- 设计一个结构体,存放一个学员信息并显示,存放两个学员信息,算他们的平均分。
c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
// 定义结构体
typedef struct
{
char name[50];
float score;
} Student;
// 函数声明
void display(Student student);
float calcu(Student student1, Student student2);
int main()
{
// 创建两个学员信息
Student student1;
Student student2;
// 输入第一个学员信息
printf("请输入第一个学员的姓名: ");
scanf("%s", student1.name);
printf("请输入第一个学员的分数: ");
scanf("%f", &student1.score);
// 输入第二个学员信息
printf("请输入第二个学员的姓名: ");
scanf("%s", student2.name);
printf("请输入第二个学员的分数: ");
scanf("%f", &student2.score);
// 显示学员信息
printf("\n第一个学员信息:\n");
display(student1);
printf("\n第二个学员信息:\n");
display(student2);
// 计算并显示平均分
float average = calcu(student1, student2);
printf("\n两个学员的平均分为: %.2f\n", average);
return 0;
}
// 显示学员信息的函数
void display(Student student)
{
printf("姓名: %s\n", student.name);
printf("分数: %.2f\n", student.score);
}
// 计算平均分的函数
float calcu(Student student1, Student student2)
{
return (student1.score + student2.score) / 2.0;
}以上代码定义了一个名为"Student"的结构体,包含学生姓名、学号和成绩三个成员变量。在主函数中,通过创建两个"Student"类型的变量student1和student2,分别赋值不同的学员信息。然后使用cout语句输出学员信息和平均分。

- 设计一个描述商品的结构体,存放一个商品信息,并显示。
c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
// 定义商品结构体
struct Product {
int id; // 商品ID
char name[50]; // 商品名称
float price; // 商品价格
int quantity; // 商品数量
};
// 显示商品信息
void displayProduct(struct Product p) {
printf("商品ID: %d\n", p.id);
printf("商品名称: %s\n", p.name);
printf("商品价格: %.2f\n", p.price);
printf("商品数量: %d\n", p.quantity);
}
int main() {
// 创建一个商品实例并初始化
struct Product product1;
product1.id = 101;
strncpy(product1.name, "苹果", sizeof(product1.name) - 1); // 使用strncpy防止缓冲区溢出
product1.name[sizeof(product1.name) - 1] = '\0'; // 确保字符串以null结尾
product1.price = 5.99;
product1.quantity = 100;
// 显示商品信息
displayProduct(product1);
return 0;
}要的数据结构是一个商品结构体,该结构体定义了商品的ID、名称、价格和数量四个属性。代码中包含了一个显示商品信息的函数displayProduct(),以及一个主函数main()。
在主函数中,首先创建了一个商品实例product1,并对其属性进行初始化。然后调用displayProduct()函数,将product1作为参数传入,以显示商品信息。
显示商品信息的函数displayProduct()使用printf()函数来输出商品的各个属性值。其中,%d用于输出整型变量,%s用于输出字符串变量,%.2f用于输出浮点型变量,并控制输出小数点后保留两位。
最后,main()函数返回0,表示程序正常结束。

-
作业2的基础之上完成以下功能:
(1)存储多个商品的信息,后显示
(2)查询价格最高的商品的信息
(3)用静态分配(结构体变量)和动态分配分别实现。
c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
struct Product {
int id;
char name[50];
float price;
int quantity;
};
// 显示所有商品信息(与静态分配中的相同)
void displayProducts(struct Product products[], int count) {
// ...(与静态分配中的代码相同)
}
// 查询价格最高的商品信息(与静态分配中的相同)
struct Product findHighestPricedProduct(struct Product products[], int count) {
// ...(与静态分配中的代码相同)
}
int main() {
struct Product *products = malloc(100 * sizeof(struct Product)); // 动态分配内存
int productCount = 0;
if (products == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "内存分配失败\n");
return 1;
}
// 初始化商品信息(与静态分配中的类似,但使用malloc分配的内存)
// ...(与静态分配中的代码类似,但使用products指针)
// 显示所有商品信息
displayProducts(products, productCount);
// 查询价格最高的商品信息
struct Product highestPricedProduct = findHighestPricedProduct(products, productCount);
printf("价格最高的商品信息:\n");
displayProducts(&highestPricedProduct, 1);
// 释放动态分配的内存
free(products);
return 0;
}在main函数中,通过调用malloc函数来动态分配了一个Product类型的数组,大小为100。如果内存分配失败,会打印错误消息并退出程序。
然后,通过调用displayProducts函数,显示所有商品的信息。这个函数接受一个Product数组和一个整数参数来表示数组的大小。在这个示例中,productCount变量表示商品数量。
接下来,通过调用findHighestPricedProduct函数来查询价格最高的商品信息。该函数也接受一个Product数组和一个整数参数来表示数组的大小。在这个示例中,它返回一个Product结构体,代表价格最高的商品。
最后,通过调用free函数来释放动态分配的内存,防止内存泄漏。

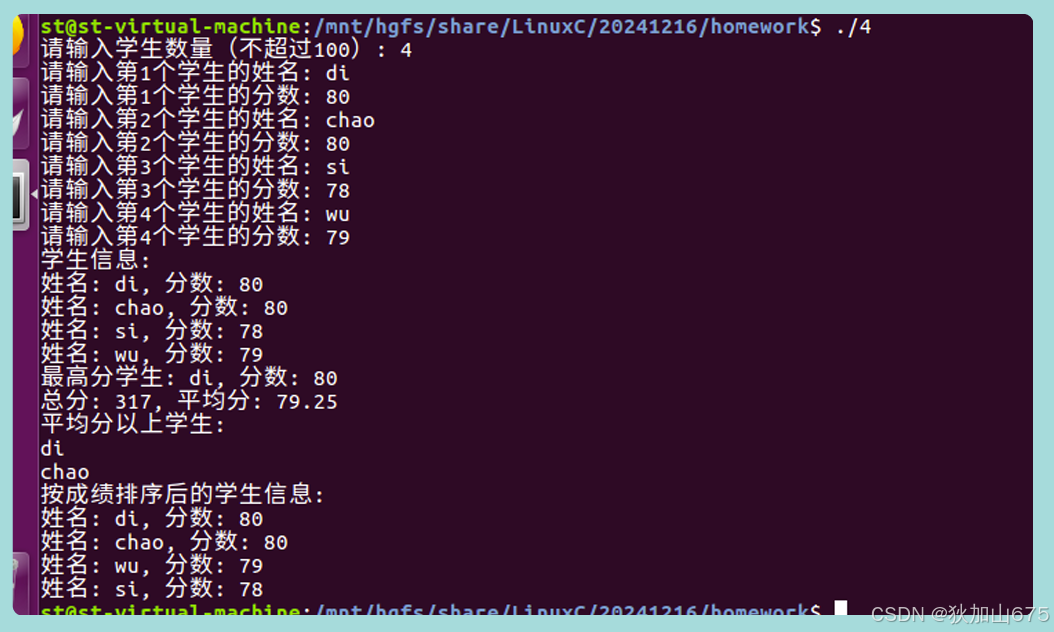
- 开发一个简易的成绩管理系统: 存储多个学员信息并处理 要求如下:
(1)申请多个空间,存入学员信息
(2)求分数最高学员姓名
(3)求总分和平均分
(4)统计查询 (查询平均分以上学员的姓名)
(5)按照成绩排序
c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAX_STUDENTS 100
typedef struct
{
char name[50];
int score;
} Student;
// 初始化学生信息(现在从用户输入获取)
void input(Student **students, int count)
{
*students = (Student *)malloc(count * sizeof(Student));
if (*students == NULL) {
printf("内存分配失败!\n");
exit(1);
}
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
printf("请输入第%d个学生的姓名: ", i + 1);
scanf("%49s", (*students)[i].name); // 注意:防止缓冲区溢出,使用%49s
printf("请输入第%d个学生的分数: ", i + 1);
scanf("%d", &(*students)[i].score);
}
}
// 查找最高分学生
void find(Student *students, int count)
{
Student highest = students[0];
for (int i = 1; i < count; i++)
{
if (students[i].score > highest.score)
{
highest = students[i];
}
}
printf("最高分学生: %s, 分数: %d\n", highest.name, highest.score);
}
// 计算总分和平均分
void calculate(Student *students, int count, int *total, float *average)
{
*total = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
*total += students[i].score;
}
*average = (float)*total / count;
printf("总分: %d, 平均分: %.2f\n", *total, *average);
}
// 统计查询:查询平均分以上学生的姓名
void query(Student *students, int count, float average)
{
printf("平均分以上学生:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
if (students[i].score > average)
{
printf("%s\n", students[i].name);
}
}
}
// 按成绩排序(冒泡排序)
void sort(Student *students, int count)
{
for (int i = 0; i < count - 1; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < count - i - 1; j++)
{
if (students[j].score < students[j + 1].score)
{
Student temp = students[j];
students[j] = students[j + 1];
students[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
// 显示学生信息
void display(Student *students, int count)
{
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
printf("姓名: %s, 分数: %d\n", students[i].name, students[i].score);
}
}
int main()
{
Student *students = NULL;
int studentCount;
int totalScore;
float averageScore;
// 输入学生数量
printf("请输入学生数量(不超过%d): ", MAX_STUDENTS);
scanf("%d", &studentCount);
// 确保输入的学生数量不超过最大限制
if (studentCount > MAX_STUDENTS || studentCount <= 0)
{
printf("学生数量超出范围或无效!\n");
return 1;
}
// 输入学生信息
input(&students, studentCount);
// 显示学生信息
printf("学生信息:\n");
display(students, studentCount);
// 查找最高分学生
find(students, studentCount);
// 计算总分和平均分
calculate(students, studentCount, &totalScore, &averageScore);
// 统计查询:查询平均分以上学生的姓名
query(students, studentCount, averageScore);
// 按成绩排序
sort(students, studentCount);
// 显示排序后的学生信息
printf("按成绩排序后的学生信息:\n");
display(students, studentCount);
// 释放内存
free(students);
return 0;
}这段代码是一个学生成绩管理系统的简单实现。代码中定义了一个结构体Student,包含了学生的姓名和分数。通过定义相关函数,实现了学生信息的输入、查找最高分学生、计算总分和平均分、查询平均分以上学生、按成绩排序和显示学生信息等功能。
主函数中,首先要求用户输入学生的数量,然后通过输入函数input()获取学生信息。接着,调用display()函数显示学生信息,调用find()函数查找最高分学生,调用calculate()函数计算总分和平均分,调用query()函数查询平均分以上学生的姓名,调用sort()函数按成绩排序,并最后调用display()函数再次显示排序后的学生信息。最后,释放了动态分配的内存。
总的来说,这段代码实现了一个简单的学生成绩管理系统,可以输入学生信息,进行相关操作,并显示结果。
-
确认电脑的主机字节序。大端(高字节的数据存放在低地址上,低字节的数据存放在高地址
上),小端(高字节的数据存放在高地址上,低字节的数据存放在低地址上)
c#include <stdio.h> int main() { unsigned int num = 0x12345678; char *ptr = (char *)# if (*ptr == 0x12) { printf("Big-Endian\n"); } else if (*ptr == 0x78) { printf("Little-Endian\n"); } else { printf("Unknown Endian\n"); } return 0; }
在代码中,首先初始化一个unsigned int类型的变量num为0x12345678,并声明一个char类型的指针ptr,指向num的地址。
接下来,通过判断ptr指向的地址上的值,来判断是大端序还是小端序。由于num的初始值为0x12345678,所以ptr指向的第一个字节的值为0x12,所以判断条件if (*ptr == 0x12)成立,输出"Big-Endian"。
如果ptr指向的第一个字节的值为0x78,则判断为小端序,输出"Little-Endian"。
如果ptr指向的值既不是0x12也不是0x78,则输出"Unknown Endian"。
最后,返回0表示程序正常结束。