基于Python实现的通用小规模搜索引擎
1.项目简介
1.1背景
《信息内容安全》网络信息内容获取技术课程项目设计
- 一个至少能支持10个以上网站的爬虫程序,且支持增量式数据采集;并至少采集10000个实际网页;
- 针对采集回来的网页内容, 能够实现网页文本的分类;
- 可进行重复或冗余网页的去重过滤;
- 对经去冗以后的内容建立倒排索引;
- 采用PageRank算法实现搜索结果的排序;
- 支持自然语言的模糊检索;
- 可实现搜索结果的可视化呈现。
- 可以在线记录每次检索的日志,井可对日志数据进统计分析和关联挖掘。
1.2运行环境
- 平台:全平台
- jdk 1.8.0
- ElasticSearch 7.4.0
- Python 3.6 及以上
-
- 安装依赖模块
-
-
- PageRank算法、AI文本分类与上传
pip install paddlepaddle numpy elasticsearch
-
-
-
- 数据的爬取与预处理
pip install requests bs4
-
1.3运行步骤
安装配置ElasticSearch并启动
- 下载 并解压Elasticsearch,详细步骤自行搜索
-
- 可以从 apt 和 yum 的软件仓库安装,也可以使用 Windows MSI 安装包安装
-
安装 IK 中文分词器,详细步骤自行搜索
-
创建索引
PUT http://127.0.0.1/page
{
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": "5",
"number_of_replicas": "0"
},
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"title": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
},
"weight": {
"type": "double"
},
"content" : {
"type" : "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
},
"content_type": {
"type": "text"
},
"url": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
},
"update_date": {
"type": "date",
"format": "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss||yyyy-MM-dd||epoch_millis"
}
}
}
} -
启动 ElasticSearch ,在 bash 中执行
bin/elasticsearch或者在 Windows 的 cmd、powershell 执行bin\elasticsearch.bat
启动Web服务
> cd WebApp
> java -jar *.jar
数据的爬取与预处理
> cd DataCrawler
> python crawler.py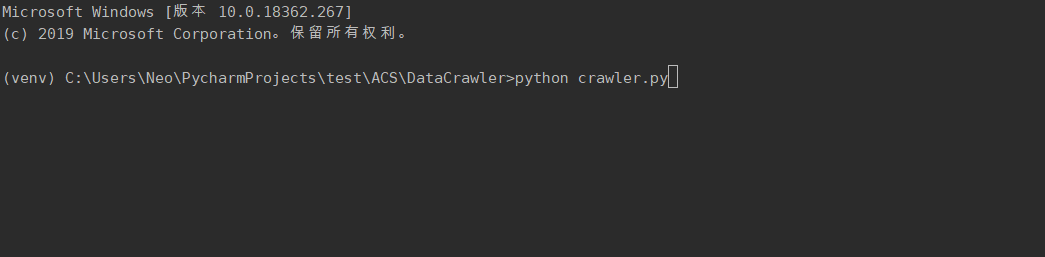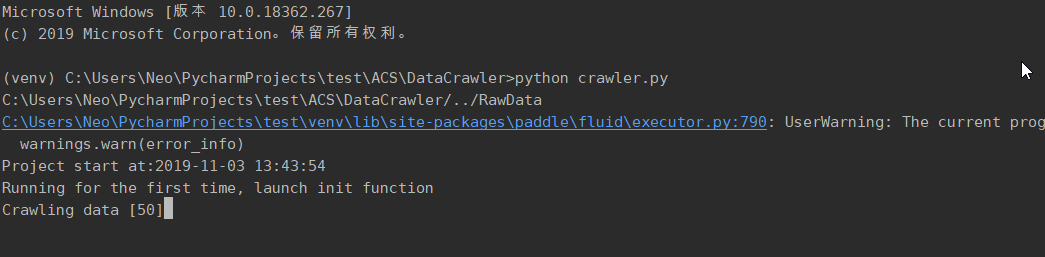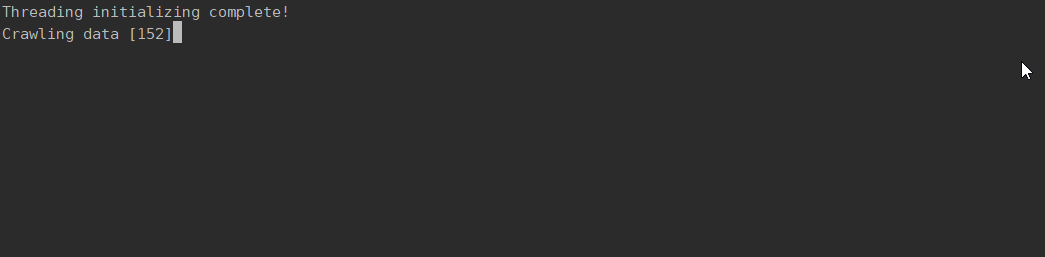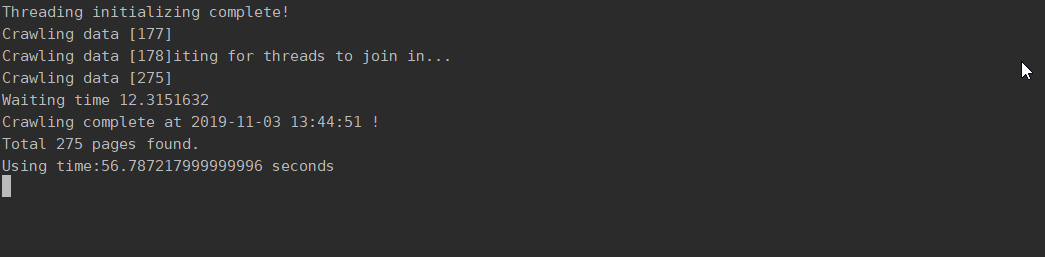
计算PageRank值
> cd DataProcess
> python PageRank.py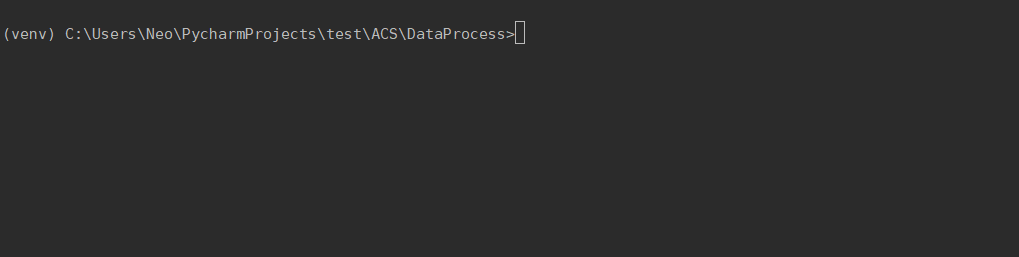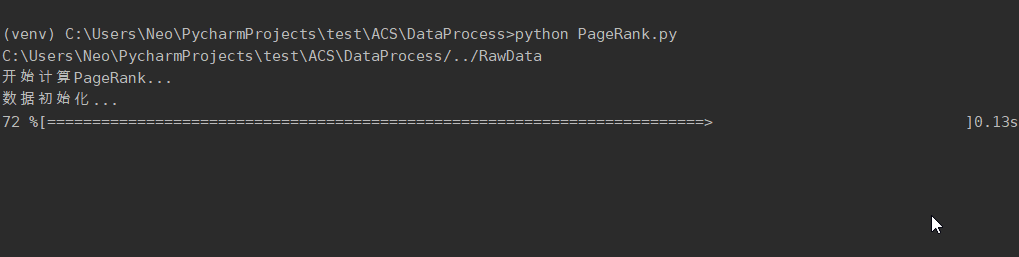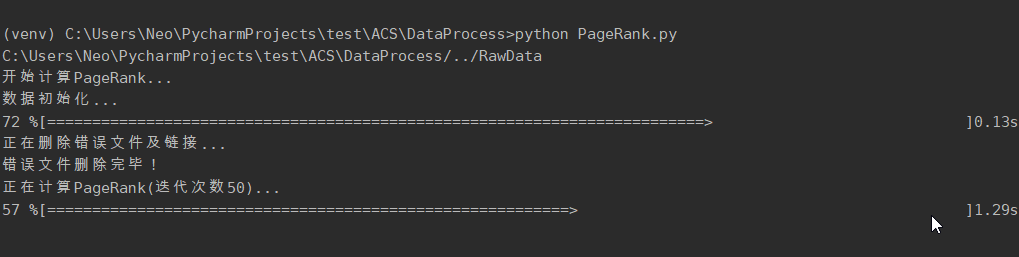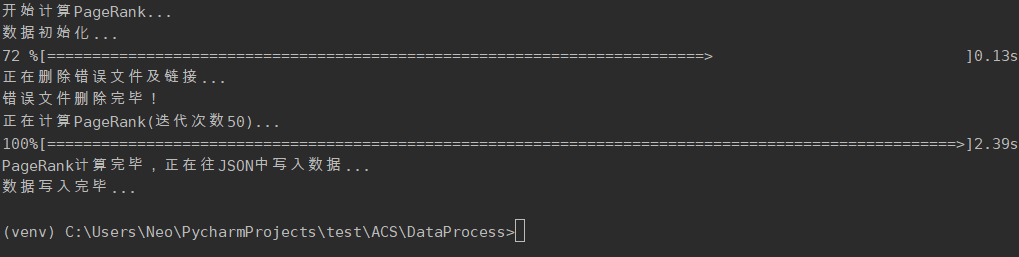
利用AI进行文本分类并上传至ES
> cd DataProcess/Text_Classification
> python Classify.py
2.需求分析
2.1数据描述
2.1.1 静态数据
|-----------------|------|
| 变量名 | 描述 |
| thread_accoun | 线程个数 |
| initial_url | 种子页面 |
2.1.2 动态数据
|---------------------|--------|----|
| 变量名 | 描述 | 类型 |
| restricted_domain | 限定域名 | 列表 |
| banned_domain | 禁止域名 | 列表 |
| thread_account | 线程个数 | 整型 |
| total_pages | 限定页面个数 | 整型 |
2.1.3索引数据字典
页面(page)信息索引:
|----------------|-----------|---------|----------|-----------------------------------------------------------|
| 数据项名称 | 含义 | 别名 | 类型 | 备注 |
| title | 网站标题 | | text | 使用ik_max_word 分词 |
| weight | PageRank值 | pr值,PR值 | double | |
| content | 网站中的内容 | | text | 使用ik_max_word 分词 |
| content_type | 网站中的内容分类 | | text | 文化, 娱乐, 体育, 财经, 房产, 汽车, 教育, 科技, 国际, 证券 |
| url | 网站的链接 | | text | 使用ik_max_word 分词 |
| update_date | 数据更新的时间 | | date | yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss ||yyyy-MM-dd ||epoch_millis |
2.2. 数据采集
种子 url 数据从 init_url 列表中选取,并按照顺序,依次以各个 url 为起点进行递归的数据采集
爬取数据的url需要限制在 restricted_url 列表里面
2.3功能需求
2.3.1 数据爬取与预处理功能
利用Python爬虫,执行以下步骤:
- 开始
- 选取一个链接作为起点
- 如果爬取的网页总数达到要求,则结束,否则执行第 4 步
- 爬取指定链接的相关信息,并获取当前网站中的所有链接
- 对 4 中获取的网站中的所有链接中的每一条数据,执行过程3
爬取网站如下信息,详细描述见3.4. 索引数据字典
- title
- content
- content_type
- update_date
- url
- link(当前网站中包含的所有链接,用于计算pr值)
2.3.2. 计算 PageRank 功能
根据link计算爬取下来的每个网站的PageRank值,迭代次数为50次。解决pr值呈周期性变化的问题。将pr值作为网站重要程度的指标,并补充到网站信息中
2.3.3. AI 文本分类并提交到 ES 功能
利用深度学习,分析每个页面的content的类别。将类别补充到网站信息中,同时删除网站信息中不再使用的link项,形成最终数据(参考3.4. 索引数据字典),并上传至ES,供用户交互功能调用。
2.3.4. 用户交互功能
设计WebApp,用户通过浏览器访问页面。用户提交搜索信息后,判断合法性,不合法则返回ERROR界面提示用户。如果合法,则后端代码从本地 ES 中查询数据,处理后将结果分条显示到前端。同时通过限制单个ip每分钟的访问次数来简单防御用户恶意搜索。
2.4. 性能需求
2.4.1. 数据精确度
对数据精确度要求不高,主要数据为:
|---------|-------------|
| 项目 | 限制 |
| 爬取的数据总量 | 每小时查询一下数据总量 |
| 查询结果数量 | 匹配的所有结果数 |
| 数据更新日期 | 精确到分钟即可 |
2.4.2. 时间特性
|-------------------------------|---------|
| 项目 | 限制 |
| 每爬取 1 万个网页耗时 | 30 分钟以内 |
| 计算 1 万个网页的pr值耗时 | 10 分钟以内 |
| 对 1 万个网页内容进行AI 进行文本分类并上传至ES耗时 | 10 分钟以内 |
| Web 首页打开耗时 | 5 秒以内 |
| 查询结果页面打开耗时 | 5 秒以内 |
2.5. 运行需求
2.5.1. 用户界面
用户通过浏览器访问,有两个页面,一个是主页,只有简单的输入框提供用户搜索;另一个是一般界面,提供高级搜索功能,并显示搜索结果。
2.5.2. 主页
|----|--------|----|
| 控件 | 作用 | 布局 |
| 图标 | 显示Logo | 居中 |
|输入框|接收用户输入的关键字|Logo图标下偏左
|按钮|提交用户输入的关键字,并返回搜索结果|输入框右|
2.5.3. 搜索结果界面
该界面分为三个部分,导航条、搜索结果、信息展示。这三个部分布局如下
|------|--------|--------|-------|
| 部分 | 位置 | height | width |
| 导航条 | 顶部 | 50px | 100% |
| 搜索结果 | 导航条左下部 | auto | 70% |
| 信息展示 | 导航条右下部 | auto | 30% |
导航条部分
以下控件从左向右依次(顺序可以任意)在导航条中排列
|-------|-----------------------------------|
| 控件 | 作用 |
| 输入框 | 接收用户输入的关键字 |
| 输入框 | 可以输入域名,将搜索结果限制在该域名内 |
| 数字输入框 | 查询结果分页显示,该框指示跳转到指定的搜索结果页 |
| 选择框 | 允许用户选择匹配方式:标题和内容(默认)、仅标题、仅内容 |
| 选择框 | 选择搜索结果的排序方式:倒排索引(默认)、 PageRank 排序 |
| 按钮 | 提交用户输入的所有数据,并返回搜索结果 |
搜索结果部分
将搜索结果以list的形式展示出来,每个list item显示匹配的网站的如下数据
- 标题
- 内容
- url
- 类别
- PageRank值
- 更新时间
在list结尾,显示分页组件,使用户可以点击跳转,样式如下:
|----|---|---|---|---|---|---|----|
| < | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | > |
信息展示部分
展示一些必要信息,如:
- 本次查询耗时
- 查询结果数
- 数据库中的数据总数
- 等等
2.5.4 软件接口
|-------------------------------------|----------------------------|---------------|---------------------------|
| 接口名 | 描述 | 所在模块 | 调用方式 |
| init_first_time() | 初次启动调用此接口 | crawler.py | 内部调用 |
| get_result(url) | 得到目标 url 的页面 | crawler.py | 内部调用 |
| spider_thread() | 爬虫线程 | crawler.py | 内部调用 |
| main() | 主任务执行线程 | crawler.py | crawler.main() |
| init() | 去掉所有未在 url 中出现的 link 及错误文件 | PageRank.py | 内部调用 |
| Rank(Value, start) | 计算PageRank | PageRank.py | 内部调用 |
| run() | 程序运行方法 | PageRank.py | PageRank.run() |
| get_data(sentence) | 获取已爬取数据 | Classify.py | 内部调用 |
| batch_reader(json_list,json_path) | 利用AI进行文本分类 | Classify.py | Classify.batch_reader() |
2.5.5. 故障处理
各个功能模块如果出问题,会出现以下情况:
|---------------|------------|------------------|
| 模块 | 出故障后 | 简单排查 |
| 爬虫 | 数据不再更新 | 检查网络,检查内存资源是否不足 |
| PageRank计算 | 数据不再更新 | 检查内存资源和CPU资源是否不足 |
| AI 文本分类 | 数据不再更新 | 检查内存资源和CPU资源是否不足 |
| ElasticSearch | 前端无法获取查询结果 | 问题比较复杂 |
| WebApp | 无法访问网站 | 问题比较复杂 |
其中,后两个模块出问题会造成严重问题,如果重启不能解决问题的话,采用如下措施
|---------------|---------------------------------------------------------|-------------------------------|
| 模块 | 故障排除 | 终极方法 |
| ElasticSearch | ①java环境是否正确 ②是否开启了9200端口 ③9200端口是否被占用 ④插件是否出错 ⑤机器资源是否不足 | 在其他机器上部署,并修改WebApp使其到该机器上获取服务 |
| WebApp | ①端口是否被占用 ②java环境是否正确 ③ElasticSearch是否正常运行 ④机器资源是否不足 | 在其他机器上部署,并修改域名解析,将域名解析到新机器上 |
2.6. 其他需求
2.6.1. 可维护性
- 网络爬虫设置了黑名单和白名单,可以限制爬取的范围。
- 各个功能分离开,协同工作。同时,只要不修改数据格式,各个模块的修改不会影响其他模块
2.6.2. 可移植性
- WebApp 使用 Spring boot 框架开发,打包后只有一个jar包,可以在任何有java环境的机器上部署
- 其他功能都用python实现,可以部署在任何有python环境的机器上
- ElasticSearch 支持分布式部署,可以部署在任意平台
2.6.3. 数据完整性
- ElasticSearch 支持分布式,会自动将数据备份在不同节点。如果某个节点出了故障,不会破坏数据,也不会影响程序的查询结果
3.代码展示
import os
import sys
import json
import numpy as np
import time
import codecs
dir_path = os.path.split(os.path.realpath(sys.argv[0]))[0] + '/../RawData'
print(dir_path)
Vexname = list(os.listdir(dir_path))
Vexnum = len(Vexname)
epoch = 50
# 初始化,去掉所有未在url中出现的link以及错误文件
def init():
global Vexnum
falsefiles={}
idx=0
start = time.perf_counter()
for file in Vexname:
if idx % 100 == 0:
a = '=' * int(idx / Vexnum * 100)
b = ' ' * (100 - int(idx / Vexnum * 100))
c = int(idx / Vexnum * 100)
dur = time.perf_counter() - start
sys.stdout.write("\r{:^3.0f}%[{}=>{}]{:.2f}s".format(c, a, b, dur))
sys.stdout.flush()
with codecs.open(os.path.join(dir_path, file), 'r', encoding='utf-8') as load_f:
try:
text = json.load(load_f)
except:
falsefiles[file]=Vexname.index(file)-len(falsefiles)
continue
try:
links = []
for link in text['link']:
if link+'.json' in Vexname:
links.append(link)
text['link'] = links.copy()
except:
pass
finally:
if 'link' in text:
text['link'].clear()
else:
text['link'] = []
with codecs.open(os.path.join(dir_path, file), 'w', encoding='utf-8') as dump_f:
json.dump(text, dump_f, ensure_ascii=False,indent=4)
idx += 1
print('正在删除错误文件及链接...')
Vexnum -= len(falsefiles)
checknum=0
checkfalse=0
for file in list(falsefiles.keys()):
os.remove(os.path.join(dir_path,file))
Vexname.remove(file)
for i in range(checknum,falsefiles[file]):
with codecs.open(os.path.join(dir_path, Vexname[i]), 'r', encoding='utf-8') as load_f:
text = json.load(load_f)
try:
for falsefile in list(falsefiles.keys())[checkfalse:]:
if falsefile in text['link']:
text['link'].remove(falsefile)
except:
text['link'].clear()
with codecs.open(os.path.join(dir_path, Vexname[i]), 'w', encoding='utf-8') as dump_f:
json.dump(text, dump_f, ensure_ascii=False,indent=4)
checknum += falsefiles[file]
checkfalse += 1
# 计算PageRank
def Rank(Value, start):
NewValue=np.zeros(Vexnum,dtype=np.double)
for iter in range(1,epoch):
a = '=' * int(iter / epoch * 100)
b = ' ' * (100 - int(iter / epoch * 100))
c = int(iter / epoch * 100)
dur = time.perf_counter() - start
sys.stdout.write("\r{:^3.0f}%[{}=>{}]{:.2f}s".format(c, a, b, dur))
sys.stdout.flush()
for i in range(Vexnum):
with open(os.path.join(dir_path, Vexname[i]), 'r', encoding='utf-8') as load_f:
text = json.load(load_f)
count = len(text['link'])
if count == 0:
NewValue[i] = Value[i]
continue
for link in text['link']:
link += '.json'
NewValue[Vexname.index(link)] += Value[i] / count
for i in range(Vexnum):
NewValue[i] = NewValue[i] / (iter + 1) + Value[i] * (iter / (iter + 1))
Value=NewValue.copy()
return Value
def run():
print('开始计算PageRank...')
print('数据初始化...')
init()
Value = np.ones(len(Vexname),dtype=np.double)*(1000.0/Vexnum)
print('错误文件删除完毕!')
print('正在计算PageRank(迭代次数{})...'.format(epoch))
start = time.perf_counter()
Value = Rank(Value, start)
a = '=' * 100
b = ' ' * 0
c = 100
dur = time.perf_counter() - start
sys.stdout.write("\r{:^3.0f}%[{}=>{}]{:.2f}s".format(c, a, b, dur))
sys.stdout.flush()
print('\nPageRank计算完毕,正在往JSON中写入数据...')
max = {}
for file in Vexname: # 将PageRank写入JSON
with open(os.path.join(dir_path, file), 'r', encoding='utf-8') as load_f:
text = json.load(load_f)
with open(os.path.join(dir_path, file), 'w', encoding='utf-8') as dump_f:
text['weight'] = Value[Vexname.index(file)]
max[file] = text['weight']
json.dump(text, dump_f, ensure_ascii=False,indent=4)
print('数据写入完毕...')
if __name__ == '__main__':
run()
# 导入必要的包
import json
import os
import sys
import time
import math
import gc
import elasticsearch
import numpy as np
import paddle.fluid as fluid
dir_path = os.path.dirname(os.path.realpath(__file__))
# 用训练好的模型进行预测并输出预测结果
# 创建执行器
place = fluid.CPUPlace()
exe = fluid.Executor(place)
exe.run(fluid.default_startup_program())
save_path = os.path.join(dir_path, 'infer_model/')
# 从模型中获取预测程序、输入数据名称列表、分类器
[infer_program, feeded_var_names, target_var] = fluid.io.load_inference_model(dirname=save_path, executor=exe)
# 主机
host = "py7hon.com:9200"
# 建立 elasticsearch 连接
try:
es = elasticsearch.Elasticsearch(hosts=host)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
exit()
# 获取数据
def get_data(sentence):
# 读取数据字典
with open(os.path.join(dir_path, 'dict_txt.txt'), 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f_data:
dict_txt = eval(f_data.readlines()[0])
dict_txt = dict(dict_txt)
# 把字符串数据转换成列表数据
keys = dict_txt.keys()
data = []
for s in sentence:
# 判断是否存在未知字符
if not s in keys:
s = '<unk>'
data.append((np.int64)(dict_txt[s]))
return data
def batch_reader(Json_list,json_path):
datas = []
gc.collect()
json_files = []
falsefiles = []
datas.clear()
falsefiles.clear()
json_files.clear()
start = time.perf_counter()
i=0
scale = 100
for file in Json_list:
if i % 100 == 0:
a = '=' * int(i / len(Json_list) * 100)
b = ' ' * (scale - int(i / len(Json_list) * 100))
c = int(i / len(Json_list) * 100)
dur = time.perf_counter() - start
sys.stdout.write("\r{:^3.0f}%[{}=>{}]{:.2f}s".format(c, a, b, dur))
sys.stdout.flush()
i+=1
with open(os.path.join(json_path, file), "r", encoding='utf-8') as f:
try:
text = json.load(f)
except:
falsefiles.append(file)
continue
json_files.append(os.path.join(json_path, file))
json_text = text['content']
data = get_data(json_text)
datas.append(data)
for file in falsefiles:
os.remove(os.path.join(dir_path, file))
file_count = len(Json_list) - len(falsefiles)
a = '=' * 100
b = ' ' * 0
c = 100
dur = time.perf_counter() - start
sys.stdout.write("\r{:^3.0f}%[{}=>{}]{:.2f}s".format(c, a, b, dur))
sys.stdout.flush()
print('\n文本数据获取完毕,共计{0}条文本数据,有效数据{2}条,无效数据{1}条(已删除)!'.format(len(Json_list),len(falsefiles),file_count))
print('AI正在加载分类模型...')
# 获取每句话的单词数量
base_shape = [[len(c) for c in datas]]
# 生成预测数据
tensor_words = fluid.create_lod_tensor(datas, base_shape, place)
# 执行预测
result = exe.run(program=infer_program,
feed={feeded_var_names[0]: tensor_words},
fetch_list=target_var)
print('模型加载完毕!')
# 分类名称
names = ['文化', '娱乐', '体育', '财经', '房产', '汽车', '教育', '科技', '国际', '证券']
count = np.zeros(10)
print('AI正在对文本数据进行分类并上传至ES:')
# 获取结果概率最大的label
start = time.perf_counter()
for i in range(file_count):
if i % 100 == 0:
a = '=' * int(i / file_count * 100)
b = ' ' * (scale - int(i / file_count * 100))
c = int(i / file_count * 100)
dur = time.perf_counter() - start
sys.stdout.write("\r{:^3.0f}%[{}=>{}]{:.2f}s".format(c, a, b, dur))
sys.stdout.flush()
lab = np.argsort(result)[0][i][-1]
# print('预测结果标签为:%d, 名称为:%s, 概率为:%f' % (lab, names[lab], result[0][i][lab]))
count[lab] += 1
with open(json_files[i], 'r', encoding='utf-8') as load_f:
try:
text = json.load(load_f)
except:
continue
text['content_type'] = names[lab]
id = json_files[i].split('\\')[-1].split('.')[0]
#try:
del text['link']
response = es.index(index='page', doc_type='_doc', id=id, body=text)
#except Exception:
# print("\n" + "数据 " + id + " 插入失败,错误信息:" + response)
# with open(os.path.join(json_path,json_files[i].split('\\')[-1]),'w') as dump_f:
# json.dump(text,dump_f)
a = '=' * 100
b = ' ' * 0
c = 100
dur = time.perf_counter() - start
sys.stdout.write("\r{:^3.0f}%[{}=>{}]{:.2f}s".format(c, a, b, dur))
sys.stdout.flush()
print("\n" + "%d条文本数据分类结束!已全部上传至ES" % (file_count))
def run():
# 获取图片数据
print('AI正在获取文本数据...')
json_path = os.path.realpath(__file__) + '/../../../RawData'
Json_list = os.listdir(json_path)
batch_size=500
if len(Json_list)>batch_size:
Json_batch=0
print('当前文本数量为{0}条,正在分批处理...'.format(len(Json_list)))
for batch_id in range(math.ceil(len(Json_list)/batch_size)):
a=(batch_size if batch_size<(len(Json_list)-Json_batch) else len(Json_list)-Json_batch)
print('正在处理第{0}批,数量为{1}...'.format(batch_id+1,a))
batch_reader(Json_list[Json_batch:Json_batch+a],json_path)
Json_batch += a
else:
batch_reader(Json_list,json_path)
if __name__ == '__main__':
run()4.系统展示