题目列表
3550. 数位和等于下标的最小下标
3551. 数位和排序需要的最小交换次数
3552. 网格传送门旅游
3553. 包含给定路径的最小带权子树 II
一、数位和等于下标的最小下标

直接模拟计算数位和即可,代码如下
cpp
// C++
class Solution {
public:
int smallestIndex(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
int x = nums[i], s = 0;
while(x){
s += x % 10;
x /= 10;
}
if(s == i)
return i;
}
return -1;
}
};
python
# Python
class Solution:
def smallestIndex(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
n = len(nums)
for i, x in enumerate(nums):
s = 0
while x:
s += x % 10
x //= 10
if i == s:
return i
return -1二、数位和排序需要的最小交换次数

由于我们可以通过排序得到每个数的最终位置,所以这题就转换成了给你两个元素相同的序列 A、B,要求将 A 通过交换转换成 B 的最小操作次数,通过对需要交换的位置加上有向边进行建图,问题就变成了对给定的有向图,如何使得它们各自成为一个独立的环的操作次数最少

这里有一个结论:最少的交换次数为结点的个数减去环的个数
代码如下(关键就是计算环的个数)
cpp
// C++
class Union{
public:
Union(int n)
:fa(n)
,cnt(n)
{
iota(fa.begin(), fa.end(), 0);
}
void merge(int x, int y){
int fa_x = find(x), fa_y = find(y);
if(fa_x != fa_y){
cnt--;
fa[fa_x] = fa_y;
}
}
int find(int x){
int pa = x;
while(pa != fa[pa]){
pa = fa[pa];
}
while(x != pa){
int tmp = fa[x];
fa[x] = pa;
x = tmp;
}
return pa;
}
int count(){
return cnt;
}
private:
vector<int> fa;
int cnt;
};
class Solution {
public:
int minSwaps(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
vector<array<int, 3>> a(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int s = 0;
for (int x = nums[i]; x > 0; x /= 10) {
s += x % 10;
}
a[i] = {s, nums[i], i};
}
ranges::sort(a);
Union un(n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
un.merge(i, a[i][2]);
}
return n - un.count();
}
};
// 迭代
class Solution {
public:
int minSwaps(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
vector<array<int, 3>> a(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int s = 0;
for (int x = nums[i]; x > 0; x /= 10) {
s += x % 10;
}
a[i] = {s, nums[i], i};
}
ranges::sort(a);
int c = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(a[i][2] < 0) continue;
c++;
int j = i;
while(a[j][2] >= 0){
int nxt = a[j][2];
a[j][2] = -1;
j = nxt;
}
}
return n - c;
}
};三、网格传送门旅游
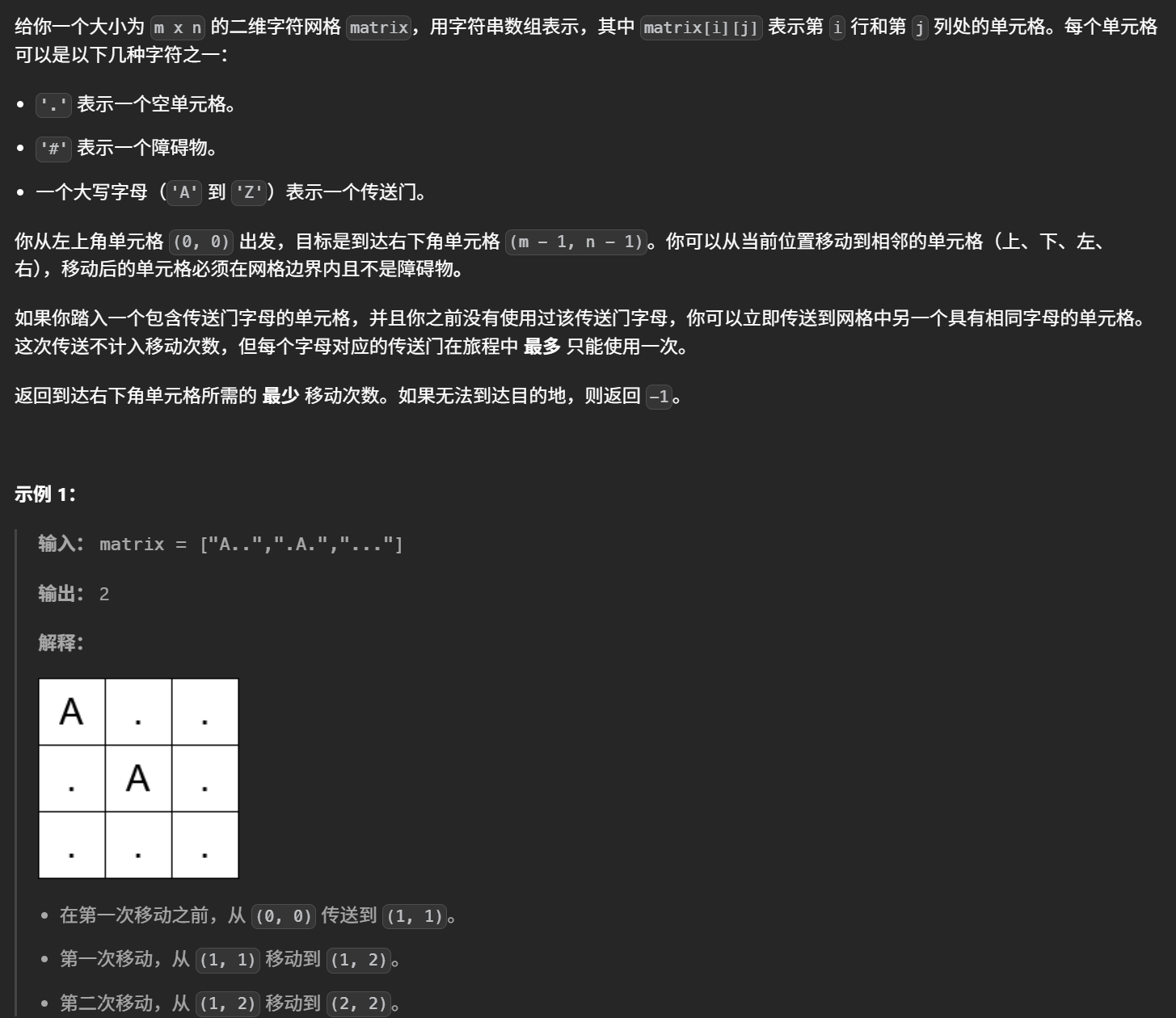
很经典的最短路问题,可以用 Dijkstra算法 来解决,需要注意的每种传送门最多传送一次,重复传送显然是无意义的,A1->A2->A3 不如直接 A1->A3,代码如下
cpp
// C++
class Solution {
static constexpr int dirs[4][2] = {{0,1}, {0,-1}, {1,0}, {-1,0}};
public:
int minMoves(vector<string>& matrix) {
int n = matrix.size(), m = matrix[0].size();
vector<vector<pair<int,int>>> g(26);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < m; j++){
if(isalpha(matrix[i][j])){
g[matrix[i][j] - 'A'].emplace_back(i, j);
}
}
}
priority_queue<tuple<int,int,int>, vector<tuple<int,int,int>>, greater<>> pq;
pq.emplace(0, 0, 0);
vector dist(n, vector<int>(m, INT_MAX));
dist[0][0] = 0;
while(pq.size()){
auto [d, x, y] = pq.top(); pq.pop();
if(x == n - 1 && y == m - 1) return d;
if(d != dist[x][y]) continue;
if(isalpha(matrix[x][y])){
int i = matrix[x][y] - 'A';
for(auto [xi, yi] : g[i]){
if(dist[xi][yi] > d){
dist[xi][yi] = d;
pq.emplace(d, xi, yi);
}
}
g[i].resize(0);
}
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
int xi = x + dirs[i][0], yi = y + dirs[i][1];
if(xi < 0 || xi >= n || yi < 0 || yi >= m || matrix[xi][yi] == '#' || dist[xi][yi] <= d + 1)
continue;
dist[xi][yi] = d + 1;
pq.emplace(d + 1, xi, yi);
}
}
return -1;
}
};
// 0-1 bfs
// 由于本题的距离只有 +0 / +1 两种选项,所以这里可以直接用双端队列模拟优先级队列(堆)
// +0 的距离依旧是队列中最小的距离,所以头插
// +1 的距离会成为最大值,所以尾插,如果不理解,建立手动模拟一下
class Solution {
static constexpr int dirs[4][2] = {{0,1}, {0,-1}, {1,0}, {-1,0}};
public:
int minMoves(vector<string>& matrix) {
int n = matrix.size(), m = matrix[0].size();
vector<vector<pair<int,int>>> g(26);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < m; j++){
if(isalpha(matrix[i][j])){
g[matrix[i][j] - 'A'].emplace_back(i, j);
}
}
}
deque<tuple<int,int,int>> dq;
dq.push_back({0, 0, 0});
vector dist(n, vector<int>(m, INT_MAX));
dist[0][0] = 0;
while(dq.size()){
auto [d, x, y] = dq.front(); dq.pop_front();
if(x == n - 1 && y == m - 1) return d;
if(d != dist[x][y]) continue;
if(isalpha(matrix[x][y])){
int i = matrix[x][y] - 'A';
for(auto [xi, yi] : g[i]){
if(dist[xi][yi] > d){
dist[xi][yi] = d;
dq.push_front({d, xi, yi});
}
}
g[i].resize(0);
}
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
int xi = x + dirs[i][0], yi = y + dirs[i][1];
if(xi < 0 || xi >= n || yi < 0 || yi >= m || matrix[xi][yi] == '#' || dist[xi][yi] <= d + 1)
continue;
dist[xi][yi] = d + 1;
dq.push_back({d + 1, xi, yi});
}
}
return -1;
}
};四、包含给定路径的最小带权子树 II
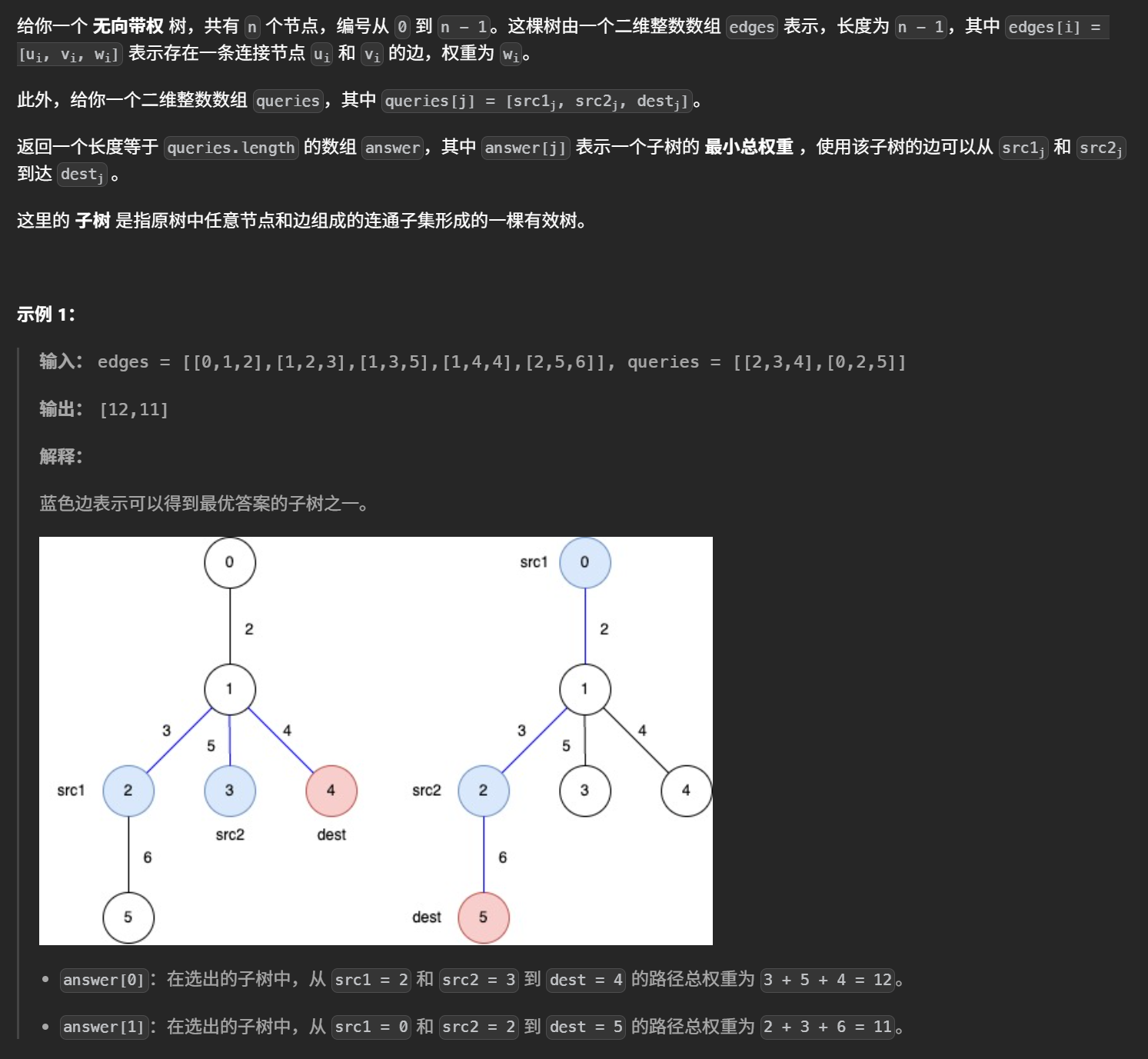
本题要求查询三个结点能够互相到达的最小权重。
思路:
-
两个结点之间能互相到达的最小权重,即两个结点的最短路径,如何求解?假设这两个结点为
A、B,它们的最近公共祖先为fa,则dist(A,B) = dist(A,root) + dist(B,root) - 2*dist(fa, root),其中 dist(x,y) 表示 x 到 y 的距离,而我们很容易得出每个结点到根节点的距离 -
如果是三个结点呢?

显然三点之间的最小权重等于
dist(A,B,C) = [dist(A,B) + dist(B,C) + dist(C, A)] / 2 -
如何求解两个节点的最近公共祖先(LCA)?用树上倍增算法,能在
O(logn)的时间内计算出来
代码如下
cpp
// C++
class LcaBinaryLifting{
vector<int> dist, depth;
vector<vector<int>> pa;
public:
LcaBinaryLifting(vector<vector<int>>& edges){
int n = edges.size() + 1;
int m = bit_width((unsigned) n);
vector<vector<pair<int,int>>> g(n);
for(auto & e : edges){
g[e[0]].emplace_back(e[1], e[2]);
g[e[1]].emplace_back(e[0], e[2]);
}
depth.resize(n);
dist.resize(n);
pa.resize(n, vector<int>(m, -1));
auto dfs = [&](this auto && dfs, int x, int fa, int s, int d)->void{
dist[x] = s;
pa[x][0] = fa;
depth[x] = d;
for(auto [y, w] : g[x]){
if(y != fa){
dfs(y, x, w + s, d + 1);
}
}
};
dfs(0, -1, 0, 0);
for(int j = 1; j < m; j++){
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(pa[i][j-1] != -1){
pa[i][j] = pa[pa[i][j-1]][j-1];
}
}
}
}
int getLCA(int a, int b){
if(depth[a] < depth[b]){
swap(a, b);
}
for(int k = depth[a] - depth[b]; k; k &= k - 1){
a = pa[a][countr_zero((unsigned)k)];
}
if(a == b) return a;
// 处于同一个深度
for(int j = pa[a].size() - 1; j >= 0; j--){
if(pa[a][j] != pa[b][j]){
a = pa[a][j];
b = pa[b][j];
}
}
return pa[a][0];
}
int getDist(int a, int b){
int c = getLCA(a, b);
return dist[a] + dist[b] - dist[c] * 2;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> minimumWeight(vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {
LcaBinaryLifting g(edges);
vector<int> ans(queries.size());
for(int i = 0; i < queries.size(); i++){
int a = queries[i][0], b = queries[i][1], c = queries[i][2];
ans[i] = (g.getDist(a, b) + g.getDist(b, c) + g.getDist(c, a)) / 2;
}
return ans;
}
};
python
# Python
class LcaBinaryLifting:
def __init__(self, edges: List[List[int]]):
n = len(edges) + 1
m = n.bit_length()
g = [[] for _ in range(n)]
for x, y, w in edges:
g[x].append((y, w))
g[y].append((x, w))
depth = [0] * n
dis = [0] * n
pa = [[-1] * m for _ in range(n)]
def dfs(x:int, fa:int)->int:
pa[x][0] = fa
for y, w in g[x]:
if y != fa:
depth[y] = depth[x] + 1
dis[y] = dis[x] + w
dfs(y, x)
dfs(0, -1)
for j in range(m - 1):
for i in range(n):
if pa[i][j] != -1:
pa[i][j+1] = pa[pa[i][j]][j]
self.depth = depth
self.dis = dis
self.pa = pa
def get_kth_ancestor(self, node:int, k:int)->int:
for i in range(k.bit_length()):
if k >> i & 1:
node = self.pa[node][i]
return node
def get_lca(self, x:int, y:int)->int:
if self.depth[x] > self.depth[y]:
x, y = y, x
y = self.get_kth_ancestor(y, self.depth[y] - self.depth[x])
if x == y:
return x
for i in range(len(self.pa[x]) - 1, -1, -1):
px, py = self.pa[x][i], self.pa[y][i]
if px != py:
x, y = py, px
return self.pa[x][0]
def get_dis(self, x:int, y:int)->int:
return self.dis[x] + self.dis[y] - 2 * self.dis[self.get_lca(x, y)]
class Solution:
def minimumWeight(self, edges: List[List[int]], queries: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
g = LcaBinaryLifting(edges)
ans = []
for a, b, c in queries:
ans.append((g.get_dis(a, b) + g.get_dis(a, c) + g.get_dis(b, c))//2)
return ans