【JavaEE】阻塞队列
- 一、什么是阻塞队列?
- 二、阻塞队列的特点
- 三、阻塞队列的常用方法
-
-
- [3.1 抛出异常](#3.1 抛出异常)
- [3.2 有返回结果,不会抛出异常](#3.2 有返回结果,不会抛出异常)
- [3.3 阻塞](#3.3 阻塞)
-
- 四、常见的阻塞队列
-
-
- [4.1 ArrayBlockingQueue](#4.1 ArrayBlockingQueue)
- [4.2 LinkedBlockingQueue](#4.2 LinkedBlockingQueue)
- [4.3 SynchronousQueue](#4.3 SynchronousQueue)
- [4.4 PriorityBlockingQueue](#4.4 PriorityBlockingQueue)
- [4.5 DelayQueue](#4.5 DelayQueue)
-
- 五、自己实现阻塞队列
-
-
- [5.1 成员变量](#5.1 成员变量)
- [5.2 构造方法](#5.2 构造方法)
- [5.3 put()方法](#5.3 put()方法)
- [5.4 take()方法](#5.4 take()方法)
- [5.5 全部代码](#5.5 全部代码)
-
- 六、阻塞队列的优点
博客结尾有此篇博客的全部的代码!!!
一、什么是阻塞队列?
前面我们学习过队列(Queue)这种数据结构---"先进先出"。
今天学的阻塞队列(BlockingQueue),它继承于Queue接口,是队列的一种。
java
public interface BlockingQueue<E> extends Queue<E>Queue和BlockingQueue都是在Java5中加入的,BlockingQueue是线程安全 的的队列,它在队列为空时,获取元素的操作将会被阻塞;在队列满时,存储元素的操作也会被阻塞。
举例说明一下:
盖房子!之前盖房子是请大工和小工,雇人盖房子!
大工:负责刷墙(将打好的灰刷在墙上)。
小工:负责打灰(将石灰和沙子搅拌在一起)。
灰盆:负责放灰的(容量大小有限)。
小工负责将打好的灰放到灰盆中,大工负责将灰盆中的灰刷到墙上。

假如小工打灰很快,他一次性打了很多灰,但是灰盆的容量是有限的,他就要等大工将灰盆中的灰用完,他才能往灰盆中再次加灰;假设大工是个老手,他粉刷很快,一下就将灰盆中的灰用完了,但是小工的下一盆灰没有及时供上,此时大工是不是就需要等待小工打好灰之后,他才能继续工作!这两种情况都是发生了阻塞等待!而灰盆则相当于阻塞队列!
这个例子就应该能帮助大家对阻塞对列有了一定的理解了吧!
二、阻塞队列的特点
- 线程安全:内部通过锁机制保证线程安全。
- 阻塞操作:当队列为空时,尝试从队列中获取元素的操作会被阻塞;当队列满时,尝试向队列中添加元素的操作会被阻塞。
- 容量限制:阻塞队列可以有容量限制,也可以是无界队列。
这里的无界队列并不是意味可以放无限个元素,无界也是有上限的!例如LinkedBlcokingQueue的上限是Integer.MAX_VALUE(-2,147,483,648到 2,147,483,647)。而有界队列就算队列中元素已满,也是不会扩容的。
三、阻塞队列的常用方法
- 抛出异常:add、remove、element。
- 返回结果但是不抛出异常:offer、poll、peek。
- 阻塞:take、put。
3.1 抛出异常
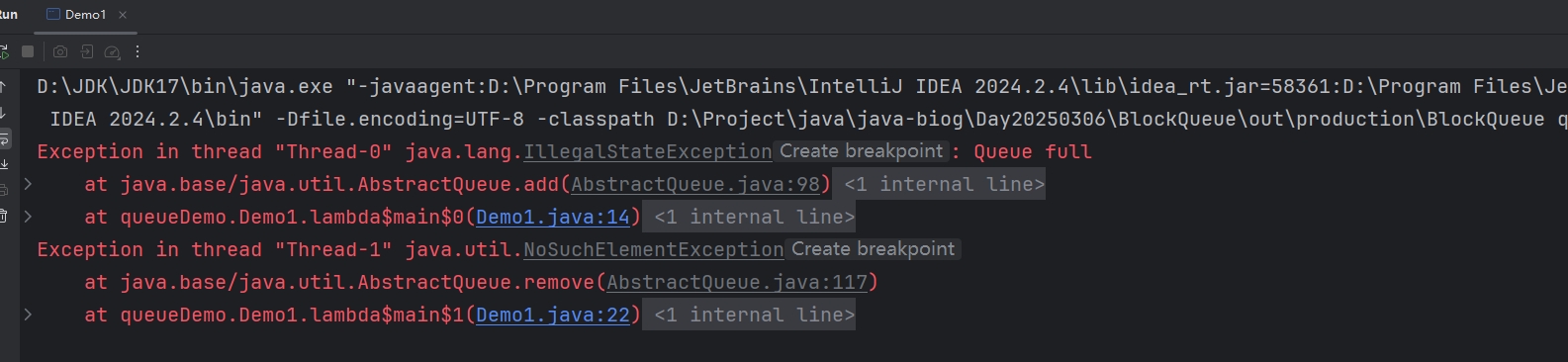
这段代码可以发现,我们将容量设置为10,t1负责add元素,t2负责remove元素,但是t2在最开始会休眠1秒钟,在休眠的时间中,t1肯定add超过10个元素放入queue中。所以这里报错。
add()抛出异常(队列中元素已满,再添加元素,就会报错):
java
public static void main(String[] args) {
BlockingQueue<Integer> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<Integer>(10);
Thread t1 = new Thread(()->{
while(true){
queue.add(1);
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(()->{
while(true){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
queue.remove();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
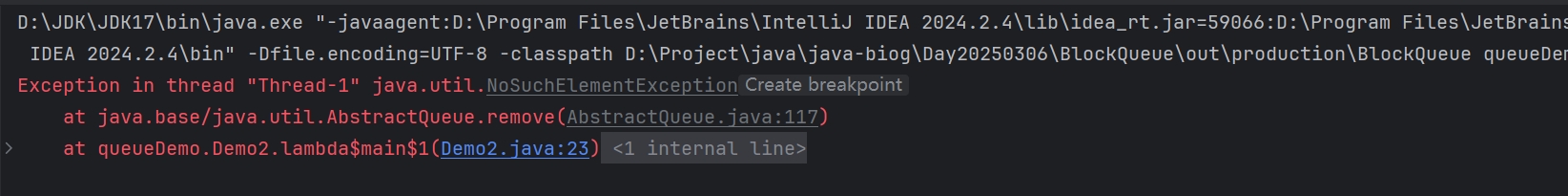
remove()抛出异常(对列中没有元素,抛出异常):
java
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BlockingQueue<Integer> queue2 = new ArrayBlockingQueue<Integer>(10);
Thread t1 = new Thread(()->{
while(true){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
queue2.add(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(()->{
while(true){
queue2.remove();
}
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
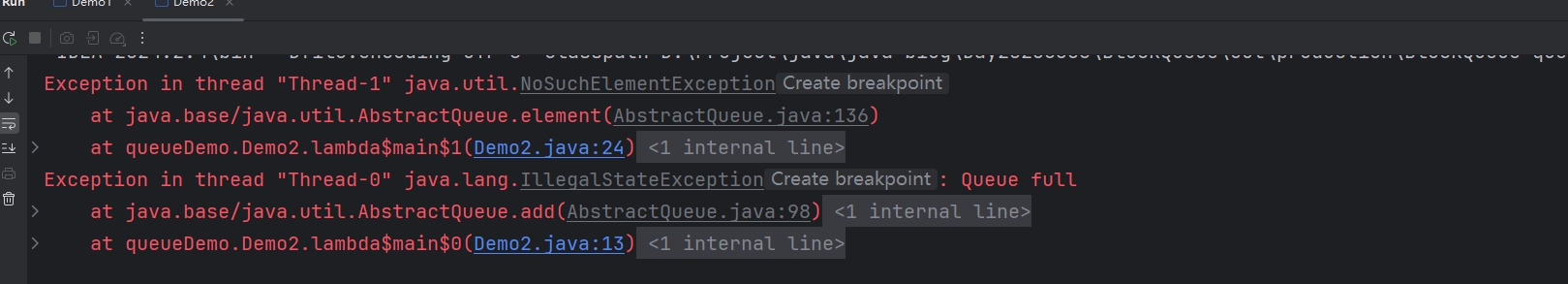
element()抛出异常(返回队列首元素,但不删除,当队列为空,抛出异常):
java
public static void main(String[] args) {
BlockingQueue<Integer> queue2 = new ArrayBlockingQueue<Integer>(10);
Thread t1 = new Thread(()->{
while(true){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
queue2.add(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(()->{
while(true){
// queue2.remove();
queue2.element();
}
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
3.2 有返回结果,不会抛出异常
offer():插入成功true,插入失败false
poll():移除成功,则打印移除元素,没有则null
peek():返回队列元素,但不删除,如果队列为空,则返回null
java
public class Demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BlockingQueue<Integer> queue4 = new ArrayBlockingQueue<Integer>(1);
Thread t1 = new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
System.out.println(queue4.offer(1));
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(queue4.poll());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
3.3 阻塞
java
public class Demo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BlockingQueue<Integer> queue5 = new ArrayBlockingQueue<Integer>(10);
Thread t1 = new Thread(()->{
while(true){
try {
queue5.put(1);
System.out.println("生产者生产元素"+queue5.size());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(()->{
while(true){
try {
queue5.take();
System.out.println("消费者消耗元素"+queue5.size());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}由于容量是10,所以生产者生产的元素就是10 以内的。

java
public class Demo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BlockingQueue<Integer> queue6 = new ArrayBlockingQueue<Integer>(10);
Thread t1 = new Thread(()->{
while(true){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
queue6.put(1);
System.out.println("生产者生产元素"+queue6.size());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(()->{
while(true){
try {
queue6.take();
System.out.println("消费者消耗元素"+queue6.size());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}这里对生产者加了休眠,所以消费者会出现阻塞等待,等待生产者生产元素。

四、常见的阻塞队列
4.1 ArrayBlockingQueue
- 基于数组实现的有界阻塞队列。
- 具有固定的容量,初始化时必须指定容量大小。
- 适合容量固定且需要高性能的场景。
4.2 LinkedBlockingQueue
- 基于链表实现的可选界阻塞队列。
- 默认为无界队列(实际是有限制的,最大容量为Integer.MAX_VALUE),也可以指定容量。
- 性能通常比ArrayBlockingQueue更好,尤其是在高并发场景下。
4.3 SynchronousQueue
- 特殊的阻塞队列,不存储元素。
- 生产者线程必须等待消费者线程取走元素后才能继续生产。
- 适合直接传递数据的场景,常用于线程池中的任务传递。
java
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.SynchronousQueue;
public class Demo7 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
BlockingQueue<Integer> queue = new SynchronousQueue<>();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(queue.take()); // 消费者线程
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
Thread.sleep(5000);
queue.put(1); // 生产者线程
}
}4.4 PriorityBlockingQueue
- 基于优先级的无界阻塞队列。
- 元素按照自然顺序或指定的比较器排序。
- 不保证线程安全的公平性,但保证优先级最高的元素总是最先被取出。
java
public class Demo8 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
BlockingQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityBlockingQueue<>();
queue.put(3);
queue.put(1);
queue.put(2);
System.out.println(queue.take()); // 输出1
}
}优先级确定方式:
- 自然排序(Comparable 接口):例如这里是从小到大,所以输出是1
- 自定义比较器(Comparator)
4.5 DelayQueue
- 基于优先级的无界阻塞队列。
- 只有当元素的延迟时间到期后,才能被取出。
- 元素必须实现Delayed接口。
java
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.DelayQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.Delayed;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
class DelayedTask implements Delayed {
private final long startTime;
private final String name;
public DelayedTask(long startTime, String name) {
this.startTime = startTime;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) {
return unit.convert(startTime - System.currentTimeMillis(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Delayed o) {
return Long.compare(this.startTime, ((DelayedTask) o).startTime);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return name;
}
}
public class DelayQueueExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
BlockingQueue<Delayed> queue = new DelayQueue<>();
queue.put(new DelayedTask(System.currentTimeMillis() + 2000, "Task1"));
queue.put(new DelayedTask(System.currentTimeMillis() + 1000, "Task2"));
System.out.println(queue.take()); // 输出Task2
}
}五、自己实现阻塞队列
5.1 成员变量
java
private int capacity = 0xffff;
private Integer[] elem ;//存储数组
private int size;//存储元素个数
private int head;//队头
private int tail;//队尾5.2 构造方法
当你传入值的时候,capacity就是你传入的那个值,就不是默认值了。
java
public MyQueue() {
elem = new Integer[capacity];
}
public MyQueue(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
elem = new Integer[capacity];
}5.3 put()方法
由于这里的put()方法涉及元素的添加,所以将这段代码放入锁中,避免了原子性带来的线程安全问题。
这里使用while不使用if,为了防止wait()被虚假唤醒,如果被虚假唤醒if就会执行后面的代码,而while还是会再检查一遍
举个例子:
- 线程A此时元素个数已满
- 线程B此时移除线程A元素,并且激活wait ()
- 线程C在此时又往线程A中添加元素,使线程A元素又达到已满状态,但此时代码会继续向下执行
java
public void put(int key) throws InterruptedException {
synchronized (this) {
while (size == elem.length) {
this.wait();
}
elem[tail] = key;
tail = (tail + 1) % capacity;
size++;
this.notify();
}
}5.4 take()方法
java
public int take() throws InterruptedException {
synchronized (this) {
while(size == 0) {
this.wait();
}
int ret = elem[head];
head = (head + 1) % capacity;
size--;
this.notify();
return ret;
}
}5.5 全部代码
java
class MyQueue {
private int capacity = 0xffff;
private Integer[] elem ;//存储数组
private int size;//存储元素个数
private int head;//队头
private int tail;//队尾
public MyQueue() {
elem = new Integer[capacity];
}
public MyQueue(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
elem = new Integer[capacity];
}
public void put(int key) throws InterruptedException {
synchronized (this) {
while (size == elem.length) {
this.wait();
}
elem[tail] = key;
tail = (tail + 1) % capacity;
size++;
this.notify();
}
}
public int take() throws InterruptedException {
synchronized (this) {
while(size == 0) {
this.wait();
}
int ret = elem[head];
head = (head + 1) % capacity;
size--;
this.notify();
return ret;
}
}
}
public class Demo9 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyQueue myQueue = new MyQueue(5);
myQueue.put(1);
myQueue.put(2);
myQueue.put(3);
myQueue.put(4);
while(true) {
System.out.println(myQueue.take());
}
}
}六、阻塞队列的优点
- 降低解耦合
假设代码1和代码2之间直接进行交互,这个时候修改代码1,代码2大概率就会受到影响,但是中间加个阻塞队列当作交互平台的话,就大大降低了代码1和代码2之间的耦合性。
- 削峰削谷
假设两个服务器进行交互请求,服务器1消耗资源少,产生请求量高,服务器2消耗资源大,接受请求量低。当正常进行交互的时候,服务器1的大量请求就会发送给服务器2,此时服务器2由于处理不了大量请求,有可能就会挂掉!
当加入阻塞队列后,服务器1的请求就会先放到阻塞队列中,服务器2就会根据自己的能力,需要接受多少请求就拿多少请求。