之前介绍了如何在Streamlit App中使用Matplotlib库来绘图。
本篇介绍 Steamlit结合Poltly的方法,相比于Matplotlib,Poltly的交互性更强,
更适合在Web应用中做为可视化的工具。
1. st.plotly_chart函数
st.plotly_chart函数专门用于在Steamlit应用中显示 Plotly 绘制的图形。
这个函数能够直接将Plotly Figure对象 或者Poltly支持的数据对象直接渲染到页面的指定位置上。
st.plotly_chart的参数不多,与st.pyplot比,多了一些交互用的参数:
| 名称 | 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| figure_or_data | Figure或Data对象 | |
| theme | str | 指定图表的主题 |
| use_container_width | bool | 决定是否使用父容器的宽度覆盖图形的原始宽度 |
| key | str | 为元素提供标识 |
| on_select | str | 控制图表如何响应用户选择事件 |
| selection_mode | str | 图表的选择模式 |
因为Plotly绘制的图形可交互,通过key参数,在交互的过程中,我们可以精确地定位到交互的图表。
on_select参数有以下几种取值:
ignore:不对图表中的任何选择事件做出反应rerun:在图表中选择数据时,会重新运行应用程序可调用对象****:会重新运行应用程序,并在应用程序的其余部分之前执行该可调用对象作为回调函数
selection_mode参数定义图表的选择模式,包括:
points:允许基于单个数据点进行选择box:允许基于矩形区域进行选择lasso:允许基于自由绘制区域进行选择
on_select不同时,页面的效果如下:
1.1. on_select=ignore
ignore是on_select的默认值,此时Plotly图形上无法选择对象。
python
import streamlit as st
import plotly.express as px
df = px.data.iris()
fig = px.scatter(df, x="sepal_width", y="sepal_length")
st.plotly_chart(fig, key="iris")
# 或者
# st.plotly_chart(fig, key="iris", on_select="ignore")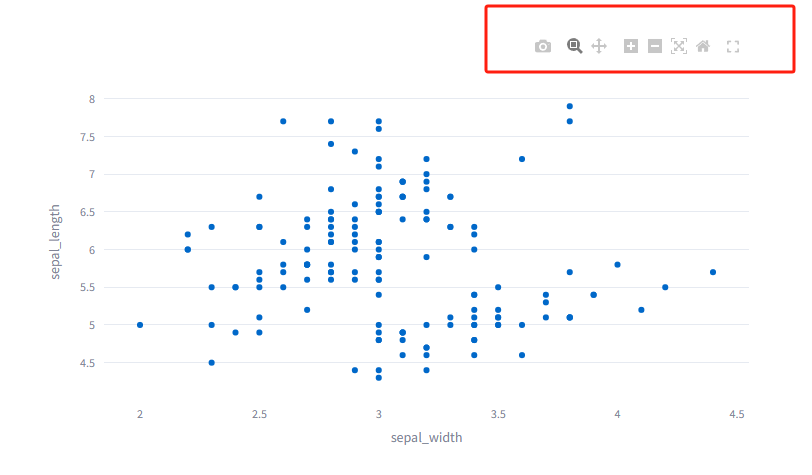
此时,工具栏上没有选择数据的小工具。
1.2. on_select=rerun
此时,st.plotly_chart会将选择的数据点返回。
选择数据点时,可以切换成矩形选择 和自由区域选择。
python
event = st.plotly_chart(fig, key="iris", on_select="rerun")
event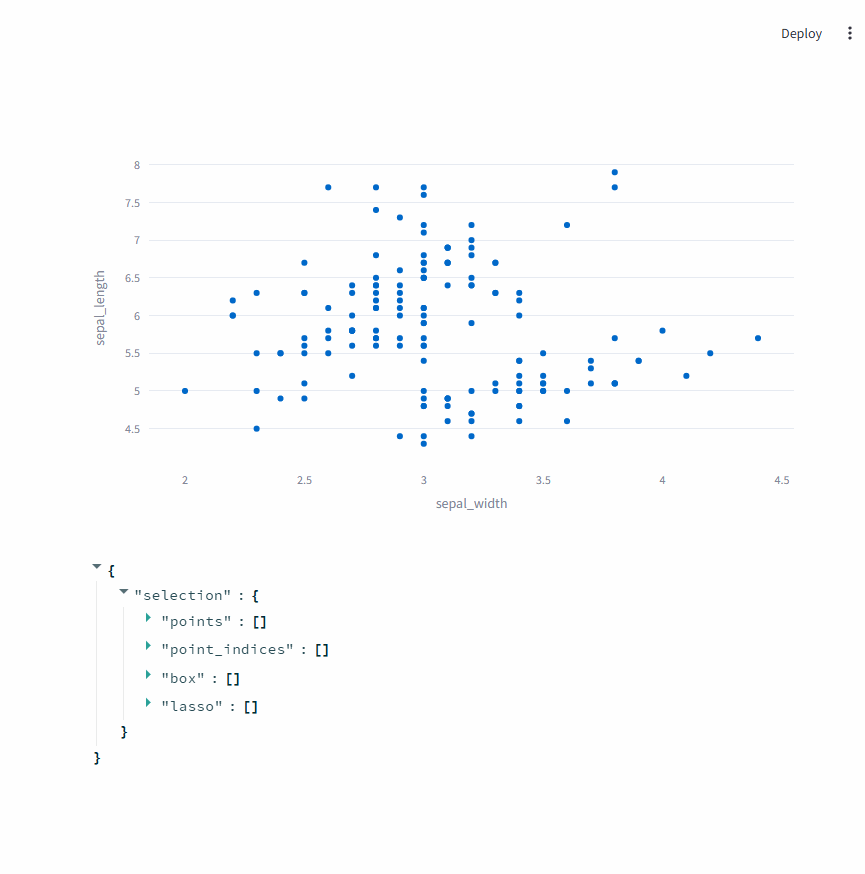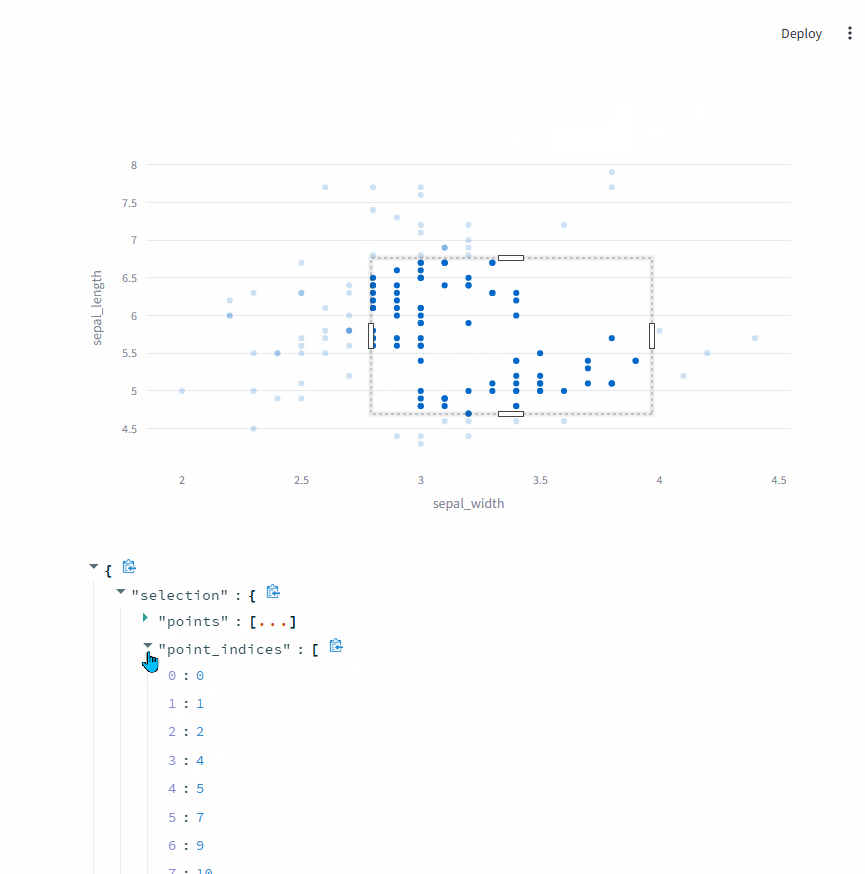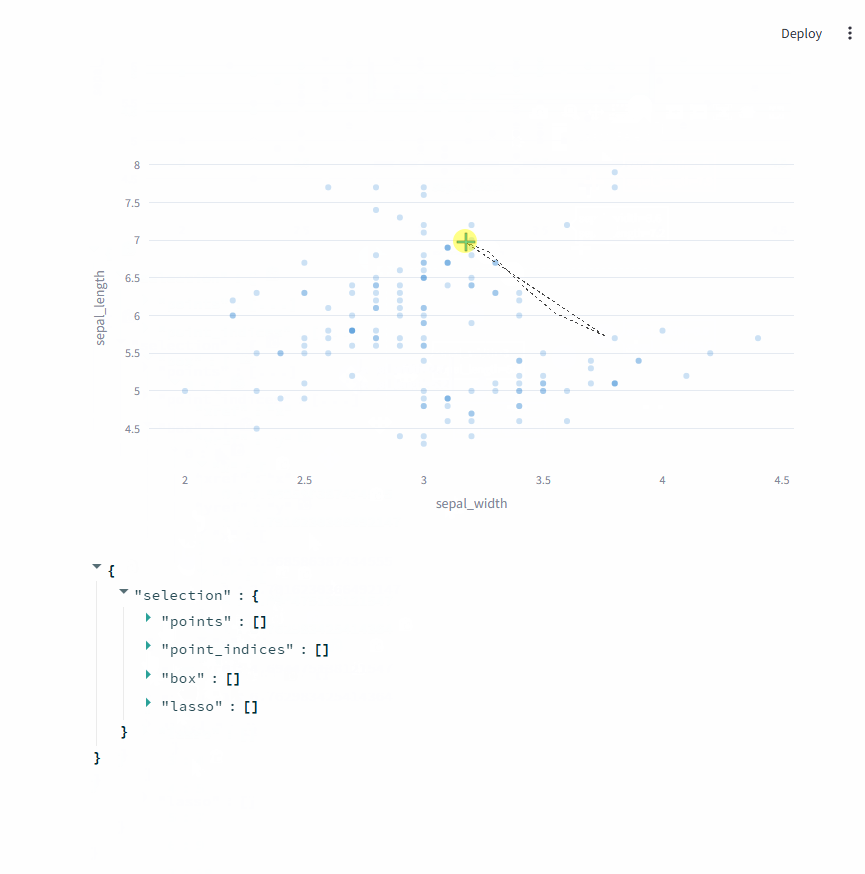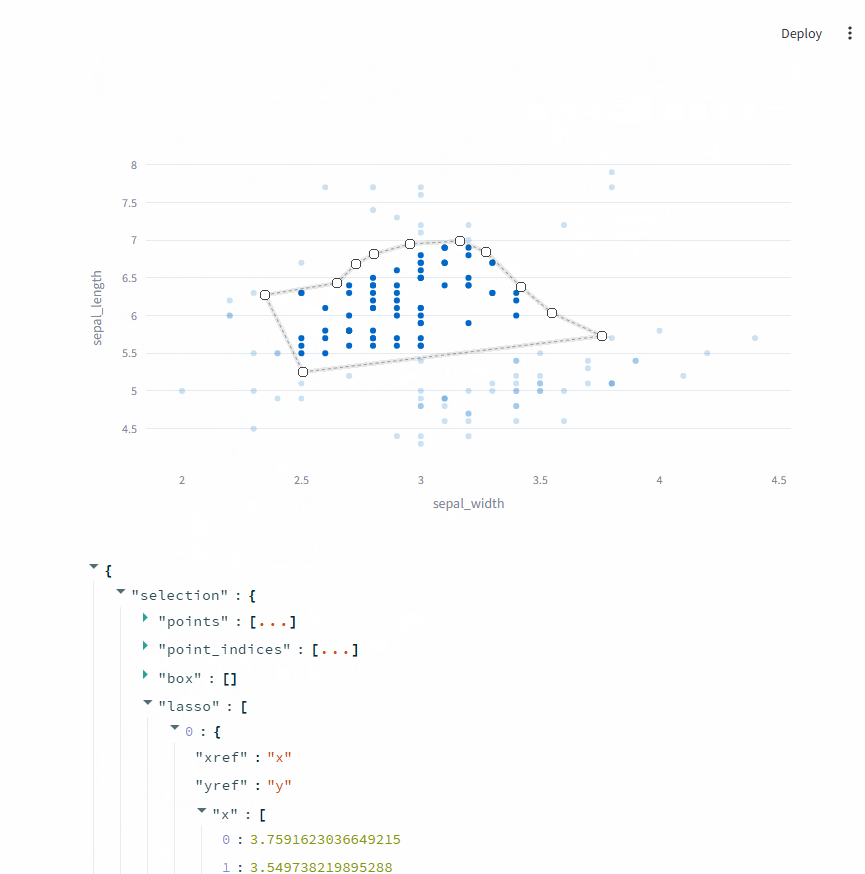
1.3. on_select=callable
on_select=callable的效果on_select=rerun差不多,也能对数据点选择并得到选择的数据点。
不同之处在于,可以在选择数据点之后,调用callable函数进行额外的处理。
python
def handle_selection():
from datetime import datetime
st.write(f"Selected data at {datetime.now()}")
event = st.plotly_chart(fig, key="iris", on_select=handle_selection)
event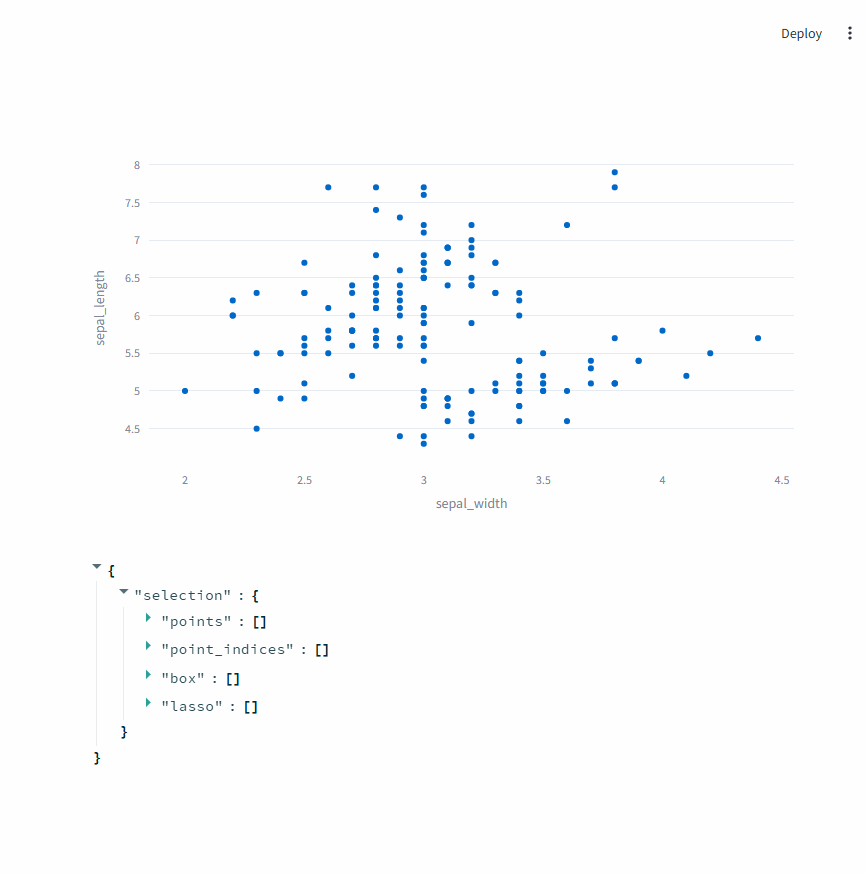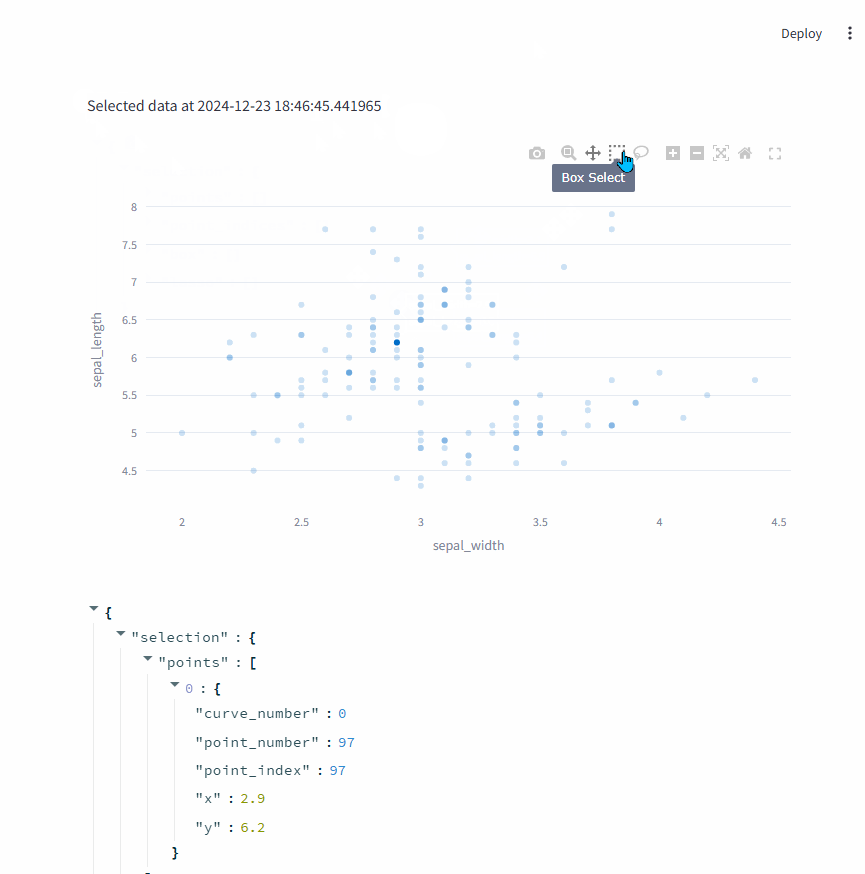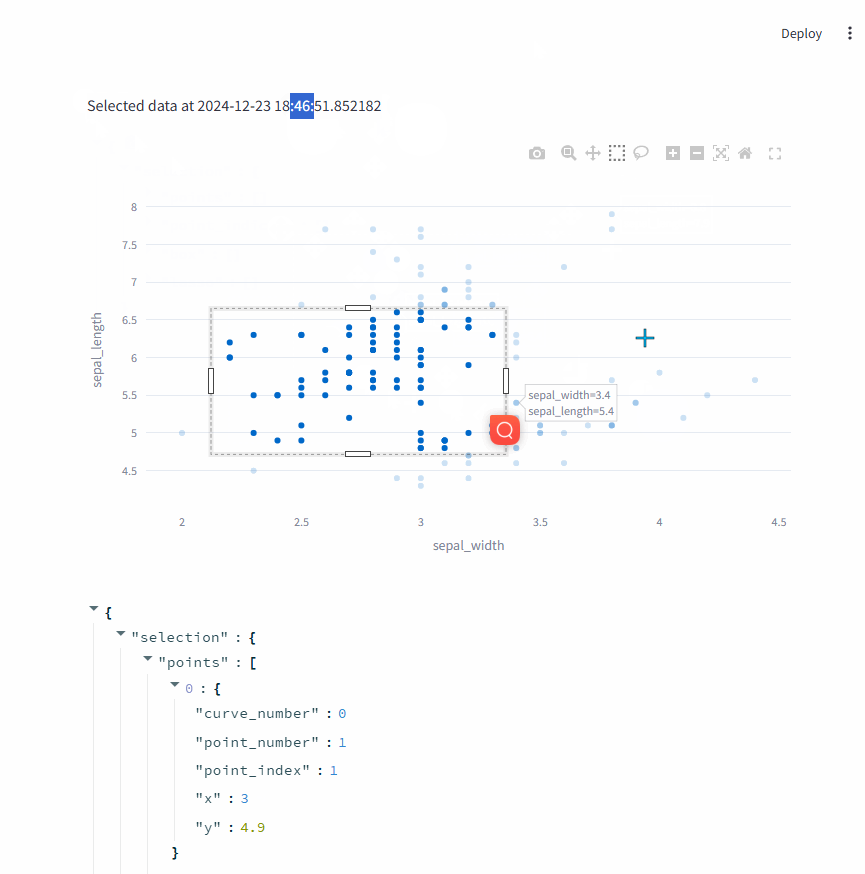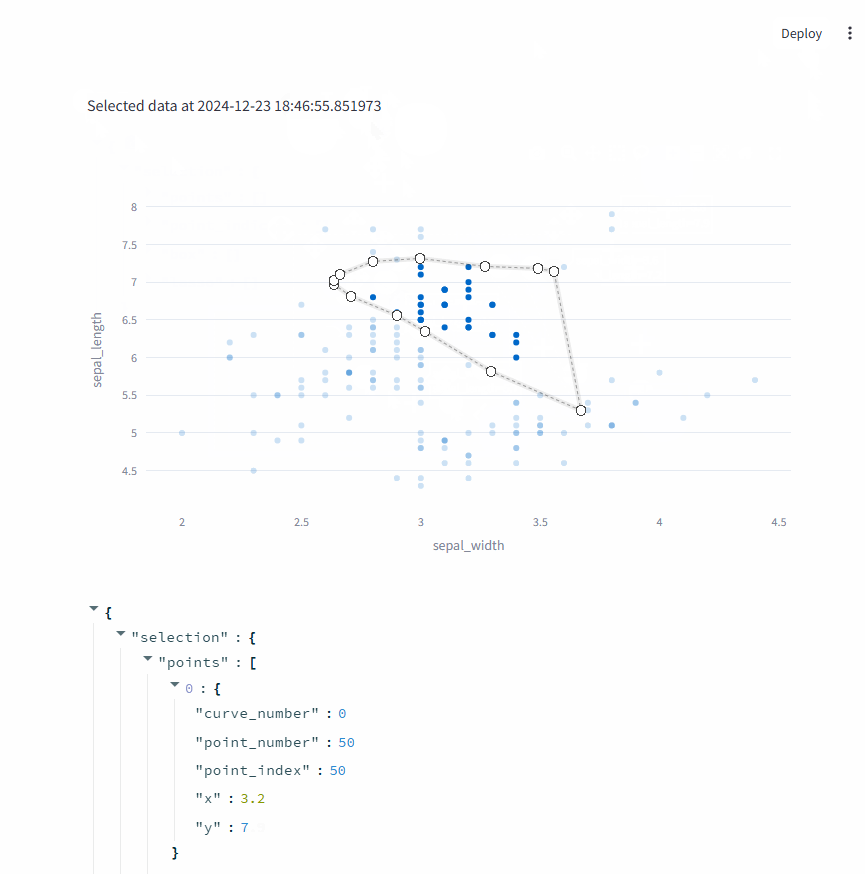
每次选择数据之后,上面的时间都会变化,说明handle_selection函数在每次选择数据之后都被回调。
2. 使用示例
下面通过示例演示实际场景中如何使用streamlit和Poltly图表。
2.1. 销售数据时间序列分析
在这个示例中,首先创建了一个模拟的销售数据时间序列,然后通过st.plotly_chart展示图表,并设置on_select回调函数来处理用户在图表上的选择操作。
当用户选择图上的点时,会在 Streamlit 应用中显示所选数据点对应的日期和销售额信息。
python
import streamlit as st
import plotly.express as px
import pandas as pd
# 模拟销售数据
data = {
"Date": pd.date_range(start="2024-01-01", periods=100),
"Sales": [i**2 + 50 + 10 * (i % 10) for i in range(100)],
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# 创建时间序列折线图
fig = px.scatter(df, x="Date", y="Sales")
# 显示图表并处理选择事件
def handle_selection():
selected_points = st.session_state["sales_chart"].selection.points
st.write("已选择的数据点:")
df = pd.DataFrame(columns=["日期", "销售额"])
for idx, p in enumerate(selected_points):
df.loc[idx, "日期"] = p["x"]
df.loc[idx, "销售额"] = p["y"]
st.dataframe(df)
st.plotly_chart(fig, key="sales_chart", on_select=handle_selection)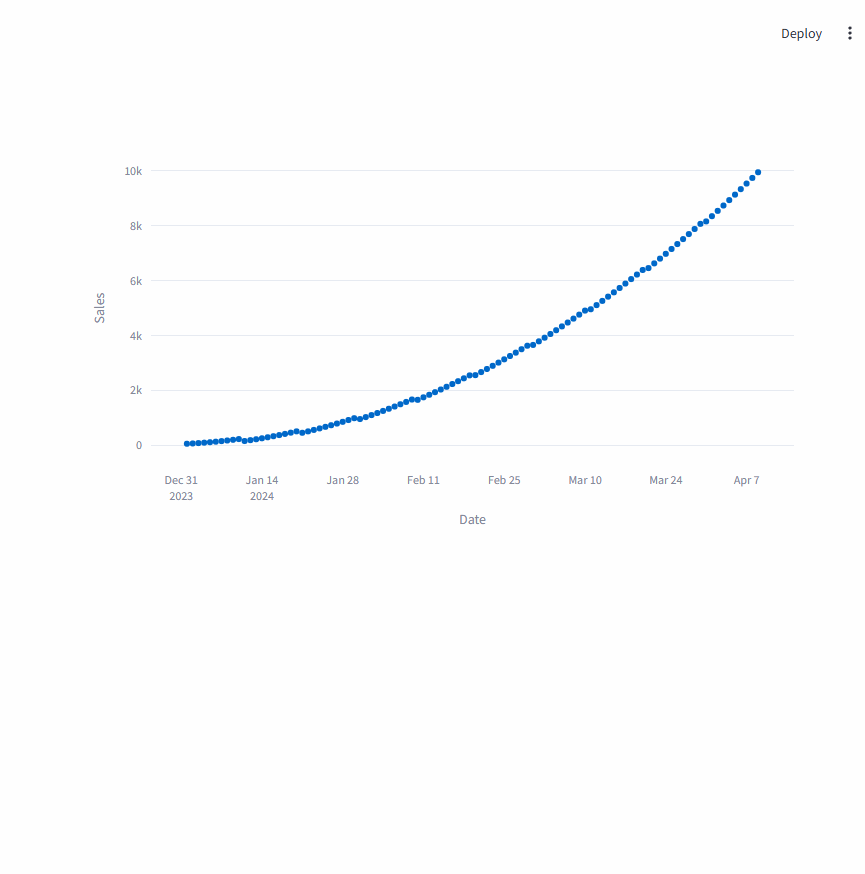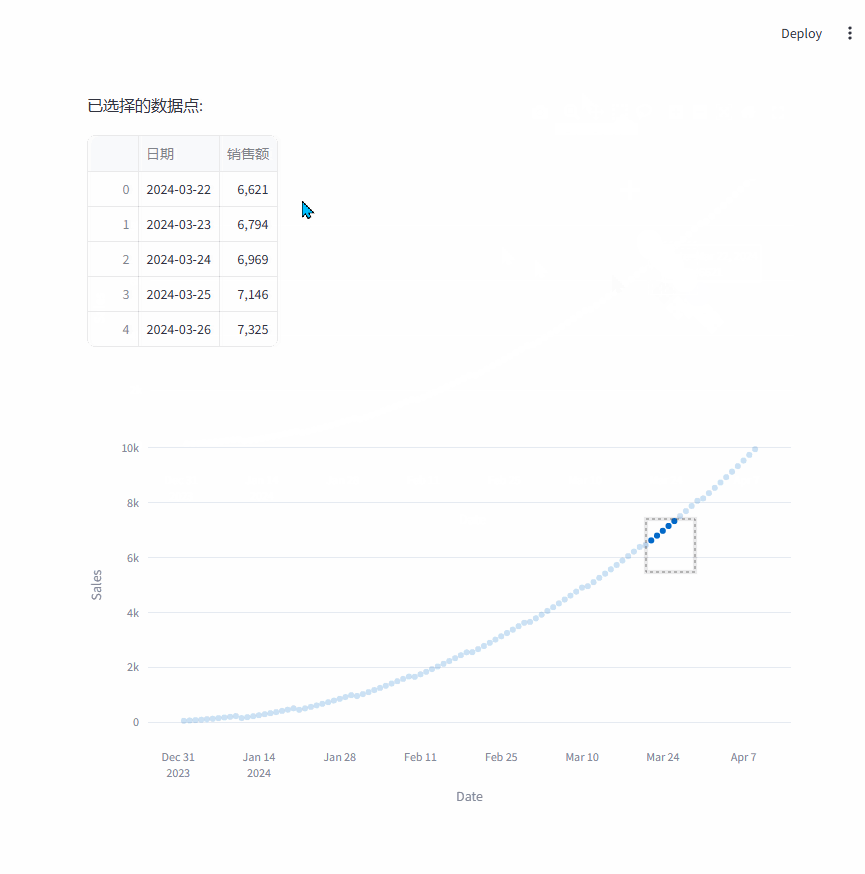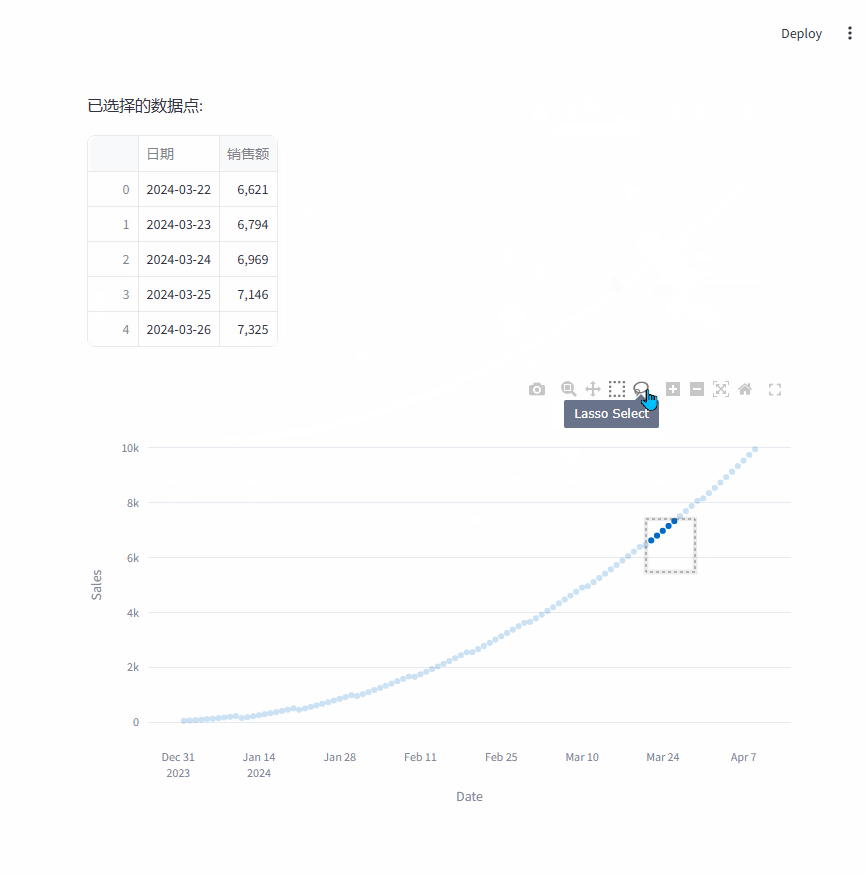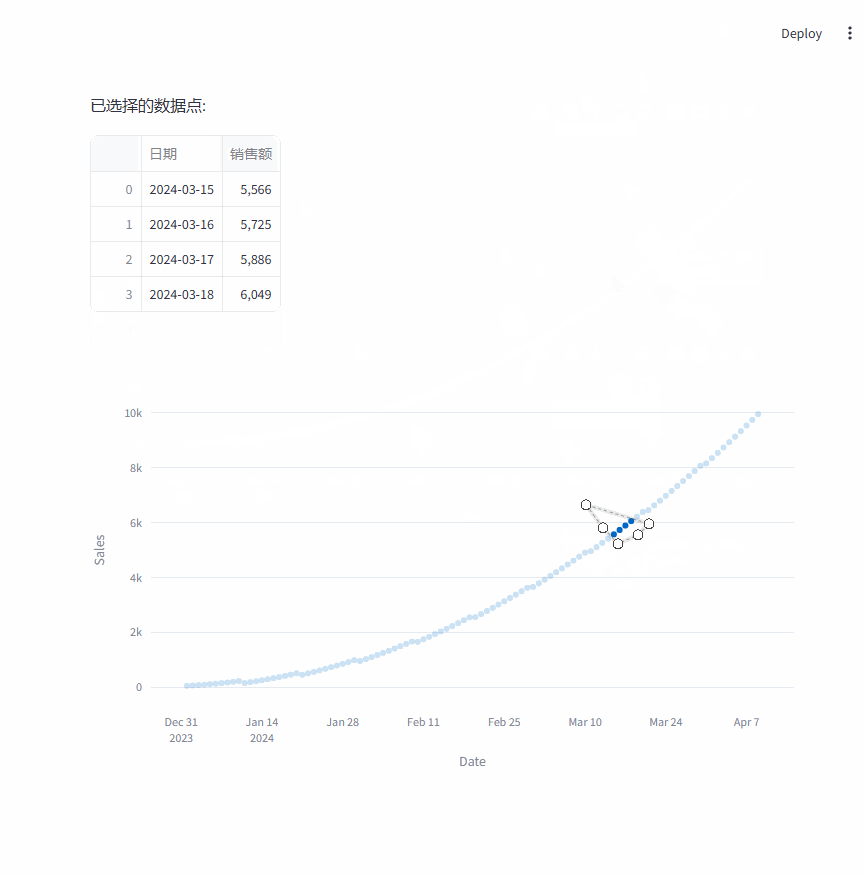
2.2. 模拟股票分析
使用generate_stock_data函数生成模拟的股票数据,再使用plotly.graph_objects创建一个烛台图,将模拟数据绘制到图表中。
编写一个回调函数,当用户在图表上选择某个点时,它会获取所选点的详细信息并在 Streamlit 应用中展示出来。
python
import streamlit as st
import plotly.graph_objects as go
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# 生成随机模拟的股票数据
def generate_stock_data(days=300):
dates = pd.date_range(start="2024-01-01", periods=days)
open_prices = np.random.rand(days) * 100 + 50
high_prices = open_prices + np.random.rand(days) * 10
low_prices = open_prices - np.random.rand(days) * 10
close_prices = open_prices + np.random.randn(days) * 5
data = {
"Date": dates,
"Open": open_prices,
"High": high_prices,
"Low": low_prices,
"Close": close_prices,
}
return pd.DataFrame(data)
# 生成模拟股票数据
df = generate_stock_data()
# 创建交互式图表
fig = go.Figure(
data=[
go.Candlestick(
x=df["Date"],
open=df["Open"],
high=df["High"],
low=df["Low"],
close=df["Close"],
)
]
)
fig.update_layout(title="模拟股票价格", xaxis_title="Date", yaxis_title="Price")
# onselect 回调函数
def handle_selection():
selected_points = st.session_state.stock_chart.selection.points
st.write("Selected Stock Data Points:")
df = pd.DataFrame(columns=["日期", "开盘价", "收盘价", "最高价", "最低价"])
for idx, p in enumerate(selected_points):
print(idx, p)
df.loc[idx, "日期"] = p["x"]
df.loc[idx, "开盘价"] = p["open"]
df.loc[idx, "收盘价"] = p["close"]
df.loc[idx, "最高价"] = p["high"]
df.loc[idx, "最低价"] = p["low"]
st.dataframe(df)
# 显示图表
st.plotly_chart(fig, key="stock_chart", on_select=handle_selection)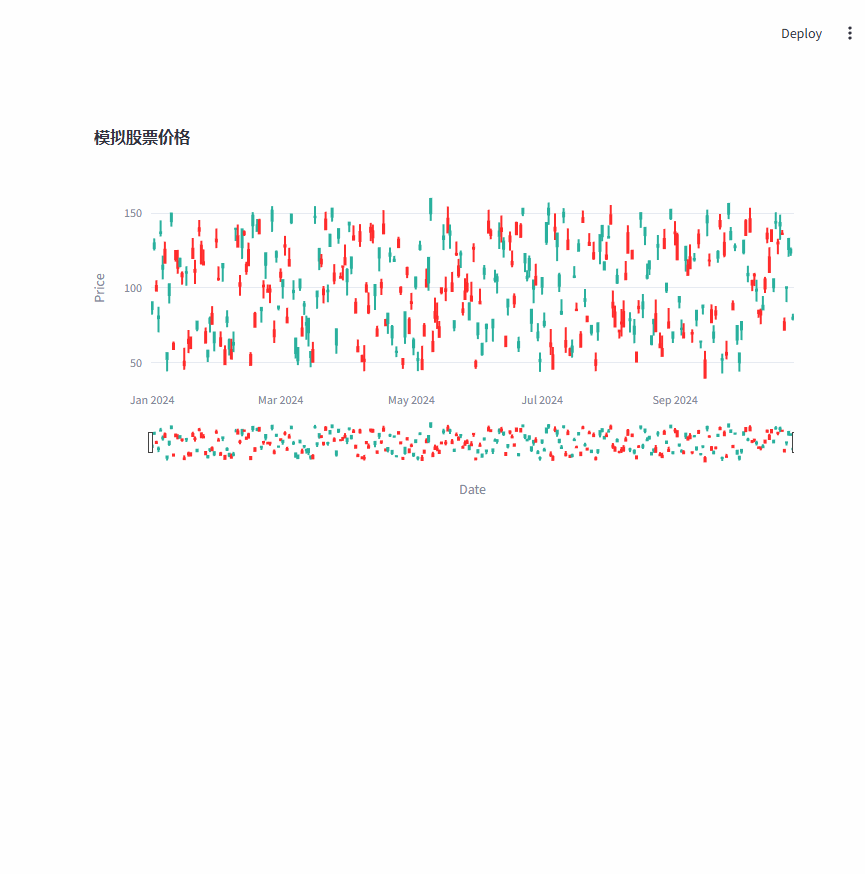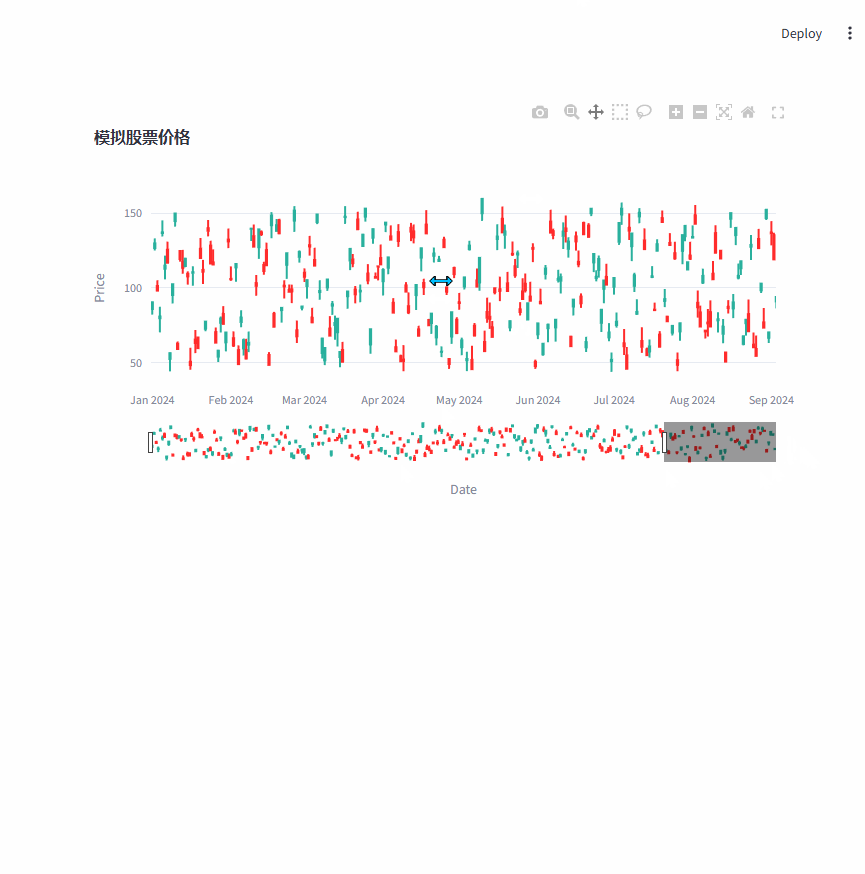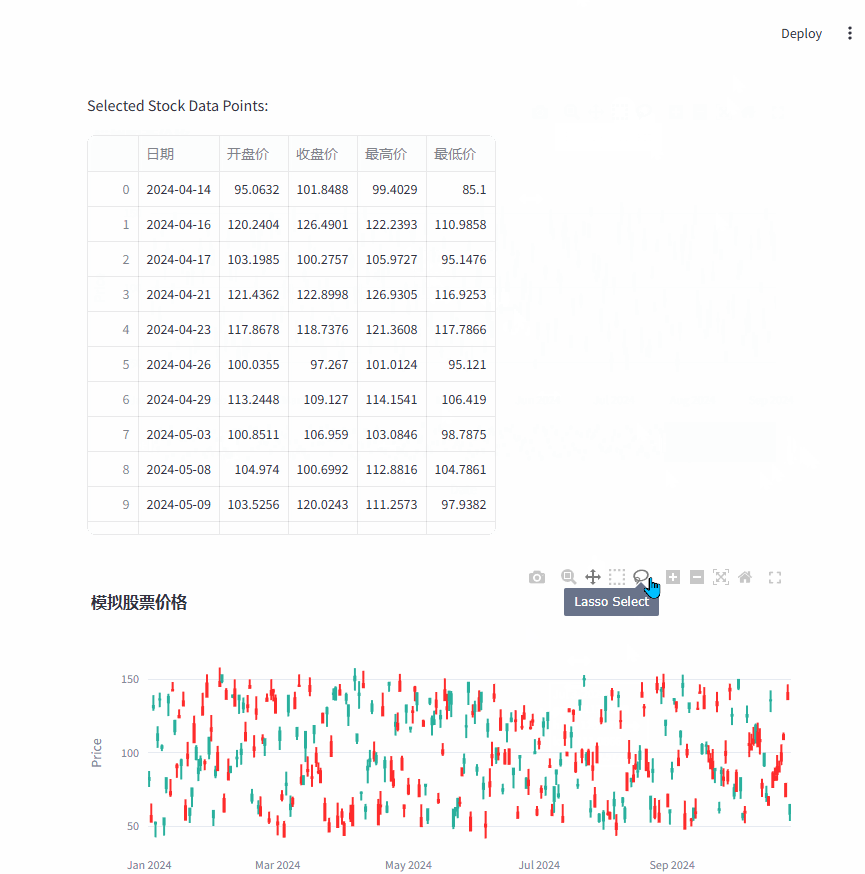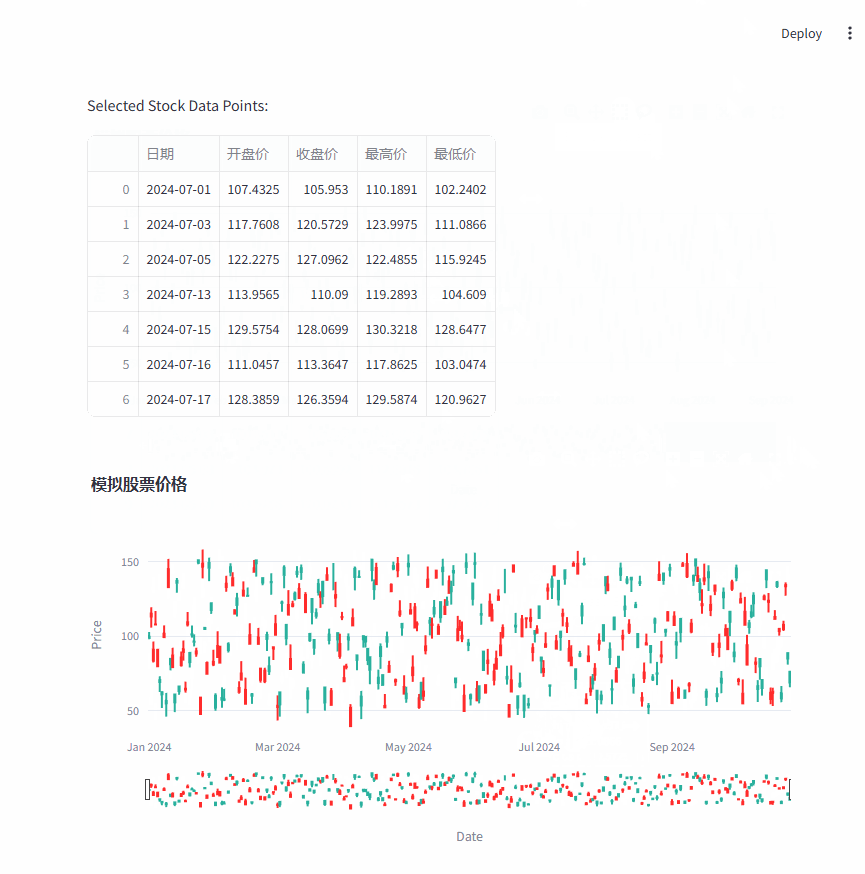
3. 总结
Streamlit 可以简化 Web 应用构建流程,Plotly 提供丰富图表类型,二者结合能快速将数据转化为交互式可视化应用,节省开发时间。
此外,Plotly 图表交互性高,在 Streamlit 应用中可实现数据探索、筛选等操作,增强用户体验。