目录
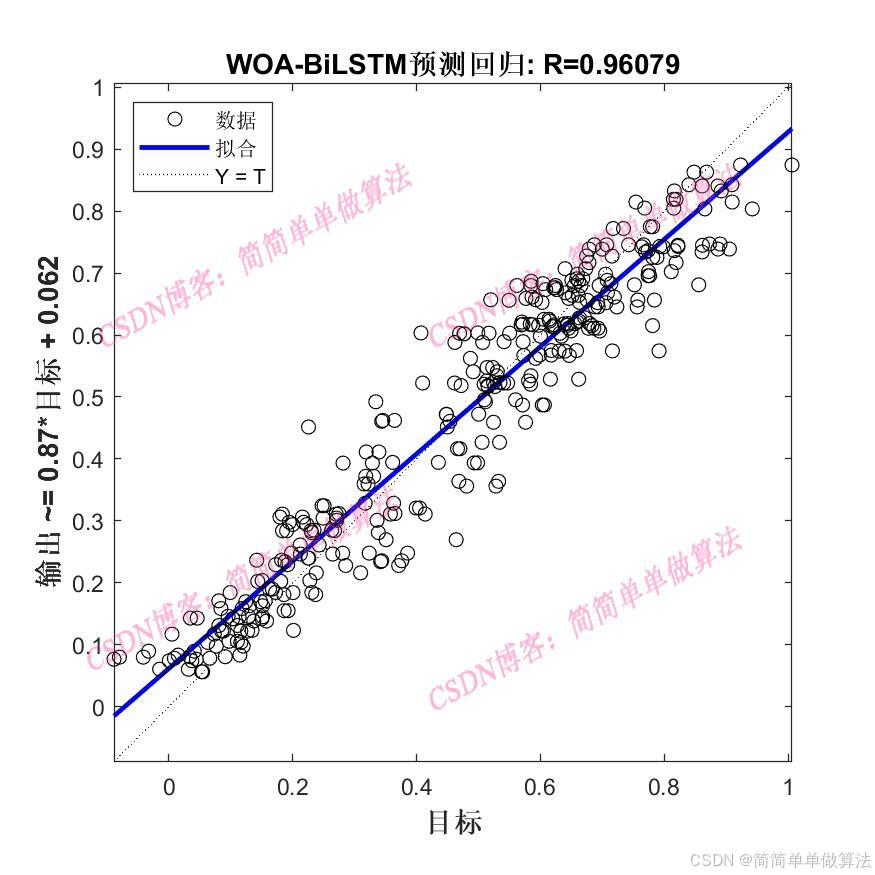
1.算法运行效果图预览
(完整程序运行后无水印)
2.算法运行软件版本
matlab2022a/matlab2024b
3.部分核心程序
(完整版代码包含详细中文注释和操作步骤视频)
.........................................................................
X = woa_idx;
%bilstm
layers=bilstm_layer(bw_in,round(X(1)),round(X(2)),bw_out,X(3),X(4),X(5));
%参数设定
opts = trainingOptions('adam', ...
'MaxEpochs',10, ...
'GradientThreshold',1,...
'ExecutionEnvironment','cpu',...
'InitialLearnRate',X(6), ...
'LearnRateSchedule','piecewise', ...
'LearnRateDropPeriod',2, ...
'LearnRateDropFactor',0.5, ...
'Shuffle','once',...
'SequenceLength',1,...
'MiniBatchSize',64,...
'Verbose',1);
%网络训练
[net1,INFO] = trainNetwork(Xtrain,Ytrain,layers,opts);
Rmsev = INFO.TrainingRMSE;
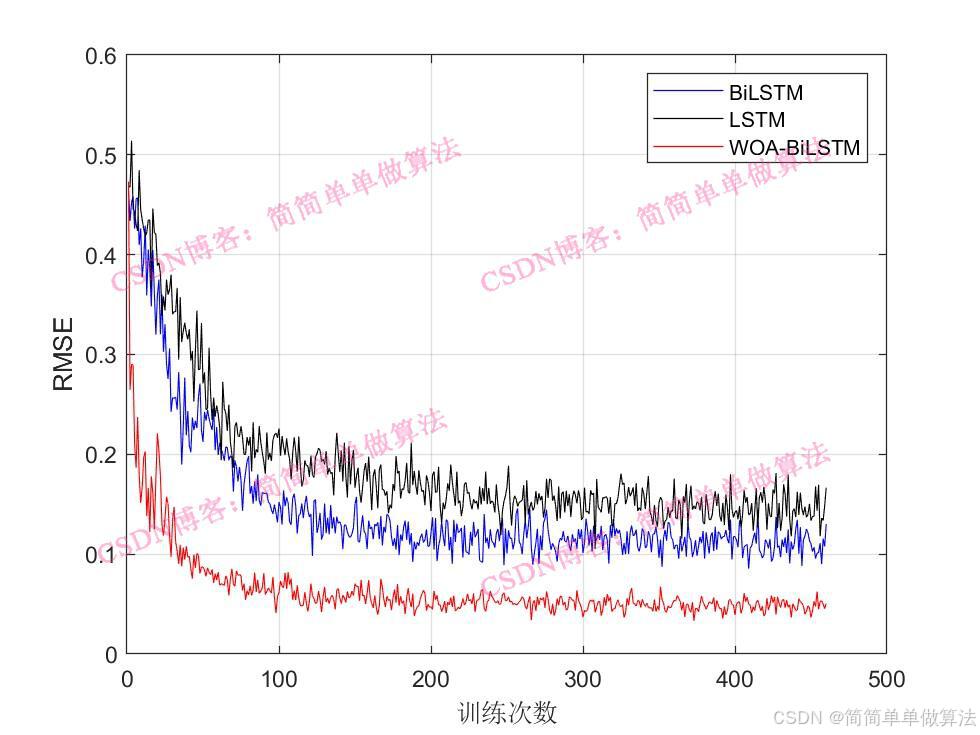
figure;
plot(Rmsev)
xlabel('训练次数');
ylabel('RMSE');
%预测
for i = 1:length(Xtest)
Ypred(i) = net1.predict(Xtest(i));
end
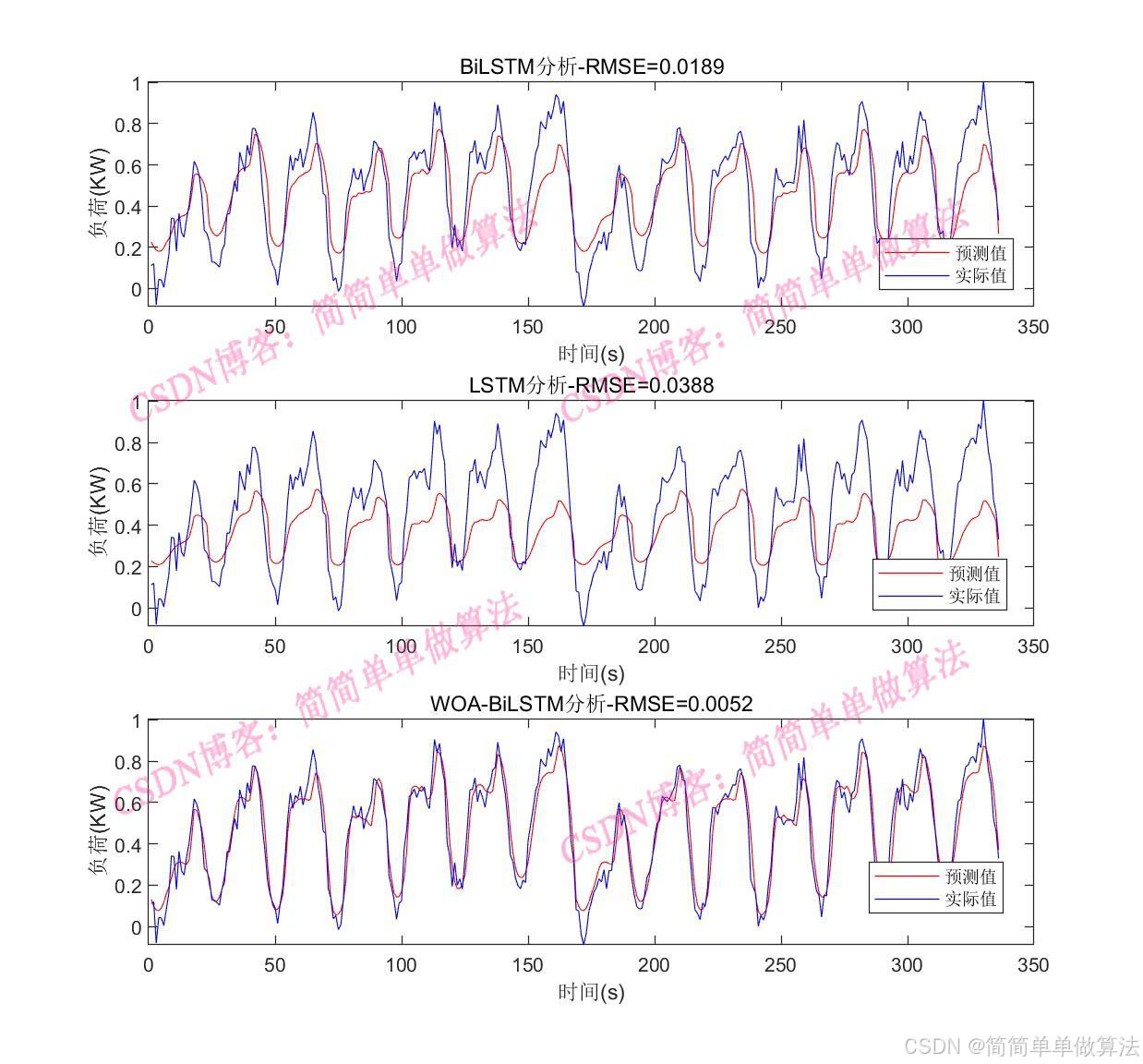
figure
plot(Ypred,'r-')
hold on
plot(Ytest','b-')
legend('预测值','实际值')
xlabel('时间(s)')
ylabel('负荷(KW)')
rmse = mean((Ypred(:)-Ytest(:)).^2);% 计算均方根误差
title(sprintf('WOA-biLSTM分析-RMSE=%.3f', rmse));
save R3.mat Ypred Ytest rmse Rmsev
2074.算法理论概述
LSTM是一种特殊的循环神经网络(RNN),旨在解决传统 RNN 在处理长序列时的梯度消失和梯度爆炸问题,从而更好地捕捉长序列中的长期依赖关系。其核心结构包含输入门、遗忘门、输出门以及记忆单元。
BiLSTM 是在 LSTM 基础上发展而来,它通过同时向前和向后处理序列,能够更好地捕捉序列中的前后文信息,从而在序列预测任务中表现更优。BiLSTM 由一个前向 LSTM 和一个后向 LSTM 组成。


这种结构使得 BiLSTM 能够同时利用序列的前文和后文信息,在处理需要全局信息的序列预测任务时具有明显优势。
在本课题中,将woa应用于BiLSTM主要是为了优化BiLSTM的超参数,如学习率、隐藏层神经元数量等,以提升其预测性能。大致的步骤如下:
1.随机初始化一群鲸鱼的位置,每个鲸鱼的位置对应一组 BiLSTM 的参数(如权重和偏置)。
2.使用训练集对 BiLSTM 进行训练,并根据验证集的预测结果定义适应度函数。常用的适应度函数是均方误差(MSE):


使用优化后的 BiLSTM 参数在训练集上进行最终训练。使用训练好的模型对测试集进行预测,并将预测结果进行反归一化处理,得到最终的预测值。WOA 具有较强的全局搜索能力,能够在参数空间中寻找最优的 BiLSTM 参数,避免陷入局部最优解。
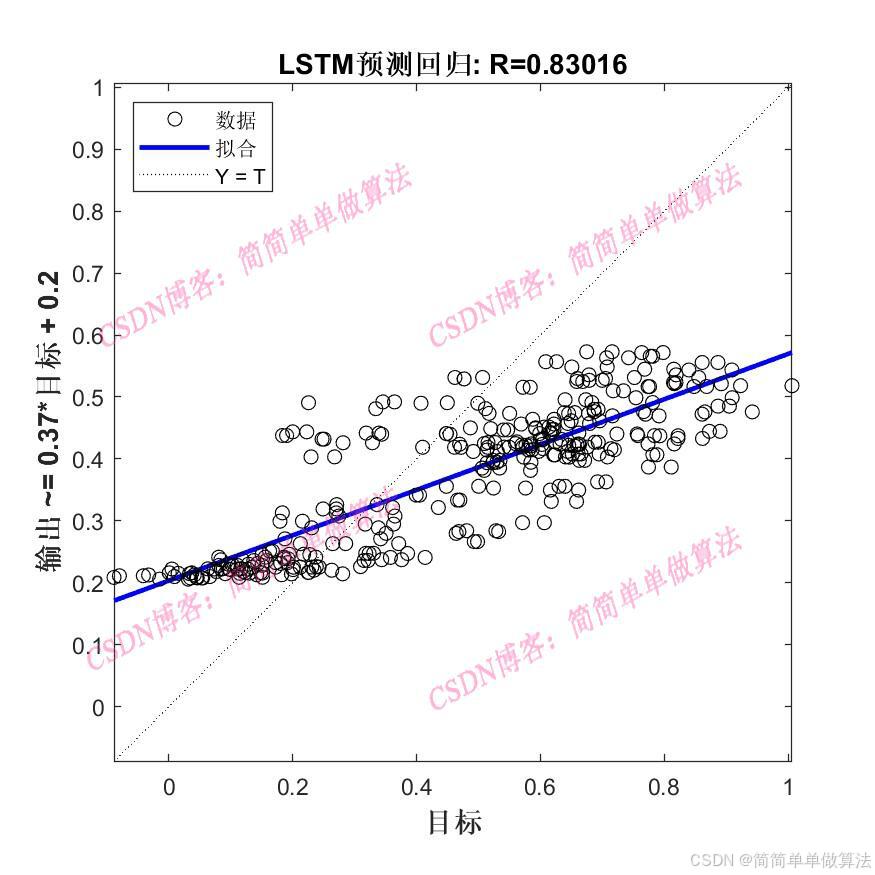
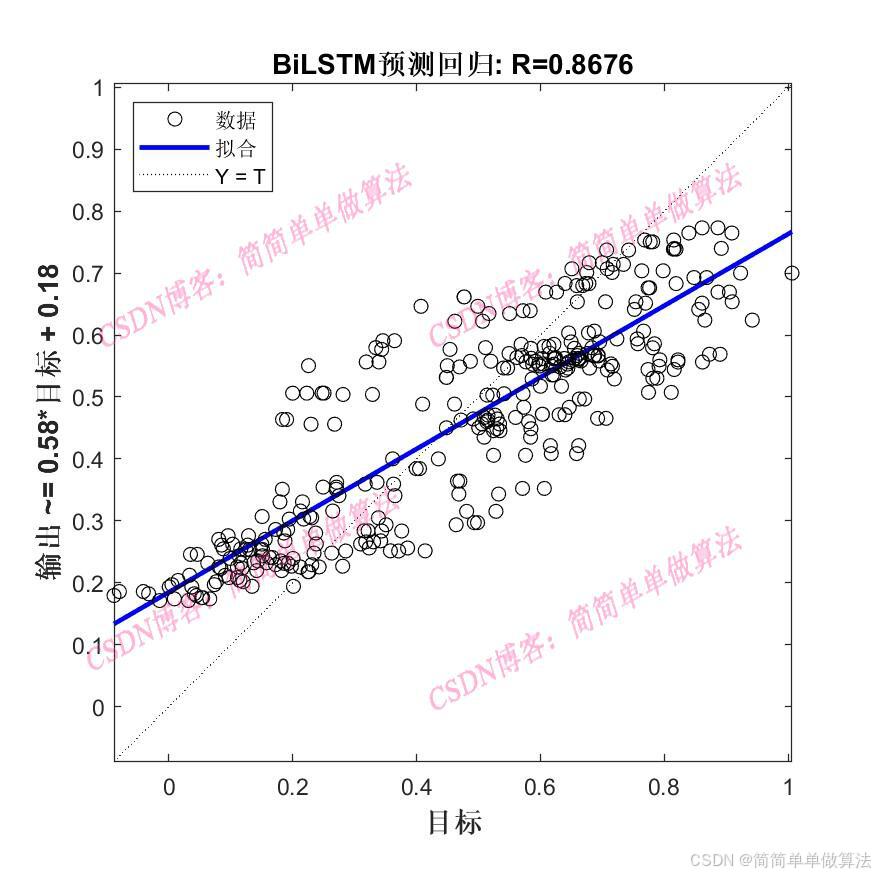
在大多数序列预测任务中,BiLSTM的预测精度优于LSTM。因为它能更全面地捕捉序列中的长期依赖关系,减少信息丢失,从而提高预测准确性。
5.算法完整程序工程
OOOOO
OOO
O