Queue
前面所说的Stack是 先入后出的原则 ,那有没有 先入先出 的原则的结构呢?这就是本篇博客所讲的Queue序列就是这个原则
队列的概念
只允许在一段进行插入数据,再另一端进行删除数据的线性表,具有的是先入先出的原则
入列端 :进行插入操作的一端,也叫队尾
出列端:进行删除数据的一端,也叫队头

队列的使用



这里的Queue只是一个接口,继承了Collection接口,Collection接口继承了Iterable接口
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| boolean offer(E e) | 入队列 |
| E poll() | 出队列 |
| peek() | 获取队头元素 |
| int size() | 队列中的有效元素个数 |
| boolean isEmpty() | 检查队列是否为空 |
因为Queue是个接⼝,底层是通过链表实现的 ,所以不能直接对其实例化,因此可以实例化链表对象
offer和poll方法
boolean offer(E e) 入队列
E poll() 出队列,将队列第一个元素出列
peek() 获取队头元素,获取队头元素,但不出列
java
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
//入列
queue.offer(1);
queue.offer(2);
queue.offer(3);
System.out.println(queue);
//出列
int ret = queue.poll();
System.out.println("队头元素:"+ret);
//获取栈顶元素,但不出列
int ret1 = queue.peek();
System.out.println("此时队头元素:"+ret1);
System.out.println("出列后列表:"+queue);
}
}运行结果如下

其实Queue中也有add方法用来从队尾添加元素,remove用来删除队头元素
add和remove方法


c
offer方法如果遇到其队列满了,就会返回false,添加不了,不会抛出异常
poll方法,如果队列为空,出列的话就返回的是null,不会抛出异常
add方法如果遇到队列满了,添加队列,则会抛出异常
remove方法,进行出列的话,如果列表为空,则会抛出异常
因此可以直到offer和poll放法配套使用,处理比较温和,不会影响程序执行
而add和remove方法配套使用,比较严谨,如果有一异常直接抛出,可能回影响程序运行正常使用是相同的,几乎没什么区别
java
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
//offer和poll方法
queue.offer(1);
queue.offer(2);
queue.offer(3);
queue.poll();//出队头元素
System.out.println(queue);
Queue<Integer> queue1 = new LinkedList<>();
queue1.add(1);
queue1.add(2);
queue1.add(3);
queue1.poll();//出队头元素
System.out.println(queue1);
}
}在正常入列和出列是正常使用的,没什么两样
但是如果

但是如果有异常的话就处理方式不一样了
java
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
System.out.println("poll方法 "+queue.poll());//poll方法
System.out.println("remove方法"+queue.remove());//remove方法
}
}这里的列表为空,使用poll方法出队列时候,如果为空就直接出栈null
而remove出队列的时候如果列表为空,则会NoSuchElementException的异常出现

设计循环队列

目的:就是用数组来实现队列
如何使用数组来实现队列呢
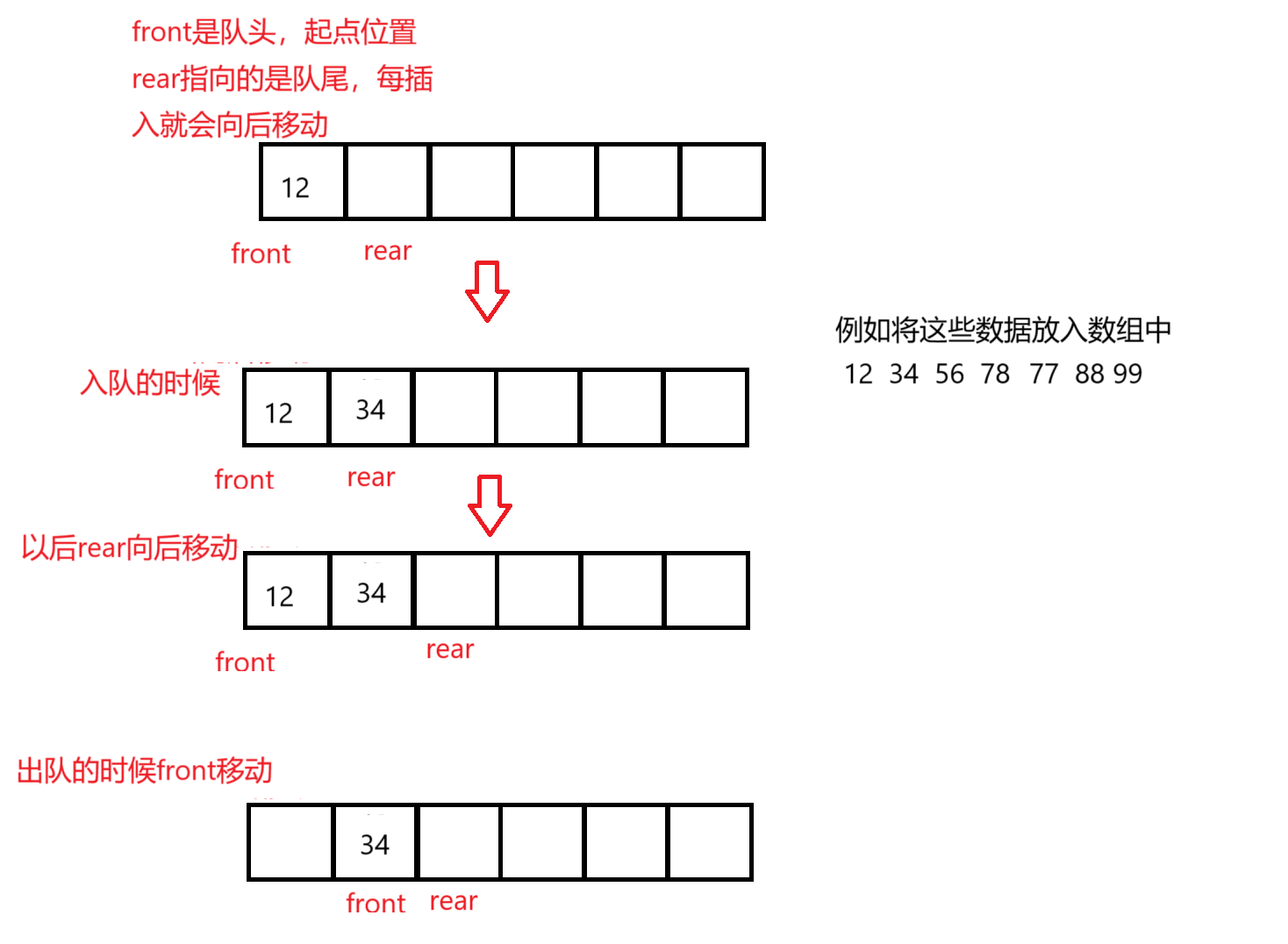

使用普通的数组使用会出现上面这种问题,这时就要使用循环队列来实现


c
在获取rear下标的元素的时候,要注意其实是rear-1下标的元素,因为如果自己
rear指向要入队列的位置,不是最后一个队列元素的位置
java
class MyCircularQueue {
public int[] elem;
public int front;//头
public int rear;//尾
public MyCircularQueue(int k) {
//多开辟一个空间,便于区分列表是空,还是满
elem = new int[k+1];
}
//入队列
public boolean enQueue(int value) {
if(isFull()){
return false;
}
elem[rear] = value;
rear = (rear+1)%elem.length;
return true;
}
//出队列
public boolean deQueue() {
if(isEmpty()){
return false;
}
front = (front+1)%elem.length;
return true;
}
public int Front() {
if(isEmpty()){
return -1;
}
return elem[front];
}
public int Rear() {
if(isEmpty()){
return -1;
}
//此时的rear可能指向了0下标
//不可以直接用rear-1下标
int index = -1;
if(rear==0){
index = elem.length-1;
}else{
index = rear-1;
}
return elem[index];
}
//判断空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return front == rear;
}
//满
public boolean isFull() {
return (rear+1)%elem.length==front;
}
}队列实现栈

目的:用队列实现栈的功能
思路:我们知道对列是先入先出,而栈是先入后出的原则,两个几乎相反的结结构,因此一个队列是不足以来是实现的,因此我们需要创建两个队列来实现其队列的功能
因此可以创建两个队列,一个qu1,一个qu2来实现
push入栈 :哪个队列不为空 就放入那个队列,如果都为空,默认放在qu1队列
pop出栈 :这时候出栈的话,入栈之后两个队列肯定有一个是空的队列,因为栈是先入后出,队列是先入先出,这时候就将不空的队列前size-1个元素放入另一个空的队列中 ,最后一个直接出队列就行其最后一个元素就行
top获取栈顶元素 :就利用和pop一样的方法,只是最后的不出队列,只是获取其元素就行】


java
class MyStack {
public Queue<Integer> qu1;
public Queue<Integer> qu2;
//创建两个队列,实例化对象
public MyStack() {
qu1 = new LinkedList<>();
qu2 = new LinkedList<>();
}
//入栈
public void push(int x) {
//都为空,就放入qu1中
if(empty()){
qu1.offer(x);
//放入不为空的那个队列
}else if(!qu1.isEmpty()){
qu1.offer(x);
}else{
qu2.offer(x);
}
}
//出栈
public int pop() {
if(empty()){
return -1;
}
//将不为空的放入为空的前n-1个
//最后将原本不为空的最后一个出栈就行了
if(!qu1.isEmpty()){
int size = qu1.size();
while(size-1!=0){
int val = qu1.poll();
qu2.offer(val);
size--;
}
return qu1.poll();
}else{
int size = qu2.size();
while(size-1!=0){
int val = qu2.poll();
qu1.offer(val);
size--;
}
return qu2.poll();
}
}
//获取栈顶元素
public int top() {
if(empty()){
return -1;
}
int val = -1;
if(!qu1.isEmpty()){
int size = qu1.size();
while(size!=0){
val = qu1.poll();
qu2.offer(val);
size--;
}
}else{
int size = qu2.size();
while(size!=0){
val = qu2.poll();
qu1.offer(val);
size--;
}
}
return val;
}
public boolean empty(){
return qu1.isEmpty()&& qu2.isEmpty();
}
}
c
这里再进行入栈、出栈和获取栈顶元素都要进行是否为空的判断
因为再获取栈顶元素和出栈都要是不为空的栈才可以正常的操作栈实现队列

目的:就是用栈来实现队列
思路:和队列实现栈类似,就是需要两个栈来操作才可以实现其对列的正常功能,这里要使用stack1和stack2这两个栈来操作
push入队列:入队列放到stack1
pop出队列:出队列的话就用stack2,如果stack2为空,stack1不为空,就将stack1的全部数据放入stack2中,再出栈
peek()获取栈顶元素:和pop类似,只是最后是获取元素,而不是出栈



c
1.这里就是用stack1用来入栈,而stack2出栈操作
因为当数据存放再stack1的时候出栈顺序是和Queue是相反的,这时候将stack1的
数据再放入stack2中,这时stack2的出栈顺序就和队列是相同的
2.出栈的时候是先出stack2中的元素,因为队列是遵从先入先出的原则
当stack2为空的时候,再将新入队列的元素放入stack2进行出栈
java
class MyQueue {
Stack<Integer> stack1;
Stack<Integer> stack2;
public MyQueue() {
stack1 = new Stack<>();
stack2 = new Stack<>();
}
//stack1用来入栈
public void push(int x) {
stack1.push(x);
}
//stack2用来出栈
public int pop() {
if(empty()){
return -1;
}
//如果stack2为空,就将stack1中元素放入stack2中
if(stack2.isEmpty()){
while(!stack1.empty()){
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
return stack2.pop();
}
public int peek() {
if(empty()){
return -1;
}
//如果stack2为空,就将stack1中元素放入stack2中
if(stack2.isEmpty()){
while(!stack1.empty()){
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
return stack2.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return stack1.isEmpty()&&stack2.isEmpty();
}
}