一、自有服务概述
服务是一些特定的进程,自有服务就是系统开机后就自动运行的一些进程,一旦客户发出请求,这些进程就自动为他们提供服务,windows系统中,把这些自动运行的进程,称为"服务"
windows自带的各种服务
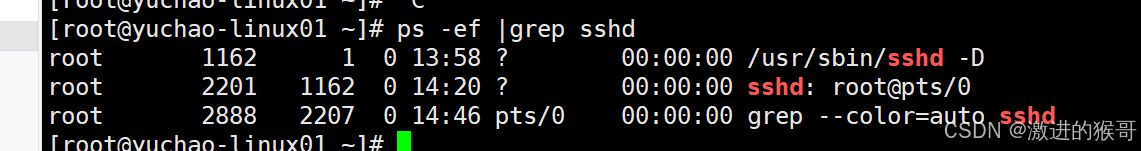
 举例:当我们使用SSH客户端软件连接linux的时候,我们的服务器为什么会对连接做出响应?是因为SSH服务开机就自动运行了。
举例:当我们使用SSH客户端软件连接linux的时候,我们的服务器为什么会对连接做出响应?是因为SSH服务开机就自动运行了。
二、systemctl管理服务命令
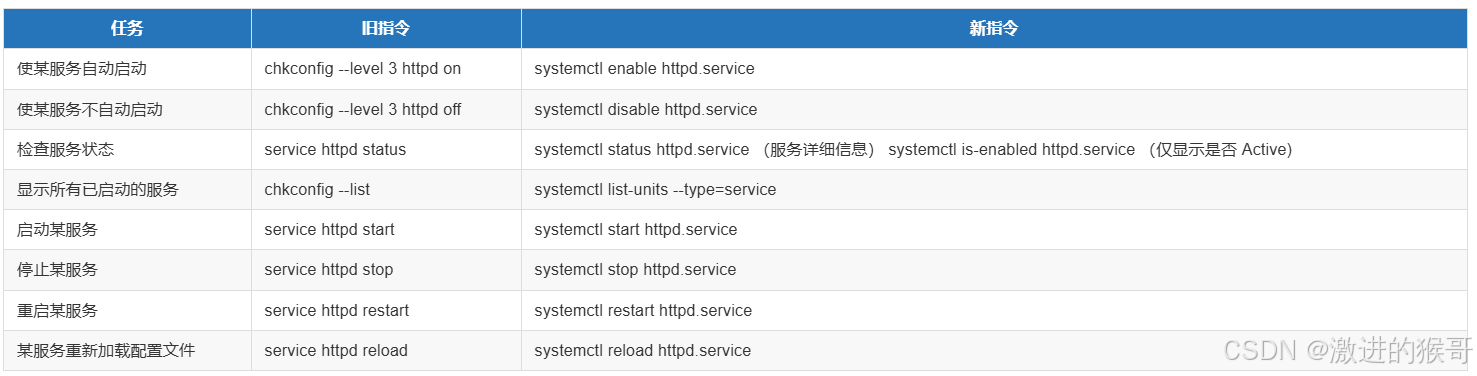
在Centos7之前,通过service 和 chkconfig两个命令来管理服务
service: 负责启动,停止服务,显示服务状态
service命令用于对系统服务进行管理,比如启动(start)、停止(stop)、重启(restart)、重新加载配置(reload)、查看状态(status)等。 # service mysqld #打印指定服务mysqld的命令行使用帮助。 # service mysqld start #启动mysqld # service mysqld stop #停止mysqld # service mysqld restart #重启mysqld
chkconfig: 指定服务是否开机启动
提供了一个维护/etc/rc[0~6] d 文件夹的命令行工具,它减轻了系统直接管理这些文件夹中的符号连接的负担。chkconfig主要包括5个原始功能:为系统管理增加新的服务、为系统管理移除服务、列出单签服务的启动信息、改变服务的启动信息和检查特殊服务的启动状态。当单独运行chkconfig命令而不加任何参数时,他将显示服务的使用信息。
[root@localhost www]# chkconfig --list #查看系统程序列表
[root@localhost www]# chkconfig httpd on #将httpd加入开机启动
[root@localhost www]# chkconfig httpd off #关闭httpd开机启动systemd命令
systemd 是目前 Linux 系统上主要的系统守护进程管理工具,由于 init 一方面对于进程的管理是串行化的,容易出现阻塞情况,另一方面 init 也仅仅是执行启动脚本,并不能对服务本身进行更多的管理。
systemctl命令
语法
systemctl [OPTIONS...] COMMAND [UNIT...]
command 选项字如下:
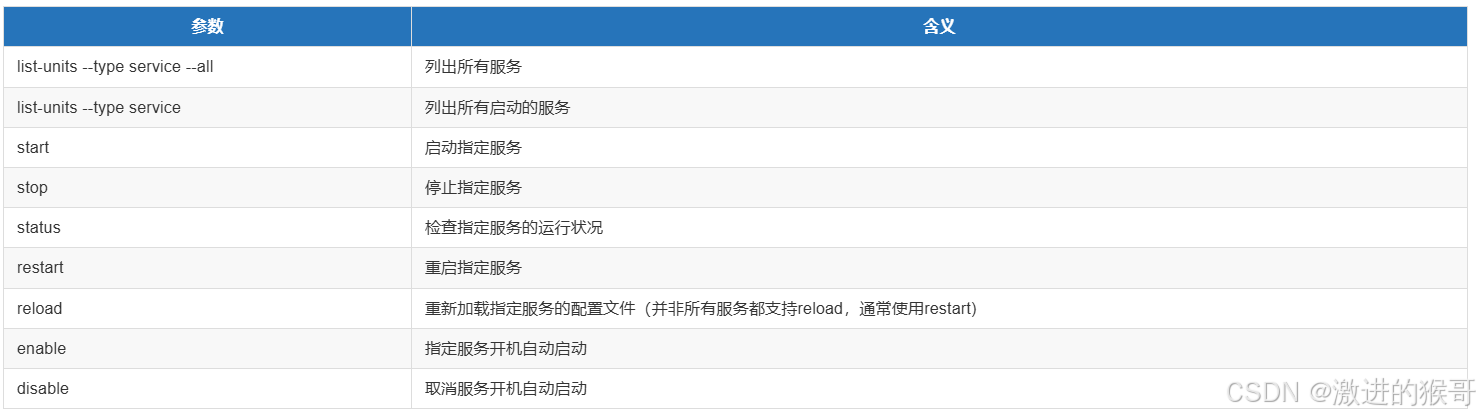
start:启动指定的 unit。
stop:关闭指定的 unit。
restart:重启指定 unit。
reload:重载指定 unit。
enable:系统开机时自动启动指定 unit,前提是配置文件中有相关配置。
disable:开机时不自动运行指定 unit。
status:查看指定 unit 当前运行状态。
参数:unit 是要配置的服务名称。
1、 显示服务
命令:systemctl
作用:管理服务
语法:#systemctl [选项]
选项:
list-units --type service --all:列出所有服务(包含启动的和没启动的)
list-units --type service:列出所有启动的服务
区别就在于--all参数列出所有服务(启动,未启动都有)
2.查看启动和停止服务
命令:systemctl
作用:管理服务
语法:#systemctl [选项] 服务名
选项:
status:检查指定服务的运行状况
start:启动指定服务
stop:停止指定服务
restart:重启指定服务
reload:重新加载指定服务的配置文件(并非所有服务都支持reload,通常使用restart)
语法
systemctl 选项 服务名
查看sshd服务的运行状态,如果这个关了,我们就无法ssh远程连接了3、服务持久化
所谓服务持久化,就是服务在开机的时候,是否自动启动。
命令:systemctl
作用:管理服务
语法:#systemctl [选项] 服务名
选项:
enable:指定服务开机自动启动
disable:取消服务开机自动启动
is-enabled :查看是否设置了开机自启
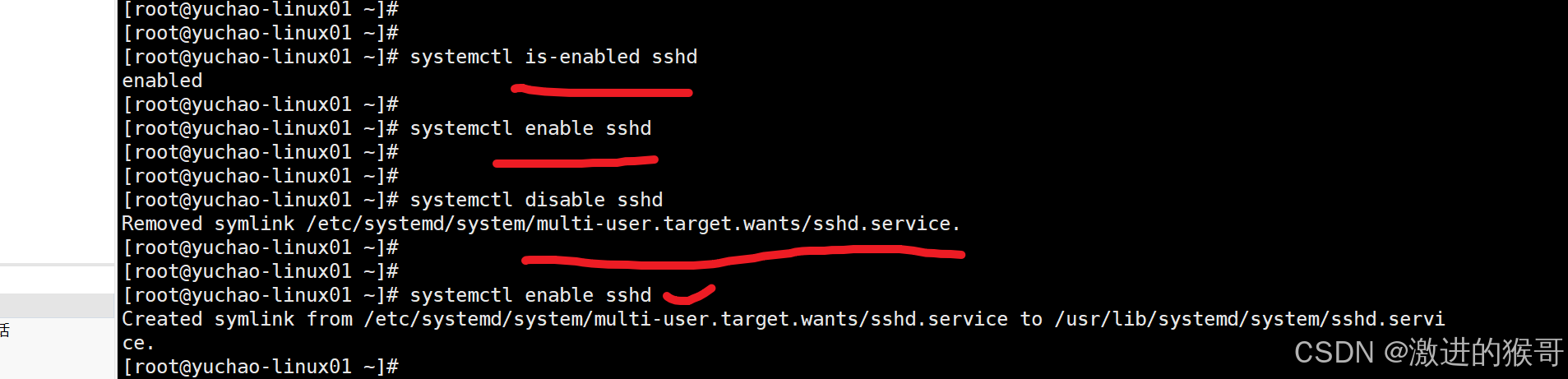
systemctl disable sshd
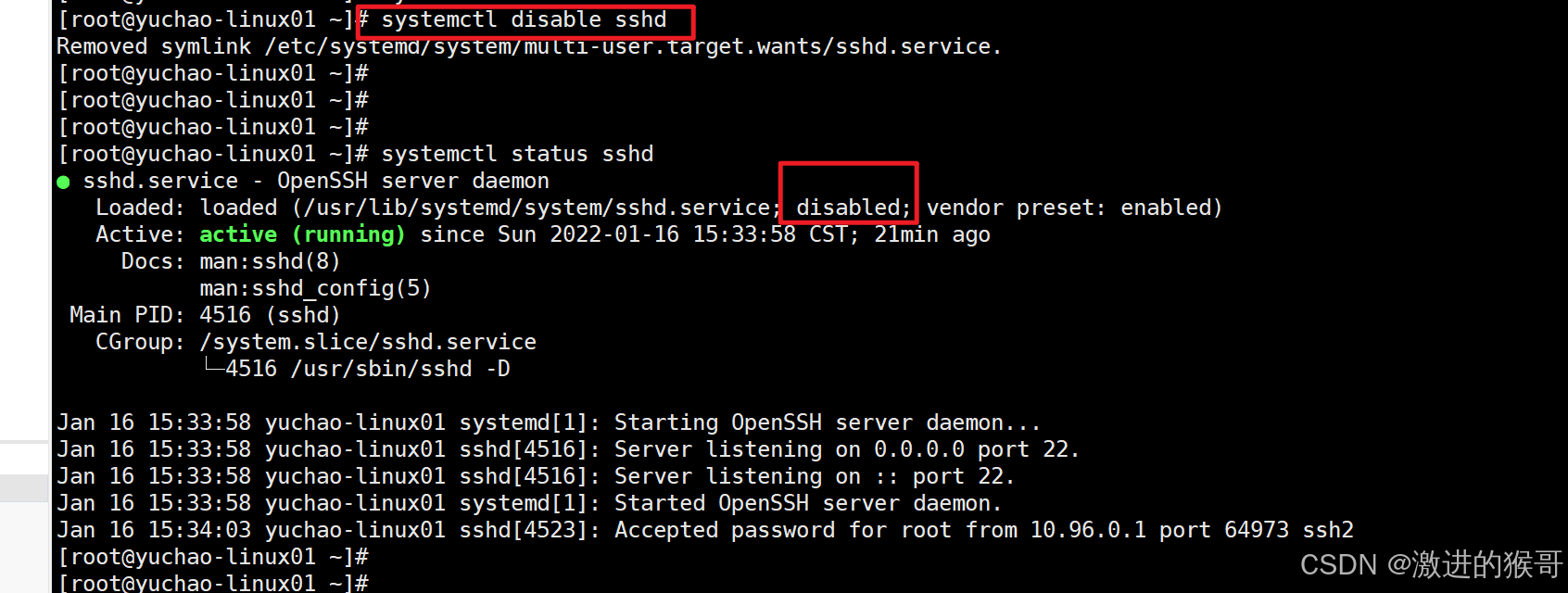
systemctl enable sshd
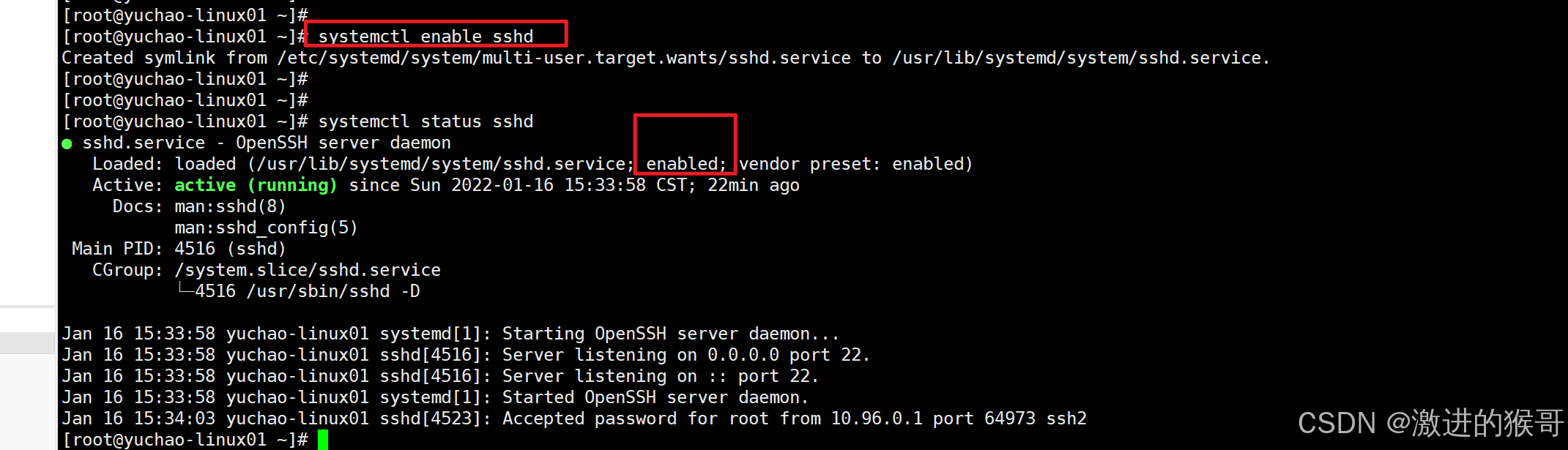
4、systemctl 小结
systemctl参数总结
三、常用自有服务(ntp,firewalld,crond)
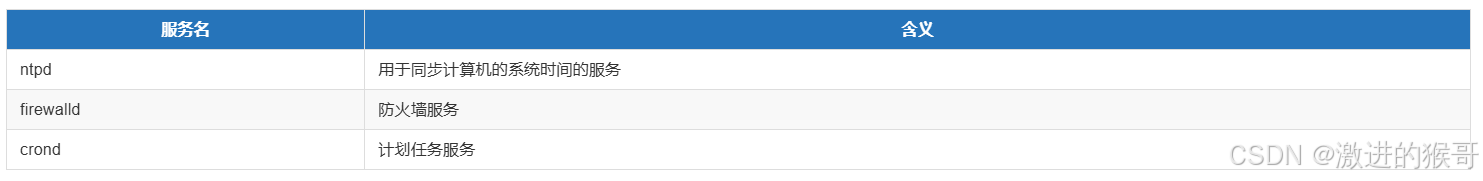
1、ntp时间同步服务
1)NTP同步服务器原理
标准时间是哪里来的?
现在的标准时间是由原子钟报时的国际标准时间UTC(Universal Time Coordinated,世界协调时),所以NTP获得UTC的时间来源可以是原子钟、天文台、卫星,也可以从Internet上获取。
在NTP中,定义了时间按照服务器的等级传播,Stratum层的总数限制在15以内
工作中,通常我们会直接使用各个组织提供的,现成的NTP服务器。
2)到哪里去找NTP服务器
NTP授时网站:服务器列表 - 全球可用的NTP服务器列表与解析服务 - ntp.org.cn & ntpdate.net
3)timedatectl 命令
timedatectl(英文全拼:timedate control)命令用于在 Linux 中设置或查询系统时间、日期和时区等配置。
centos6时代,修改系统的时区、时间,需要用到
修改时间、日期、date命令
修改时区,cp /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai /etc/localtime
修改硬件时间、hwclock命令
在centos7提供了更强大的timedatectl命令,整合了时间、时区操作。在 Linux 运维中,通常使用此命令来设置或更改当前的日期、时间和时区,或启用自动系统时钟与远程 NTP 服务器同步,以确保 Linux 系统始终保持正确的时间。
语法
timedatectl [OPTIONS...] COMMAND ...
命令command
status :显示当前的时间设置。
show :显示 systemd-timedated 的属性。
set-time TIME :设置系统时间。
set-timezone ZONE :设置系统时区。
list-timezones :显示已知时区。
set-local-rtc BOOL :控制 RTC 是否在当地时间。(BOOL 的值可以是 1 / true 或 0 / false)
set-ntp BOOL :启用或禁用网络时间同步。(BOOL 的值可以是 1 / true 或 0 / false)
timesync-status :显示 systemd-timesyncd 的状态。
show-timesync :显示 systemd-timesyncd 的属性。
选项
选项:
-h, --help :显示帮助信息。
--version :显示软件包版本。
--no-pager :不用将输出通过管道传输到寻呼机(pager)。
--no-ask-password :不提示输入密码。
-H, --host=[USER@]HOST :在远程主机上操作。
-M, --machine=CONTAINER :在本地容器上操作。
--adjust-system-clock :更改本地 RTC 模式时调整系统时钟。
--monitor :监控 systemd-timesyncd 的状态。
-p, --property=NAME :仅显示此名称的属性。
-a, --all :显示所有属性,包括空属性。
--value :显示属性时,只打印值。
timedatectl实战
显示当前系统时间、日期
世界时间查询,世界时间查询_国际时间对照表
[root@yuanlai-0224 ~]# timedatectl status
Local time: Thu 2022-03-17 18:11:37 CST
Universal time: Thu 2022-03-17 10:11:37 UTC
RTC time: Thu 2022-03-17 10:11:37
Time zone: Asia/Shanghai (CST, +0800)
NTP enabled: n/a
NTP synchronized: no
RTC in local TZ: no
DST active: n/a
解释:
当地时间
世界时间
RTC时间,本地硬件时钟(主板上的纽扣电池供电,提供机器的时间正确,在主板的集成电路上)默认以UTC为准了
时区,亚洲上海
是否启用NTP
NTP同步状态
本地时区的RTC
DST是否激活
CST解释
CST(北京时间)
北京时间,China Standard Time,中国标准时间。
在时区划分上,属东八区,比协调世界时早8小时,记为UTC+8。
UTC
UTC(世界标准时间)
协调世界时,又称世界标准时间或世界协调时间,简称UTC(从英文"Coordinated Universal Time")
整个地球分为二十四时区,每个时区都有自己的本地时间,在国际无线电通信场合,为了统一起见,使用一个统一的时间,称为通用协调时。
GMT
格林威治标准时间指位于英国伦敦郊区的皇家格林尼治天文台的标准时间,因为本初子午线被定义在通过那里的经线(UTC与GMT时间基本相同)。
DST
夏令时指在夏天太阳升起的比较早时,将时间拨快一小时,以提早日光的使用,中国不使用。列出机器上支持的所有时区
root@yuanlai-0224 \~\]# timedatectl list-timezones
将本地时区从上海(Asia/Shanghai)设置为阿姆斯特丹(Europe/Amsterdam)
bash
[root@yuanlai-0224 ~]#
[root@yuanlai-0224 ~]# timedatectl set-timezone "Europe/Amsterdam"
[root@yuanlai-0224 ~]# timedatectl show
Unknown operation show
[root@yuanlai-0224 ~]# timedatectl status
Local time: Thu 2022-03-17 10:28:08 CET
Universal time: Thu 2022-03-17 09:28:08 UTC
RTC time: Thu 2022-03-17 17:28:07
Time zone: Europe/Amsterdam (CET, +0100)
NTP enabled: n/a
NTP synchronized: no
RTC in local TZ: no
DST active: no
Last DST change: DST ended at
Sun 2021-10-31 02:59:59 CEST
Sun 2021-10-31 02:00:00 CET
Next DST change: DST begins (the clock jumps one hour forward) at
Sun 2022-03-27 01:59:59 CET
Sun 2022-03-27 03:00:00 CEST
[root@yuanlai-0224 ~]#
[root@yuanlai-0224 ~]#本地时区,恢复为亚洲、上海
bash
[root@yuanlai-0224 ~]# timedatectl set-timezone "Asia/Shanghai"
[root@yuanlai-0224 ~]# timedatectl status
Local time: Thu 2022-03-17 17:32:34 CST
Universal time: Thu 2022-03-17 09:32:34 UTC
RTC time: Thu 2022-03-17 17:32:33
Time zone: Asia/Shanghai (CST, +0800)
NTP enabled: n/a
NTP synchronized: no
RTC in local TZ: no
DST active: n/a4)时间同步操作
机器时间错乱后,可以进行
- 时间同步,搭建ntpd服务
- 时间校准,ntpdate命令
同步服务器时间方式有2 个:一次性同步手动同步、通过服务自动同步。
时间同步注意点(生产经验的坑)
ntpd在实际同步时间时是一点点的校准过来时间的,最终把时间慢慢的校正对
而ntpdate不会考虑其他程序是否会阵痛,直接调整时间。一个是校准时间,一个是调整时间。
因为许多应用程序依赖连续的时钟,而使用ntpdate这样的时钟跃变,有时候会导致很严重的问题,如数据库事务操作等。
并且,还有如下缺陷
- 安全问题
ntpdate的设置依赖于ntp服务器的安全性,攻击者可以利用一些软件设计上的缺陷,拿下ntp服务器并令与其同步的服务器执行某些消耗性的任务。
- 太过于暴力
ntpdate是急变,是立即修改系统时间,非常依赖于时序的程序可能会出错,比如根据时间执行备份动作的脚本,或者一些监控程序。
因此,企业服务器里一般会部署ntpd服务,让服务器自动、定期的进行时间同步,且以公共时间服务器池为准,保证服务器集群的时间正确且一致。
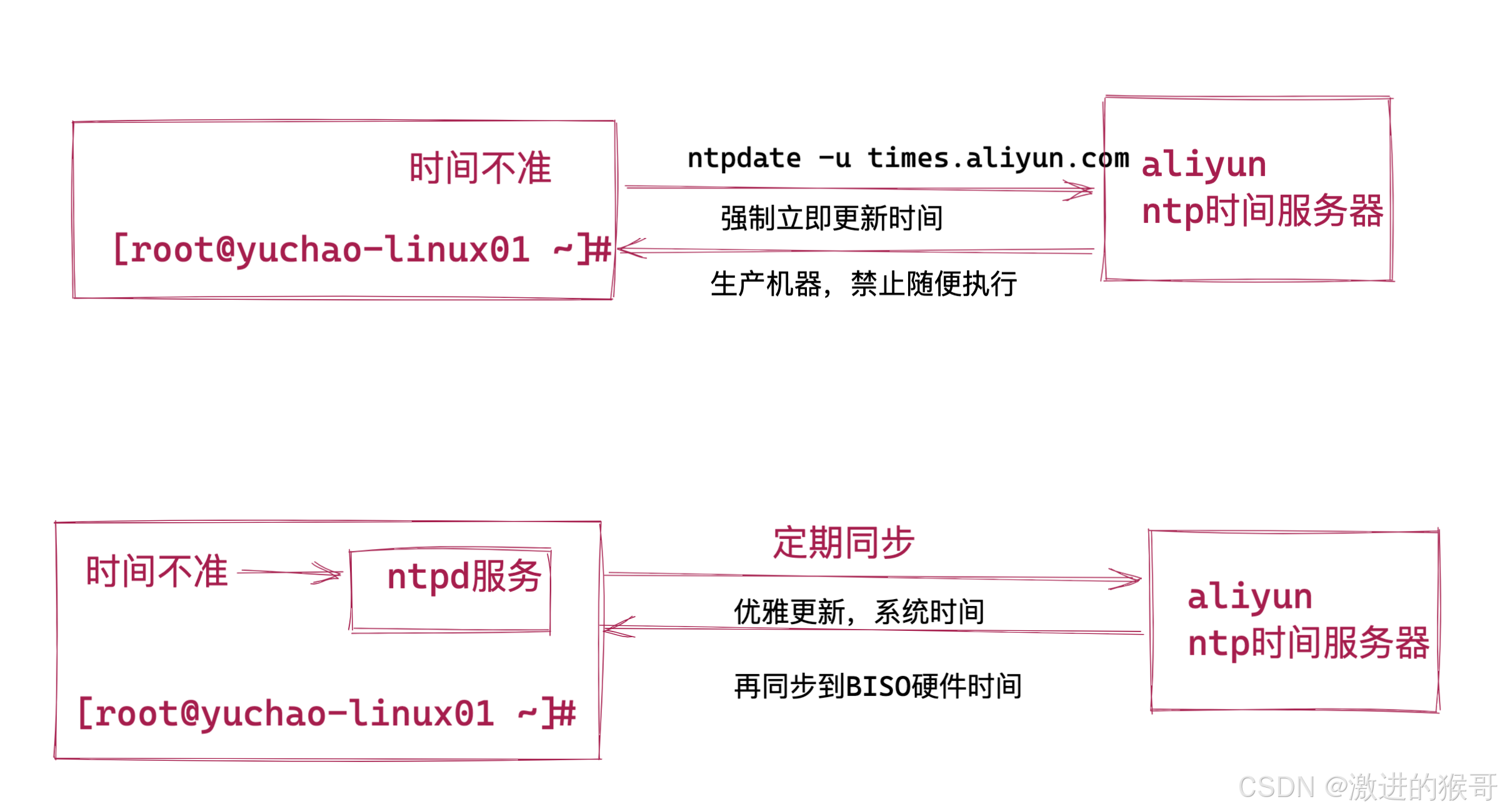
手动同步ntpdate
该ntpdate命令需要单独安装。
yum install ntpdate -yntpdate使用语法
ntpdate 时间服务器地址
# NTP中国服务器,cn.ntp.org.cn
# 用法
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# ntpdate cn.ntp.org.cn
16 Jan 16:30:08 ntpdate[5312]: step time server 182.92.12.11 offset 45505765.702122 sec友情提示,错误情况,你可能输入的NTP服务器地址有误
1.要么是你机器无法上网
2.要么是输入的NTP服务器有问题
3.你输入错误
自动同步ntpd服务(推荐使用)
1.ntpd服务安装
# 查看是否安装
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]#
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# rpm -q ntp
package ntp is not installed
# 如果没有安装过的话,可以执行此命令安装
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# yum install ntp -y自动同步需要开启linux的ntp服务。
systemctl start/stop/restart ntpd每次开机,自动启动ntpd服务,就能够自动同步时间,保证服务器时间精准。
关于ntpd服务,默认用的哪些时间服务器地址,配置信息在
bash
修改 /etc/ntp.conf 配置文件,参考如下修改
3 # #系统时间与BIOS事件的偏差记录
4 driftfile /var/lib/ntp/drift
5
6 # by yuchao create ntpd.log
7 logfile /var/log/ntpd.log
8
9 # by yuchao create ntpd.pid
10 pidfile /var/run/ntpd.pid
注释掉默认的这几行
19 # Use public servers from the pool.ntp.org project.
20 # Please consider joining the pool (http://www.pool.ntp.org/join.html).
21 #server 0.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
22 #server 1.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
23 #server 2.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
24 #server 3.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
添加新的互联网中ntp服务器
# prefer表示为优先,表示本机优先同步该服务器时间
# 阿里云的延迟明显很低 https://help.aliyun.com/document_detail/92704.html
server times.aliyun.com iburst prefer
server ntp.aliyun.com iburst
server cn.pool.ntp.org iburst
添加新的ntp服务器地址,参数解释 iburst,当某一个ntp挂掉时,向它发送一些数据包,检测是否挂掉。
########## 参数解释
ntpd.conf配置文件采用restrict实现权限控制
Restrict [IP] mask [netmask_IP] [parameter]
Parameter 的
ignore :拒绝所有类型的NTP联机。
nomodify: 客户端不能使用ntpc与ntpq这两个程序来修改服务器的时间参数,但客户端可透过这部主机来进行网络校时;
noquery:客户端不能够使用ntpc与ntpq等指令来查询时间服务器,不提供NTP的网络校时。
notrap:不提供trap 这个运程事件登入的功能。
notrust:拒绝没有认证的客户端。
Kod:kod技术可以阻止"Kiss of Death "包对服务器的破坏。
Nopeer:不与其他同一层的NTP服务器进行时间同步。
利用server 设定上层NTP服务器,格式如下:
server [IP or hostname] [prefer]
参数主要如下:
perfer:表示优先级最高
burst :当一个运程NTP服务器可用时,向它发送一系列的并发包进行检测。
iburst :当一个运程NTP服务器不可用时,向它发送一系列的并发包进行检测。
用法如
server times.aliyun.com iburst prefer # prefer表示为优先,表示本机优先同步该服务器时间
server ntp.aliyun.com iburst
server cn.pool.ntp.org iburst设置系统时间和硬件时间同步
实现clock时间与system时间同步,配置/etc/sysconfig/ntpd文件
ntp服务,默认只会同步系统时间。
如果想要让ntp同时同步硬件时间,可以设置/etc/sysconfig/ntpd文件,在/etc/sysconfig/ntpd文件中,添加 SYNC_HWCLOCK=yes这样,就可以让硬件时间与系统时间一起同步。
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# cat /etc/sysconfig/ntpd
# Command line options for ntpd
OPTIONS="-g"
SYNC_HWCLOCK=yes启动ntpd服务
启动ntpd程序
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# systemctl start ntpd
检查ntpd运行后,生成的相关文件
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# ll /var/log/ntpd.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 864 Mar 17 18:25 /var/log/ntpd.log
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# ll /var/run/ntpd.pid
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4 Mar 17 18:25 /var/run/ntpd.pidntpstat
确认本地NTP与上层NTP服务器是否联通
bash
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# ntpstat
# 以和162.159.200.123服务器同步过
synchronised to NTP server (162.159.200.123) at stratum 4
# 时间校正到相差1110ms之内
time correct to within 1110 ms
# 每64秒会向上级NTP轮询更新一次时间
polling server every 64 sntpq
查看时间同步状态
-p 显示时间服务器列表
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# ntpq -p
remote refid st t when poll reach delay offset jitter
==============================================================================
*120.25.115.20 10.137.53.7 2 u 20 64 7 41.614 19.046 4.108
+203.107.6.88 10.137.38.86 2 u 24 64 7 15.996 23.737 6.711
+time.cloudflare 10.28.12.207 3 u 23 64 17 282.792 -14.257 59.448参数详解
remote :本地主机所连接的上层NTP服务器,最左边的符号如下:
如果有[*] 代表目前正在使用当中的上层NTP服务器。
如果有[+] 代表也有连上上层NTP服务器,可以作为提高时间更新的候选NTP服务器
如果有[-] 代表同步的该NTP服务器被认为是不合格的NTP Server
如果有[x] 代表同步的外网NTP服务器不可用
refid :指的是给上层NTP服务器提供时间校对的服务器。
St:上层NTP服务器的级别。
When: 上一次与上层NTP服务器进行时间校对的时间(单位:s)
Poll :本地主机与上层NTP服务器进行时间校对的周期(单位:s)
reach:已经向上层 NTP 服务器要求更新的次数
delay:网络传输过程当中延迟的时间,单位为 10^(-6) 秒
offset:时间补偿的结果,单位为10^(-6) 秒
jitter:Linux 系统时间与 BIOS 硬件时间的差异时间, 单位为 10^(-6) 秒。5)date/hwclock/clock命令
date
可用来设置系统日期与时间。只有管理员才有设置日期与时间的权限,一般用户只能用date 命令显示时间。
若不加任何参数,data 会显示目前的日期与时间。
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# date
Thu Mar 17 18:59:49 CST 2022语法,参数
-s, --set=STRING
根据 STRING 设置时间
格式化修改时间+日期
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# date -s '20180808 13:13:13'
Wed Aug 8 13:13:13 CST 2018
格式化修改时间
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# date -s '18:00:00'
Wed Aug 8 18:00:00 CST 2018
格式化修改日期
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# date -s '20120606'
Wed Jun 6 00:00:00 CST 2012
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]#
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# date '+%F'
2012-06-06hwclock
hwclock命令是一个硬件时钟访问工具,它可以显示当前时间、设置硬件时钟的时间和设置硬件时钟为系统时间,也可设置系统时间为硬件时钟的时间。
在Linux中有硬件时钟与系统时钟两种时钟。
硬件时钟是指主机板上的时钟设备,也就是通常可在BIOS画面设定的时钟。
系统时钟则是指kernel中的时钟。当Linux启动时,系统时钟会去读取硬件时钟的设定,之后系统时钟即独立运作。
所有Linux相关指令与函数都是读取系统时钟的设定。
语法参数
--systohc 将硬件时钟调整为与目前的系统时钟一致。
--hctosys 将系统时钟调整为与目前的硬件时钟一致。
--show 显示硬件时钟的时间与日期。
--debug 显示hwclock执行时详细的信息。
-w, --systohc set the hardware clock from the current system time
--systz set the system time based on the current timezone
--adjust adjust the RTC to account for systematic drift since以系统时间为准,修改硬件时钟
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# hwclock --hctosys
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# hwclock --show
Thu 17 Mar 2022 07:07:42 PM CST -0.833680 seconds
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]#以硬件时间为准,修改系统时间
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# hwclock --systohc
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# hwclock --show
Thu 17 Mar 2022 07:08:18 PM CST -0.740291 seconds6)开机自启ntpd
# 默认为CentOS7的配置,CentOS6中需要使用chkconfig命令
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# systemctl enable ntpd
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/ntpd.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/ntpd.service.2、firewalld防火墙
什么是防火墙
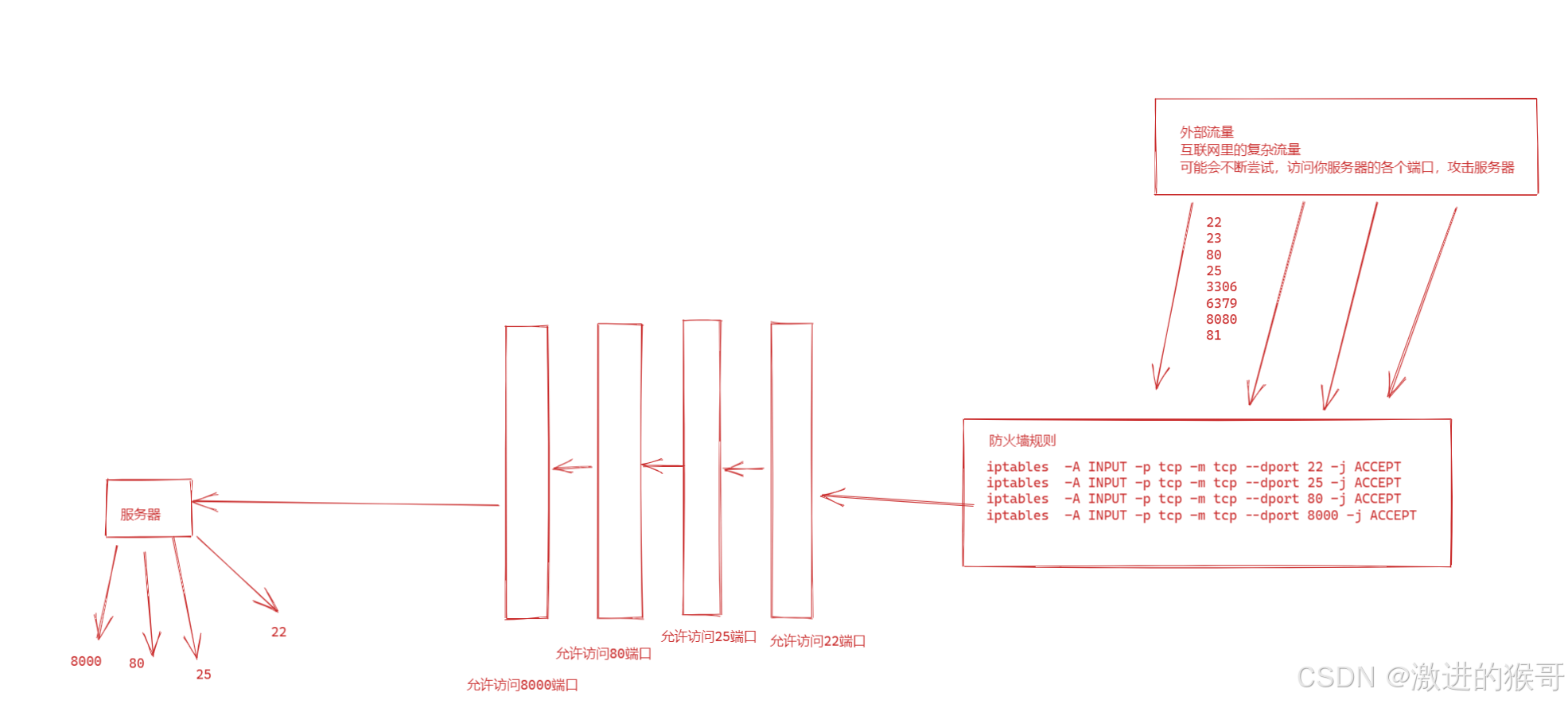
防火墙:防范一些网络攻击。有软件防火墙、硬件防火墙之分。
防火墙的作用
防火墙具有很好的保护作用。入侵者必须首先穿越防火墙的安全防线,才能接触目标计算机。
防火墙的功能
防火墙对流经它的网络通信进行扫描,这样能够过滤掉一些攻击,以免其在目标计算机上被执行。防火墙还可以关闭不使用的端口。而且它还能禁止特定端口的流出通信。
最后,它可以禁止来自特殊站点的访问,从而防止来自不明入侵者的所有通信。
防火墙概念
防火墙一般有硬件防火墙和软件防火墙
硬件防火墙:在硬件级别实现部分防火墙功能,另一部分功能基于软件实现,性能高,成本高。
软件防火墙:应用软件处理逻辑运行于通用硬件平台之上的防火墙,性能低,成本低
图解:
3、firewalld防火墙的概念
1)区域
CentOS6x中防火墙叫做iptables
CentOS7.x 中默认使用的防火墙是firewalld,但是依然更多的是使用iptables,firewalld默认都关了。
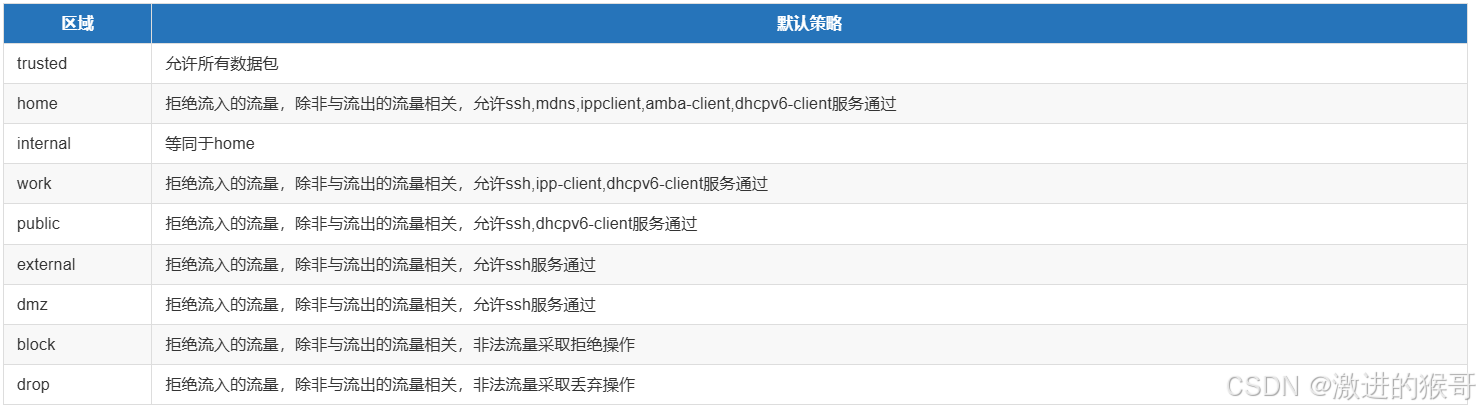
firewalld增加了区域的概念,所谓区域是指,firewalld预先准备了几套防火墙策略的集合 ,类似于策略的模板,用户可以根据需求选择区域。
常见区域及相应策略规则
2)运行模式和永久模式
运行模式:此模式下,配置的防火墙策略立即生效,但是不写入配置文件
永久模式:此模式下,配置的防火墙策略写入配置文件,但是需要reload重新加载才能生效。
==firewall默认采用运行模式==
4、firewalld防火墙的配置
1)查看,开启和停止firewalld服务
命令:systemctl
作用:管理服务
语法:#systemctl [选项] firewalld
选项:
status:检查指定服务的运行状况
start:启动指定服务
stop:停止指定服务
restart:重启指定服务
reload:重新加载指定服务的配置文件(并非所有服务都支持reload,通常使用restart)
2) 管理firewall配置
命令:firewall-cmd
作用:管理firewall具体配置
语法:#firewall-cmd [参数选项1] ....[参数选项n]
常用选项:
查看默认使用的区域
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# firewall-cmd --get-default-zone
public查看所有可用区域
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# firewall-cmd --get-zones
block dmz drop external home internal public trusted work列出当前使用区域配置
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# firewall-cmd --list-all
public (active)
target: default
icmp-block-inversion: no
interfaces: ens33
sources:
services: ssh dhcpv6-client # 允许的是ssh服务,也就是22端口的流量,是允许登录的
ports:
protocols:
masquerade: no
forward-ports:
source-ports:
icmp-blocks:
rich rules:列出所有区域的配置信息
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# firewall-cmd --list-all-zones添加允许通过的服务或端口(python,ntp)
你的linux机器,当前使用的是public区域的规则
默认信任的服务是,ssh,dhcp
准备一个web服务,通过python提供的简单命令,
python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80
此时的防火墙,是没有允许80端口的请求,进入到服务器的,除非你加一个规则,允许80端口的请求通过。
bash
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=80/tcp
success
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]#
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]#
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# firewall-cmd --zone=public --list-all
public (active)
target: default
icmp-block-inversion: no
interfaces: ens33
sources:
services: ssh dhcpv6-client
ports: 80/tcp # 允许80端口通过了
protocols:
masquerade: no
forward-ports:
source-ports:
icmp-blocks:
rich rules:去掉允许通过的端口
比如刚才你临时个服务器,添加了一个文件下载的服务,需要访问80端口
你现在不需要这个功能了,想去掉防火墙规则,继续加强服务器安全。
bash
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# firewall-cmd --zone=public --remove-port=80/tcp
success
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]#
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# firewall-cmd --zone=public --list-all
public (active)
target: default
icmp-block-inversion: no
interfaces: ens33
sources:
services: ssh dhcpv6-client
ports: # 端口被移除了
protocols:
masquerade: no
forward-ports:
source-ports:
icmp-blocks:
rich rules:添加允许ntp的防火墙策略
bash
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=ntp
success
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]#
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# firewall-cmd --reload
success
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# firewall-cmd --list-all
public (active)
target: default
icmp-block-inversion: no
interfaces: ens33
sources:
services: ssh dhcpv6-client ntp
ports: 80/tcp
protocols:
masquerade: no
forward-ports:
source-ports:
icmp-blocks:
rich rules:
检查iptables语句
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# iptables -L |grep ntp
ACCEPT udp -- anywhere anywhere udp dpt:ntp ctstate NEW永久模式参数
permaent(永久性的)
bash
# 永久性添加规则,并未立即生效
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=80/tcp
success
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]#
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]#
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# firewall-cmd --list-all
public (active)
target: default
icmp-block-inversion: no
interfaces: ens33
sources:
services: ssh dhcpv6-client
ports: # 端口规则还未生成
protocols:
masquerade: no
forward-ports:
source-ports:
icmp-blocks:
rich rules:
# 重新加载防火墙规则
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# firewall-cmd --reload
success
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# firewall-cmd --zone=public --list-all
public (active)
target: default
icmp-block-inversion: no
interfaces: ens33
sources:
services: ssh dhcpv6-client
ports: 80/tcp
protocols:
masquerade: no
forward-ports:
source-ports:
icmp-blocks:
rich rules:
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# iptables -L |grep tcp
ACCEPT tcp -- anywhere anywhere tcp dpt:ssh ctstate NEW
ACCEPT tcp -- anywhere anywhere tcp dpt:http ctstate NEW
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]#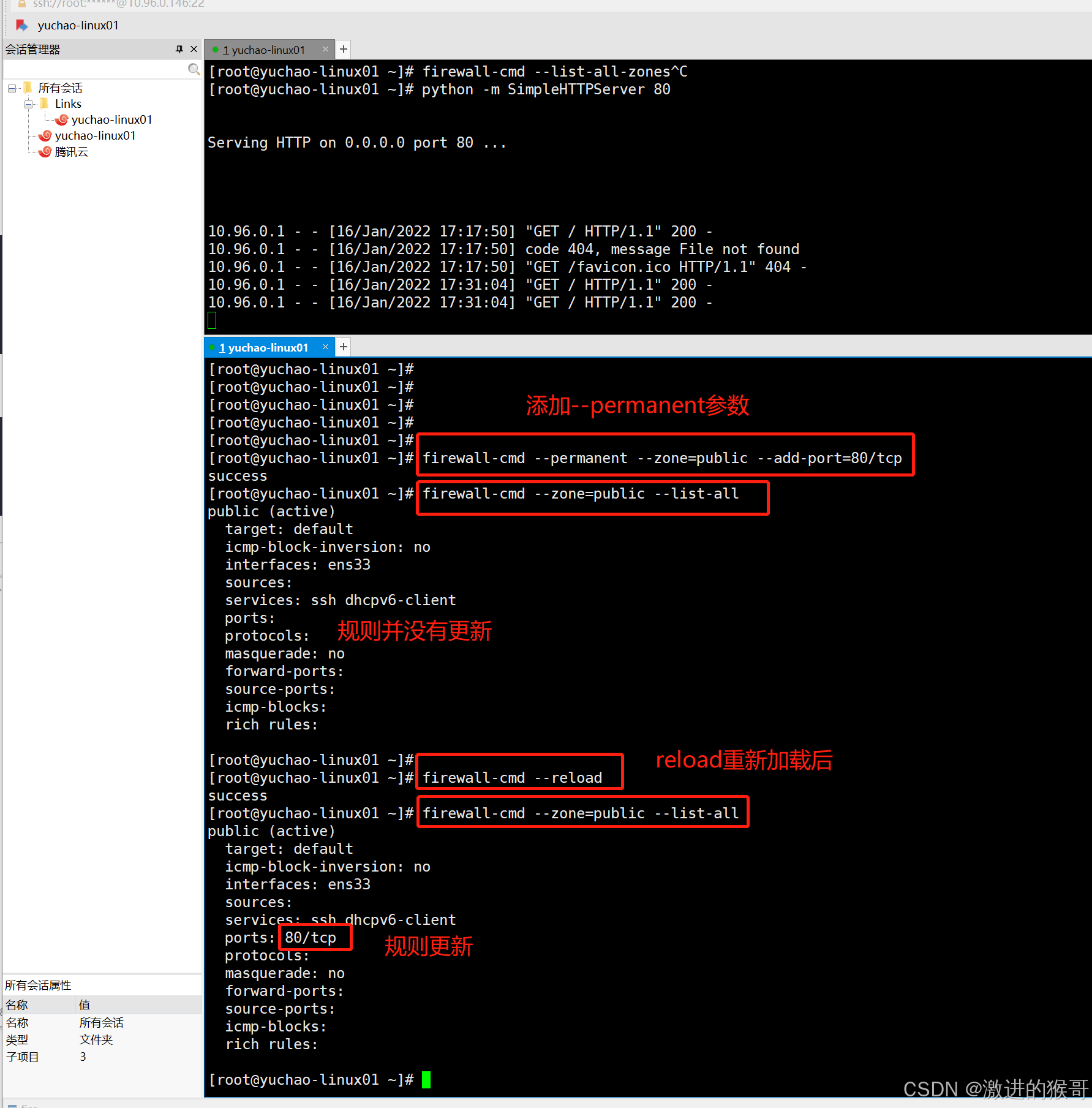
5、计划任务crontab
1)计划任务的作用
作用:
操作系统不可能24 小时都有人在操作,有些时候想在指定的时间点去执行任务(例如:每天凌晨 2 点去重新启动Apache),此时不可能真有人每天夜里 2 点去执行命令,这就可以交给计划任务程序去执行操作了。
2)查看计划任务
==语法:# crontab 选项==
常用选项:
-l:list,列出指定用户的计划任务列表==
-e:edit,编辑指定用户的计划任务列表,简单来说,计划任务就是一个文件==
-u:user,指定的用户名,如果不指定,则表示当前用户
-r:remove,删除指定用户的计划任务列表
示例代码:列出当前用户的计划任务列表
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# crontab -l
no crontab for root3)编辑计划任务(重点)
进入计划任务编辑文件
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# crontab -e打开计划任务编辑文件后,可以在此文件中编写我们自定义的计划任务:
计划任务的规则语法格式,以行为单位,一行则为一个计划:
==分 时 日 月 周 需要执行的命令==
3.1) crontab语法(重点)
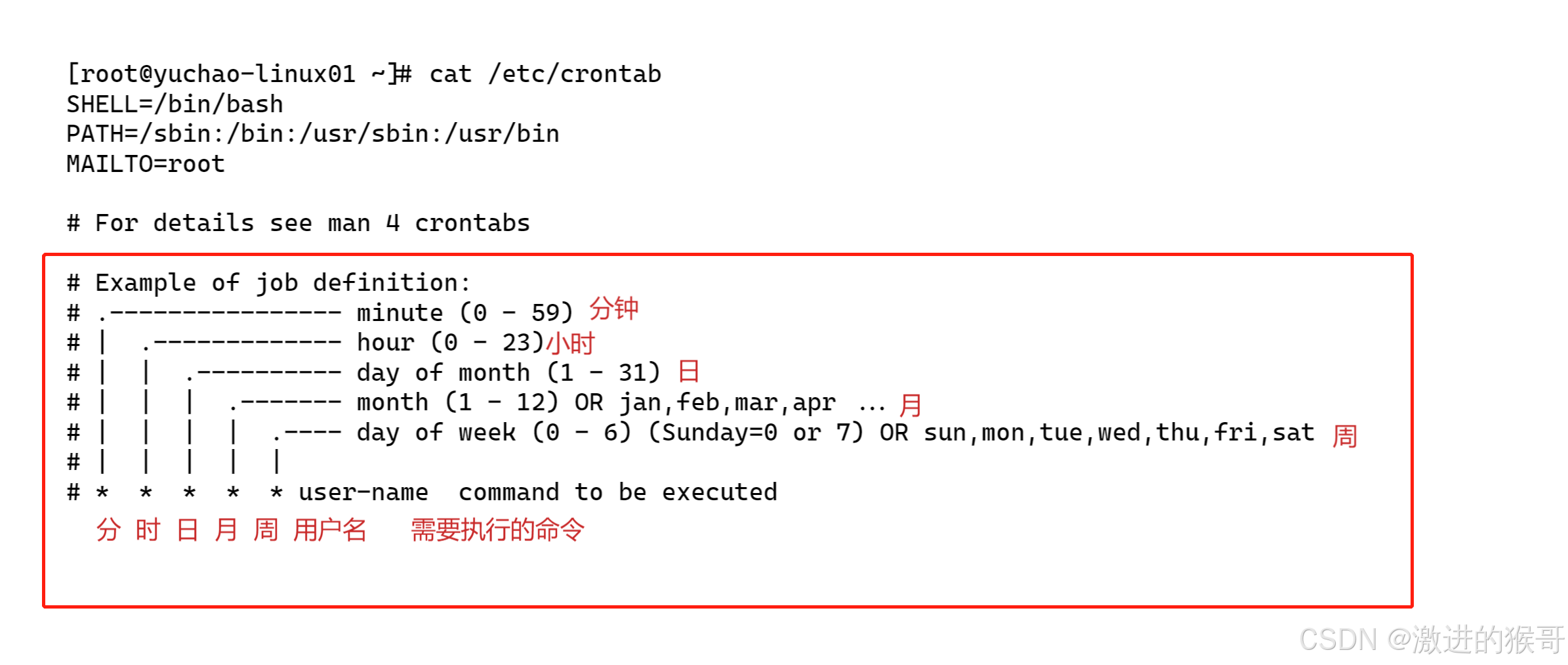
取值范围(常识):
分:0~59
时:0~23
日:1~31
月:1~12
周:0~6,0 和 7 表示星期天
四个符号:
*:表示取值范围中的每一个数字
-:做连续区间表达式的,要想表示1~7,则可以写成:1-7
/:表示每多少个,例如:想每 10 分钟一次,则可以在分的位置写:*/10
,:表示多个取值,比如想在 1 点,2 点 6 点执行,则可以在时的位置写:1,2,6
并且在定时任务里,命令,请写上绝对路径。
通过whereis命令搜索 绝对路径
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# whereis systemctl
systemctl: /usr/bin/systemctl /usr/share/man/man1/systemctl.1.gz语法实践基础题
0 0 * * * 每天0点执行
15 1 * * * 每天夜里1点15分执行
* * * * * 每分钟执行
0 * * * * 每小时整点执行
0 */2 * * * 每隔2小时执行
*/30 * * * * 每隔30分钟执行
00 01 15 * * 每个月15号的夜里1点执行
00 05 1-14 * * 每个月的1到14号的凌晨5点执行
00 6-8 */5 * * 每隔5天的凌晨6-8点之间的整点执行
00 20-23/2 * * * 每天晚上8点到11点之间,每隔2小时的整点执行
00 23 * * 1-3 每周1到周三的晚上11点整执行问题1:每月1、10、22 日的4:45 重启network 服务
45 4 1,10,22 * * /usr/bin/systemctl restart network问题2:每周六、周日的1:10 重启network 服务
10 1 * * 6,7 /usr/bin/systemctl restart network问题3:每天18:00 至23:00 之间每隔30 分钟重启network 服务
*/30 18-23 * * * /usr/bin/systemctl restart network问题4:每隔两天的上午8 点到11 点的第3 和第15 分钟执行一次重启
3,15 8-11 */2 * * /usr/sbin/reboot问题5 :每天凌晨整点重启nginx服务。
00 * * * * /usr/bin/systemctl restart nginx问题6:每周4的凌晨2点15分执行命令
15 2 * * 4 command问题7:工作日的工作时间内的每小时整点执行脚本。
00 9-18 * * 1-5 /usr/bin/bash my.sh问题8:如果定时任务的时间,没法整除,定时任务就没有意义了,得通过其他手段,自主控制定时任务频率。
问题9:crontab提供最小分钟级别的任务,想完成秒级别的任务,得通过编程语言自己写。
问题10:每1分钟向文件里写入一句话"超哥666",且实时监测文件内容变化。
1.写入计划任务
crontab -e
2.写入语句
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# crontab -e
no crontab for root - using an empty one
crontab: installing new crontab
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]#
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# crontab -l
* * * * * /usr/bin/echo '超哥666' >> /tmp/chaoge.txt
# 3.等待定时任务执行
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# tail -F /tmp/chaoge.txt
tail: cannot open '/tmp/chaoge.txt' for reading: No such file or directory
tail: '/tmp/chaoge.txt' has appeared; following end of new file
超哥666
超哥666
# 4. 删除用户的定时任务
crontab -r问题11:每天凌晨2点30,执行ntpdate命令同步times.aliyun.com,并且sys同步到硬件时钟,且不输出任何信息。
1.ntpdate同步成功后,会生成同步的结果日志
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# ntpdate -u ntp.aliyun.com
可以重定向标准输出结果到黑洞文件,
ntpdate -u ntp.aliyun.com &> /dev/null
2.编写定时任务语句
30 2 * * * /usr/sbin/ntpdate -u ntp.aliyun.com &> /dev/null;/usr/sbin/hwclock -w &> /dev/null6、定时任务经验总结(规范)
-
编写定时任务要有注释说明
-
编写定时任务路径信息尽量使用绝对路径
-
编写定时任务命令需要采用绝对路径执行
- /etc/crontab文件中定义了crontab可用的PATH搜索路径
-
编写定时任务时,可以将输出到屏幕上的信息保存到黑洞中,避免占用磁盘空间
* * * * * sh test.sh &>/dev/null- 或者重定向到文件中,便于排查问题
-
定时任务中执行命令,如果产生输出到屏幕的信息,都会以邮件方式告知用户
/var/spool/mail/root,该日志会不断增大,占用磁盘空间- 关闭本地邮件服务即可,
systemctl stop postfix
-
当定时任务需要执行复杂任务的时候,需要编写为shell脚本再去运行了,注意脚本得有x权限
vim backup.sh 写入
cp -a /data /backup
tar zcvf /backup/data.tar.gz /data写入配置文件
crontab -e
这是于超老师写的备份脚本,用于定时任务
-
-
-
-
- /bin/sh /server/scripts/backup.sh &>/dev/null
-
-
-
-
