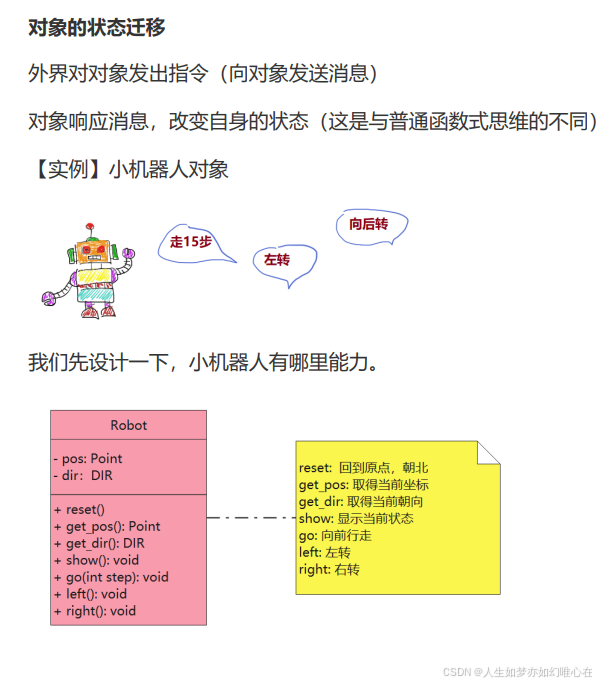

最后,实现小机器人类:
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
enum DIR{
NORTH, EAST, SOUTH, WEST
};
struct Point{
int x;
int y;
Point(){
x = 0;
y = 0;
}
void show(){
printf("(%d,%d)", x, y);
}
};
class Robot{
public:
Robot(){
dir = NORTH;
}
Robot& go(int step){
switch (dir) {
case NORTH:
pt.y += step;
break;
case EAST:
pt.x += step;
break;
case SOUTH:
pt.y -= step;
break;
case WEST:
pt.x -= step;
break;
}
return *this;
}
Robot& left(){
dir = (DIR)((dir-1+4)%4);
return *this;
}
Robot& right(){
dir = (DIR)((dir+1)%4);
return *this;
}
void show() {
pt.show(); cout << " ";
switch (dir) {
case NORTH:
cout << "north";
break;
case EAST:
cout << "east";
break;
case SOUTH:
cout << "south";
break;
case WEST:
cout << "west";
}
cout << endl;
}
void reset(){
pt.x = 0; pt.y = 0;
dir = NORTH;
}
private:
Point pt; //当前坐标
DIR dir; // 朝向
};
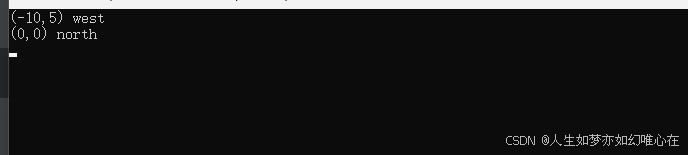
int main()
{
Robot a;
a.go(5);
a.right();
a.go(10);
a.left().left().go(20); //需要支持链式
a.show();
a.reset();
a.show();
return 0;
}





对象内存结构


cpp
Stu(int id, char* name){
this->id = id;
this->name = new char
[strlen(name)+1];
strcpy(this->name, name);
score = 0;
}
~Stu(){
delete [] name;
}
void inc(int x=1){ score += x; }
void dec(int x) { score -= x; }
void show(){
cout << id << ": " << name << "," <<
score << endl;
}
private:
int id;
char* name;
int score;
};

cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class Stu{
public:
Stu(){
id = -1;
name = NULL;
score = -9999;
}
Stu(int id, char* name):Stu(){
init(id, name, 0);
}
~Stu(){
if(name){
delete [] name;
name = NULL;
}
cout << "destroy.. " << id << endl;
}
void init(int id, char* name, int score){
this->id = id;
if(this->name) delete [] this->name;
this->name = new char [strlen(name)+1];
strcpy(this->name, name);
this->score = score;
}
void inc(int x=1){ score += x; }
void dec(int x) { score -= x; }
void show(){
cout << id << ": " << name << "," << score << endl;
}
private:
int id;
char* name;
int score;
};
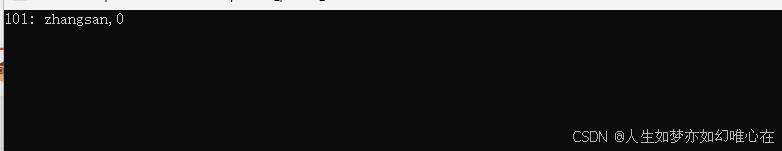
int main()
{
Stu* a[5]; //指针数组
for(int i=0; i<5; i++){
a[i] = new Stu(101+i, "noname");
a[i]->show();
}
for(int i=0; i<5; i++) delete a[i];
return 0;
}
数组替代指针
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class Stu{
public:
Stu(){
id = -1;
name[0] = '\0';
score = -9999;
}
Stu(int id, char* name){
init(id, name, 0);
}
~Stu(){
cout << "destroy.. " << id << endl;
}
void init(int id, char* name, int score){
this->id = id;
strncpy(this->name, name, 25);
this->score = score;
}
void inc(int x=1){ score += x; }
void dec(int x) { score -= x; }
void show(){
cout << id << ": " << name << "," << score << endl;
}
private:
int id;
char name[30];
int score;
};
int main()
{
Stu* a[5]; //指针数组
for(int i=0; i<5; i++){
a[i] = new Stu(101+i, "noname");
a[i]->show();
}
for(int i=0; i<5; i++) delete a[i];
return 0;
}
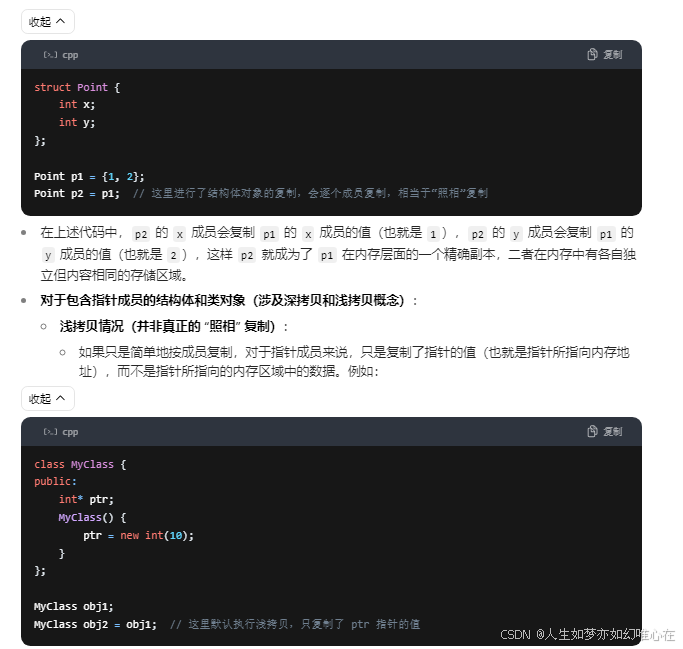
拷贝构造

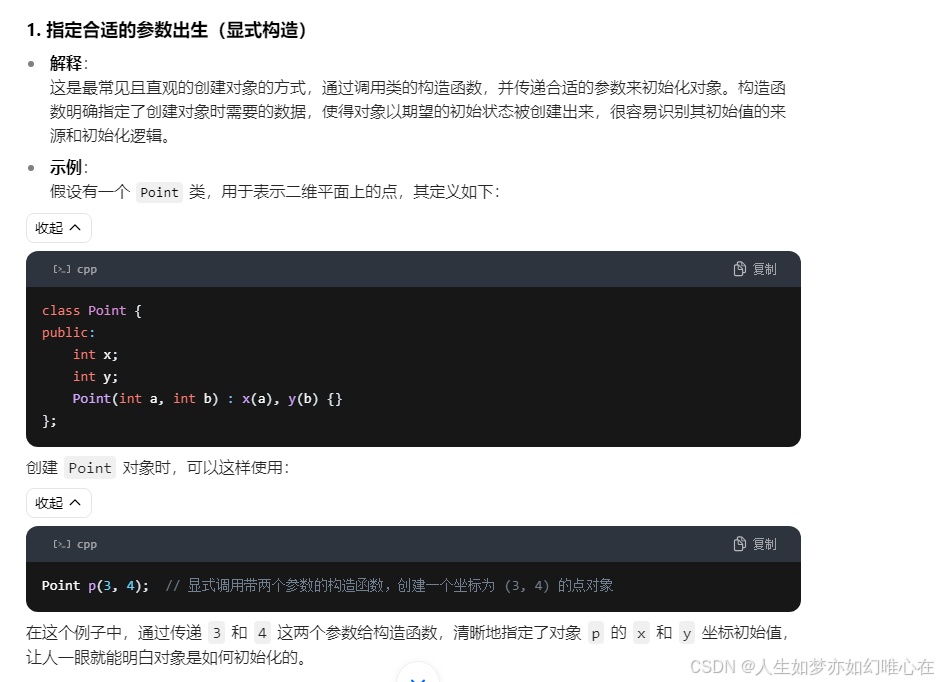
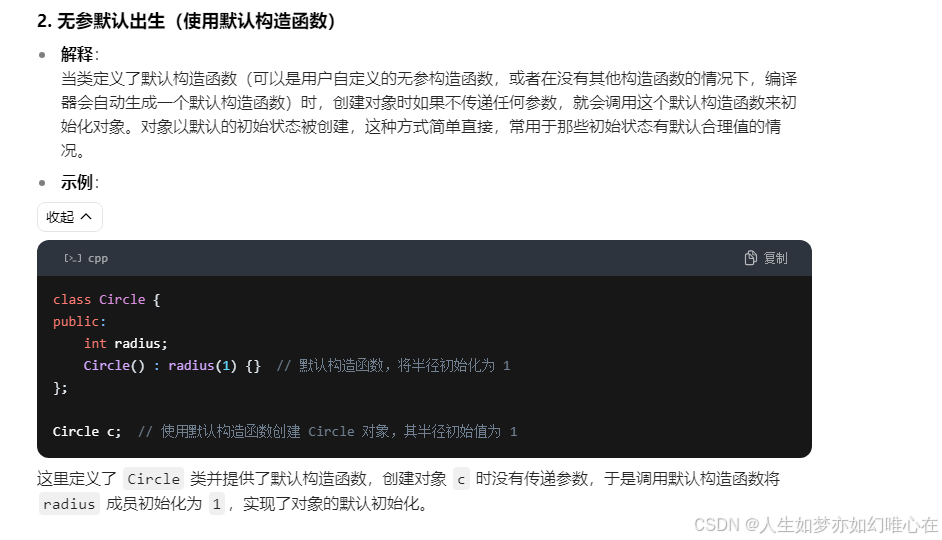

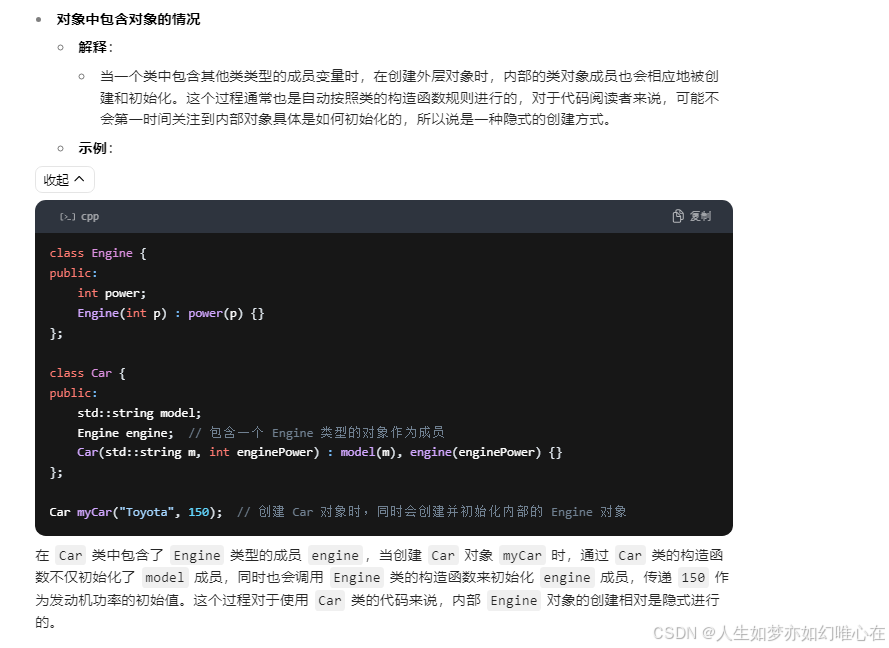
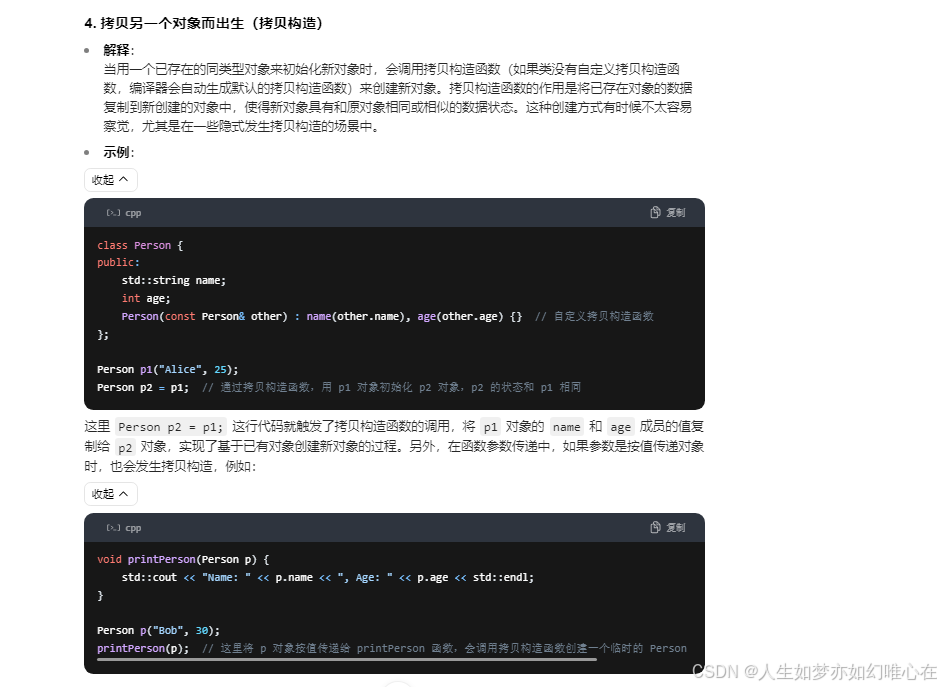
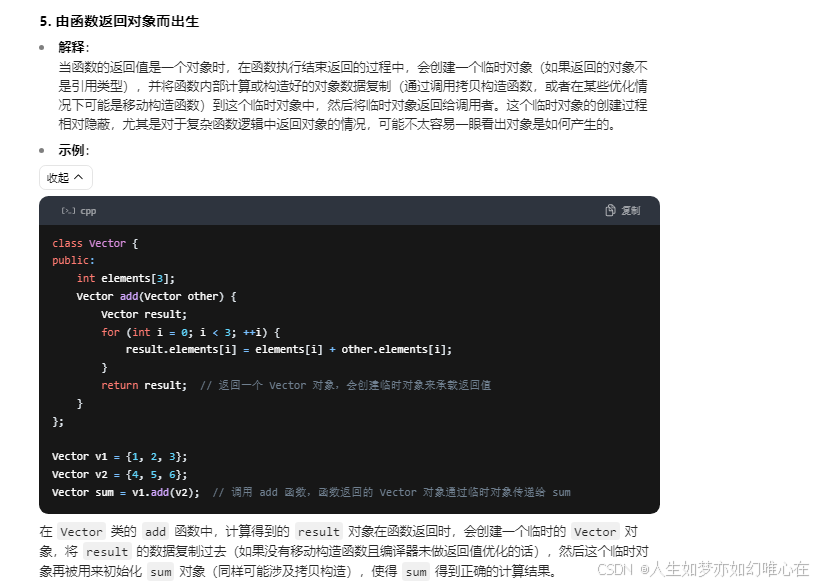
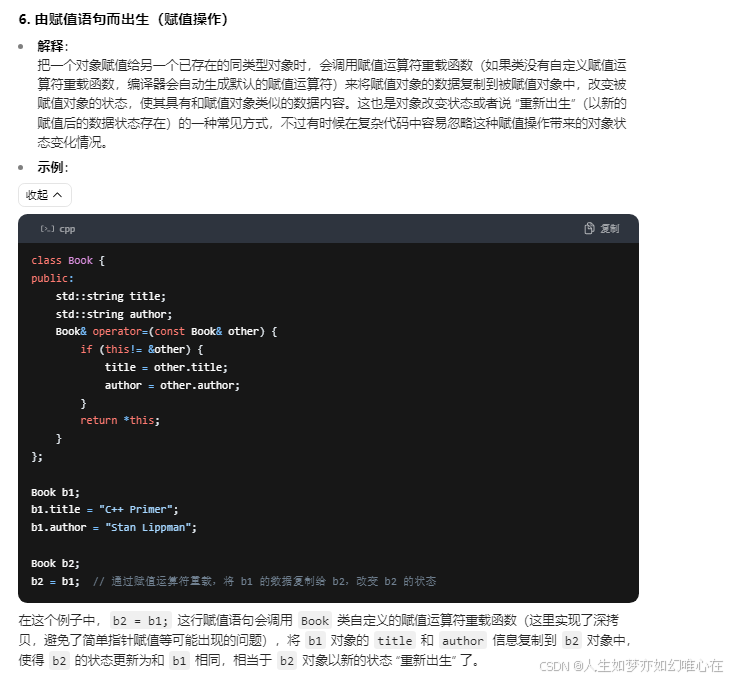

cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class A{
public:
A(){ cout << "default create" << endl; }
A(A& x){ cout << "copy create" << endl; }
~A(){ cout << "destroy " << endl; }
};
int main()
{
A a;
A b = a; // 拷贝构造和下面的创建方式效果相同
A c(a); // 拷贝构造
b = c; // 这是对象赋值,并没有新的对象出生,因而无所谓:"构造"
return 0;
}
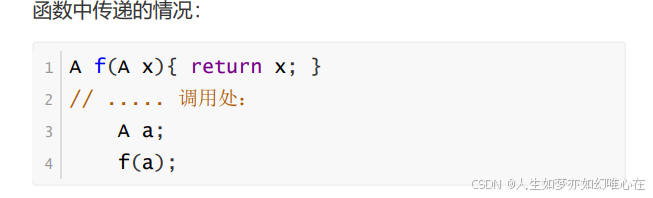
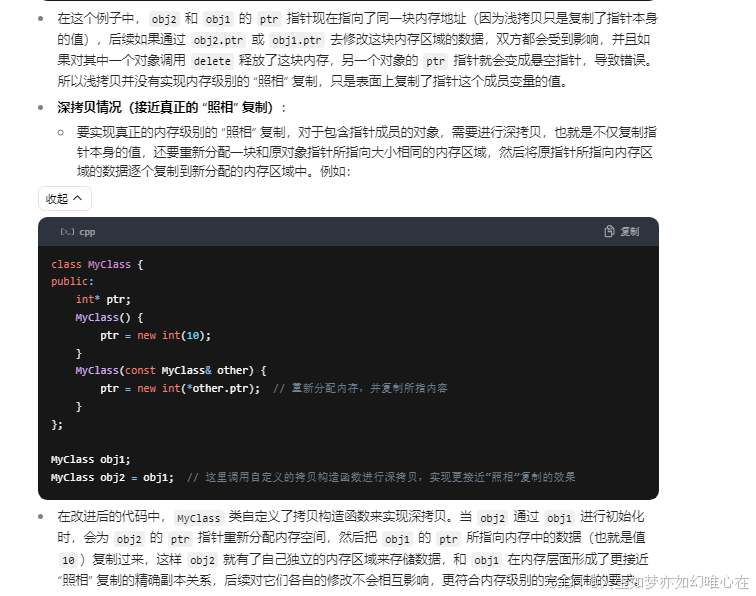
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class A{
public:
A(){ cout << "default create" << endl; }
A(A& x){ cout << "copy create" << endl; }
~A(){ cout << "destroy " << endl; }
};
A f(A x){ return x; }
int main()
{
A a;
f(a);
return 0;
}
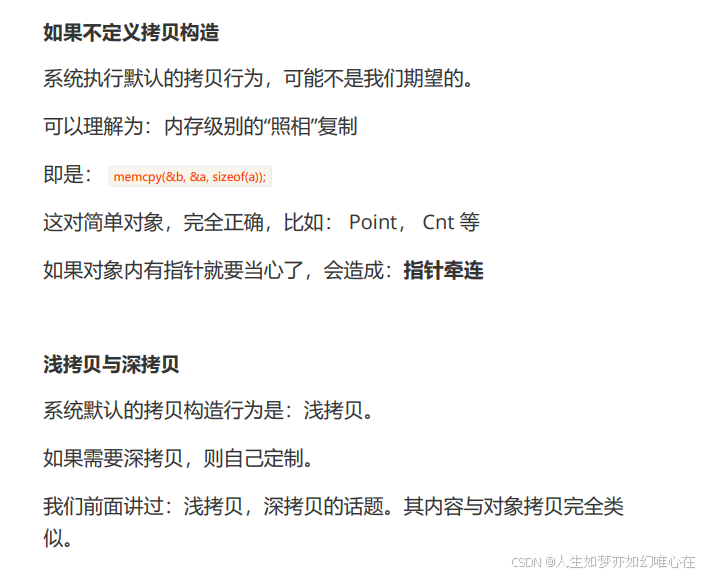

cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node{
int data;
Node* next;
Node(int x){
data = x;
next = NULL;
}
};
class Que{
public:
Que() { head=NULL; tail=NULL; }
~Que() { int x; while(pop(x)); }
Que& push(int x){
Node* t = new Node(x);
if(tail){
tail->next = t;
tail = t;
}else{
tail = t;
head = t;
}
return *this;
}
bool pop(int& x){
if(head==NULL) return false;
Node* t = head;
if(head==tail){
head = NULL;
tail = NULL;
}else{
head = t->next;
}
x = t->data;
delete t;
return true;
}
private:
Node* head;
Node* tail;
};
int main()
{
Que a;
a.push(10).push(20).push(30);
int x;
while(a.pop(x)) cout << x << endl;
return 0;
}
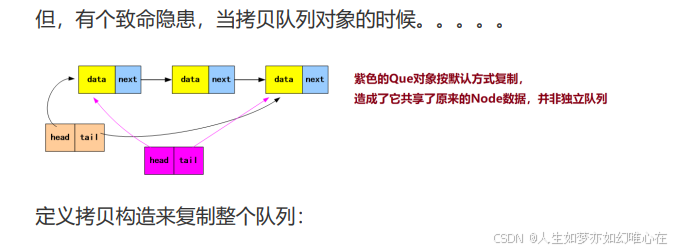

cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node{
int data;
Node* next;
Node(int x){
data = x;
next = NULL;
}
};
class Que{
public:
Que() { head=NULL; tail=NULL; }
Que(Que& t):Que(){
Node* p = t.head;
while(p){
push(p->data);
p=p->next;
}
}
~Que() { int x; while(pop(x)); }
Que& push(int x){
Node* t = new Node(x);
if(tail){
tail->next = t;
tail = t;
}else{
tail = t;
head = t;
}
return *this;
}
bool pop(int& x){
if(head==NULL) return false;
Node* t = head;
if(head==tail){
head = NULL;
tail = NULL;
}else{
head = t->next;
}
x = t->data;
delete t;
return true;
}
private:
Node* head;
Node* tail;
};
int main()
{
Que a;
a.push(10).push(20).push(30);
Que b(a);
int x;
a.pop(x);
while(b.pop(x)) cout << x << endl;
return 0;
}
内存级别的"照相"复制


赋值函数
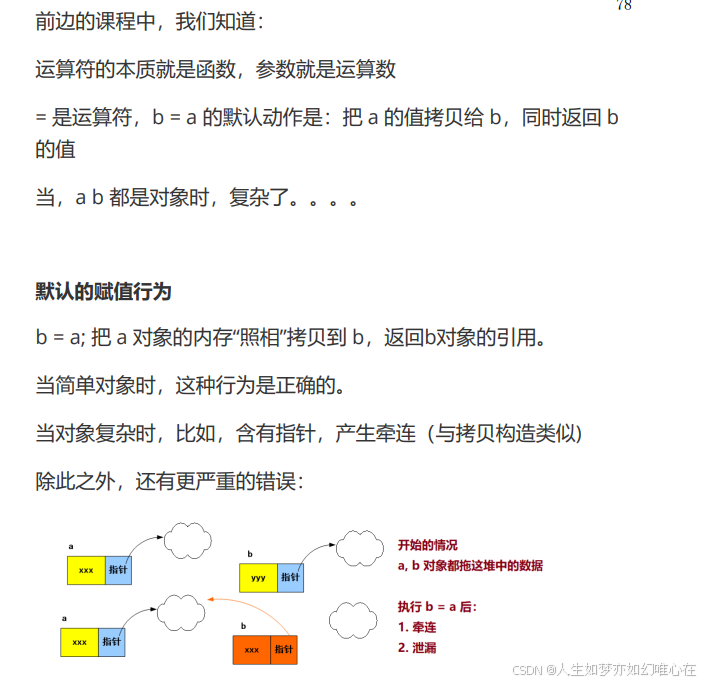
上一节的 Que 类
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 链表的节点
struct Node{
int data;
Node* next;
Node(int x){
data = x;
next = NULL;
}
}
//先进先出的队列
class Que{
public:
Que() { head=NULL; tail=NULL; }
Que(Que& t):Que(){ //保证在拷贝构造前,head,tail为NULL
Node* p = t.head;
while(p){
push(p->data);
p=p->next;
}
}
~Que() { int x; while(pop(x)); }
Que& push(int x){ //返回Que& 为了链式操作
Node* t = new Node(x);
if(tail){
tail->next = t;
tail = t;
}else{
tail = t;
head = t;
}
return *this;
}
bool pop(int& x){ //不设计为直接返回 int,因为有队列空的情况
if(head==NULL) return false;
Node* t = head;
if(head==tail){
head = NULL;
tail = NULL;
}else{
head = t->next;
}
x = t->data;
delete t;
return true;
}
private:
Node* head; //指向对头,从这里弹出数据
Node* tail; //指向队尾,在其后压入数据
}; 
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node{
int data;
Node* next;
Node(int x){
data = x;
next = NULL;
}
};
class Que{
public:
Que() { head=NULL; tail=NULL; }
Que(Que& t):Que(){
Node* p = t.head;
while(p){
push(p->data);
p=p->next;
}
}
~Que() { clear(); }
void clear(){ int x; while(pop(x)); }
Que& operator=(Que& t){
clear();
Node* p = t.head;
while(p){
push(p->data);
p=p->next;
}
return *this;
}
Que& push(int x){
Node* t = new Node(x);
if(tail){
tail->next = t;
tail = t;
}else{
tail = t;
head = t;
}
return *this;
}
bool pop(int& x){
if(head==NULL) return false;
Node* t = head;
if(head==tail){
head = NULL;
tail = NULL;
}else{
head = t->next;
}
x = t->data;
delete t;
return true;
}
private:
Node* head;
Node* tail;
};
int main()
{
Que a; a.push(10).push(20).push(30);
Que b; b.push(33).push(99);
b = a;
int x; b.pop(x); b.pop(x);
while(a.pop(x)) cout << x << endl;
return 0;
}
友元函数


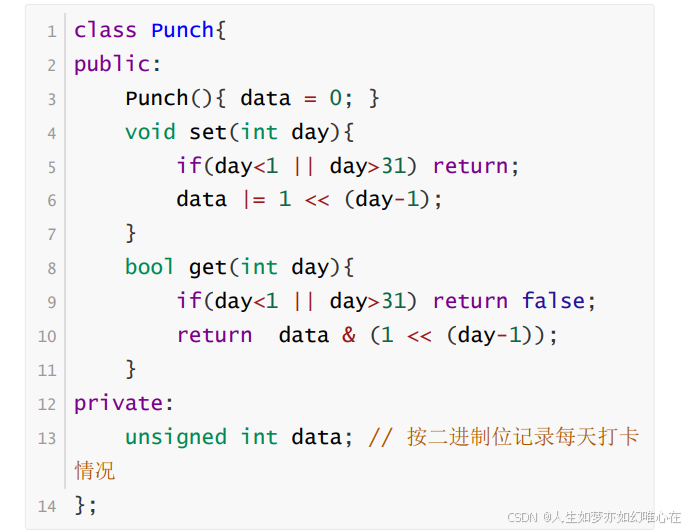
真实的例子(月结打卡类Punch)

cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Punch{
public:
Punch(){ data = 0; }
Punch& set(int day){
if(day<1 || day>31) return *this;
data |= 1 << (day-1);
return *this;
}
bool get(int day){
if(day<1 || day>31) return false;
return data & (1 << (day-1));
}
friend void debug_punch(Punch& x);
private:
unsigned int data; // 按二进制位记录每天打卡情况
};
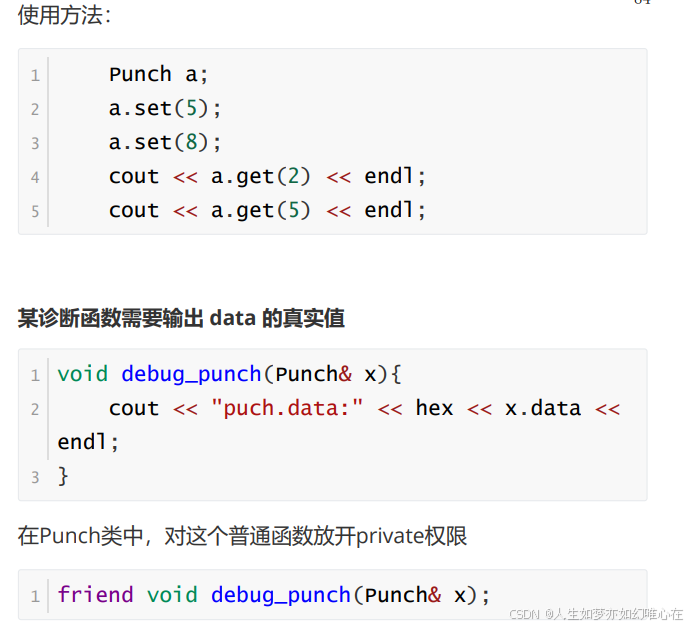
void debug_punch(Punch& x){
cout << "puch.data:" << hex << x.data << endl;
}
int main()
{
Punch a;
a.set(5).set(10).set(12);
cout << a.get(2) << endl;
cout << a.get(5) << endl;
debug_punch(a);
return 0;
}
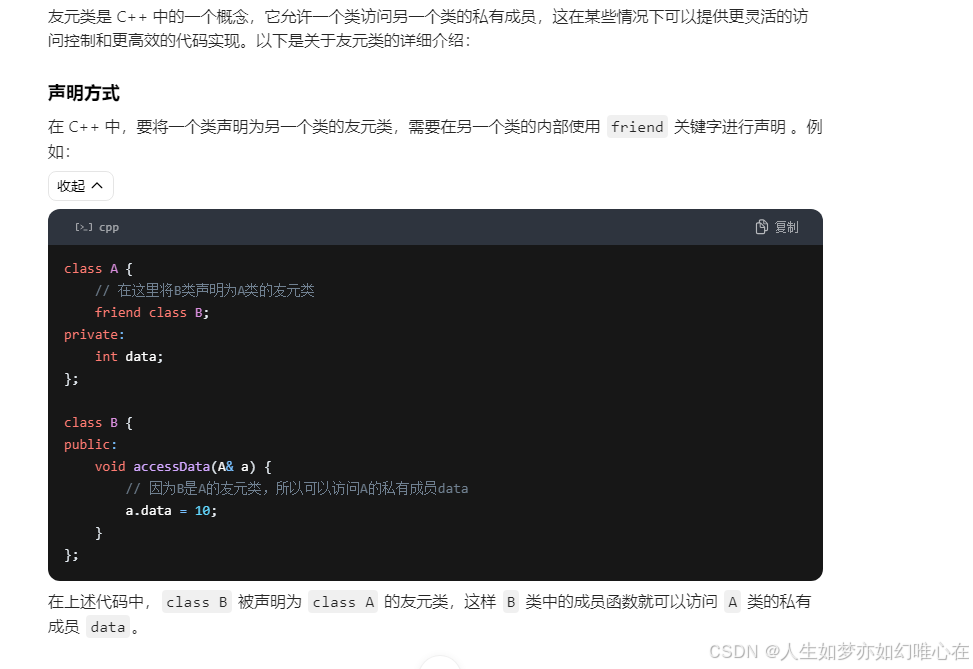
友元类


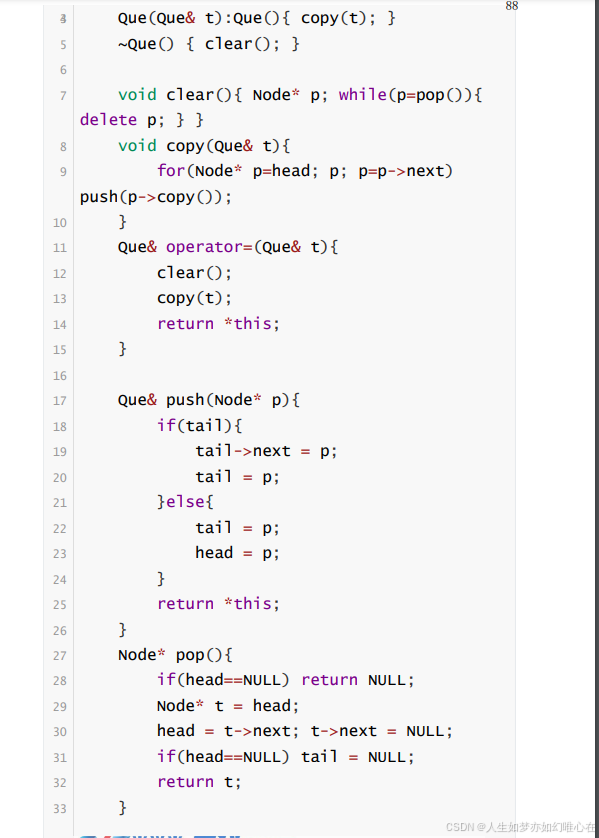

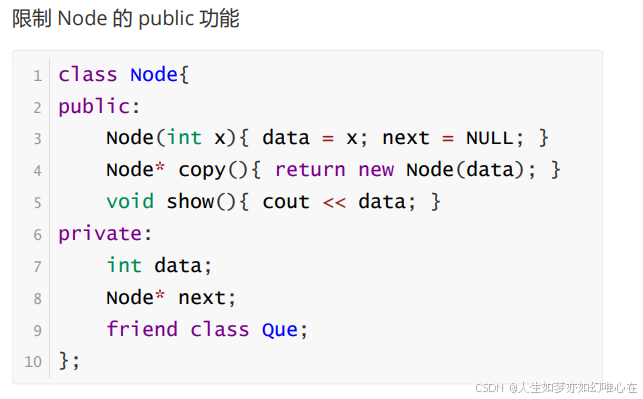
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node{
public:
Node(int x){ data = x; next = NULL; }
Node* copy(){ return new Node(data); }
void show(){ cout << data; }
private:
int data;
Node* next;
friend class Que;
};
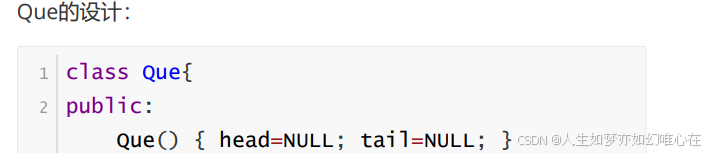
class Que{
public:
Que() { head=NULL; tail=NULL; }
Que(Que& t):Que(){ copy(t); }
~Que() { clear(); }
void clear(){ Node* p; while(p=pop()){ delete p; } }
void copy(Que& t){
for(Node* p=head; p; p=p->next) push(p->copy());
}
Que& operator=(Que& t){
clear();
copy(t);
return *this;
}
Que& push(Node* p){
if(tail){
tail->next = p;
tail = p;
}else{
tail = p;
head = p;
}
return *this;
}
Node* pop(){
if(head==NULL) return NULL;
Node* t = head;
head = t->next; t->next = NULL;
if(head==NULL) tail = NULL;
return t;
}
void show(){
for(Node* p=head; p; p=p->next){
p->show(); cout << " ";
}
}
private:
Node* head;
Node* tail;
};
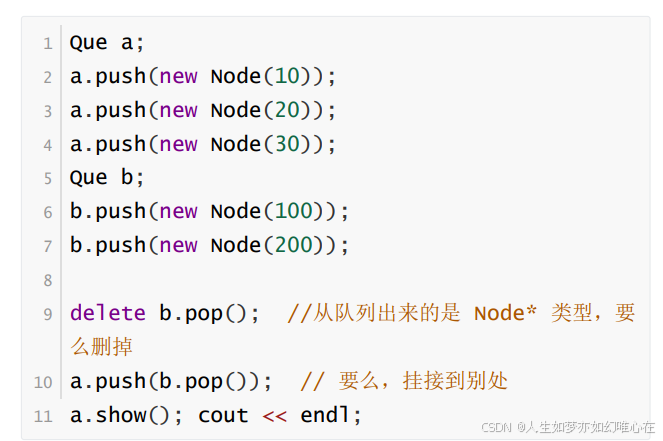
int main()
{
Que a;
a.push(new Node(10));
a.push(new Node(20));
a.push(new Node(30));
Que b;
b.push(new Node(100));
b.push(new Node(200));
delete b.pop();
a.push(b.pop());
a.show(); cout << endl;
return 0;
}


内部类



cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Que{
public:
class Node{
public:
Node(int x){ data = x; next = NULL; }
Node* copy(){ return new Node(data); }
void show(){ cout << data; }
private:
int data;
Node* next;
friend class Que;
};
public:
Que() { head=NULL; tail=NULL; }
Que(Que& t):Que(){ copy(t); }
~Que() { clear(); }
void clear(){ Node* p; while(p=pop()){ delete p; } }
void copy(Que& t){
for(Node* p=head; p; p=p->next) push(p->copy());
}
Que& operator=(Que& t){
clear();
copy(t);
return *this;
}
Que& push(Node* p){
if(tail){
tail->next = p;
tail = p;
}else{
tail = p;
head = p;
}
return *this;
}
Node* pop(){
if(head==NULL) return NULL;
Node* t = head;
head = t->next; t->next = NULL;
if(head==NULL) tail = NULL;
return t;
}
void show(){
for(Node* p=head; p; p=p->next){
p->show(); cout << " ";
}
}
private:
Node* head;
Node* tail;
};
int main()
{
Que a;
a.push(new Que::Node(10));
a.push(new Que::Node(20));
a.push(new Que::Node(30));
Que b;
b.push(new Que::Node(100));
b.push(new Que::Node(200));
delete b.pop();
a.push(b.pop());
a.show(); cout << endl;
return 0;
}

运算符重载




cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Cnt{
public:
Cnt(){ x=0; }
Cnt& inc() { x++; return *this; }
Cnt& dec() { x--; return *this; }
int get() { return x; }
Cnt operator+(Cnt& t){ return Cnt(x+t.x); }
Cnt operator+(int t){return Cnt(x+t); }
private:
Cnt(int a){ x = a; }
int x;
friend Cnt operator+(int, Cnt&);
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, Cnt&);
};
Cnt operator+(int a, Cnt& b) { return Cnt(a + b.x); }
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, Cnt& t) { os << t.x; return os; }
int main()
{
Cnt a; a.inc(); a.inc();
Cnt b; b.inc();
Cnt c = 100 + a + b + 10;
cout << c.get() << endl;
cout << c << endl;
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Cnt{
public:
Cnt(){ x=0; }
Cnt& inc() { x++; return *this; }
Cnt& dec() { x--; return *this; }
int get() { return x; }
Cnt operator+(Cnt& t){ return Cnt(x+t.x); }
Cnt operator+(int t){return Cnt(x+t); }
private:
Cnt(int a){ x = a; }
int x;
friend Cnt operator+(int, Cnt&); //友元函数
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, Cnt&);
};
Cnt operator+(int a, Cnt& b) { return Cnt(a + b.x); }
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, Cnt& t) { os << t.x; return os; }
int main()
{
Cnt a; a.inc(); a.inc();
Cnt b; b.inc();
Cnt c = 100 + a + b + 10;
cout << c.get() << endl;
cout << c << endl;
return 0;
}
重载运算符基本规则




cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Cnt{
public:
Cnt(){ x=0; }
Cnt& inc() { x++; return *this; }
Cnt& dec() { x--; return *this; }
int get() { return x; }
Cnt& operator++(){ x++; return *this; }
Cnt operator++(int){ Cnt t = *this; x++; return t; }
private:
Cnt(int a){ x = a; }
int x;
};
int main()
{
Cnt a; ++a;
Cnt b = a++;
cout << a.get() << endl;
cout << b.get() << endl;
return 0;
}


特殊运算符的重载


cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Punch{
public:
Punch(){ data = 0; }
void set(int day){
if(day<1 || day>31) return;
data |= 1 << (day-1);
}
bool get(int day){
if(day<1 || day>31) return false;
return data & (1 << (day-1));
}
bool operator[](int day){ return get(day); }
private:
unsigned int data; // 按二进制位记录每天打卡情况
};
int main()
{
Punch a;
a.set(5);
cout << a[5] << endl;
return 0;
}


cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 用户类型
struct T{
void f() { cout << "T::f()..." << endl; }
};
// 服务于 T 的智能指针
class PT{
public:
PT(){ p = new T; }
~PT() {
cout << "free T ..." << endl;
delete p;
}
T* operator->(){ return p; }
private:
T* p;
};
int main()
{
PT p;
p->f();
// T* p = new T;
// p->f();
return 0;
}
const修饰符


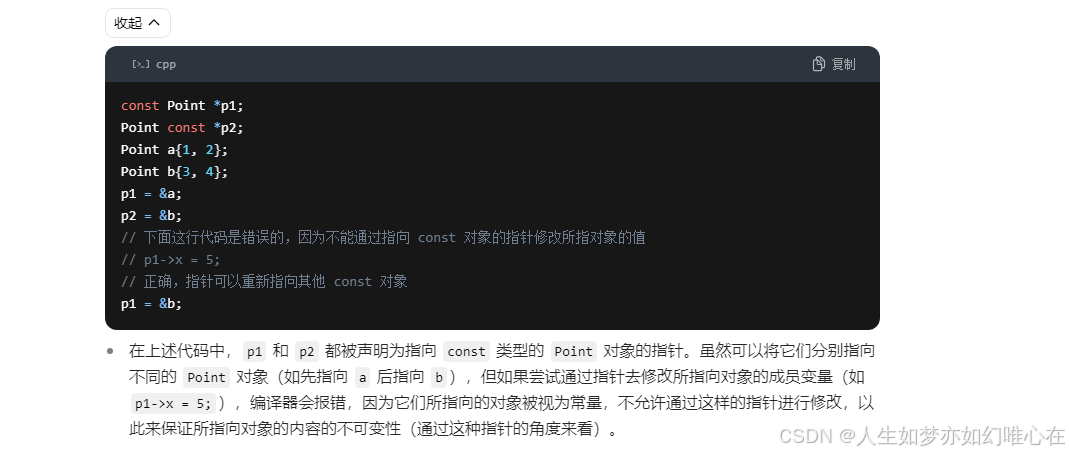
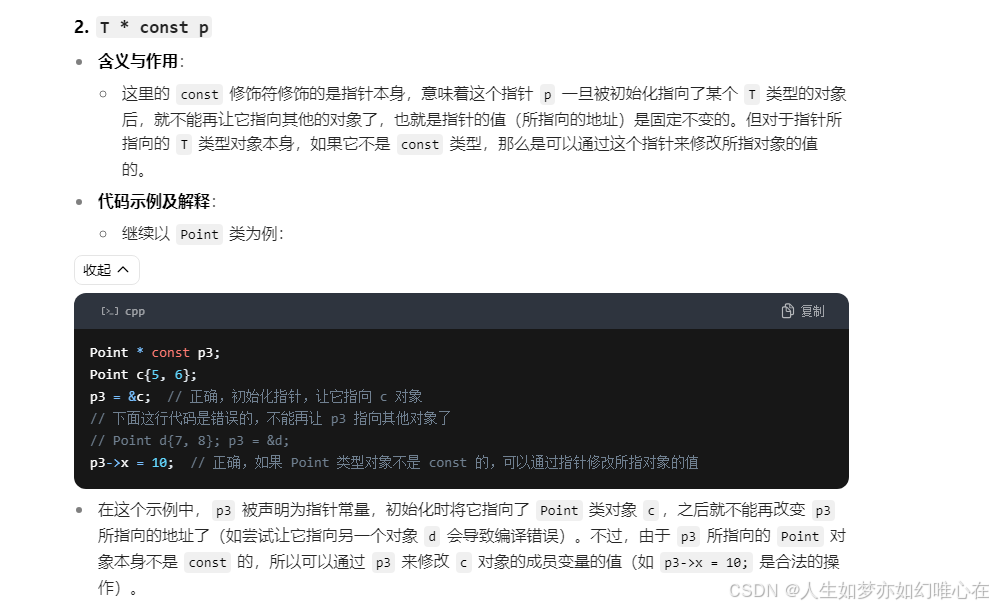
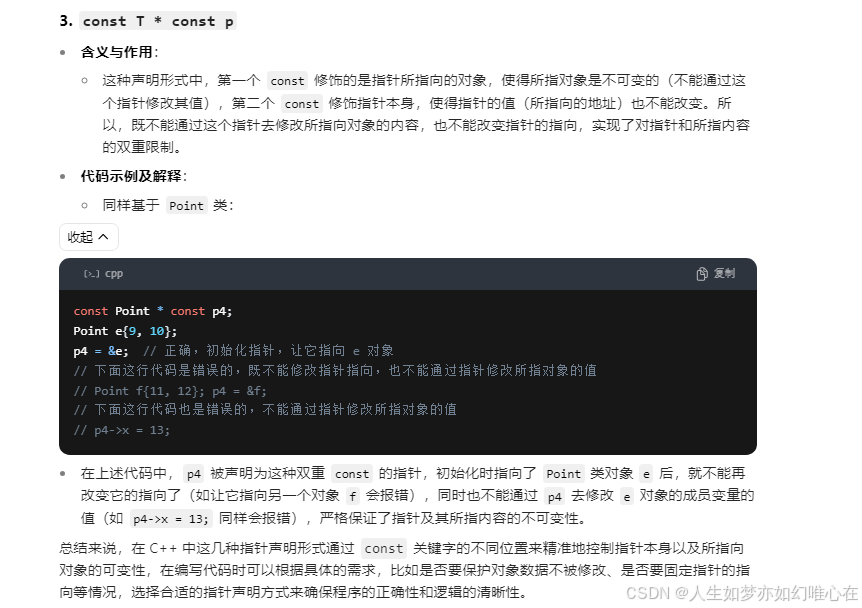



cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class T{
public:
T():x(100){}
void f() const { cout << y << endl; }
void g() {y++;}
private:
const int x;
int y;
};
int main()
{
const T a;
//a.g(); // g() 非const函数,不可调用
const_cast<T&>(a).g(); //强制后,去掉了const约束
return 0;
}成员对象与封闭类

cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A{
public:
A(){ cout << "A()" << endl; }
A(int a) { cout << "A(a)" << endl; this->a = a; }
private:
int a;
};
class B{
public:
B(int a, int b):x(a){ y = b; }
private:
A x;
int y;
};
int main()
{
B t(1,2);
return 0;
}
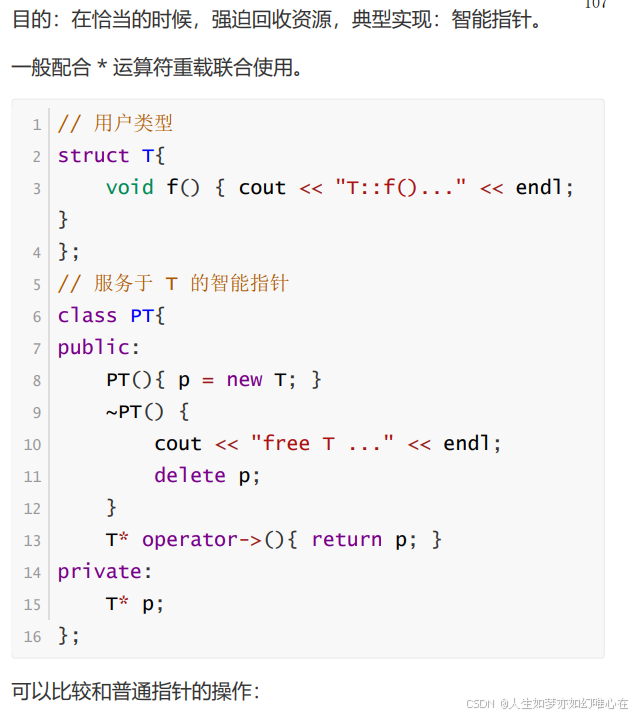
智能指针是 C++ 中用于自动管理动态分配内存的对象,它能够帮助开发者避免手动管理内存时可能出现的内存泄漏、悬空指针等问题。

cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class T{
public:
class P{
public:
P(T* p):p(p){}
~P(){ if(p){delete p; p=NULL;} }
T* operator->(){ return p; }
private:
T* p;
};
T(){ cout << "T() .. " << endl; }
~T() { cout << "~T() .. " << endl; }
void f() { cout << "T::f() .. " << endl; }
};
int main()
{
T::P p = new T();
p->f();
return 0;
}



cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class T{
public:
class P{
public:
P(T* p):p(p){}
~P(){ if(p){delete p; p=NULL;} }
T* operator->(){ return p; }
private:
T* p;
};
T(){ cout << "T() .. " << endl; }
~T() { cout << "~T() .. " << endl; }
void f() { cout << "T::f() .. " << endl; }
};
struct Node{
Node(T* t):data(t){next=NULL;}
T::P data;
Node* next;
};
int main()
{
Node a(new T());
Node b(new T());
a.next = &b;
// T::P p = new T();
// p->f();
return 0;
}
智能指针之引用计数

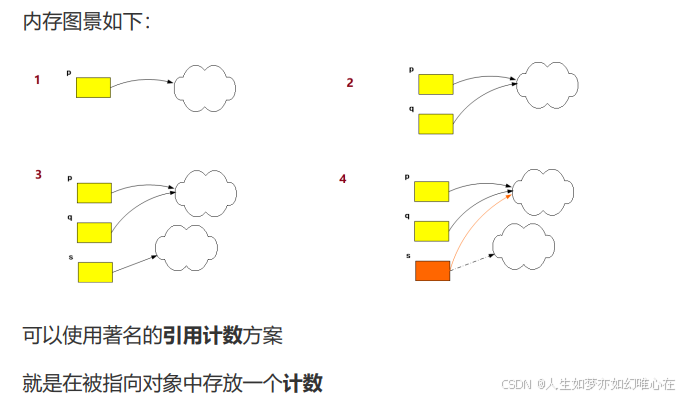

cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class T{
public:
class P{
public:
P(T* p):p(p){ p->n++; }
P(P& t){ copy(t); }
~P(){ clear(); }
void clear(){
p->n--;
if(p->n == 0) { delete p; p=NULL; }
}
void operator=(P& t){ clear(); copy(t); }
T* operator->(){ return p; }
private:
void copy(P& t){ p = t.p; p->n++; }
T* p;
};
T(){ cout << "T() .. " << endl; n=0; }
~T() { cout << "~T() .. " << endl; }
void f() { cout << "T::f() .. " << endl; }
private:
int n; // 本对象的引用计数
};
int main()
{
T::P p(new T()); // 构造
p->f();
T::P q = p; // 拷贝构造
T::P s(new T());
s = q; // 对象赋值
return 0;
}

日期类型



cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Date{
public:
Date(){ k=0; }
Date(int y, int m, int d){ k = ymd_to_k(y,m,d); }
int year() { int y, m, d; k_to_ymd(k, y, m, d); return y; }
int month() { int y, m, d; k_to_ymd(k, y, m, d); return m; }
int day() { int y, m, d; k_to_ymd(k, y, m, d); return d; }
int week_day() { return k % 7; }
int operator-(Date& t){ return k - t.k; }
Date operator+(int x){ Date t; t.k = k + x; return t; }
Date operator-(int x){ return *this + (-x); }
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, Date& t);
private:
static bool leap_year(int y){
return (y%4==0 && y%100!=0) || y%400==0;
}
static int ymd_to_k(int y, int m, int d);
static void k_to_ymd(int k, int& y, int& m, int& d);
int k; //记录距离 公元1年1月1日,过去了多少天。
};
//输出
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, Date& t)
{
printf("%04d-%02d-%02d", t.year(), t.month(), t.day());
return os;
}
// 年月日 转为: 距离公元元年经过天数
int Date::ymd_to_k(int y, int m, int d)
{
int M[] = {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
if(Date::leap_year(y)) M[2]++;
int k = 0;
for(int i=1; i<y; i++) k += 365 + leap_year(i);
for(int i=1; i<m; i++) k += M[i];
return k + d;
}
// 距离公元元年经过天数 转为: 年月日
void Date::k_to_ymd(int k, int& y, int& m, int& d)
{
int M[] = {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
for(int i=1;; i++){
int t = 365 + Date::leap_year(i);
if(k<=t){
y = i;
break;
}
k -= t;
}
if(Date::leap_year(y)) M[2]++;
for(int i=1;;i++){
if(k<=M[i]){
m = i;
break;
}
k -= M[i];
}
d = k;
}
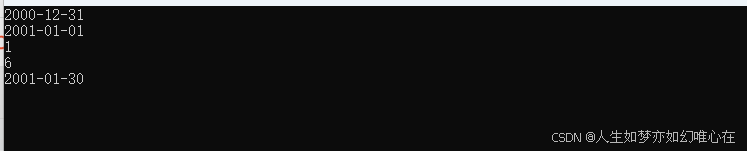
int main()
{
Date a(2000,12,31);
cout << a << endl;
Date b(2001,1,1);
cout << b << endl;
cout << (b-a) << endl;
cout << Date(2022,1,15).week_day() << endl;
Date c = a + 30;
cout << c << endl;
return 0;
}
D:\work\C_Project\demo\demo\main.cpp:73: error: invalid initialization of non-const reference of type 'Date&' from an rvalue of type 'Date' cout << (a+30) << endl; ^

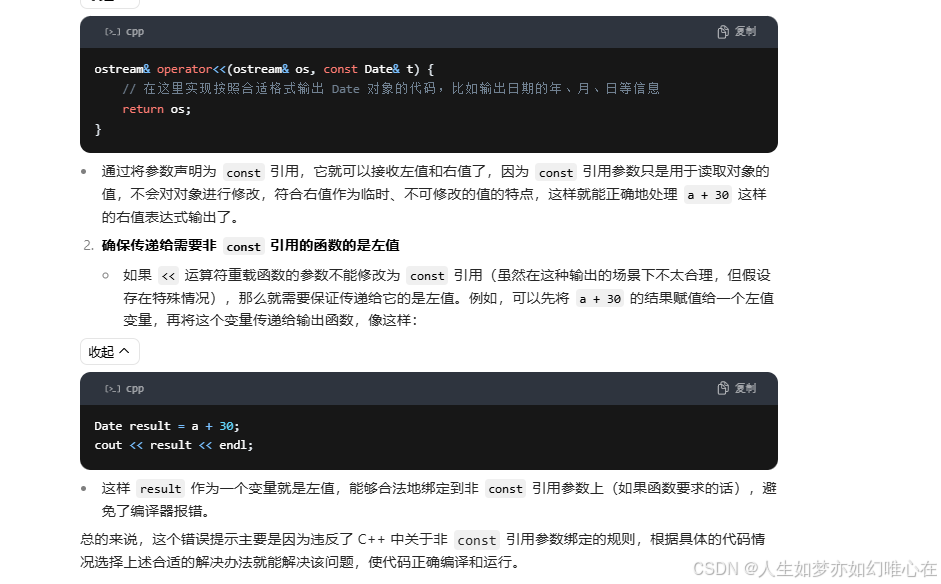
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Date{
public:
Date(){ k=0; }
Date(int y, int m, int d){ k = ymd_to_k(y,m,d); }
int year() const { int y, m, d; k_to_ymd(k, y, m, d); return y; }
int month() const { int y, m, d; k_to_ymd(k, y, m, d); return m; }
int day() const { int y, m, d; k_to_ymd(k, y, m, d); return d; }
int week_day() const { return k % 7; }
int operator-(Date& t){ return k - t.k; }
Date operator+(int x){ Date t; t.k = k + x; return t; }
Date operator-(int x){ return *this + (-x); }
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const Date& t);
private:
static bool leap_year(int y){
return (y%4==0 && y%100!=0) || y%400==0;
}
static int ymd_to_k(int y, int m, int d);
static void k_to_ymd(int k, int& y, int& m, int& d);
int k; //记录距离 公元1年1月1日,过去了多少天。
};
//输出
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const Date& t)
{
printf("%04d-%02d-%02d", t.year(), t.month(), t.day());
return os;
}
// 年月日 转为: 距离公元元年经过天数
int Date::ymd_to_k(int y, int m, int d)
{
int M[] = {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
if(Date::leap_year(y)) M[2]++;
int k = 0;
for(int i=1; i<y; i++) k += 365 + leap_year(i);
for(int i=1; i<m; i++) k += M[i];
return k + d;
}
// 距离公元元年经过天数 转为: 年月日
void Date::k_to_ymd(int k, int& y, int& m, int& d)
{
int M[] = {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
for(int i=1;; i++){
int t = 365 + Date::leap_year(i);
if(k<=t){
y = i;
break;
}
k -= t;
}
if(Date::leap_year(y)) M[2]++;
for(int i=1;;i++){
if(k<=M[i]){
m = i;
break;
}
k -= M[i];
}
d = k;
}
int main()
{
Date a(2000,12,31);
cout << a << endl;
Date b(2001,1,1);
cout << b << endl;
cout << (b-a) << endl;
cout << Date(2022,1,15).week_day() << endl;
//Date c = a + 30;
cout << (a+30) << endl;
return 0;
}


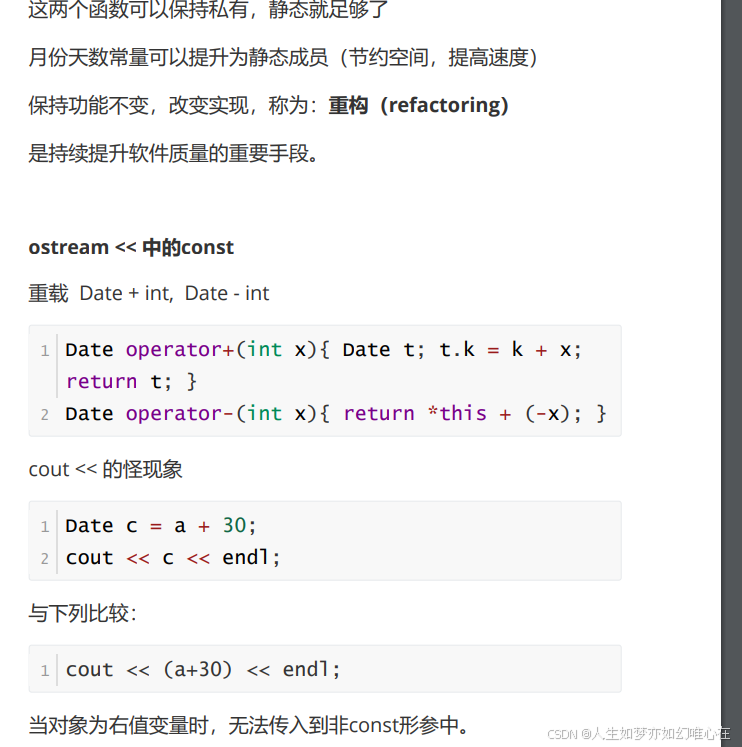
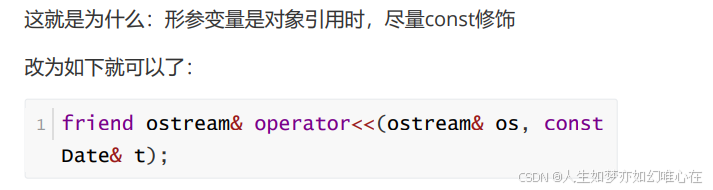
cpp
// 年月日 转为: 距离公元元年经过天数
int Date::ymd_to_k(int y, int m, int d)
{
int M[] = {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
if(Date::leap_year(y)) M[2]++;
int k = 0;
for(int i=1; i<y; i++) k += 365 + leap_year(i);
for(int i=1; i<m; i++) k += M[i];
return k + d;
}
// 距离公元元年经过天数 转为: 年月日
void Date::k_to_ymd(int k, int& y, int& m, int& d)
{
int M[] = {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
for(int i=1;; i++){
int t = 365 + Date::leap_year(i);
if(k<=t){
y = i;
break;
}
k -= t;
}
if(Date::leap_year(y)) M[2]++;
for(int i=1;;i++){
if(k<=M[i]){
m = i;
break;
}
k -= M[i];
}
d = k;
}

有理数类



cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Rati{
public:
Rati(){ p=1; q=1; }
Rati(int a, int b){ int g=gcd(a,b); p=a/g; q=b/g; }
Rati(int a){ p=a; q=1; }
Rati operator+(const Rati& t) const
{ return Rati(p*t.q+q*t.p, q*t.q); }
Rati operator+(int t) const
{ return *this + Rati(t); }
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const Rati& t);
friend Rati operator+(int t1, const Rati& t2);
private:
static int gcd(int a, int b){
if(b==0) return a;
return gcd(b,a%b);
}
int p; // 分子
int q; // 分母
};
Rati operator+(int t1, const Rati& t2)
{
return t2 + t1;
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const Rati& t)
{
cout << t.p;
if(t.q != 1) cout << "/" << t.q;
return os;
}
int main()
{
Rati a(30,50);
cout << a << endl;
cout << Rati(2) << endl;
cout << Rati(1,3) + Rati(1,6) << endl;
return 0;
}

字符串类
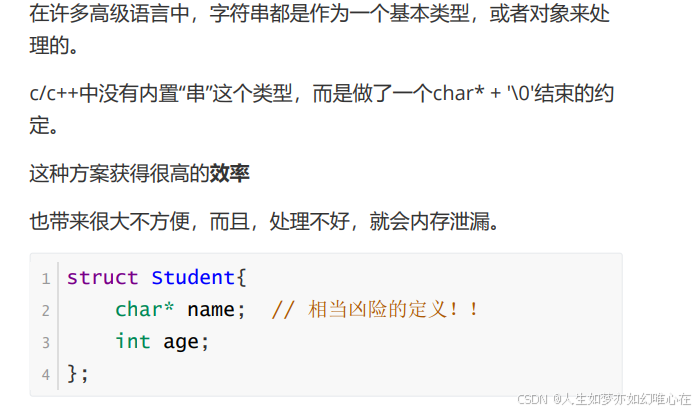


cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class Str{
public:
Str(){ ps = NULL; }
Str(const char* s){ copy(s); }
Str(const Str& t):Str(t.ps){}
~Str(){ clear(); }
Str& operator=(const Str& t){ return *this = t.ps; }
Str& operator=(const char* s) {
clear();
copy(s);
return *this;
}
Str operator+(const char* s) const {
int n1 = ps? strlen(ps) : 0;
int n2 = s? strlen(s) : 0;
Str t;
t.ps = new char [n1+n2+1];
t.ps[0] = 0;
if(ps) strcat(t.ps, ps);
if(s) strcat(t.ps,s);
return t;
}
operator const char*() const { return ps; } // Str -> const char*
private:
void clear(){
if(ps){
delete [] ps;
ps=NULL;
}
}
void copy(const char* s){
if(s==NULL) {
ps = NULL;
return;
}
ps = new char[strlen(s)+1];
strcpy(ps, s);
}
char* ps; // 被包装
};
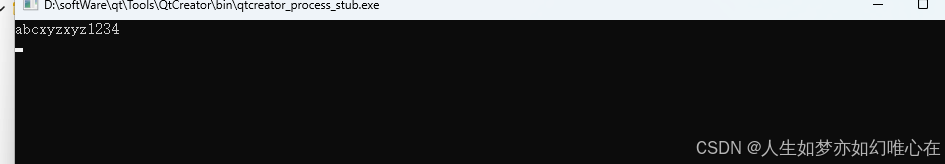
int main()
{
Str a("abc"); // 需要由 const char* 构造
Str b = "xyz"; // 需要由 const char* 构造
Str c = b; // 需要由 Str 拷贝构造
Str d = a + b + c + "1234";
// Str + Str; Str + char*;
// char* + Str; Str = char*; Str = Str
cout << d << endl; // ostream << Str
return 0;
}
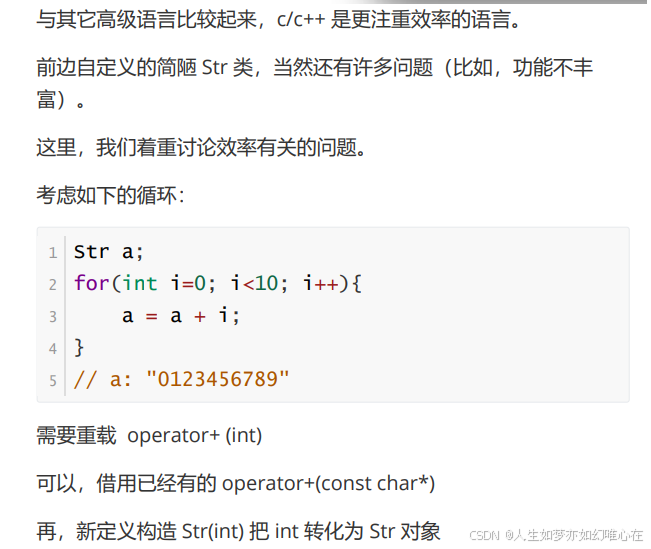
字符串类(2)


cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class Str{
public:
Str(){ ps = NULL; }
Str(const char* s){ copy(s); }
Str(const Str& t):Str(t.ps){}
Str(int x){
ps = new char[30];
itoa(x, ps, 10);
}
~Str(){ clear(); }
Str& operator=(const Str& t){ return *this = t.ps; }
Str& operator=(const char* s) {
clear();
copy(s);
return *this;
}
Str operator+(int x) const { return *this + Str(x); }
Str operator+(const char* s) const {
int n1 = ps? strlen(ps) : 0;
int n2 = s? strlen(s) : 0;
Str t;
t.ps = new char [n1+n2+1];
t.ps[0] = 0;
if(ps) strcat(t.ps, ps);
if(s) strcat(t.ps,s);
return t;
}
void reverse(){ if(ps) strrev(ps); }
operator const char*() const { return ps; } // Str -> const char*
private:
void clear(){
if(ps){
delete [] ps;
ps=NULL;
}
}
void copy(const char* s){
if(s==NULL) {
ps = NULL;
return;
}
ps = new char[strlen(s)+1];
strcpy(ps, s);
}
char* ps; // 被包装
};
int main()
{
Str a;
for(int i=0; i<10; i++){
a = a + i;
}
cout << a << endl;
return 0;
}
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class Str{
public:
Str(){ ps = NULL; }
Str(const char* s){ copy(s); }
Str(const Str& t):Str(t.ps){}
Str(int x){
ps = new char[30];
itoa(x, ps, 10);
}
~Str(){ clear(); cout << "~ ";}
Str& operator=(const Str& t){ return *this = t.ps; }
Str& operator=(const char* s) {
clear();
copy(s);
return *this;
}
Str operator+(int x) const { return *this + Str(x); }
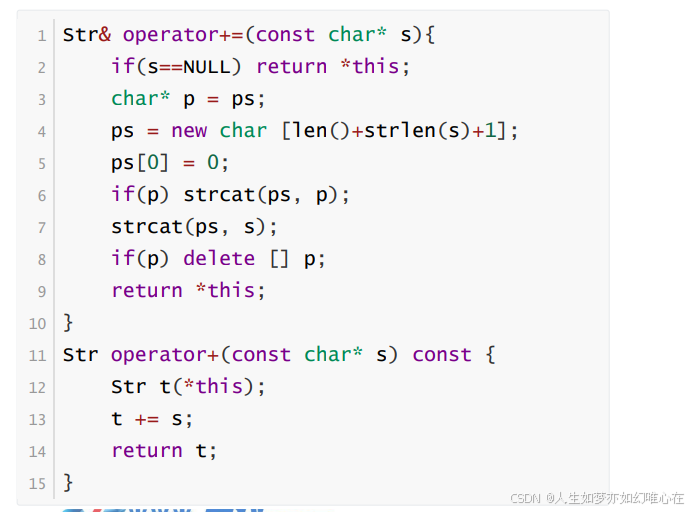
Str& operator+=(const char* s){
if(s==NULL) return *this;
char* p = ps;
ps = new char [len()+strlen(s)+1];
ps[0] = 0;
if(p) strcat(ps, p);
strcat(ps, s);
if(p) delete [] p;
return *this;
}
Str operator+(const char* s) const {
Str t(*this);
t += s;
return t;
}
int len(){
if(ps==NULL) return 0;
return strlen(ps);
}
void reverse(){ if(ps) strrev(ps); }
operator const char*() const { return ps; } // Str -> const char*
private:
void clear(){
if(ps){
delete [] ps;
ps=NULL;
}
}
void copy(const char* s){
if(s==NULL) {
ps = NULL;
return;
}
ps = new char[strlen(s)+1];
strcpy(ps, s);
}
char* ps; // 被包装
};
int main()
{
Str a;
for(int i=0; i<10; i++){
a += Str(i);
}
cout << a << endl;
return 0;
}
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class Str{
public:
Str(int n){
if(n<10) n=10;
cap = n;
ps = new char [cap];
*ps = '\0';
}
Str():Str(10){}
Str(const char* s):Str((s?strlen(s):0)+1){
if(s) strcpy(ps, s);
}
Str(const Str& t):Str(t.ps){}
~Str(){
delete [] ps;
//cout << "~ ";
}
Str& operator=(const Str& t){ return *this = t.ps; }
Str& operator=(const char* s) {
int n = (s? strlen(s) : 0) + 1;
if(cap < n){
cap = n * 2;
delete [] ps;
ps = new char [cap];
}
if(s)
strcpy(ps, s);
else
*ps = '\0';
return *this;
}
Str operator+(int x) const { return *this + Str(x); }
Str& operator+=(const char* s){
if(s==NULL) return *this;
char* p = ps;
int n = strlen(ps) + strlen(s) + 1;
if(cap < n){
cap = n * 2; // 多分配些
ps = new char [cap];
strcpy(ps, p);
delete [] p;
}
strcat(ps, s);
return *this;
}
Str operator+(const char* s) const {
Str t(*this);
t += s;
return t;
}
// 为了隐式转换
operator const char*() const { return ps; } // Str -> const char*
// 显示转换:从 Int 转为 Str
static Str from(int x){
Str t(30);
itoa(x, t.ps, 10);
return t;
}
private:
char* ps; // 被包装主体
int cap;
};
int main()
{
Str a;
for(int i=0; i<10; i++){
a += Str::from(i);
}
cout << a << endl;
return 0;
}

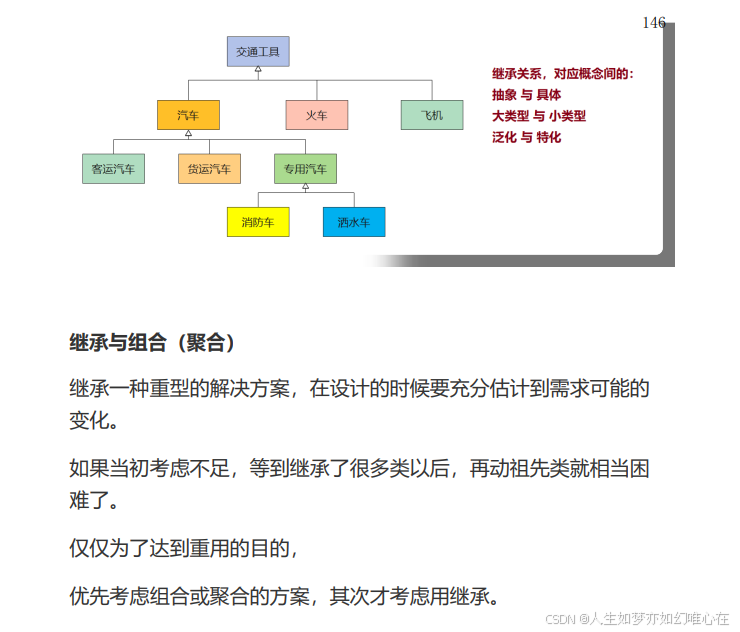
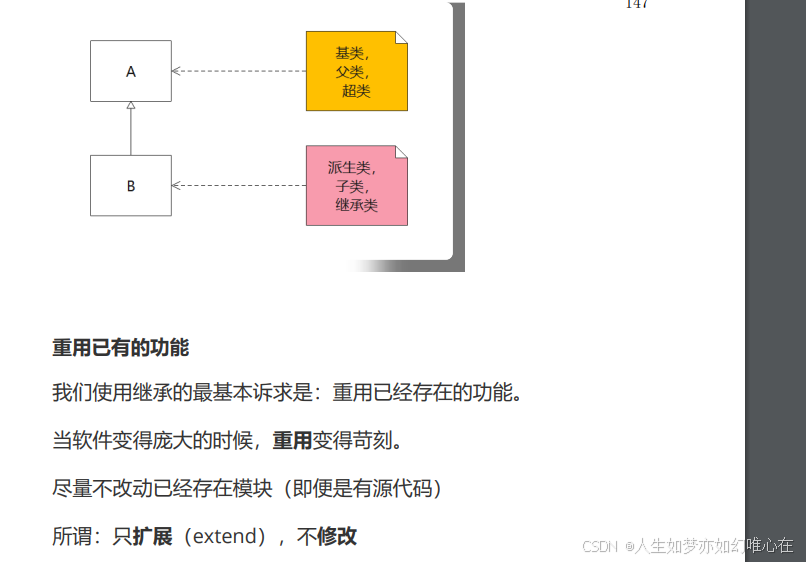
继承







cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Cnt{
public:
Cnt(){n=0;}
void inc(){n++;}
int get(){return n;}
private:
int n;
};
class Cnt2: public Cnt{
public:
Cnt2(int m){ max = m; }
Cnt2& inc(){
if(get() >= max) return *this;
Cnt::inc();
return *this;
}
private:
int max;
};
class Cnt3{
public:
Cnt3(int m){ max = m; }
Cnt3& inc(){
if(cnt.get() >= max) return *this;
cnt.inc();
return *this;
}
int get() { return cnt.get(); }
private:
int max;
Cnt cnt;
};
void f(Cnt& x)
{
cout << x.get() << endl;
}
int main()
{
Cnt2 a(3);
a.inc().inc().inc().inc();
f(a);
// Cnt3 a(3);
// a.inc().inc().inc().inc();
// cout << a.get() << endl;
return 0;
}
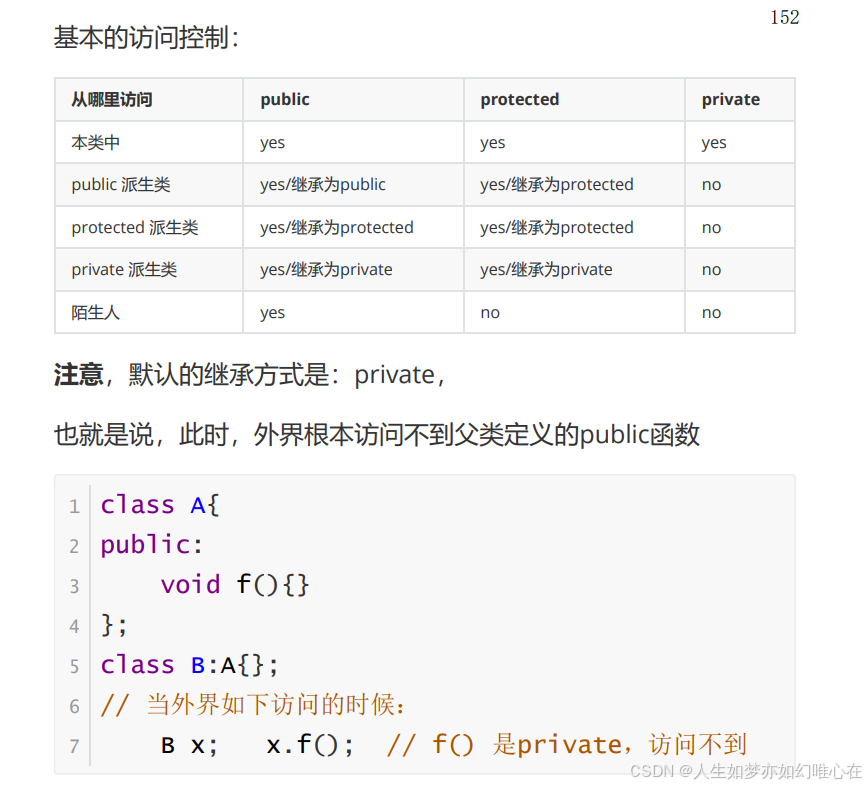
继承后的权限

cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Cnt{
public:
Cnt(){n=0;}
void inc(){n++;}
int get(){return n;}
private:
int n;
};
class Cnt2: public Cnt{
public:
Cnt2(int m){ max = m; }
Cnt2& inc(){
if(get() >= max) return *this;
Cnt::inc();
return *this;
}
private:
int max;
};
class Cnt3{
public:
Cnt3(int m){ max = m; }
Cnt3& inc(){
if(cnt.get() >= max) return *this;
cnt.inc();
return *this;
}
int get() { return cnt.get(); }
private:
int max;
Cnt cnt;
};
void f(Cnt& x)
{
cout << x.get() << endl;
}
class A{
public:
void f(){}
};
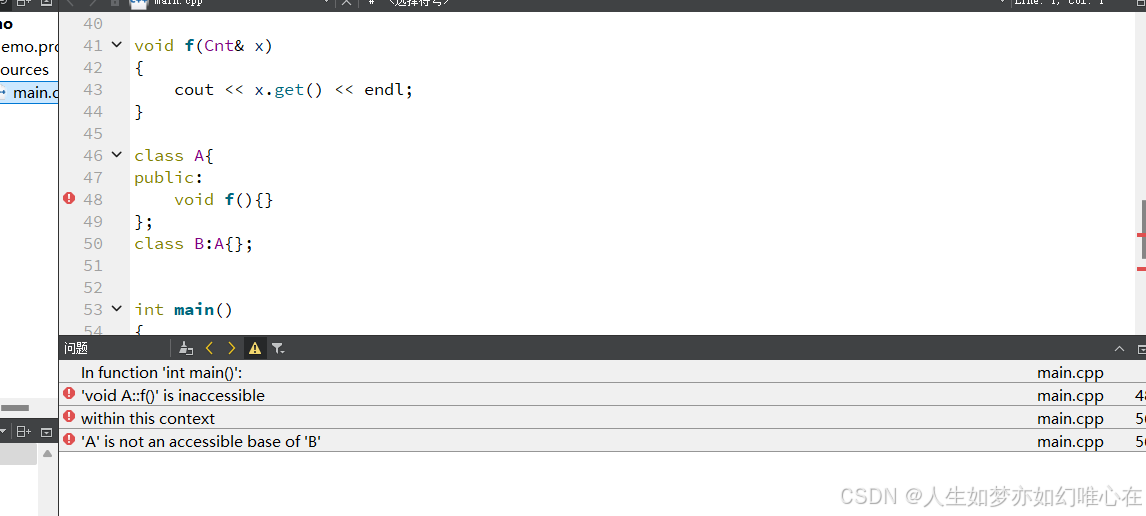
class B:A{};
int main()
{
B x;
x.f();
// Cnt2 a(3);
// a.inc().inc().inc().inc();
// f(a);
// Cnt3 a(3);
// a.inc().inc().inc().inc();
// cout << a.get() << endl;
return 0;
}



cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A{
public:
friend void fa(A& t);
private:
int a;
};
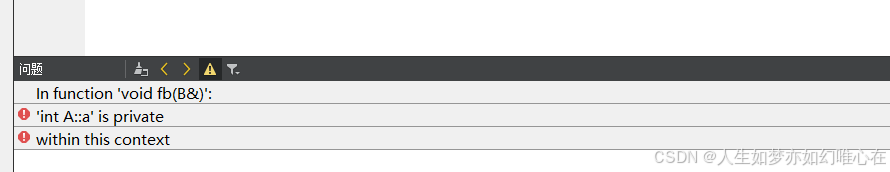
class B: public A{
public:
friend void fb(B& t);
private:
int b;
};
void fa(A& t){ t.a++; }
void fb(B& t){ t.b++; t.a++; } // 不可以,必须在A类中授权
int main()
{
return 0;
}
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class B;
class A{
public:
friend void fa(A& t);
friend void fb(B& t);
private:
int a;
};
class B: public A{
public:
friend void fb(B& t);
private:
int b;
};
void fa(A& t){ t.a++; }
void fb(B& t){ t.b++; t.a++; } // 不可以,必须在A类中授权
int main()
{
return 0;
}
多继承与二义性






cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A{
public:
int a;
};
class B1: public A{};
class B2: public A{};
class C:public B1, public B2{};
int main()
{
C x;
x.B1::a = 10;
x.B2::a = 20;
cout << x.B1::a << "," << x.B2::a << endl;
return 0;
}
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A{
public:
int a;
};
class B1: virtual public A{};
class B2: virtual public A{};
class C:public B1, public B2{};
int main()
{
C x;
x.B1::a = 10;
x.B2::a = 20;
cout << x.B1::a << "," << x.B2::a << endl;
return 0;
}
继承中的构造函数
总结构造函数:

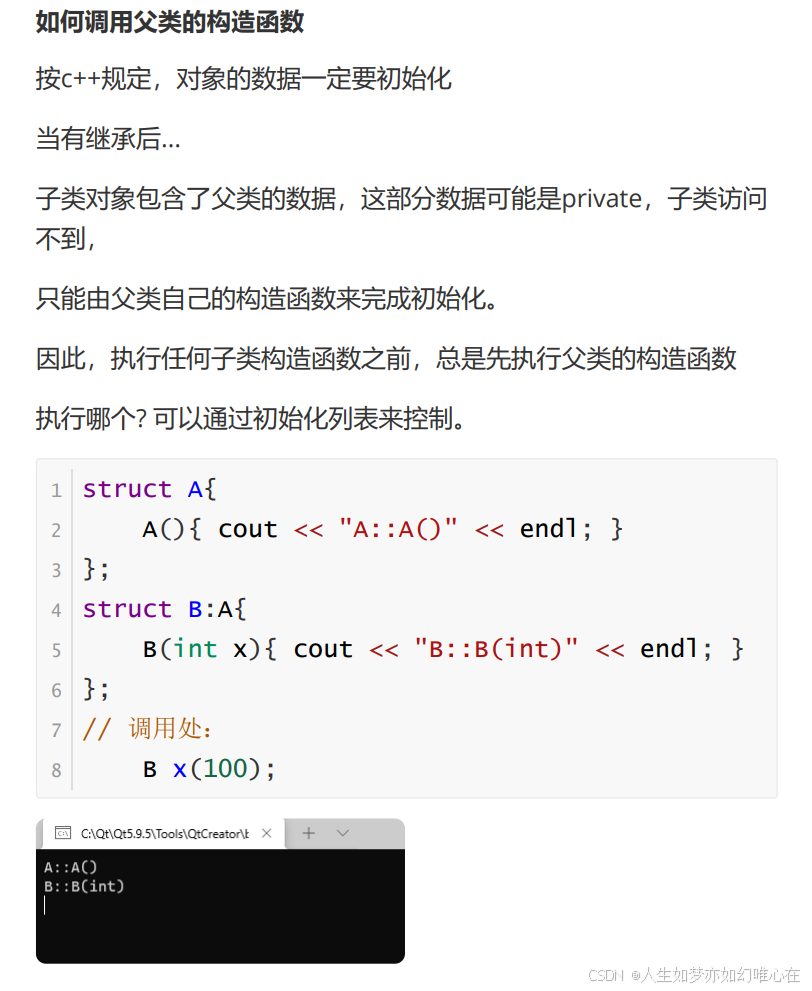






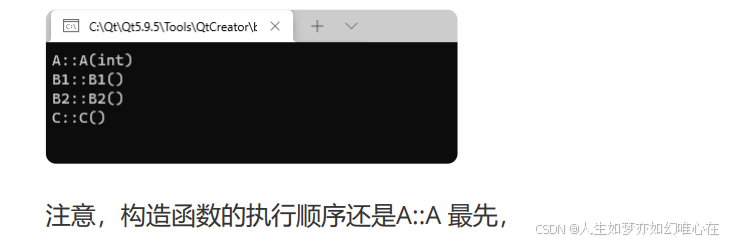

cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct A{
A(){ cout << "A::A()" << endl; }
};
struct B:A{
B(int x){ cout << "B::B(int)" << endl; }
};
int main()
{
B x(100);
return 0;
}
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct A{
A(){ cout << "A::A()" << endl; }
A(int a, char* b){ cout << "A::A(int, char*)" << endl; }
};
struct B: public A{
B():A(10,"abc"){ cout << "B::B()" << endl; }
B(int x){ cout << "B::B(int)" << endl; }
};
int main()
{
B x(100);
B y;
return 0;
}
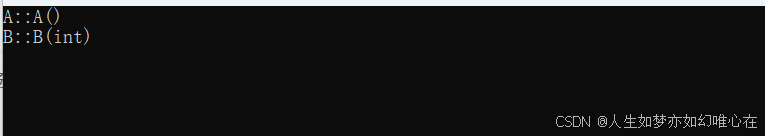
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct A{
A(){ cout << "A::A()" << endl; }
A(int){ cout << "A::A(int)" << endl; }
};
struct B1: virtual public A{
B1(){ cout << "B1::B1()" << endl; }
};
struct B2: virtual public A{
B2(){ cout << "B2::B2()" << endl; }
};
struct C: public B1, public B2{
C():A(33){ cout << "C::C()" << endl; }
};
int main()
{
C x;
return 0;
}
继承下的内存模型





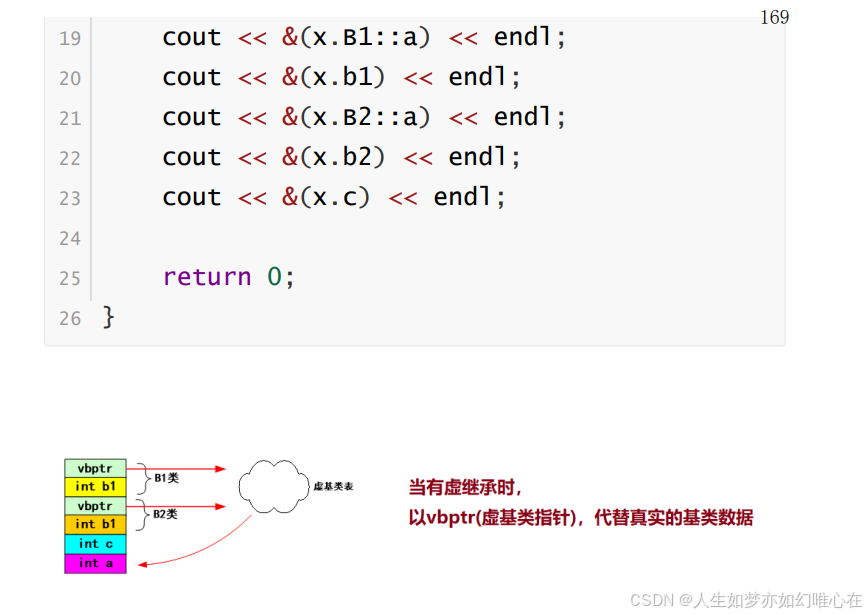

cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct A{
int a;
};
struct B1: A{
int b1;
};
struct B2: A{
int b2;
};
struct C:B1,B2{
int c;
};
int main()
{
C x;
cout << sizeof(x) << endl;
cout << &(x.B1::a) << endl;
cout << &(x.b1) << endl;
cout << &(x.B2::a) << endl;
cout << &(x.b2) << endl;
cout << &(x.c) << endl;
return 0;
}
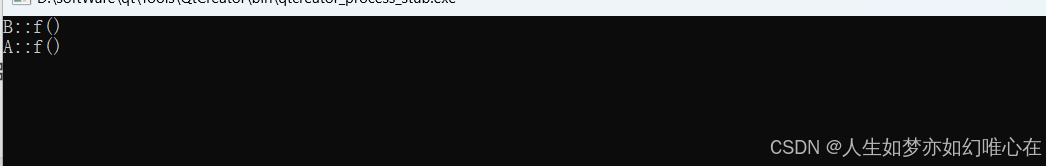
指针的泛化

cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A{
public:
void f() { cout << "A::f()" << endl; }
private:
int a;
};
class B: public A{
public:
void f() { cout << "B::f()" << endl; }
private:
int b;
};
int main()
{
B x;
x.f();
A* p = &x;
p->f();
return 0;
}


cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct A{
void f() { cout << "A::f()" << endl; }
int a;
};
struct A2{
int a2;
};
struct B: A, A2{
void f() { cout << "B::f()" << endl; }
int b;
};
int main()
{
B x;
cout << &x << endl;
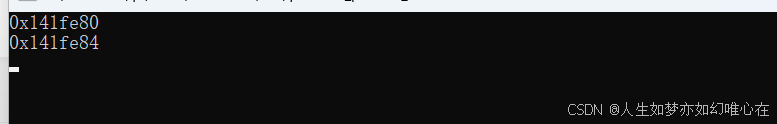
A2* p = &x;
cout << p << endl;
return 0;
}




多态


cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct A{
virtual void f(){ cout << "A::f" << endl; }
};
struct B1:A{
virtual void f(){ cout << "B1::f" << endl; }
};
struct B2:A{
virtual void f(){ cout << "B2::f" << endl; }
};
int main()
{
A* p;
int x;
cin >> x;
if(x<5)
p = new B1();
else
p = new B2();
p->f(); // 如何编译这个 f()?
return 0;
}




虚函数表
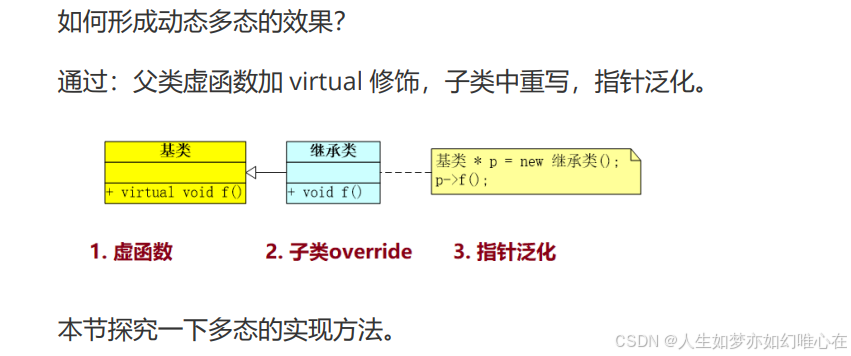





cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct A{
virtual void fa(){ cout << "A:fa()" << endl; }
virtual void fb(){ cout << "A:fb()" << endl; }
void ga(){ cout << "A:ga()" << endl; }
void gb(int);
int a;
};
struct B:A{
virtual void fa(){ cout << "B:fa()" << endl; }
void ga(){ cout << "B:ga()" << endl; }
int a;
};
int main()
{
A* p = new B();
p->fa();
p->fb();
p->ga();
return 0;
}


cpp
#include <iostream>
class Base {
public:
virtual void func() {
std::cout << "Base::func()" << std::endl;
}
int a;
};
class Derived : public Base {
public:
void func() override {
std::cout << "Derived::func()" << std::endl;
}
int b;
};
int main() {
Base* ptr = new Derived();
ptr->func();
return 0;
}

虚析构函数


cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Shape{
Shape(){ cout << "create Shape" << endl; }
~Shape() { cout << "destroy Shape" << endl; }
};
struct Circle:Shape{
Circle(){ cout << "create Circle" << endl; }
~Circle(){ cout << "destroy Circle" << endl; }
};
struct Rect:Shape{
Rect(){ cout << "create Rect" << endl; }
~Rect(){ cout << "destroy Rect" << endl; }
};
struct Triangle:Shape{
Triangle(){ cout << "create Triangle" << endl; }
~Triangle(){ cout << "destroy Triangle" << endl; }
};
int main()
{
Shape* x[3];
x[0] = new Circle();
x[1] = new Rect();
x[2] = new Triangle();
for(int i=0; i<3; i++) delete x[i];
return 0;
}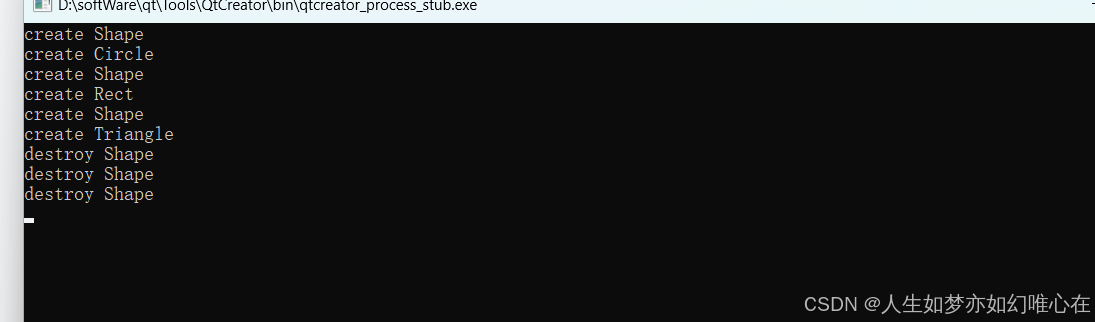
子类对象指针并没有回收
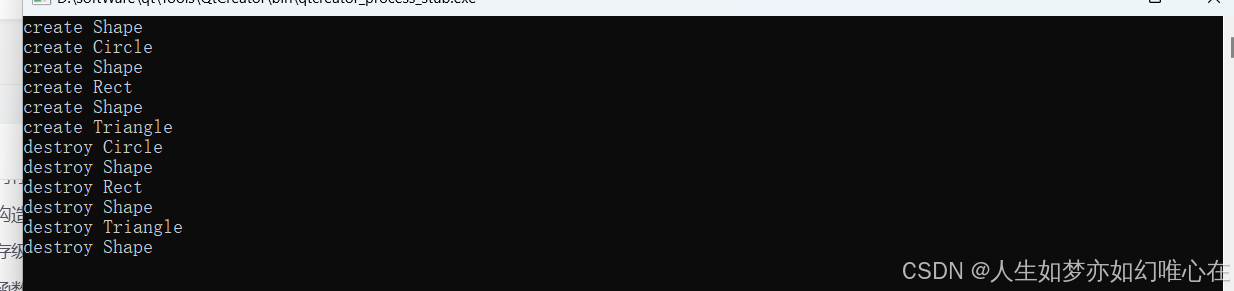
加了虚析构函数之后的效果
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Shape{
Shape(){ cout << "create Shape" << endl; }
virtual ~Shape() { cout << "destroy Shape" << endl; }
};
struct Circle:Shape{
Circle(){ cout << "create Circle" << endl; }
virtual ~Circle(){ cout << "destroy Circle" << endl; }
};
struct Rect:Shape{
Rect(){ cout << "create Rect" << endl; }
virtual ~Rect(){ cout << "destroy Rect" << endl; }
};
struct Triangle:Shape{
Triangle(){ cout << "create Triangle" << endl; }
virtual ~Triangle(){ cout << "destroy Triangle" << endl; }
};
int main()
{
Shape* x[3];
x[0] = new Circle();
x[1] = new Rect();
x[2] = new Triangle();
for(int i=0; i<3; i++) delete x[i];
return 0;
}
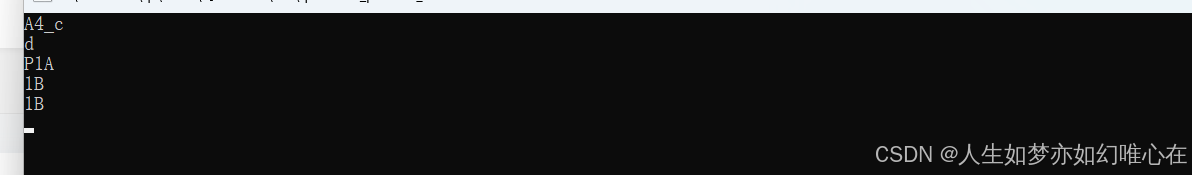
RTTI机制

cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <typeinfo>
using namespace std;
struct A{virtual void f(){}};
struct B:A{int x;};
int main()
{
A* p = new B();
cout << typeid("abc").name() << endl;
cout << typeid(123.5).name() << endl;
cout << typeid(p).name() << endl;
cout << typeid(*p).name() << endl;
cout << typeid(B).name() << endl;
return 0;
}


cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <typeinfo>
using namespace std;
struct A{
virtual void f(){ cout << "A::f()" << endl; }
};
struct B{
virtual void g(){ cout << "B::g()" << endl; }
};
struct C:A,B{
void h() { cout << "C::h()" << endl; }
};
int main()
{
B* p = new C();
if(typeid(*p)==typeid(C)){
C* q = dynamic_cast<C*>(p);
q->h();
}
return 0;
}
为什么当有多继承的时候,父类指针的值并不一定等于子类对 象的首地址?

cpp
class Base1 {
public:
int base1Data;
};
class Base2 {
public:
int base2Data;
};
class Derived : public Base1, public Base2 {
public:
int derivedData;
};
cpp
- 在这个例子中,`Derived`类对象的内存布局可能是先存放`Base1`部分(包含`base1Data`),然后是`Base2`部分(包含`base2Data`),最后是`Derived`自身部分(包含`derivedData`)。
2. **父类指针与子类对象地址关系**
- **当父类指针指向派生类对象的第一个基类部分时**:
- 如果有一个`Base1`类型的指针指向`Derived`类对象,这个指针的值等于`Derived`类对象的首地址,因为`Derived`对象的内存布局中第一个部分就是`Base1`部分。例如:
```cpp
int main() {
Derived d;
Base1* pBase1 = &d;
std::cout << "Address of d: " << &d << std::endl;
std::cout << "Value of pBase1: " << pBase1 << std::endl;
return 0;
}
cpp
int main() {
Derived d;
Base2* pBase2 = &d;
std::cout << "Address of d: " << &d << std::endl;
std::cout << "Value of pBase2: " << pBase2 << std::endl;
return 0;
}
cpp
- 此时`pBase2`的值是`Derived`对象中`Base2`部分的起始地址,它大于`Derived`对象的首地址,两者的差值等于`Base1`部分在`Derived`对象内存中占用的大小。
3. **指针偏移的计算(与虚函数表相关情况更复杂)**
- 在没有虚函数等复杂情况时,编译器可以根据对象的内存布局和指针类型计算正确的偏移量。例如,从`Base2`指针转换回`Derived`指针(假设正确使用`dynamic_cast`等安全转换方式),编译器知道`Base2`在`Derived`对象中的位置,能够正确地调整指针值,使其指向`Derived`对象的首地址。
- 但如果涉及虚函数,每个包含虚函数的基类都可能有自己的虚函数表指针,这会使对象的内存布局更加复杂。在多继承并且存在虚函数的情况下,编译器需要考虑更多因素来正确处理指针转换和偏移,以确保能够正确地调用虚函数并且在不同的基类指针和派生类指针之间进行正确的转换。例如,当通过一个非首地址的基类指针(如上述`Base2`指针)调用虚函数时,编译器需要根据虚函数表和对象内存布局来找到正确的函数版本进行调用。抽象类型

cpp
class AbstractClass {
public:
virtual void pureVirtualFunction() = 0;
};
int main() {
// 以下代码会导致编译错误,因为不能实例化抽象类
AbstractClass a;
return 0;
}
cpp
- **作为基类使用**:
- 抽象类主要的用途是作为基类,为派生类提供一个接口规范。派生类必须实现抽象类中的纯虚函数,否则派生类自己也会成为抽象类。例如:
```cpp
class AbstractClass {
public:
virtual void pureVirtualFunction() = 0;
};
class DerivedClass : public AbstractClass {
public:
void pureVirtualFunction() override {
std::cout << "Implementation in DerivedClass" << std::endl;
}
};
int main() {
DerivedClass d;
d.pureVirtualFunction();
return 0;
}
cpp
class Shape {
public:
virtual void draw() = 0;
};
class Circle : public Shape {
public:
void draw() override {
std::cout << "Drawing a circle" << std::endl;
}
};
class Square : public Shape {
public:
void draw() override {
std::cout << "Drawing a square" << std::endl;
}
};
cpp
- 这里`Shape`类通过`draw`纯虚函数定义了一个所有图形都应该实现的绘制接口。`Circle`和`Square`等派生类根据自己的特点实现了`draw`函数,这样就可以通过一个统一的`Shape`指针或引用(多态性)来调用不同图形的绘制函数,例如:
```cpp
int main() {
Shape* shapePtr1 = new Circle();
Shape* shapePtr2 = new Square();
shapePtr1->draw();
shapePtr2->draw();
delete shapePtr1;
delete shapePtr2;
return 0;
}


cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class SavAcc{
public:
SavAcc() { balance = 0; }
virtual int year_interest() final{
int sum = balance;
for(int i=0; i<12; i++){
sum += (int)(sum * mon_inter_rate(i) / 100 + 0.5);
}
return sum - balance;
}
virtual double mon_inter_rate(int x) = 0; // 强制子类必须完成
void deposit(int x){ //存款
balance += x;
}
int get_balance() { return balance; }
protected:
int balance; //余额
};
class T1SavAcc: public SavAcc{
public:
virtual double mon_inter_rate(int x) override {
if(x<3) return 0.3;
return 0.25;
}
};
class T2SavAcc: public SavAcc{
public:
virtual double mon_inter_rate(int x) override {
return 0.3;
}
};
int main()
{
T1SavAcc a;
a.deposit(10000);
cout << a.year_interest() << endl;
cout << a.get_balance() << endl;
return 0;
}
接口

cpp
class IPrintable {
public:
virtual void print() = 0;
};
cpp
- 这里`IPrintable`可以看作是一个接口,它规定了任何实现这个接口的类(即派生类)都必须实现`print`函数。这个接口类没有成员变量,只有一个纯虚函数`print`,用于定义打印相关的行为。
3. **接口的实现(通过派生类)**
- 当一个类想要实现接口时,它需要从接口类派生,并实现接口中的所有纯虚函数。例如:
```cpp
class Document : public IPrintable {
public:
void print() override {
std::cout << "Document is printing..." << std::endl;
}
};
cpp
class IStorable {
public:
virtual void save() = 0;
virtual void load() = 0;
};
class PDFDocument : public Document, public IStorable {
public:
void save() override {
std::cout << "PDFDocument is saving..." << std::endl;
}
void load() override {
std::cout << "PDFDocument is loading..." << std::endl;
}
};
cpp
- 这里`PDFDocument`类继承了`Document`类(它已经实现了`IPrintable`接口)和`IStorable`接口,并且实现了`IStorable`接口中的`save`和`load`函数。这样`PDFDocument`类就同时实现了打印功能(通过`IPrintable`接口)和存储功能(通过`IStorable`接口)。
5. **接口与多态性**
- 接口是实现多态性的重要工具。通过接口指针或引用,可以调用实现接口的不同派生类中的函数,实现根据对象实际类型调用相应函数的效果。例如:
```cpp
void printDocument(IPrintable* doc) {
doc->print();
}
int main() {
Document doc;
printDocument(&doc);
PDFDocument pdfDoc;
printDocument(&pdfDoc);
return 0;
}

cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
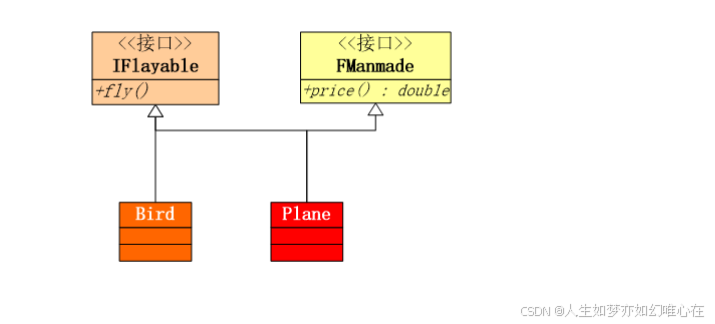
struct IFlyable{
virtual void fly() = 0;
virtual ~IFlyable(){}
};
struct IManmade{
virtual double price() = 0;
virtual ~IManmade() {}
};
class Bird: public IFlyable{
public:
virtual void fly() override {
cout << "I am a bird, flying..." << endl;
}
};
class Plane: public IFlyable, public IManmade {
public:
virtual void fly() override {
cout << "a plane can fly..." << endl;
}
virtual double price() {
return 112345.6;
}
};
void f(IFlyable& x)
{
cout << "beijing--->shanghai" << endl;
x.fly();
}
void g(IManmade& x)
{
if(x.price() < 1000)
cout << "cheap!" << endl;
else
cout << "expensive!" << endl;
}
int main()
{
Plane a;
f(a);
g(a);
return 0;
}
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
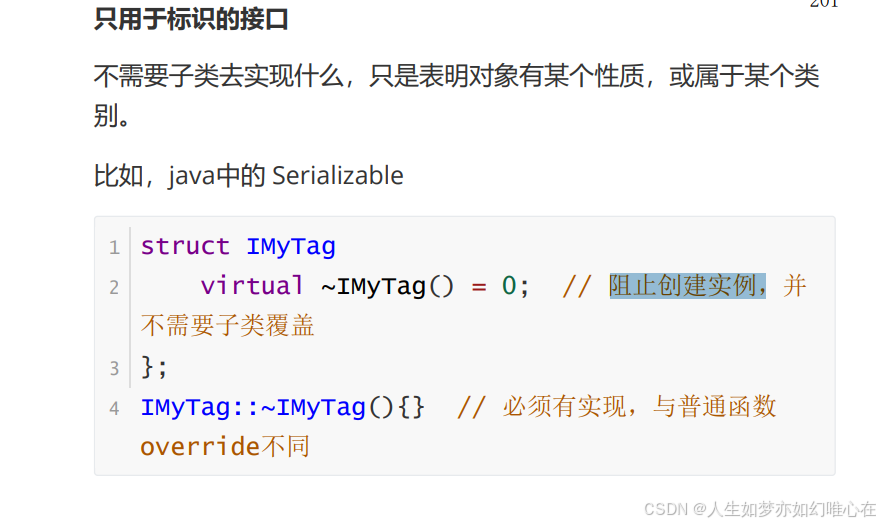
class IMyTag{
public:
virtual ~IMyTag() =0 ;
};
IMyTag::~IMyTag(){}
class A:public IMyTag{
public:
//virtual ~A(){}
};
int main()
{
IMyTag* p = new A();
delete p;
return 0;
}

cpp
class A:public IMyTag{
public:
virtual ~A() {
// 可以在这里添加一些针对 A 类资源清理的特定代码,如果有的话
IMyTag:: ~IMyTag();
}
};
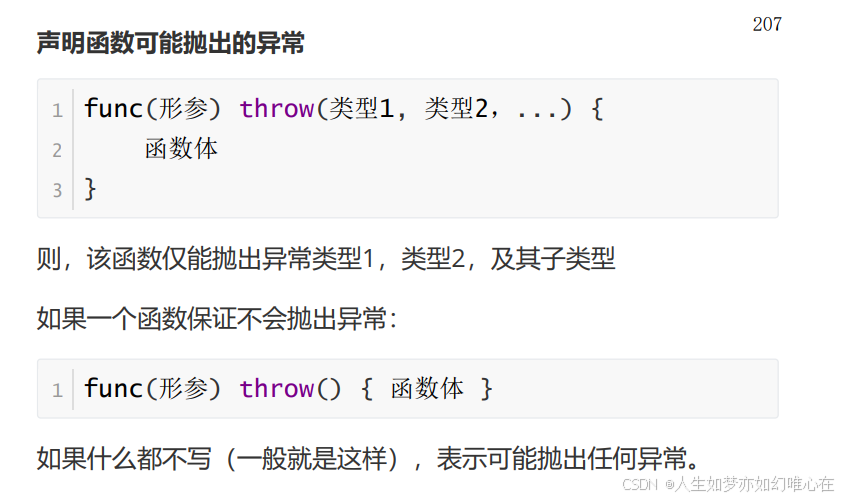
异常处理






cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class MyArray{
public:
MyArray(int size){
pData = new int [size];
this->size = size;
}
int& operator[] (int x){
if(x<0 || x >=size) throw "bad index";
return pData[x];
}
~MyArray(){
delete [] pData;
}
private:
int* pData;
int size;
};
int main()
{
try{
MyArray a(10);
a[10] = 555;
cout << a[15] << endl;
}
catch(const char* e){
cout << "ERR: " << e << endl;
}
catch(bad_array_new_length& e){
cout << "ERR: " << e.what() << endl;
}
return 0;
}

cpp
double divide(double dividend, double divisor) {
if (divisor == 0) {
throw "Division by zero error";
}
return dividend / divisor;
}
int main() {
try {
double result = divide(5.0, 0.0);
std::cout << "Result: " << result << std::endl;
} catch (const char* errorMessage) {
std::cerr << "Error: " << errorMessage << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
cpp
- **解释说明**:
- 在`divide`函数中,如果除数`divisor`为0,就抛出一个字符串类型的异常(`throw "Division by zero error";`)。
- 在`main`函数中,通过`try - catch`块来捕获可能抛出的异常。`try`块中包含可能会抛出异常的代码,在这里是调用`divide`函数。
3. **异常的捕获(`try - catch`)**
- **语法与示例**:
- `try - catch`块用于捕获和处理异常。`try`块包围着可能抛出异常的代码,`catch`块用于捕获特定类型的异常并进行处理。可以有多个`catch`块来捕获不同类型的异常。例如:
```cpp
class FileOpenError {};
void openFile(const char* filename) {
// 假设这里有文件打开失败的情况
throw FileOpenError();
}
int main() {
try {
openFile("nonexistent_file.txt");
} catch (const FileOpenError& error) {
std::cerr << "File open error occurred." << std::endl;
} catch (const char* errorMessage) {
std::cerr << "Error: " << errorMessage << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
cpp
class Resource {
public:
Resource() {
std::cout << "Resource acquired." << std::endl;
}
~Resource() {
std::cout << "Resource released." << std::endl;
}
};
void func2() {
Resource res;
throw "An error occurred in func2";
}
void func1() {
try {
func2();
} catch (const char* errorMessage) {
std::cerr << "Caught error in func1: " << errorMessage << std::endl;
}
}
int main() {
func1();
return 0;
}
cpp
- 在这个例子中,`func2`函数中创建了一个`Resource`类的对象`res`,然后抛出一个异常。当异常抛出后,由于`func2`函数没有捕获这个异常,异常会传播到`func1`函数。在异常传播过程中,会自动调用`res`对象的析构函数(栈展开),释放资源。然后`func1`函数中的`catch`块会捕获这个异常并进行处理。
5. **标准异常类(`std::exception`及其派生类)**
- C++标准库提供了一系列标准的异常类,它们都派生自`std::exception`类。这些标准异常类包括`std::runtime_error`(用于表示运行时错误)、`std::logic_error`(用于表示逻辑错误)等。例如:
```cpp
#include <stdexcept>
double divide(double dividend, double divisor) {
if (divisor == 0) {
throw std::runtime_error("Division by zero");
}
return dividend / divisor;
}
int main() {
try {
double result = divide(5.0, 0.0);
std::cout << "Result: " << result << std::endl;
} catch (const std::runtime_error& error) {
std::cerr << "Error: " << error.what() << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
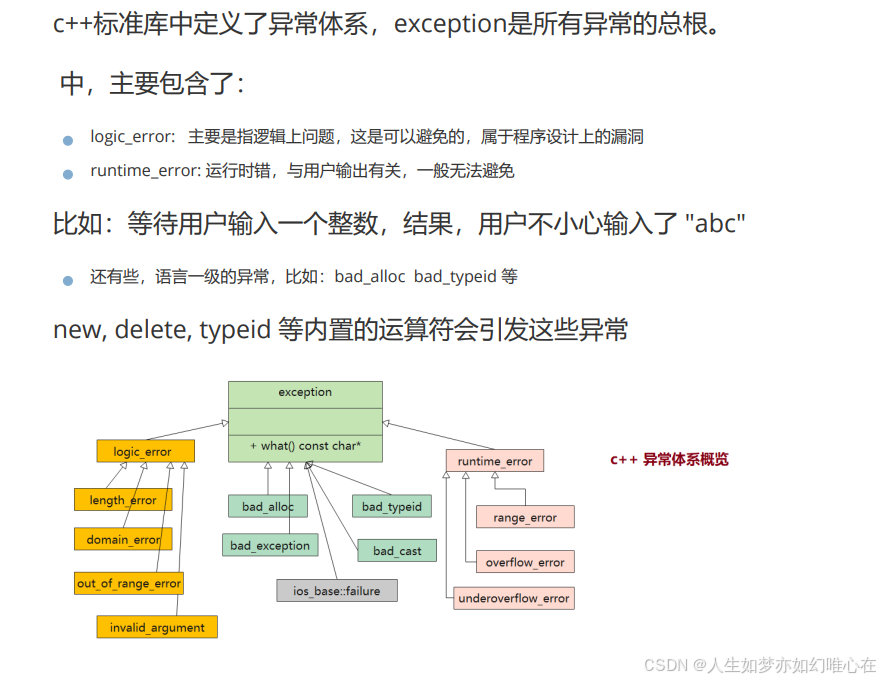
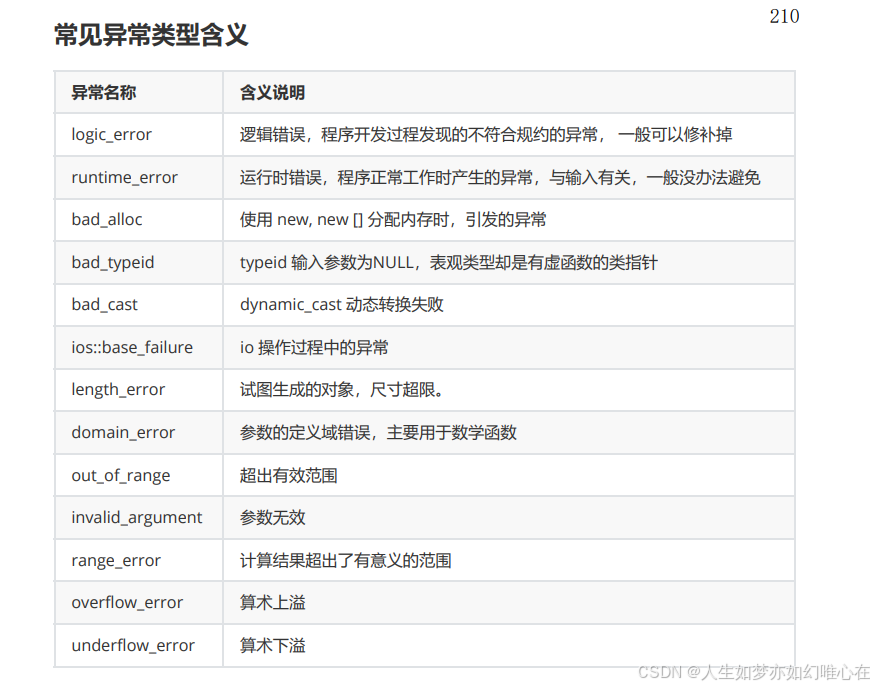
标准库中的异常类



cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
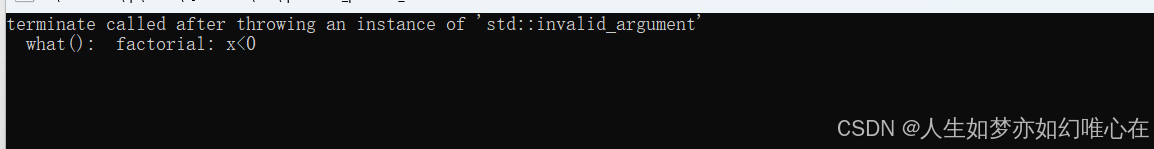
long long fac(int x)
{
if(x<0) throw invalid_argument("factorial: x<0");
if(x==0) return 1LL;
return fac(x-1) * x;
}
int main()
{
fac(-10);
// try{
// int* a = new int[-10];
// }
// catch(bad_array_new_length& e){
// cout << e.what() << endl;
// }
return 0;
}
自定义异常类型

cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct IndexError: logic_error{
IndexError(int min, int max, int x):logic_error(""){
sprintf(err,"index must between %d-%d, but get: %d",
min, max, x);
}
virtual const char* what() const throw() override{
return err;
}
char err[100];
};
class MyArray{
public:
MyArray(int size){
pData = new int [size];
this->size = size;
}
int& operator[] (int x){
if(x<0 || x >=size) throw IndexError(0,size-1,x);
return pData[x];
}
~MyArray(){
delete [] pData;
}
private:
int* pData;
int size;
};
int main()
{
try{
MyArray a(20);
a[9] = 555;
cout << a[25] << endl;
}
catch(IndexError& e){
cout << e.what() << endl;
}
}
RAII
c++ 标准支持try...catch 结构,却没有提供对 try..finally 的支持。





cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct A{
A() { cout << "acquire resource..." << endl; }
~A() { cout << "free resource...." << endl; }
};
void f()
{
cout << "begin..." << endl;
A a;
throw "bad argument";
cout << "after exception.." << endl;
}
int main()
{
try{
f();
}
catch(...){
}
return 0;
}


栈

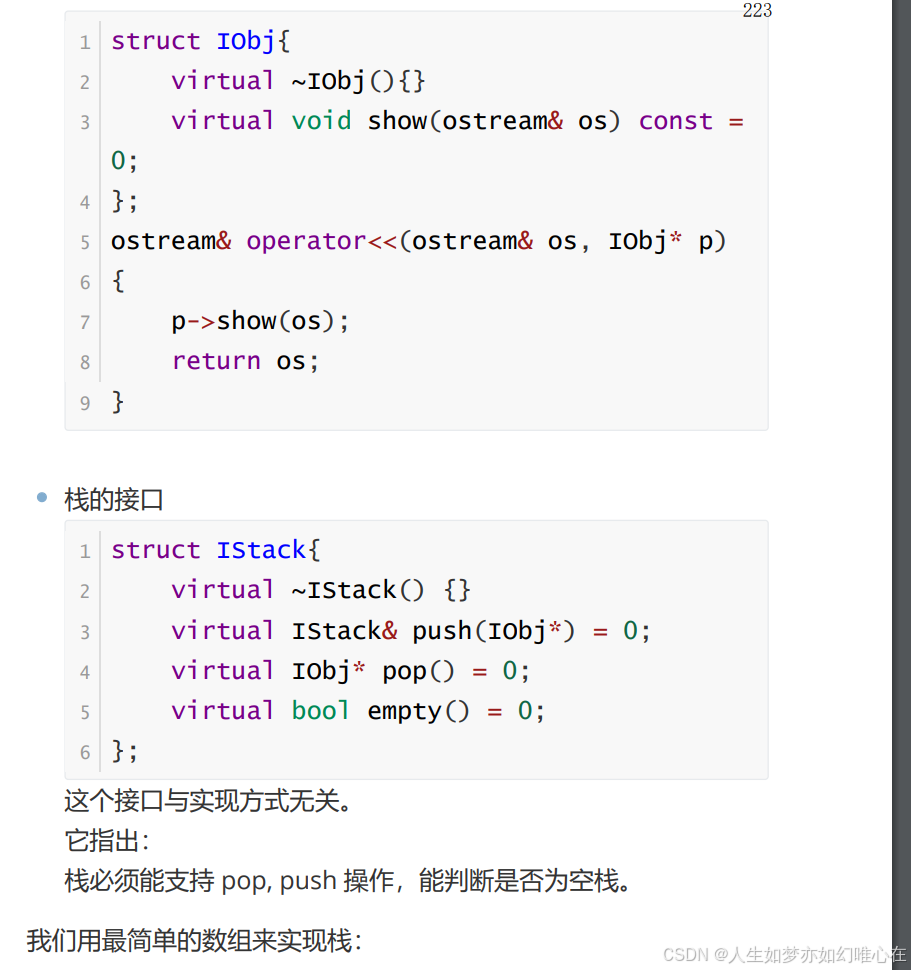


cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct IObj{
virtual ~IObj(){}
virtual void show(ostream& os) const = 0;
};
struct IStack{
virtual ~IStack() {}
virtual IStack& push(IObj*) = 0;
virtual IObj* pop() = 0;
virtual bool empty() = 0;
};
class MyStack:public IStack{
public:
MyStack() { n = 0; }
virtual MyStack& push(IObj* x) override{
if(n>=100) throw "stack overflow";
data[n++] = x;
return *this;
}
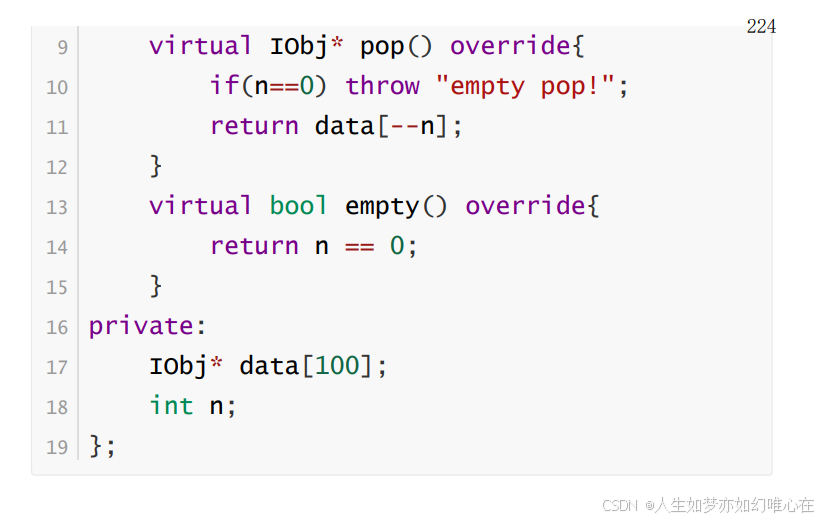
virtual IObj* pop() override{
if(n==0) throw "empty pop!";
return data[--n];
}
virtual bool empty() override{
return n == 0;
}
private:
IObj* data[100];
int n;
};
struct Point: public IObj{
Point():Point(0,0){}
Point(int x, int y){this->x=x; this->y=y;}
virtual void show(ostream& os) const override{
os << "(" << x << "," << y << ")";
}
int x;
int y;
};
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, IObj* p)
{
p->show(os);
return os;
}
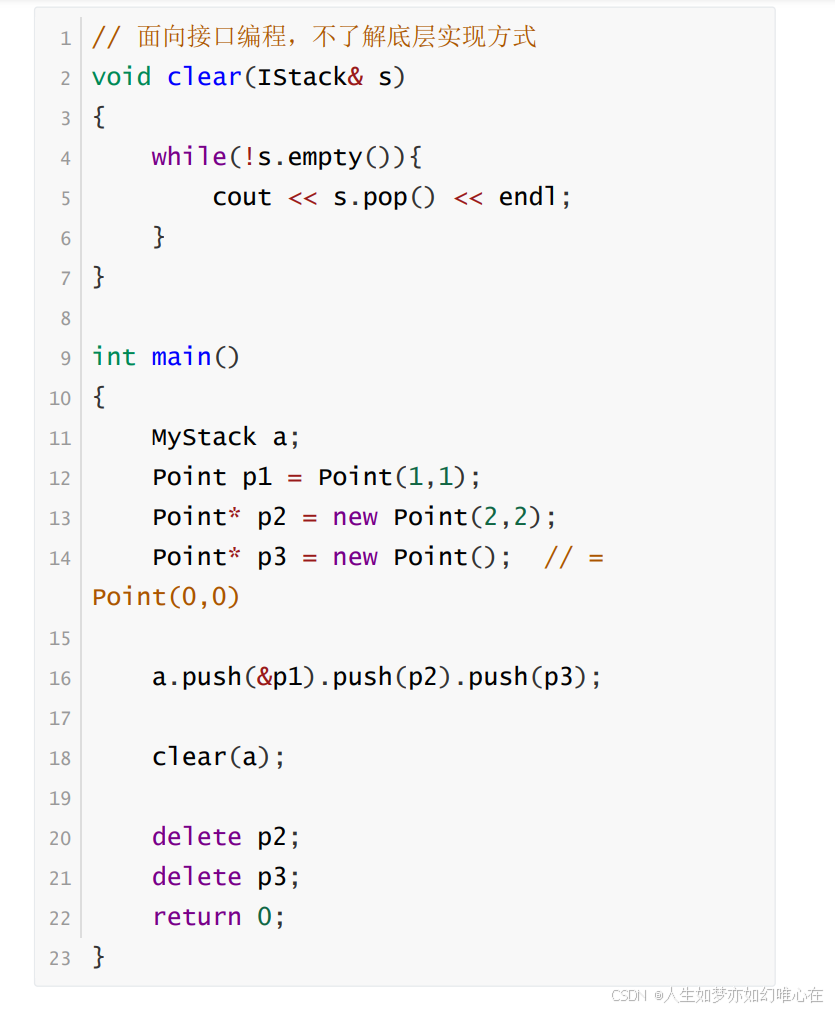
// 面向接口编程,不了解底层实现方式
void clear(IStack& s)
{
while(!s.empty()){
cout << s.pop() << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
MyStack a;
Point p1 = Point(1,1);
Point* p2 = new Point(2,2);
Point* p3 = new Point(); // = Point(0,0)
a.push(&p1).push(p2).push(p3);
clear(a);
delete p2;
delete p3;
return 0;
}
栈的链式实现

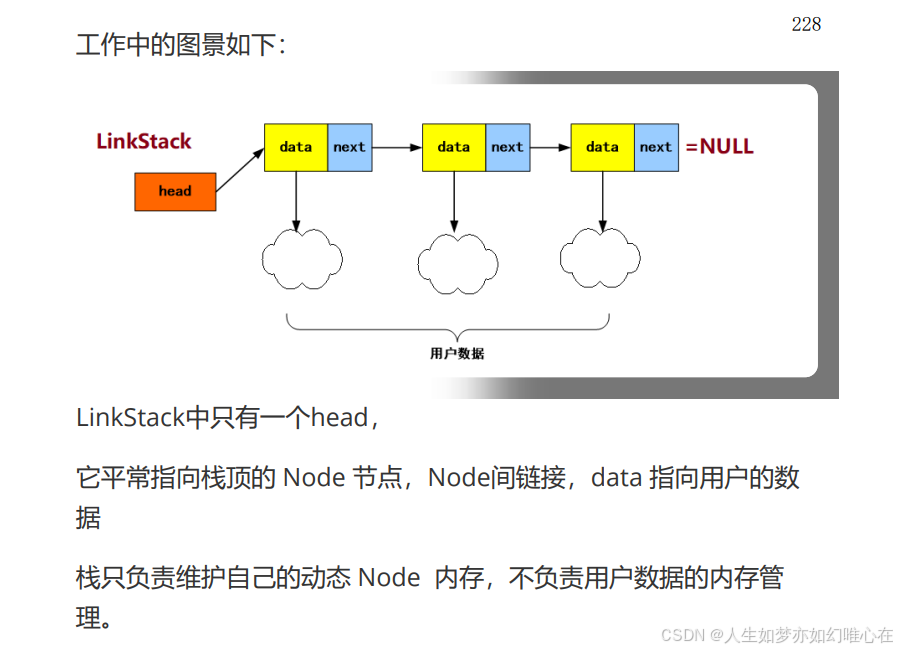
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct IObj{
virtual ~IObj(){}
virtual void show(ostream& os) const = 0;
};
struct IStack{
virtual ~IStack() {}
virtual IStack& push(IObj*) = 0;
virtual IObj* pop() = 0;
virtual bool empty() = 0;
};
class LinkStack:public IStack{
public:
LinkStack() { head = NULL; }
virtual LinkStack& push(IObj* x) override{
head = new Node{x, head};
return *this;
}
virtual IObj* pop() override{
if(head==NULL) throw "empty pop!";
Node* t = head;
IObj* rt = t->data;
head = head->next;
delete t;
return rt;
}
virtual bool empty() override{
return head==NULL;
}
private:
struct Node{
IObj* data;
Node* next;
};
private:
Node* head;
};
struct Point: public IObj{
Point():Point(0,0){}
Point(int x, int y){this->x=x; this->y=y;}
virtual void show(ostream& os) const override{
os << "(" << x << "," << y << ")";
}
int x;
int y;
};
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, IObj* p)
{
p->show(os);
return os;
}
// 面向接口编程,不了解底层实现方式
void clear(IStack& s)
{
while(!s.empty()){
cout << s.pop() << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
LinkStack a;
Point p1 = Point(1,1);
Point* p2 = new Point(2,2);
Point* p3 = new Point(); // = Point(0,0)
a.push(&p1).push(p2).push(p3);
clear(a);
delete p2;
delete p3;
return 0;
}
栈的块链实现

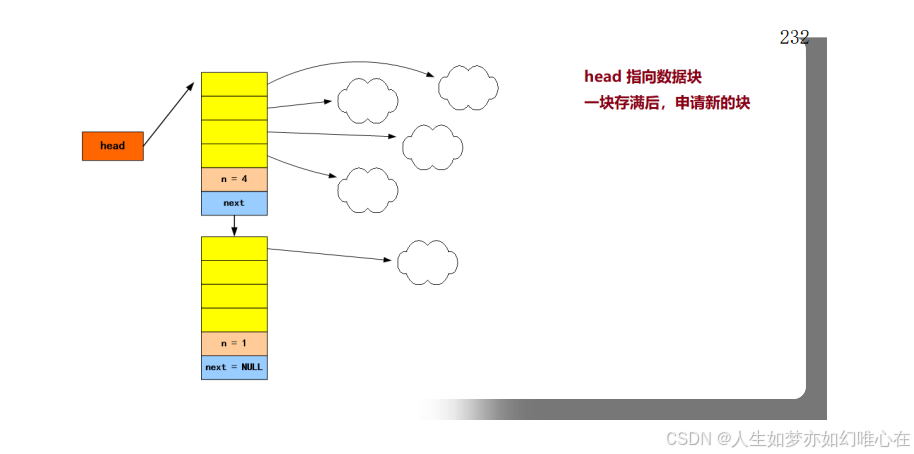
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct IObj{
virtual ~IObj(){}
virtual void show(ostream& os) const = 0;
};
struct IStack{
virtual ~IStack() {}
virtual IStack& push(IObj*) = 0;
virtual IObj* pop() = 0;
virtual bool empty() = 0;
};
class BlockStack:public IStack{
public:
BlockStack() { head = NULL; }
~BlockStack() { while(!empty()) delete pop(); }
virtual BlockStack& push(IObj* x) override{
if(head==NULL || head->n==BS) {
Node* t = new Node();
t->next = head;
head = t;
}
head->data[head->n++] = x;
return *this;
}
virtual IObj* pop() override{
if(head==NULL) throw "empty pop!";
IObj* rt = head->data[--head->n];
if(head->n==0){
Node* t = head;
head = t->next;
delete t;
}
return rt;
}
virtual bool empty() override{
return head == NULL;
}
private:
static const int BS = 5;
struct Node{
Node() { n=0; next=NULL; }
IObj* data[BS];
int n;
Node* next;
};
private:
Node* head;
};
struct MyInt: public IObj{
MyInt(int x){ this->x = x; }
virtual void show(ostream& os) const override{
os << x;
}
int x;
};
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, IObj* p)
{
p->show(os);
return os;
}
// 面向接口编程,不了解底层实现方式
void clear(IStack& s)
{
while(!s.empty()){
IObj* p = s.pop();
cout << p << endl;
delete p;
}
}
int main()
{
BlockStack a;
for(int i=0; i<100; i++) a.push(new MyInt(i));
// clear(a);
return 0;
}括号匹配问题


cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Stack{
public:
Stack() { n = 0; }
void push(char x) { data[n++] = x; }
char pop() {
if(empty()) throw -1;
return data[--n];
}
bool empty() { return n==0; }
private:
char data[100];
int n;
};
bool good(const char* s)
{
Stack a;
try{
while(*s){
if(*s=='(') a.push(')');
if(*s=='[') a.push(']');
if(*s=='{') a.push('}');
if(*s==')' || *s==']' || *s=='}'){
if(a.pop() != *s) return false;
}
s++;
}
}
catch(int e){
return false;
}
return a.empty();
}
int main()
{
cout << good(".(.[..).]..") << endl;
cout << good(".(...).]..") << endl;
cout << good(".(.(..)...") << endl;
cout << good(".(.[.].){.}..") << endl;
return 0;
}
循环队列


cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class MyQue{
public:
MyQue(){ rear=0; front=0; }
MyQue& enque(int x){
if((rear + 1) % N == front) throw -1;
buf[rear] = x;
rear = (rear + 1) % N;
return *this;
}
int deque(){
if(empty()) throw -2;
int rt = buf[front];
front = (front + 1) % N;
return rt;
}
bool empty(){ return front==rear; }
private:
static const int N = 5;
int buf[N];
int rear;
int front;
};
int main()
{
MyQue a;
a.enque(1).enque(2).enque(3).enque(4);
while(!a.empty()) cout << a.deque() << endl;
return 0;
}
STL的string
可参考API在线文档: https://www.cplusplus.com/reference/string/
string 类的成员函数概览
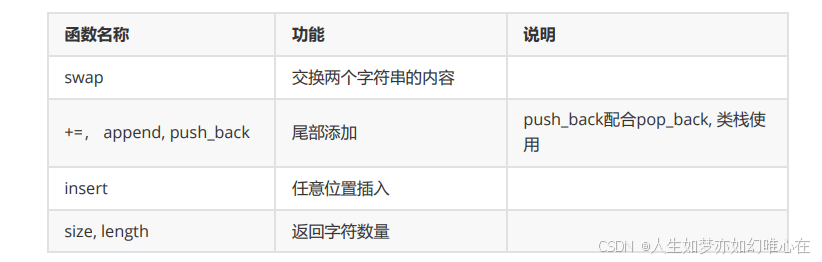
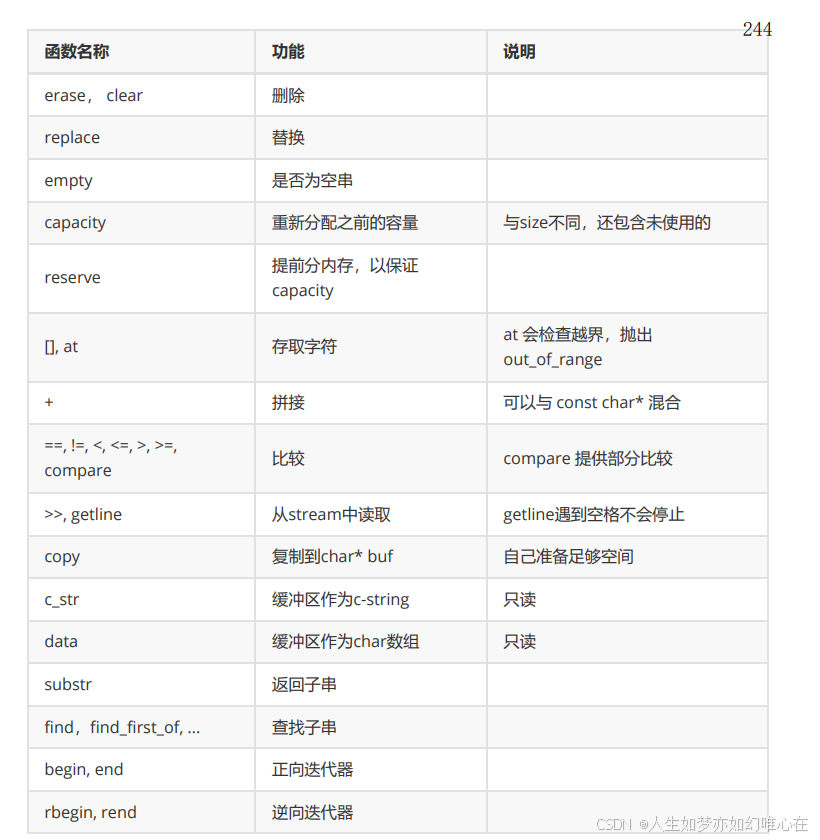




cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1; // 空串
string s2("1234567"); // 从 c-string 拷贝构造
string s3(s2); // 拷贝构造
string s4(s2,3); // s2 中从下标3开始
string s5(s2,3,2); // s2 中从下标3开始,2个字符
string s6(4,'x'); // 4 个 'x'
string s7(s2.end()-3,s2.end()); // 迭代器区间,最后3个char
cout << s1.length() << endl;
cout << s2 << endl;
cout << s3 << endl;
cout << s4 << endl;
cout << s5 << endl;
cout << s6 << endl;
cout << s7 << endl;
return 0;
}
STL的string(2)


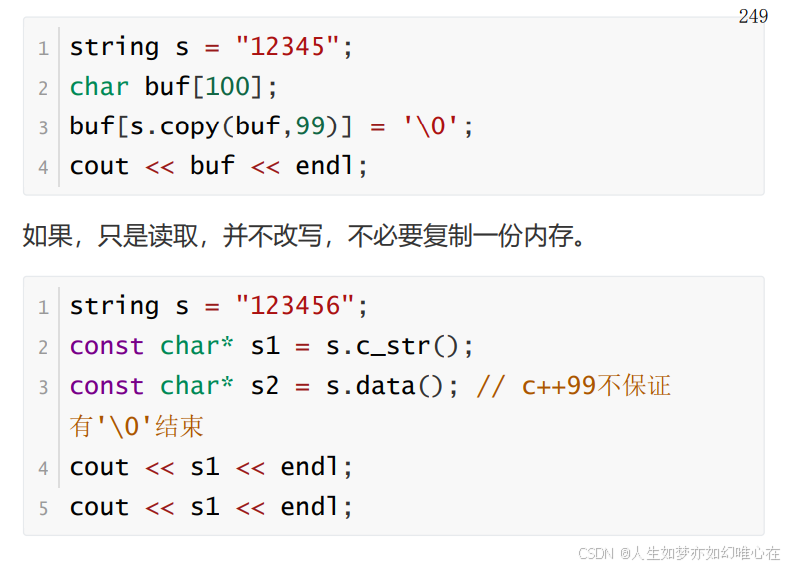


cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// string s = "12345";
// char buf[100];
// buf[s.copy(buf,99)] = '\0';
// cout << buf << endl;
// string s = "123";
// int a = atoi(s.c_str());
// cout << a << endl;
// string s = "123";
// stringstream ss; // 操作类似于 cin, cout,只是针对串
// int a;
// ss << s;
// ss >> a;
// cout << a << endl;
string s1 = "1234";
string s2 = "ff";
string s3 = "1010";
string s4 = "0x7f";
cout << stoi(s1) << endl;
cout << stoi(s2,NULL,16) << endl;
cout << stoi(s3,NULL,2) << endl;
cout << stoi(s4,NULL,0) << endl;
return 0;
}
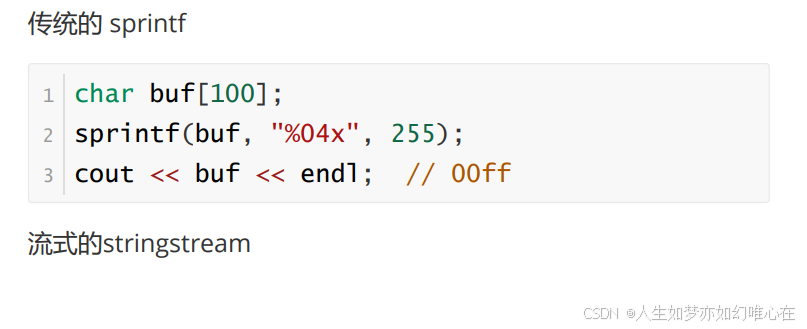
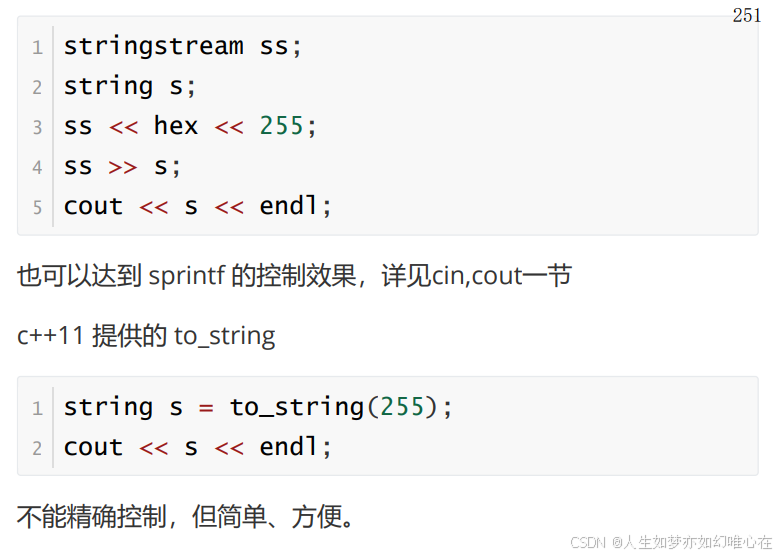
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// char buf[100];
// itoa(255,buf,16);
// cout << buf << endl;
// char buf[100];
// sprintf(buf, "%04x", 255);
// cout << buf << endl; // 00ff
stringstream ss;
string s;
ss << hex << 255;
ss >> s;
cout << s << endl;
return 0;
}
std::string 应用示例





cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s = " abc 1234 xyz kkkk ";
int p1 = 0;
while(1){
int p2 = s.find(" ", p1);
if(p2 == string::npos) {
cout << s.substr(p1) << endl;
break;
}
string s1 = s.substr(p1, p2-p1);
if(!s1.empty()) cout << s1 << endl;
p1 = s.find_first_not_of(" ", p2);
if(p1 == string::npos) break;
}
return 0;
}
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// char buf[100] = " abcd xyz 1234 ";
// char* p = strtok(buf, " ");
// while(p){
// cout << p << endl;
// p = strtok(NULL, " ");
// }
string s = " abcd ";
s.erase(0, s.find_first_not_of(" "));
s.erase(s.find_last_not_of(" ")+1);
cout << s << endl;
cout << s.length() << endl;
return 0;
}
标准库的cin,cout





cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a;
while(1){
cin >> a;
if(cin.good()) break;
cout << "err data, input again!" << endl;
cin.clear(); // 清空状态标志
while(cin.get()!='\n'); // 清空缓冲区
}
cout << "a: " << a << endl;
return 0;
}
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
ifstream in("d:\\1.txt");
if(!in) {
cout << "no such file!" << endl;
return -1;
};
char buf[100];
while(in.getline(buf, 80)){
cout << buf << endl;
}
return 0;
}标准输入输出的重定向





cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// freopen("d:\\out.txt", "w", stdout);
// cout << "haha" << endl;
// cout << 123 << endl;
freopen("d:\\in.txt", "r", stdin);
string s;
while(getline(cin, s)){
cout << s << endl;
}
return 0;
}
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
stringstream ss;
ss << "1 2 3" << "\n";
ss << "4 5";
streambuf* old = cin.rdbuf(ss.rdbuf());
int a = 0;
int t;
while(cin >> t) a += t;
cout << a << endl;
cin.rdbuf(old);
return 0;
}