文章目录
📘 PySide6.QtCore.QRect 使用整数精度定义平面矩形区域,其官方文档参考这里。
一、构造与初始化方法
| 方法签名 |
说明 |
QRect() |
构造空矩形(宽高为0) |
QRect(x: int, y: int, width: int, height: int) |
通过坐标和尺寸构造 |
QRect(topLeft: QPoint, size: QSize) |
通过顶点和尺寸构造 |
QRect(topLeft: QPoint, bottomRight: QPoint) |
通过对角点构造(不推荐) |
python
复制代码
# 空矩形
null_rect = QRect()
# 标准构造
rect1 = QRect(10, 20, 300, 400)
# QPoint+QSize构造
rect2 = QRect(QPoint(10, 20), QSize(300, 400))
二、坐标与尺寸获取
| 方法 |
返回值 |
说明 |
left() |
int |
左边界x坐标 |
top() |
int |
上边界y坐标 |
right() |
int |
右边界x坐标(含历史原因带来的偏移: left() + width() - 1) |
bottom() |
int |
下边界y坐标(含历史偏移:top() + height() - 1) |
width() |
int |
实际宽度(可能负数) |
height() |
int |
实际高度(可能负数) |
topLeft() |
QPoint |
左上角坐标 |
bottomRight() |
QPoint |
右下角坐标(含偏移) |
center() |
QPoint |
中心点坐标 |
size() |
QSize |
尺寸对象 |
python
复制代码
rect = QRect(10, 20, 30, 40)
print(rect.right()) # 39 (10+30-1)
print(rect.size()) # QSize(30, 40)
print(rect.top()) # 20
print(rect.width()) # 30
print(rect.height()) # 40
print(rect.x()) # 10
print(rect.y()) # 20
print(rect.bottom()) # 59 (20+40-1)
print(rect.left()) # 10,和x()一样
三、坐标与尺寸设置
| 方法 |
参数 |
说明 |
setLeft(x: int) |
新左边界 |
保持右边界不变 |
setRight(x: int) |
新右边界 |
改变宽度 |
setTop(y: int) |
新上边界 |
保持下边界不变 |
setBottom(y: int) |
新下边界 |
改变高度 |
setTopLeft(p: QPoint) |
新顶点 |
改变位置,保持右下 |
setBottomRight(p: QPoint) |
新对角点 |
改变尺寸 |
setWidth(w: int) |
新宽度 |
右边界自动计算 |
setHeight(h: int) |
新高度 |
下边界自动计算 |
setSize(s: QSize) |
新尺寸 |
保持左上角不变 |
setCoords(x1: int, y1: int, x2: int, y2: int) |
四坐标 |
直接设置四个边界 |
setRect(x: int, y: int, w: int, h: int) |
坐标+尺寸 |
重置整个矩形 |
python
复制代码
rect = QRect(10, 20, 30, 40)
rect.setRight(50) # 新宽度=50-10+1=41
rect.setSize(QSize(20, 60)) # 变为(10,20,20,60)
四、几何运算方法
| 方法 |
返回值 |
说明 |
contains(QPoint) |
bool |
点是否在矩形内 |
contains(QRect) |
bool |
是否完全包含另一矩形 |
intersects(QRect) |
bool |
是否有重叠区域 |
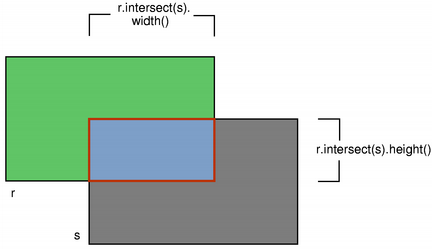
intersected(QRect) |
QRect |
返回交集区域 |
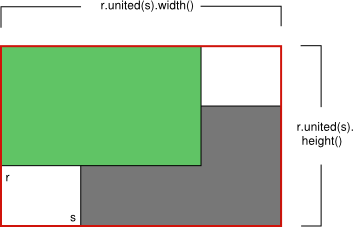
united(QRect) |
QRect |
返回并集区域 |
adjusted(dx1: int, dy1: int, dx2: int, dy2: int) |
QRect |
调整边界后的新矩形 |
normalized() |
QRect |
标准化后的正尺寸矩形 |
python
复制代码
rect_a = QRect(0, 0, 100, 100)
rect_b = QRect(50, 50, 100, 100)
print(rect_a.intersected(rect_b)) # QRect(50,50,50,50)
print(rect_a.contains(QPoint(30,30))) # True
五、移动与调整方法
| 方法 |
参数 |
说明 |
translate(dx: int, dy: int) |
偏移量 |
相对移动 |
translated(dx: int, dy: int) |
偏移量 |
返回移动后的新矩形 |
moveTo(x: int, y: int) |
新坐标 |
绝对移动左上角 |
moveTopLeft(p: QPoint) |
新顶点 |
移动左上角 |
adjust(dx1: int, dy1: int, dx2: int, dy2: int) |
调整量 |
直接修改边界 |
marginsAdded(QMargins) |
边距 |
增加外边距后的新矩形 |
marginsRemoved(QMargins) |
边距 |
移除外边距后的新矩形 |
python
复制代码
rect = QRect(10, 20, 30, 40)
rect.translate(5, -5) # 新位置(15,15,30,40)
new_rect = rect.translated(0, 10) # (15,25,30,40)
new_rect.moveTo(0, 0) # (0,0,30,40)
六、状态判断方法
| 方法 |
返回值 |
说明 |
isEmpty() |
bool |
是否面积为零(允许负尺寸) |
isNull() |
bool |
是否宽高均为0 |
isValid() |
bool |
是否满足 left<=right 且 top<=bottom |
python
复制代码
rect1 = QRect(10,10,-5,20)
print(rect1.isEmpty()) # True (宽度为负)
print(rect1.isValid()) # False
rect2 = QRect()
print(rect2.isNull()) # True
七、类型转换方法
| 方法 |
返回值 |
说明 |
toRectF() |
QRectF |
转为浮点矩形 |
getCoords() |
(x1, y1, x2, y2) |
获取四个边界坐标 |
getRect() |
(x, y, w, h) |
获取左上坐标和尺寸 |
python
复制代码
rect = QRect(10, 20, 30, 40)
print(rect.getCoords()) # (10, 20, 39, 59)
print(rect.toRectF()) # QRectF(10.0,20.0,30.0,40.0)
八、操作符重载
| 操作符 |
等效方法 |
说明 |
& |
intersected() |
交集运算 |
| ` |
` |
united() |
+= |
marginsAdded() |
增加边距 |
-= |
marginsRemoved() |
移除边距 |
== |
坐标相等判断 |
完全一致 |
- |
差集运算 |
返回缩小后的矩形 |
python
复制代码
rect1 = QRect(0,0,100,100)
rect2 = QRect(50,50,100,100)
print(rect1 & rect2) # QRect(50,50,50,50)
print(rect1 | rect2) # QRect(0,0,150,150)
九、静态方法
| 方法 |
说明 |
span(p1: QPoint, p2: QPoint) |
创建包含两点的最小矩形 |
python
复制代码
p1 = QPoint(10, 20)
p2 = QPoint(50, 60)
span_rect = QRect.span(p1, p2) # QRect(10,20,41,41)
十、特殊方法
| 方法 |
说明 |
__reduce__() |
序列化支持 |
__repr__() |
字符串表示 |
transposed() |
宽高交换后的新矩形 |
python
复制代码
rect = QRect(10, 20, 30, 40)
print(rect.transposed()) # QRect(10,20,40,30)
附录
方法速查表
| 类别 |
方法 |
| 构造 |
QRect(), QRect(x,y,w,h), QRect(QPoint,QSize) |
| 坐标获取 |
left(), right(), top(), bottom(), topLeft(), bottomRight(), center() |
| 尺寸获取 |
width(), height(), size() |
| 坐标设置 |
setLeft(), setRight(), setTop(), setBottom(), setTopLeft(), setBottomRight() |
| 尺寸设置 |
setWidth(), setHeight(), setSize(), setCoords(), setRect() |
| 几何运算 |
contains(), intersects(), intersected(), united(), adjusted(), normalized() |
| 移动调整 |
translate(), translated(), moveTo(), adjust(), marginsAdded(), marginsRemoved() |
| 状态判断 |
isEmpty(), isNull(), isValid() |
| 类型转换 |
toRectF(), getCoords(), getRect() |
| 操作符 |
&, ` |
| 特殊方法 |
transposed(), span() |
注意的问题
实际开发中需特别注意:
- 历史坐标偏移问题(right/bottom返回值)
- 负尺寸需用
normalized()标准化
- 移动与调整方法的原地修改 与返回新对象的区别
- 有效性验证应在几何运算前完成
交集和并集图解
intersect
united