1. 路由
gin 框架中采用的路优酷是基于httprouter做的
HttpRouter 是一个高性能的 HTTP 请求路由器,适用于 Go 语言。它的设计目标是提供高效的路由匹配和低内存占用,特别适合需要高性能和简单路由的应用场景。
主要特点
- 显式匹配:与其他路由器不同,HttpRouter 只支持显式匹配,即一个请求只能匹配一个或不匹配任何路由。这避免了意外匹配,提高了 SEO 和用户体验。
- 自动处理尾部斜杠 :HttpRouter 会自动重定向缺少或多余尾部斜杠的请求,前提是新路径有处理程序。如果不需要这种行为,可以关闭2。
- 路径自动校正 :除了处理尾部斜杠,HttpRouter 还可以修正错误的大小写和多余的路径元素(如 .../ 或 //)。
- 路由参数:支持在路由模式中使用命名参数和捕获所有参数,简化了 URL 路径的解析。
- 零垃圾:匹配和分发过程不会产生垃圾,只有在路径包含参数时才会进行堆分配。
- 最佳性能:使用压缩动态 trie(基数树)结构进行高效匹配,性能优异。
1.1 基本路由
go
package one
import (
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"net/http"
)
func index() {
r := gin.Default()
r.GET("/", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.String(http.StatusOK, "Hello Gin")
})
r.POST("/", func(c *gin.Context) {})
r.DELETE("/", func(c *gin.Context) {})
r.PUT("/", func(c *gin.Context) {})
r.Run(":8081")
}- gin支持Restful风格的API
- 即Representational State Transfer的缩写。直接翻译的意思是"表现层状态转化",是一种互联网应用程序的API设计理念:URL定位资源,用HTTP描述操作
1.获取文章:/blog/getXxx Get blog/Xxx
2.添加:/blog/addXxx POST blog/Xxx
3.修改:/blog/updateXxx PUT blog/Xxx
4.删除:/blog/delXxxx DELETE blog/Xxx
另一种方式
go
package main
import (
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"net/http"
)
func sayHello(c *gin.Context) {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"message": "hello",
})
}
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
r.GET("/test1", sayHello)
r.Run(":8080")
}1.2 API 参数
请求方式的方法可以通过函数来接受,从而获得请求传来的参数
go
package main
import (
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"net/http"
)
func sayHello(c *gin.Context) {
name := c.Param("name")
age := c.Param("age")
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"name": name,
"age": age,
})
}
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
// 请求:localhost/test1/xxx/ooo
// 响应:{"name":xxx,"age":ooo}
r.GET("/test1/:name/:age", sayHello)
r.Run(":8080")
}需要注意:gin默认开启restful风格语法,所以可以直接在请求路径上添加名称,属性名是拟定在请求的路径上的
r.GET("/test1/:name/:age", sayHello)这里请求路径拟定了方法内
c *gin.Context中的参数名称;这里默认有 name 和 age 属性
请求:http://localhost:8080/test1/张三/18
响应结果:
json
{
"age": "18",
"name": "张三"
}1.3 URL 参数
路径参数,就不会使用restful风格语法进行接受请求参数
go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"net/http"
)
func sayHello(c *gin.Context) {
// Query方法,若不存在则返回空字符串
name := c.Query("name")
age := c.Query("age")
fmt.Println("========================")
fmt.Println("名称", name)
fmt.Println("年龄", name)
fmt.Println("========================")
name1 := c.DefaultQuery("name", "默认名称")
fmt.Println("defaultName", name1)
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"name": name,
"age": age,
"name1": name1,
})
}
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
// 请求:localhost/test1/?xxx=xxx&ooo=000
// 响应:{"name":xxx,"age":ooo}
r.GET("/test1", sayHello)
r.Run(":8080")
}- URL参数可以通过DefaultQuery()或Query()方法获取
- DefaultQuery()若参数不存在,返回默认值,Query()若不存在,返回空串
两种请求:
-
请求1:
http://localhost:8080/test1?age=19 -
响应数据1:
json
{
"age": "19",
"name": "",
"name1": "默认名称"
}- 请求2:
http://localhost:8080/test1?name=张三&age=19 - 响应数据2:
json
{
"age": "19",
"name": "张三",
"name1": "张三"
}1.4 表单参数
- 表单传输为post请求,http常见的传输格式为四种:
- application/json
- application/x-www-form-urlencoded
- application/xml
- multipart/form-data
- 表单参数可以通过PostForm()方法获取,该方法默认解析的是x-www-form-urlencoded或from-data格式的参数
测试的html文件
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="http://localhost:8080/form" method="post" action="application/x-www-form-urlencoded">
用户名:<input type="text" name="username" placeholder="请输入你的用户名"> <br>
密 码:<input type="password" name="user_password" placeholder="请输入你的密码"> <br>
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
</body>
</html>- index.go
go
package main
import (
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"net/http"
)
func sayHello(c *gin.Context) {
types := c.DefaultPostForm("type", "post")
// 接受参数
name := c.PostForm("username") // 对应页面传入的name值或者json的属性
password := c.PostForm("user_password")
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"types": types,
"name": name,
"password": password,
})
}
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
r.POST("/form", sayHello)
r.Run(":8080")
}返回数据:
json
{
"name": "rx",
"password": "123",
"types": "post"
}1.5 上传单个文件
multipart/form-data格式用于文件上传- gin文件上传与原生的net/http方法类似,不同在于gin把原生的request封装到c.Request中
demo2.html
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="http://localhost:8080/upload" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
上传文件:<input type="file" name="file" >
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
</body>
</html>- index.go
go
package __single_file
import (
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"net/http"
)
func DefaultFunction(c *gin.Context) {
// 上传单个文件
file, _ := c.FormFile("file")
if file == nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusInternalServerError, gin.H{
"code": http.StatusInternalServerError,
"message": "文件为空",
})
return
}
c.SaveUploadedFile(file, file.Filename)
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"file": file.Filename,
})
}
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
r.POST("/upload", DefaultFunction)
r.Run(":8080")
}数据响应:
json
{"file":"Picture3.png"}1.6 上传单个文件------添加限制
go
package __single_file_restrict
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"log"
"net/http"
)
func DefaultFunction(c *gin.Context) {
// 上传单个文件_携带限制
_, file, err := c.Request.FormFile("file")
if err != nil {
log.Printf("Error when try to get file: %v", err)
}
//file.Size 获取文件大小
if file.Size > 1024*1024*2 {
fmt.Println("文件太大了")
return
}
//file.Header.Get("Content-Type")获取上传文件的类型
if file.Header.Get("Content-Type") != "image/png" {
fmt.Println("只允许上传png图片")
return
}
c.SaveUploadedFile(file, file.Filename)
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"file": file.Filename,
})
}
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
r.POST("/upload", DefaultFunction)
r.Run(":8080")
}数据响应:
json
{"file":"Picture3.png"}1.7 上传多个文件
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="http://localhost:8000/upload" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
上传文件:<input type="file" name="files" multiple>
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
</body>
</html>
go
package main
import (
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"net/http"
"fmt"
)
// gin的helloWorld
func main() {
// 1.创建路由
// 默认使用了2个中间件Logger(), Recovery()
r := gin.Default()
// 限制表单上传大小 8MB,默认为32MB
r.MaxMultipartMemory = 8 << 20
r.POST("/upload", func(c *gin.Context) {
form, err := c.MultipartForm()
if err != nil {
c.String(http.StatusBadRequest, fmt.Sprintf("get err %s", err.Error()))
}
// 获取所有图片
files := form.File["files"]
// 遍历所有图片
for _, file := range files {
// 逐个存
if err := c.SaveUploadedFile(file, file.Filename); err != nil {
c.String(http.StatusBadRequest, fmt.Sprintf("upload err %s", err.Error()))
return
}
}
c.String(200, fmt.Sprintf("upload ok %d files", len(files)))
})
//默认端口号是8080
r.Run(":8000")
}1.8 路由组-routers group
go
package main
import (
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"net/http"
)
func cat(c *gin.Context) {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"cat": c.Query("cat"),
})
}
func dog(c *gin.Context) {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"dog": c.Query("dog"),
})
}
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
animal := r.Group("/animal")
// http://localhost:8080/animal/cat?cat=tom
animal.GET("/cat", cat)
animal.GET("/dog", dog)
// 第二种写法
// http://localhost:8080/animal2/cat?cat=tom
animal2 := r.Group("/animal2")
{
animal2.GET("/cat", cat)
animal2.GET("/dog", dog)
}
r.Run(":8080")
}路由组有两种写法
-
动态配置,将变量声明出来可以在任意位置配置路由
goanimal := r.Group("/animal") // http://localhost:8080/animal/cat?cat=tom animal.GET("/cat", cat) animal.GET("/dog", dog) -
对象配置,直接使用对象进行配置
go// http://localhost:8080/animal2/cat?cat=tom animal2 := r.Group("/animal2") { animal2.GET("/cat", cat) animal2.GET("/dog", dog) }
注意路由组配置:组路径下的请求配置,必须加上
/例如: animal2.GET("/cat", cat)
1.9 httprotuer路由原理
1.9.1 Radix Tree(压缩前缀树)
基数树(Radix Tree)又称为PAT位树(Patricia Trie or crit bit tree),是一种更节省空间的前缀树(Trie Tree)。对于基数树的每个节点,如果该节点是唯一的子树的话,就和父节点合并
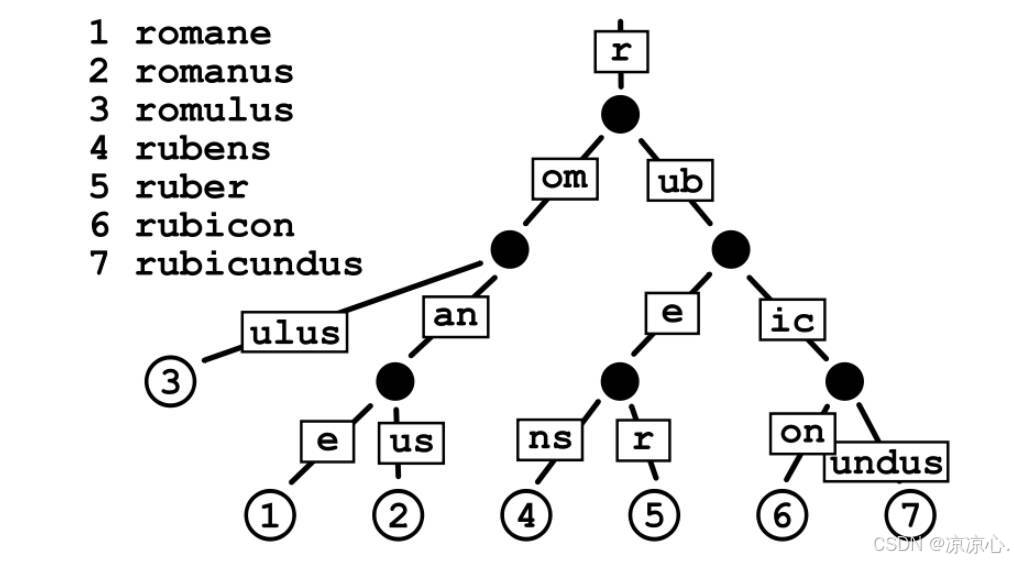
Radix Tree可以被认为是一棵简洁版的前缀树。其注册路由的过程就是构造前缀树的过程,具有公共前缀的节点也共享一个公共父节点。假设注册以下路由信息:
go
r := gin.Default()
r.GET("/", func1)
r.GET("/search/", func2)
r.GET("/support/", func3)
r.GET("/blog/", func4)
r.GET("/blog/:post/", func5)
r.GET("/about-us/", func6)
r.GET("/about-us/team/", func7)
r.GET("/contact/", func8)生成的路由树信息如下:
json
Priority Path Handle
9 \ *<1>
3 ├s nil
2 |├earch\ *<2>
1 |└upport\ *<3>
2 ├blog\ *<4>
1 | └:post nil
1 | └\ *<5>
2 ├about-us\ *<6>
1 | └team\ *<7>
1 └contact\ *<8>最右列每个***<数字>表示Handle处理函数的内存地址(一个指针)**。
- 从根节点遍历到叶子节点就能得到完整的路由表。
例如:blog/:post其中:post只是实际文章名称的占位符(参数)。
与hash-maps不同,Radix Tree结构还允许使用像:post参数这种动态部分,因为Radix Tree实际上是根据路由模式进行匹配,而不仅仅是比较哈希值。
由于URL路径具有层次结构,并且只使用有限的一组字符(字节值),所以很可能有许多常见的前缀。这使开发者可以很容易地将路由简化为更小的问题。
- 此外,路由器为每种请求方法管理一棵单独的树。
- 一方面,它比在每个节点中都保存一个method-> handle map更加节省空间,而且还使开发者甚至可以在开始在前缀树中查找之前大大减少路由问题。
为了获得更好的可伸缩性,每个树级别上的子节点都按Priority(优先级)排序,其中优先级(最左列)就是在子节点(子节点、子子节点等等)中注册的句柄的数量。
这样做有两个好处:
优先匹配被大多数路由路径包含的节点。这样可以让尽可能多的路由快速被定位。- 类似于成本补偿。最长的路径可以被优先匹配,补偿体现在最长的路径需要花费更长的时间来定位,如果最长路径的节点能被优先匹配(即每次拿子节点都命中),那么路由匹配所花的时间不一定比短路径的路由长。
下面展示了节点(每个-可以看做一个节点)匹配的路径:从左到右,从上到下。
json
├------------
├---------
├-----
├----
├--
├--
└-1.9.2 httproute 特点
路由器支持路由模式中的变量,并与请求方法进行匹配。其伸缩性相较于原生net/http库更好。
明确的路由匹配,一个path对应一个Handler。
不用关心/,例如当请求/foo/时,此path不存在,如果有/foo会自动302转发
path自动修正,例如//foo转化成/foo
httprouter使用的数据结构就是压缩字典树。
典型的压缩字典树结构如下:

1.9 参考文章:https://blog.csdn.net/ygq13572549874/article/details/130281909