1. 项目背景
Spring Cache是Spring框架提供的一个缓存抽象层,它简化了缓存的使用和管理。Spring Cache默认使用服务器内存,并无法控制缓存时长,查找缓存中的数据比较麻烦。
因此Spring Cache支持将缓存数据集成到各种缓存中间件中。本文已常用的Redis作为缓存中间件作为示例,详细讲解项目中如何使用Cache提高系统性能。
2. Spring Cache介绍
Spring Cache是Spring框架提供的一种缓存解决方案,基于AOP原理,实现了基于注解的缓存功能,只需要简单地加一个注解就能实现缓存功能,对业务代码的侵入性很小。
使用Spring Cache的方法很简单,只需要在方法上添加注解即可实现将方法返回数据存入缓存,以及清理缓存等注解的使用。
2.1 主要特点
- 统一的缓存抽象:Spring Cache为应用提供了一种统一的缓存抽象,可以轻松集成各种缓存提供者(如Ehcache、Redis、Caffeine等),使用统一的API。
- 注解驱动 :Spring Cache通过简单的注解配置,如
@Cacheable、@CachePut、@CacheEvict等,可以快速实现缓存功能,而无需处理底层缓存逻辑。 - 灵活性和扩展性 :Spring Cache允许根据业务需求自定义缓存策略,如缓存的失效时间、缓存的淘汰策略等。同时,它也提供了
CacheManager接口和Cache接口,可以实现降低对各种缓存框架的耦合。
2.2 常用注解
@EnableCaching
- 作用:开启Spring的缓存注解支持。
- 使用场景:在配置类上添加此注解,以启用Spring Cache的注解处理功能。
- 注意 :此注解本身并不提供缓存实现,而是允许你使用
@Cacheable、@CachePut、@CacheEvict等注解来定义缓存行为。
@Cacheable
- 作用:在方法执行前检查缓存,如果缓存中存在数据则直接返回,否则执行方法并将结果缓存。
- value :指定缓存的名称(或名称数组)。缓存名称与
CacheManager中配置的缓存对应。 - key:用于生成缓存键的表达式(可选)。如果不指定,则默认使用方法的参数值作为键。
- condition:条件表达式(可选),用于决定是否执行缓存操作。
- unless:否定条件表达式(可选),用于在方法执行后决定是否缓存返回值。
@Cacheable注解配置参数说明
-
value/cacheNames:
- 用于指定缓存的名称(或名称数组),缓存名称作为缓存key的前缀。这是缓存的标识符,用于在
CacheManager中查找对应的缓存。 value和cacheNames是互斥的,即只能指定其中一个。
- 用于指定缓存的名称(或名称数组),缓存名称作为缓存key的前缀。这是缓存的标识符,用于在
-
key:
- 用于生成缓存键的表达式。这个键用于在缓存中唯一标识存储的值。
- 如果不指定
key,则默认使用方法的参数值(经过某种转换)作为键。 - 可以使用Spring Expression Language(SpEL)来编写
key表达式,以实现动态键的生成。
-
keyGenerator:
- 指定一个自定义的键生成器(实现 org.springframework.cache.interceptor.KeyGenerator 接口的类),用于生成缓存的键。与 key 属性互斥,二者只能选其一。
- 如果同时指定了
key和keyGenerator,则会引发异常,因为它们是互斥的。 - 开发者可以编写自己的
KeyGenerator实现,并将其注册到Spring容器中,然后在@Cacheable注解中引用。
-
cacheManager:
CacheManager表示缓存管理器,通过缓存管理器可以设置缓存过期时间。- 用于指定要使用的
CacheManager。这是一个可选参数,通常不需要显式指定,因为Spring会默认使用配置的CacheManager。 - 如果系统中配置了多个
CacheManager,则需要通过此参数指定使用哪一个。
-
cacheResolver:
- 缓存解析器,用于解析缓存名称并返回相应的
Cache对象。这也是一个可选参数。 - 类似于
cacheManager,如果系统中配置了多个缓存解析逻辑,可以通过此参数指定使用哪一个。
- 缓存解析器,用于解析缓存名称并返回相应的
-
condition:
- 条件表达式,用于决定是否执行缓存操作。这是一个可选参数。
- 条件表达式使用SpEL编写,如果表达式返回
true,则执行缓存操作;否则不执行。
-
unless:
- 否定条件表达式,用于在方法执行后决定是否缓存返回值。这也是一个可选参数。
- 与
condition类似,unless也使用SpEL编写,但它是在方法执行后才进行评估的。 - 如果
unless表达式返回true,则不缓存返回值;否则缓存。
-
sync:
- 是否使用异步模式进行缓存操作。这是一个可选参数,通常不需要显式指定。
- 在多线程环境中,如果多个线程同时请求相同的数据并触发缓存操作,使用异步模式可以避免线程阻塞和重复计算。
@Cacheable注解的这些参数是互斥或相互关联的,例如value和cacheNames不能同时指定,key和keyGenerator也不能同时指定。此外,cacheManager和cacheResolver也是互斥的,因为它们都用于指定缓存的解析和管理方式。
对于前两个注解的应用:
java
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "cache:cacheByKey", key = "#id")
public Integer cacheByKey(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) throws InterruptedException {
Thread.sleep(5000);
log.info("执行了cacheByKey方法" + id);
return id;
}看注释掉的那行,取缓存名称为cache:cacheByKey,参数id的值作为key,最终缓存key为:缓存名称+"::"+key,例如:上述代码id为123,最终的key为:cache:cacheByKey::123
SpEL(Spring Expression Language)是一种在 Spring 框架中用于处理字符串表达式的强大工具,它可以实现获取对象的属性,调用对象的方法操作。
- 单个缓存名称 :
@Cacheable(value = "myCache")表示使用名为myCache的缓存。 - 多个缓存名称 :
@Cacheable(value = {"cache1", "cache2"})表示方法的结果将同时缓存到cache1和cache2中。 - 与
@CacheConfig结合使用 :如果类上使用了@CacheConfig注解,并且指定了cacheNames属性,那么类中的方法在使用@Cacheable时可以省略value属性,直接使用类级别的缓存配置。
@CacheEvict
- 作用:从缓存中删除数据。
- value:指定要删除的缓存的名称(或名称数组)。
- key:用于指定要删除的缓存键(可选)。如果不指定,则默认使用方法的参数值作为键。
- allEntries:布尔值,指定是否删除缓存中的所有条目(而不是仅删除与指定键匹配的条目)。
- beforeInvocation :布尔值,指定是否在方法执行之前删除缓存(默认为
false,即在方法执行之后删除)。
@CachePut
- 作用:更新缓存中的数据,无论方法是否成功执行,都会将结果放入缓存。
- value 、key 、condition 、unless :与
@Cacheable中的这些属性相同。
@Caching
- 作用 :允许在同一个方法上组合使用多个缓存注解(如
@Cacheable、@CachePut、@CacheEvict)。 - 属性:包含一个或多个缓存注解。
@CacheConfig
- 作用:为类级别提供缓存相关的默认配置。
- cacheNames:指定该类中所有方法使用的默认缓存名称(或名称数组)。
- keyGenerator:指定自定义的键生成器(可选)。
- cacheManager :指定要使用的
CacheManager(可选)。
3. 示例代码
项目依赖于Redis配置,这里就不多赘述了。
缓存管理器配置:
定义了两个缓存管理器,默认cacheManager(使用@Primary标注),一个缓存返回值为null的管理器cacheNullManager,详情看下面代码。
java
package com.maple.redis.config;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.cache.Cache;
import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachingConfigurerSupport;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
import org.springframework.cache.interceptor.CacheErrorHandler;
import org.springframework.cache.interceptor.KeyGenerator;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializationContext;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.time.Duration;
/**
* @author 笑小枫
* @date 2025/1/7
*/
@Slf4j
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
public class CacheConfig extends CachingConfigurerSupport {
/**
* 默认缓存管理器
* 只有CacheManger才能扫描到cacheable注解
* spring提供了缓存支持Cache接口,实现了很多个缓存类,其中包括RedisCache。但是我们需要对其进行配置,这里就是配置RedisCache
*/
@Bean
@Primary
public CacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
return RedisCacheManager.RedisCacheManagerBuilder
//Redis链接工厂
.fromConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory)
//缓存配置 通用配置 默认存储一小时
.cacheDefaults(getCacheConfigurationWithTtl(Duration.ofHours(1)))
//配置同步修改或删除 put/evict
.transactionAware()
//对于不同的cacheName我们可以设置不同的过期时间
.withCacheConfiguration("cache2:cacheByUser", getCacheConfigurationWithTtl(Duration.ofHours(2)))
.build();
}
/**
* 创建并返回一个CacheManager Bean,用于管理Redis缓存。
* 主要返回结果为null时使用,会缓存null值,缓存时间为10分钟,防止缓存穿透。
* 使用时通过 cacheManager = "cacheNullManager" 指定使用该缓存管理器。
*/
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheNullManager(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
return RedisCacheManager.RedisCacheManagerBuilder
//Redis链接工厂
.fromConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory)
//缓存配置 通用配置 默认存储一小时
.cacheDefaults(RedisCacheConfiguration
.defaultCacheConfig()
// 设置key为String
.serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer()))
// 设置value 为自动转Json的Object
.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(RedisSerializer.json()))
.entryTtl(Duration.ofMinutes(10)))
//配置同步修改或删除 put/evict
.transactionAware()
.build();
}
/**
* 缓存的基本配置对象
*/
private RedisCacheConfiguration getCacheConfigurationWithTtl(Duration duration) {
return RedisCacheConfiguration
.defaultCacheConfig()
//设置key value的序列化方式
// 设置key为String
.serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer()))
// 设置value 为自动转Json的Object
.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(RedisSerializer.json()))
// 不缓存null
.disableCachingNullValues()
// 设置缓存的过期时间
.entryTtl(duration);
}
/**
* 缓存的异常处理
*/
@Bean
@Override
public CacheErrorHandler errorHandler() {
// 异常处理,当Redis发生异常时,打印日志,但是程序正常走
log.info("初始化 -> [{}]", "Redis CacheErrorHandler");
return new CacheErrorHandler() {
@Override
public void handleCacheGetError(RuntimeException e, Cache cache, Object key) {
log.error("Redis occur handleCacheGetError:key -> [{}]", key, e);
}
@Override
public void handleCachePutError(RuntimeException e, Cache cache, Object key, Object value) {
log.error("Redis occur handleCachePutError:key -> [{}];value -> [{}]", key, value, e);
}
@Override
public void handleCacheEvictError(RuntimeException e, Cache cache, Object key) {
log.error("Redis occur handleCacheEvictError:key -> [{}]", key, e);
}
@Override
public void handleCacheClearError(RuntimeException e, Cache cache) {
log.error("Redis occur handleCacheClearError:", e);
}
};
}
@Override
@Bean("myKeyGenerator")
public KeyGenerator keyGenerator() {
return new KeyGenerator() {
@Override
public Object generate(Object target, Method method, Object... params) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
sb.append(target.getClass().getName());
sb.append(method.getName());
for (Object obj : params) {
sb.append(obj.toString());
}
return sb.toString();
}
};
}
}使用案例:
User对象就id、name两个字段,大家随意~
java
package com.maple.redis.controller;
import com.maple.redis.bean.User;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheEvict;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Caching;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
/**
* @author 笑小枫
* @date 2025/1/7
*/
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/cache")
public class TestCacheController {
/**
* 获取简单缓存数据。
*
* <p>通过@Cacheable注解,该方法的结果会被缓存到名为"cache:simpleCache"的缓存中。
* 如果在缓存中找到相同请求的结果,将直接返回缓存的值,避免重复执行方法体中的逻辑。
*
* <p>方法内部,使用Thread.sleep(5000)模拟了一个耗时操作,
*/
@GetMapping("/simpleCache")
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "cache:simpleCache")
public String simpleCache() throws InterruptedException {
Thread.sleep(5000);
log.info("执行了simpleCache方法");
return "test";
}
/**
* 如果缓存中存在对应的ID,则直接从缓存中获取结果,避免重复执行耗时操作。
* 如果缓存中不存在,则执行方法体中的逻辑,将结果存入缓存并返回。
* 方法执行过程中,通过Thread.sleep模拟了一个耗时操作。
*/
@GetMapping("/{id}")
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "cache:cacheByKey", key = "#id")
public Integer cacheByKey(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) throws InterruptedException {
Thread.sleep(5000);
log.info("执行了cacheByKey方法" + id);
return id;
}
/**
* <p>该方法使用@Caching注解集成了多个缓存策略:</p>
* <ul>
* <li>
* 当方法返回值为null时(即缓存穿透情况),使用名为"cacheNullManager"的CacheManager进行缓存处理,
* 缓存名称为"cache2:cacheByKey",缓存键为传入的用户ID,并设置缓存过期时间为10分钟。
* 这通过@Cacheable注解的cacheManager属性指定缓存管理器,unless属性设置缓存条件(当结果为null时缓存)。
* </li>
* <li>
* 当方法返回值不为null时,使用默认的CacheManager进行缓存处理,
* 缓存名称和键的设置与上述相同,但此时缓存管理器为默认配置。
* 这通过另一个@Cacheable注解实现,其unless属性设置为当结果为null时不缓存。
* </li>
* </ul>
*
* <p>在方法执行过程中,通过Thread.sleep模拟了一个耗时操作。</p>
*/
@Caching(
cacheable = {
//result为null时,属于缓存穿透情况,使用cacheNullManager缓存管理器进行缓存,并且设置过期时间为10分钟。
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "cache2:cacheByKey", key = "#id", unless = "#result != null", cacheManager = "cacheNullManager"),
//result不为null时,使用默认缓存管理器进行缓存。
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "cache2:cacheByKey", key = "#id", unless = "#result == null")
}
)
@GetMapping("/cacheMore/{id}")
public User cacheMore(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) throws InterruptedException {
Thread.sleep(5000);
if (id > 100) {
return null;
} else {
return new User(id, "zhangsan");
}
}
@PostMapping("/cacheByUser")
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "cache2:cacheByUser", key = "#user.id")
public User cacheByUser(@RequestBody User user) throws InterruptedException {
Thread.sleep(5000);
log.info("执行了cacheByUser方法" + user.getId());
return user;
}
@PostMapping("/cacheByIdAndName")
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "cache2:cacheByUser", key = "#user.id")
public User cacheByIdAndName(@RequestBody User user) throws InterruptedException {
Thread.sleep(5000);
log.info("执行了cacheByUser方法" + user.getId());
return user;
}
/**
* 根据用户ID大于100的条件进行缓存处理。
*
* @param user 用户对象,包含用户ID等信息。
* @return 返回传入的用户对象。
* @throws InterruptedException 如果线程被中断,则抛出此异常。
*
* 通过@Cacheable注解实现了缓存功能,当请求的用户ID大于100时,会触发缓存机制。
* 缓存的名称设置为"cache2:cacheByUser",缓存的键为传入的用户对象的ID。
* 如果缓存中已存在对应的用户数据,则直接从缓存中获取并返回,避免重复执行耗时操作。
* 如果缓存中不存在,则执行方法体中的逻辑,将结果存入缓存并返回。
* 在方法执行过程中,通过Thread.sleep模拟了一个耗时操作。
*/
@PostMapping("/cacheByUserIdGt100")
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "cache2:cacheByUser", key = "#user.id", condition = "#user.id > 100")
public User cacheByUserIdGt100(@RequestBody User user) throws InterruptedException {
Thread.sleep(5000);
log.info("执行了cacheByUser方法" + user.getId());
return user;
}
/**
* 更新用户信息。
* <p>
* 使用@CachePut注解将更新后的用户信息存入缓存中。
* 缓存的名称设置为"cache2:cacheByUser",缓存的键为传入的User对象的ID。
* 如果缓存中已存在对应的用户数据,则更新缓存中的值;如果不存在,则创建新的缓存条目。
* 在方法执行过程中,通过Thread.sleep模拟了一个耗时操作。
*/
@PostMapping("/updateUser")
@CachePut(cacheNames = "cache2:cacheByUser", key = "#user.id")
public User updateUser(@RequestBody User user) throws InterruptedException {
Thread.sleep(5000);
log.info("执行了saveUser方法" + user.getId());
return user;
}
/**
* 删除指定ID的用户,并从缓存中移除对应的数据。
* <p>
* 使用@CacheEvict注解用于从缓存中移除指定ID的用户数据。
* 缓存的名称设置为"cache2:cacheByUser",缓存的键为传入的用户ID。
* 在执行删除操作前,方法通过Thread.sleep模拟了一个耗时操作。
*/
@DeleteMapping("/{id}")
@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "cache2:cacheByUser", key = "#id")
public void deleteUser(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) throws InterruptedException {
Thread.sleep(10000);
log.info("执行了deleteUser方法" + id);
}
}模拟了多种缓存使用的方式
updateUser使用@CachePut对数据进行缓存或更新。deleteUser使用@CacheEvict删除缓存。cacheMore根据条件选择不同的缓存管理器进行缓存数据。
简单附几张测试截图吧
第一次查询,没有缓存截图:
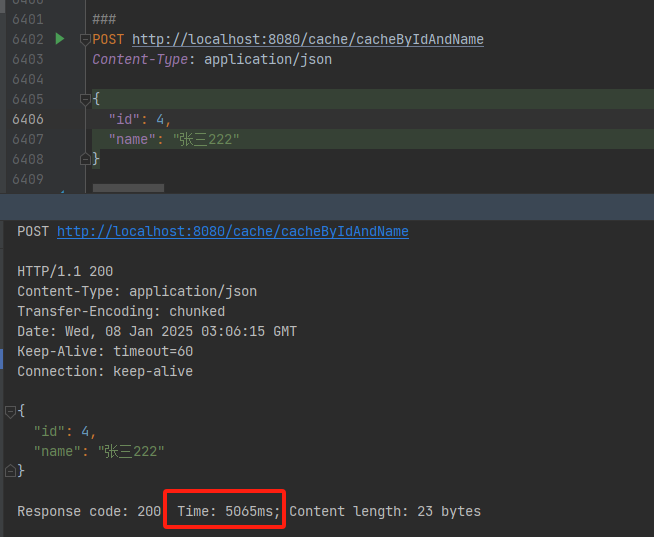
后续查询走缓存的截图
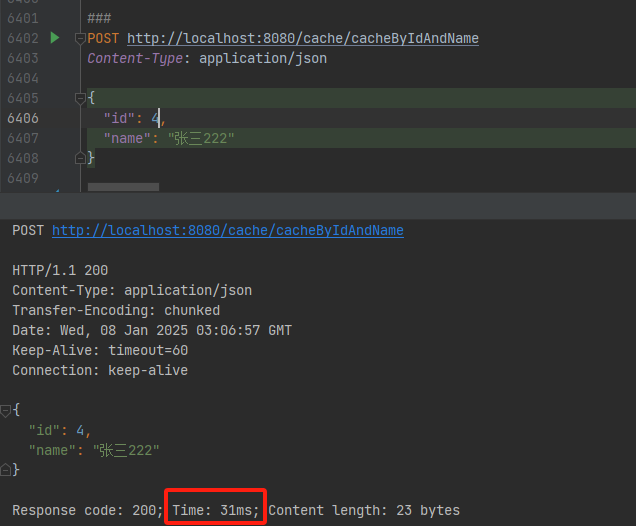
redis缓存数据格式:
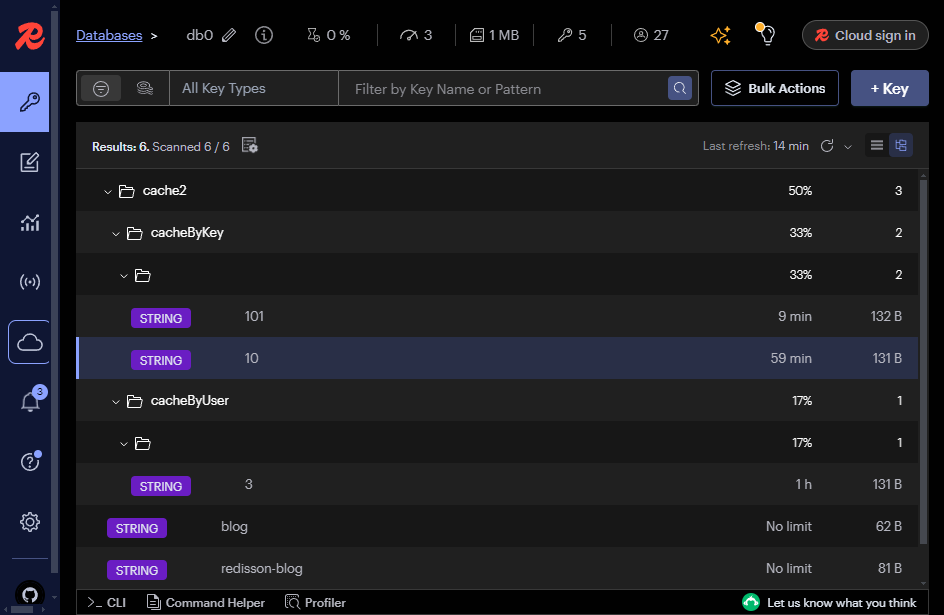
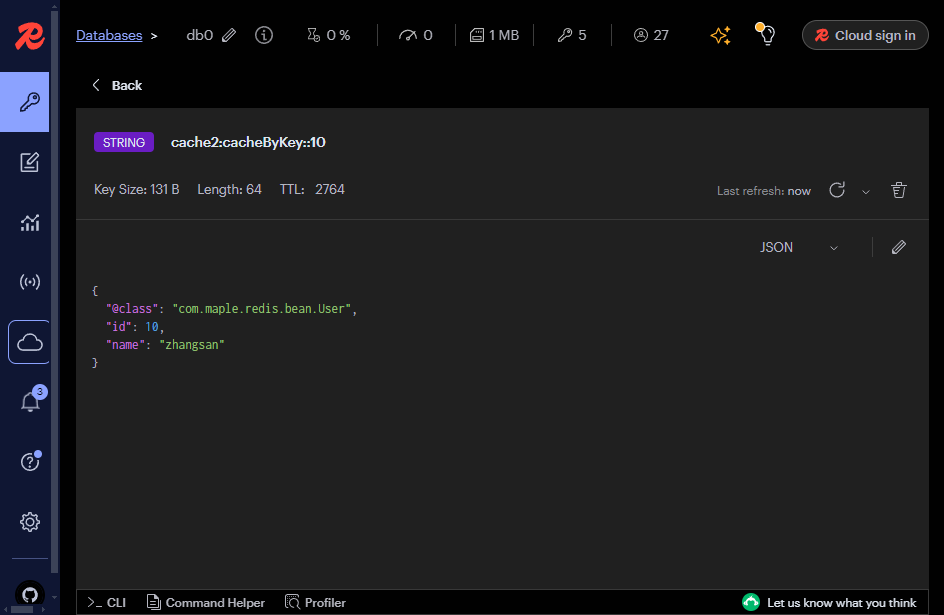
redis缓存数据详情:
4. SpEL在Spring Cache中的应用
4.1 SpEL概述
SpEL是Spring框架提供的一种功能强大的表达式语言,它能够在运行时查询和操作对象图。SpEL的语法简洁,支持方法调用、字符串模板、集合操作、逻辑运算等复杂功能,使得在Spring配置和代码中能够更轻松地处理复杂的逻辑和数据结构。
4.2 SpEL应用
-
动态生成缓存键
- 在Spring Cache中,缓存键(Key)用于在缓存中唯一标识数据。通过使用SpEL表达式,可以根据方法参数、返回值等动态生成缓存键。
- 例如,在@Cacheable注解中,可以使用key属性配合SpEL表达式来指定缓存键的生成规则。
-
条件缓存
- Spring Cache允许通过condition属性来指定缓存的条件。当条件满足时,才会执行缓存操作(如缓存数据或移除缓存)。
-
除非条件
- unless属性与condition属性类似,但它用于指定不执行缓存操作的条件。
- 当unless条件满足时,即使方法被调用,其结果也不会被缓存。
- unless属性同样支持SpEL表达式。
4.3 SpEL表达式在Spring Cache中的常用变量
-
#参数名:
- 表示方法参数。可以通过参数名来引用方法参数的值。
- 例如,#param1表示第一个参数的值。
-
#result:
- 表示方法的返回值。在@CachePut和@CacheEvict注解中,可以使用#result来引用方法的返回值。
-
#root:
- 表示缓存表达式根对象(CacheExpressionRootObject)。它提供了对缓存操作上下文的访问。
- 通过#root,可以获取到缓存的详细信息,如缓存名称、方法参数等。
注意:
condition属性在Spring Cache中用于在方法执行前判断是否执行缓存操作,并且不能引用方法的返回值;而unless属性则用于在方法执行后根据返回值或其他条件来决定是否缓存数据。
5. 工作原理
Spring Cache是基于AOP原理,对添加注解@Cacheable的类生成代理对象,在方法执行前查看是否有缓存对应的数据,如果有直接返回数据,如果没有调用源方法获取数据返回,并缓存起来,下边跟踪Spring Cache的切面类CacheAspectSupport.java中的private Object execute(final CacheOperationInvoker invoker, Method method, CacheOperationContexts contexts)方法。
java
@Nullable
private Object execute(final CacheOperationInvoker invoker, Method method, CacheOperationContexts contexts) {
if (contexts.isSynchronized()) {
CacheOperationContext context = (CacheOperationContext)contexts.get(CacheableOperation.class).iterator().next();
if (!this.isConditionPassing(context, CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT)) {
return this.invokeOperation(invoker);
}
Object key = this.generateKey(context, CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT);
Cache cache = (Cache)context.getCaches().iterator().next();
try {
return this.wrapCacheValue(method, this.handleSynchronizedGet(invoker, key, cache));
} catch (Cache.ValueRetrievalException var10) {
Cache.ValueRetrievalException ex = var10;
ReflectionUtils.rethrowRuntimeException(ex.getCause());
}
}
this.processCacheEvicts(contexts.get(CacheEvictOperation.class), true, CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT);
Cache.ValueWrapper cacheHit = this.findCachedItem(contexts.get(CacheableOperation.class));
List<CachePutRequest> cachePutRequests = new ArrayList();
if (cacheHit == null) {
this.collectPutRequests(contexts.get(CacheableOperation.class), CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT, cachePutRequests);
}
Object cacheValue;
Object returnValue;
if (cacheHit != null && !this.hasCachePut(contexts)) {//如果缓存有,则从缓存取
cacheValue = cacheHit.get();
returnValue = this.wrapCacheValue(method, cacheValue);
} else {//缓存没有,执行原始方法
returnValue = this.invokeOperation(invoker);
cacheValue = this.unwrapReturnValue(returnValue);//再存缓存
}
this.collectPutRequests(contexts.get(CachePutOperation.class), cacheValue, cachePutRequests);
Iterator var8 = cachePutRequests.iterator();
while(var8.hasNext()) {
CachePutRequest cachePutRequest = (CachePutRequest)var8.next();
cachePutRequest.apply(cacheValue);
}
this.processCacheEvicts(contexts.get(CacheEvictOperation.class), false, cacheValue);
return returnValue;
}6. 本文源码
使用Redis的过程中还会有很多问题,比如缓存数据一致性,缓存数据持久化,内存淘汰机制,缓存雪崩等等等,在面试的时候也经常会用到,博主整理了一份Redis常见的面试,感兴趣的朋友可以看下:
本文源码:https://github.com/hack-feng/maple-product/
其中maple-redis模块即为本文的Demo源码。需要的朋友可以看下。
感兴趣的朋友可以帮忙点个star⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐后续会有更多Java相关的集成Demo,让我来做你的百宝袋吧。
🐾我是笑小枫,全网皆可搜的【笑小枫】