前言
最近在做局域网相关的程序,分别是局域网多端控制和p2p传输,主要原因是为了适应更多的场景,如车载、TV等。实际上,在纯移动端,局域网相关的应用很多是伪需求,甚至价值很低,但在iOT开发领域,多设备互动有一定的市场热度。
比如TV领域,TV上,我们互动往往遇到最头疼的问题就是文字输入了,抛开文档编辑问题,目前火热的AI模型文字输入就非常有难度,常见的问题还有在TV上进行问题反馈等。
当然,文本输入仅仅是一方面,还有通过手机控制局域网中的多台设备,也是有一定的需求市场。
本篇要点
实际上,局域网是最简的网络环境,因为所有的数据传输都在内网,因此,这里我们通常遇到的问题并不是如何创建程序,而是状态同步。怎么理解这个问题呢?
假设张三有A、B、C三台手机,分别在A、B、C上做不同的事来控制TV,那么A、B、C最终的状态应该一致才对。
另外,本篇还有就是P2P数据传输,如今通过P2P节省服务器资源的案例非常多,因此,本篇顺带简单实现一下。
本篇我们通过局域网聊天程序来简单实现状态控制,当然,部分5G频段路由下,很多主机直接存在连接失败的,目前没有找到合适的解决方法,因此,下面的程序建议在2.4G频段下使用。
局域网聊程序
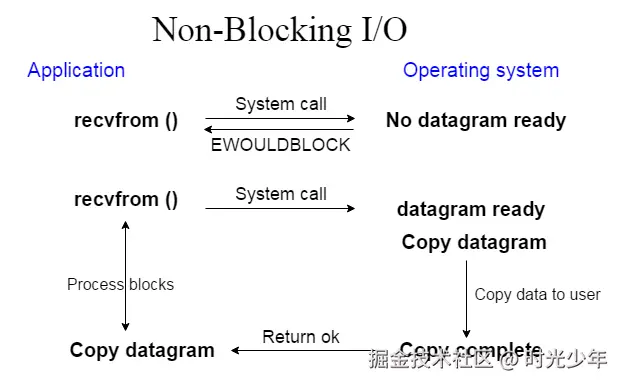
通过这个简单的程序,我们了解下NIO的具体用法,同时,在下面的代码中broadcast方法实现多端数据同步。这个案例可以让我们学习到更简单的状态同步,以往的方式是对Socket进行管理,而通过NIO的Selector就能实现连接管理。
另外,NIO的另一个优势是可以减少线程的开销,我们只使用一个线程便可以处理多个请求,实际上,NIO之所以优势明显,主要原因是充分利用了系统底层的多路复用机制和I/O非阻塞机制,在之前的文章中我们说过,系统层面的I/O并不消耗CPU,因为内存、磁盘都有自己的芯片可以处理数据拷贝,传统的I/O阻塞并不是因为真正阻塞了,而是程序设计出来的,方便我们按顺序执行代码。
服务器端
下面是小程序的服务端,理论上,局域网聊天没有太多意义,大部分局域网都在同一个家庭里,直接面对面聊天效率高的多。
但是,这个程序的目的是理解NIO机制和状态同步,因此,我们有必要了解下。
java
public class ChatServer {
private static final int PORT = 8888;
private Selector selector;
private ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel;
public ChatServer() {
try {
// 创建Selector
selector = Selector.open();
// 创建ServerSocketChannel
serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
// 设置为非阻塞模式
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 绑定端口
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(PORT));
// 注册到Selector,监听连接事件
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
System.out.println("服务器启动成功,监听端口:" + PORT);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void start() {
try {
while (true) {
// 阻塞等待就绪的Channel
selector.select();
// 获取就绪的SelectionKey集合
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
iterator.remove();
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
// 处理新的客户端连接
handleAccept(key);
} else if (key.isReadable()) {
// 处理客户端消息
handleRead(key);
}
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void handleAccept(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
ServerSocketChannel serverChannel = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel clientChannel = serverChannel.accept();
clientChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 注册到Selector,监听读事件
clientChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
System.out.println("客户端连接成功:" + clientChannel.getRemoteAddress());
}
private void handleRead(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
SocketChannel clientChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int bytesRead = clientChannel.read(buffer);
if (bytesRead > 0) {
buffer.flip();
byte[] bytes = new byte[buffer.remaining()];
buffer.get(bytes);
String message = new String(bytes);
System.out.println("收到消息:" + message);
// 广播消息给所有客户端
broadcast(message, clientChannel);
} else if (bytesRead == -1) {
// 客户端断开连接
System.out.println("客户端断开连接:" + clientChannel.getRemoteAddress());
key.cancel();
clientChannel.close();
}
}
private void broadcast(String message, SocketChannel excludeChannel) throws IOException {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(message.getBytes());
// 遍历所有已注册的通道
for (SelectionKey key : selector.keys()) {
Channel targetChannel = key.channel();
if (targetChannel instanceof SocketChannel && targetChannel != excludeChannel) {
SocketChannel dest = (SocketChannel) targetChannel;
dest.write(buffer);
buffer.rewind();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ChatServer server = new ChatServer();
server.start();
}
} 客户端
下面是局域网聊天的客户端,实际上,和服务端的很多代码类似,但对于C/S架构,区别是connect部分,而Server端是bind方法即可。
ini
public class ChatClient {
private static final String HOST = "localhost";
private static final int PORT = 8888;
private Selector selector;
private SocketChannel socketChannel;
private String username;
public ChatClient(String username) {
this.username = username;
try {
// 创建Selector
selector = Selector.open();
// 创建SocketChannel
socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
// 设置为非阻塞模式
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 连接服务器
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(HOST, PORT));
// 注册到Selector,监听连接事件
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void start() {
try {
// 启动消息接收线程
new Thread(this::receiveMessage).start();
// 处理用户输入
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
String message = scanner.nextLine();
if (message.equals("exit")) {
break;
}
sendMessage(message);
}
scanner.close();
close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void receiveMessage() {
try {
while (true) {
selector.select();
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
iterator.remove();
if (key.isConnectable()) {
handleConnect(key);
} else if (key.isReadable()) {
handleRead(key);
}
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void handleConnect(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
if (channel.isConnectionPending()) {
channel.finishConnect();
}
channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
System.out.println("已连接到服务器");
}
private void handleRead(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int bytesRead = channel.read(buffer);
if (bytesRead > 0) {
buffer.flip();
byte[] bytes = new byte[buffer.remaining()];
buffer.get(bytes);
String message = new String(bytes);
System.out.println(message);
} else if (bytesRead == -1) {
System.out.println("服务器断开连接");
key.cancel();
channel.close();
}
}
private void sendMessage(String message) throws IOException {
String formattedMessage = username + ": " + message;
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(formattedMessage.getBytes());
// 设置写入超时时间(毫秒)
long timeout = 5000;
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
int totalBytes = buffer.remaining();
int bytesWritten = 0;
while (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
int written = socketChannel.write(buffer);
if (written > 0) {
bytesWritten += written;
} else if (written == 0) {
// 缓冲区已满,等待一小段时间后重试
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
break;
}
}
// 检查是否超时
if (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime > timeout) {
System.out.println("消息发送超时,已发送 " + bytesWritten + "/" + totalBytes + " 字节");
break;
}
}
if (bytesWritten < totalBytes) {
System.out.println("警告:消息未完全发送,已发送 " + bytesWritten + "/" + totalBytes + " 字节");
}
}
private void close() throws IOException {
if (socketChannel != null) {
socketChannel.close();
}
if (selector != null) {
selector.close();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入用户名:");
String username = scanner.nextLine();
ChatClient client = new ChatClient(username);
client.start();
}
} 以上是局域网聊天程序的案例,下面我们进入P2P通信。
P2P通信实现
p2p最多的用法除了资源下载之外,还有个就是实现多屏同显,当然,不可否认,也有很多程序通过webRTC实现,在正常的开发过程中,简单的p2p通信下面的案例即可,但是遇到信令、协议兼容问题,建议使用SRS(Simple Realtime Server)或者WebRTC吧。
下面是核心逻辑
java
public class Peer {
private static final int MULTICAST_PORT = 8888;
private static final String MULTICAST_GROUP = "230.0.0.1";
private static final int HEARTBEAT_INTERVAL = 5000; // 5 seconds
private String username;
private MulticastSocket multicastSocket;
private ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel;
private Selector selector;
private Map<String, SocketChannel> peers;
private Timer heartbeatTimer;
public Peer(String username) {
this.username = username;
this.peers = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
try {
setupMulticast();
setupServer();
startHeartbeat();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void setupMulticast() throws IOException {
multicastSocket = new MulticastSocket(MULTICAST_PORT);
InetAddress group = InetAddress.getByName(MULTICAST_GROUP);
multicastSocket.joinGroup(group);
// 启动多播监听线程
new Thread(() -> {
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(buffer, buffer.length);
while (!multicastSocket.isClosed()) {
try {
multicastSocket.receive(packet);
String message = new String(packet.getData(), 0, packet.getLength());
handleMulticastMessage(message, packet.getAddress());
} catch (IOException e) {
if (!multicastSocket.isClosed()) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}).start();
}
private void setupServer() throws IOException {
selector = Selector.open();
serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(0)); // 随机端口
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
// 启动服务器监听线程
new Thread(() -> {
try {
while (!serverSocketChannel.isClosed()) {
selector.select();
Set<SelectionKey> keys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = keys.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
iterator.remove();
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
handleAccept(key);
} else if (key.isReadable()) {
handleRead(key);
}
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
}
private void startHeartbeat() {
heartbeatTimer = new Timer();
heartbeatTimer.scheduleAtFixedRate(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
sendMulticastMessage("HEARTBEAT:" + username + ":" +
serverSocketChannel.socket().getLocalPort());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, 0, HEARTBEAT_INTERVAL);
}
private void handleMulticastMessage(String message, InetAddress senderAddress) {
String[] parts = message.split(":");
if (parts.length != 3 || !parts[0].equals("HEARTBEAT")) return;
String peerUsername = parts[1];
int peerPort = Integer.parseInt(parts[2]);
if (!peerUsername.equals(username) && !peers.containsKey(peerUsername)) {
try {
connectToPeer(peerUsername, senderAddress, peerPort);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private void connectToPeer(String peerUsername, InetAddress address, int port) throws IOException {
SocketChannel channel = SocketChannel.open();
channel.configureBlocking(false);
channel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(address, port));
if (channel.finishConnect()) {
channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
peers.put(peerUsername, channel);
System.out.println("已连接到对等节点: " + peerUsername);
}
}
private void handleAccept(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
ServerSocketChannel serverChannel = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel clientChannel = serverChannel.accept();
clientChannel.configureBlocking(false);
clientChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
private void handleRead(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int bytesRead = channel.read(buffer);
if (bytesRead > 0) {
buffer.flip();
byte[] bytes = new byte[buffer.remaining()];
buffer.get(bytes);
String message = new String(bytes);
System.out.println("收到消息: " + message);
} else if (bytesRead == -1) {
channel.close();
key.cancel();
// 从peers中移除断开连接的节点
peers.entrySet().removeIf(entry -> entry.getValue() == channel);
}
}
public void sendMessage(String peerUsername, String message) throws IOException {
SocketChannel channel = peers.get(peerUsername);
if (channel != null && channel.isConnected()) {
String formattedMessage = username + ": " + message;
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(formattedMessage.getBytes());
channel.write(buffer);
} else {
System.out.println("无法发送消息: 对等节点未连接");
}
}
private void sendMulticastMessage(String message) throws IOException {
byte[] data = message.getBytes();
InetAddress group = InetAddress.getByName(MULTICAST_GROUP);
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(data, data.length, group, MULTICAST_PORT);
multicastSocket.send(packet);
}
public void close() {
try {
heartbeatTimer.cancel();
multicastSocket.leaveGroup(InetAddress.getByName(MULTICAST_GROUP));
multicastSocket.close();
serverSocketChannel.close();
selector.close();
for (SocketChannel channel : peers.values()) {
channel.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入用户名: ");
String username = scanner.nextLine();
Peer peer = new Peer(username);
System.out.println("P2P节点已启动,等待连接...");
while (true) {
System.out.print("输入命令 (send <用户名> <消息>, list, exit): ");
String command = scanner.nextLine();
if (command.equals("exit")) {
break;
} else if (command.equals("list")) {
System.out.println("已连接的对等节点: " + peer.peers.keySet());
} else if (command.startsWith("send ")) {
String[] parts = command.split(" ", 3);
if (parts.length == 3) {
try {
peer.sendMessage(parts[1], parts[2]);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("发送消息失败: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
}
peer.close();
scanner.close();
}
} 总结
本篇我们主要实现了2个案例,足以应对局域网中的常见需求。