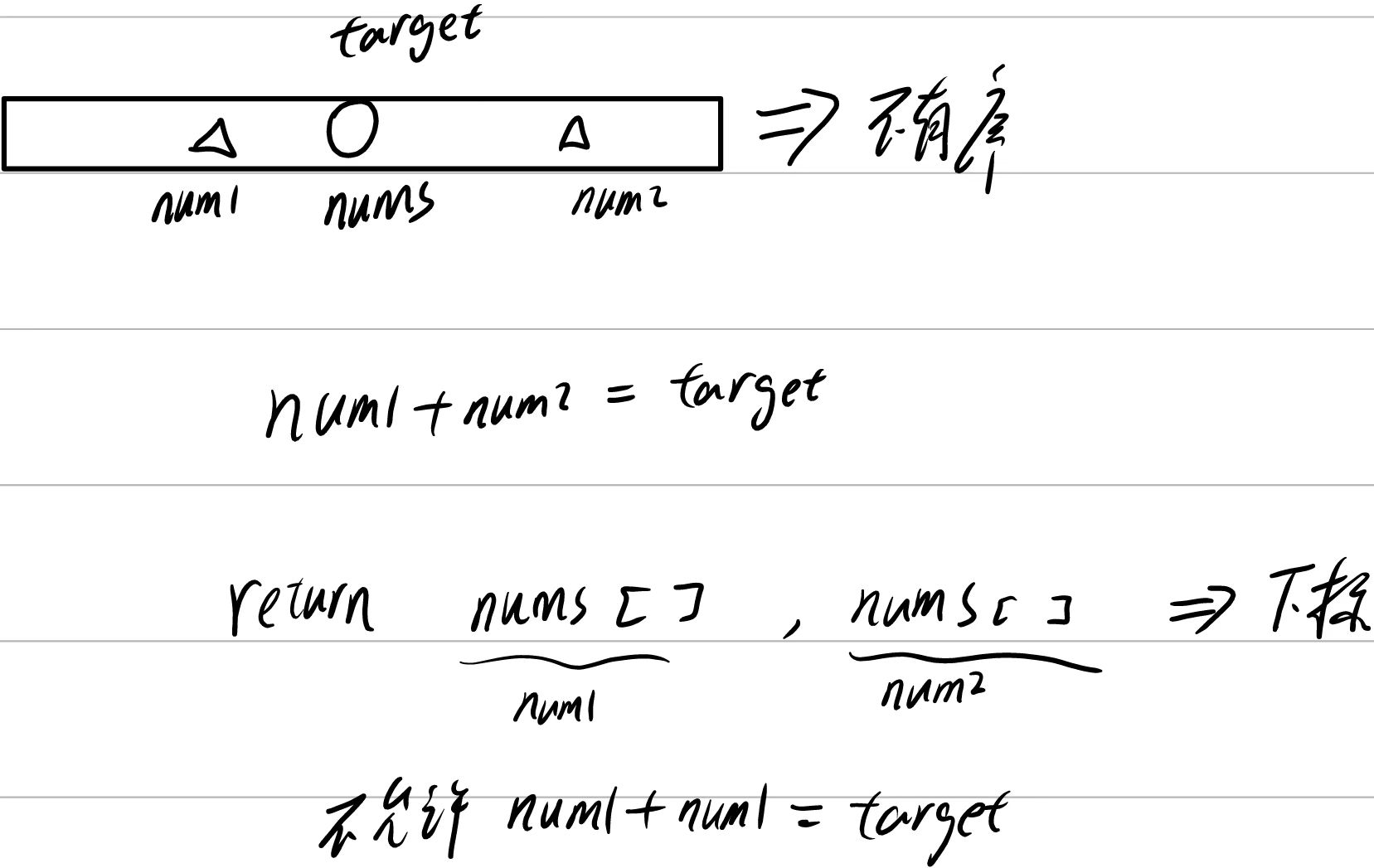
1. 两数之和

自己做
分析
解法1:暴力解
cpp
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
int num1 = 0; //下标
int num2 = 0;
vector<int> s; //保存结果
for(vector<int>::iterator it1 = nums.begin(); it1 != nums.end()-1; it1++){
num2 = num1+1;
for(vector<int>::iterator it2 = it1+1; it2 != nums.end(); it2++){
if(*it1+*it2 == target){
s.push_back(num1);
s.push_back(num2);
return s;
}
num2++;
}
num1++;
}
return {0,0};
}
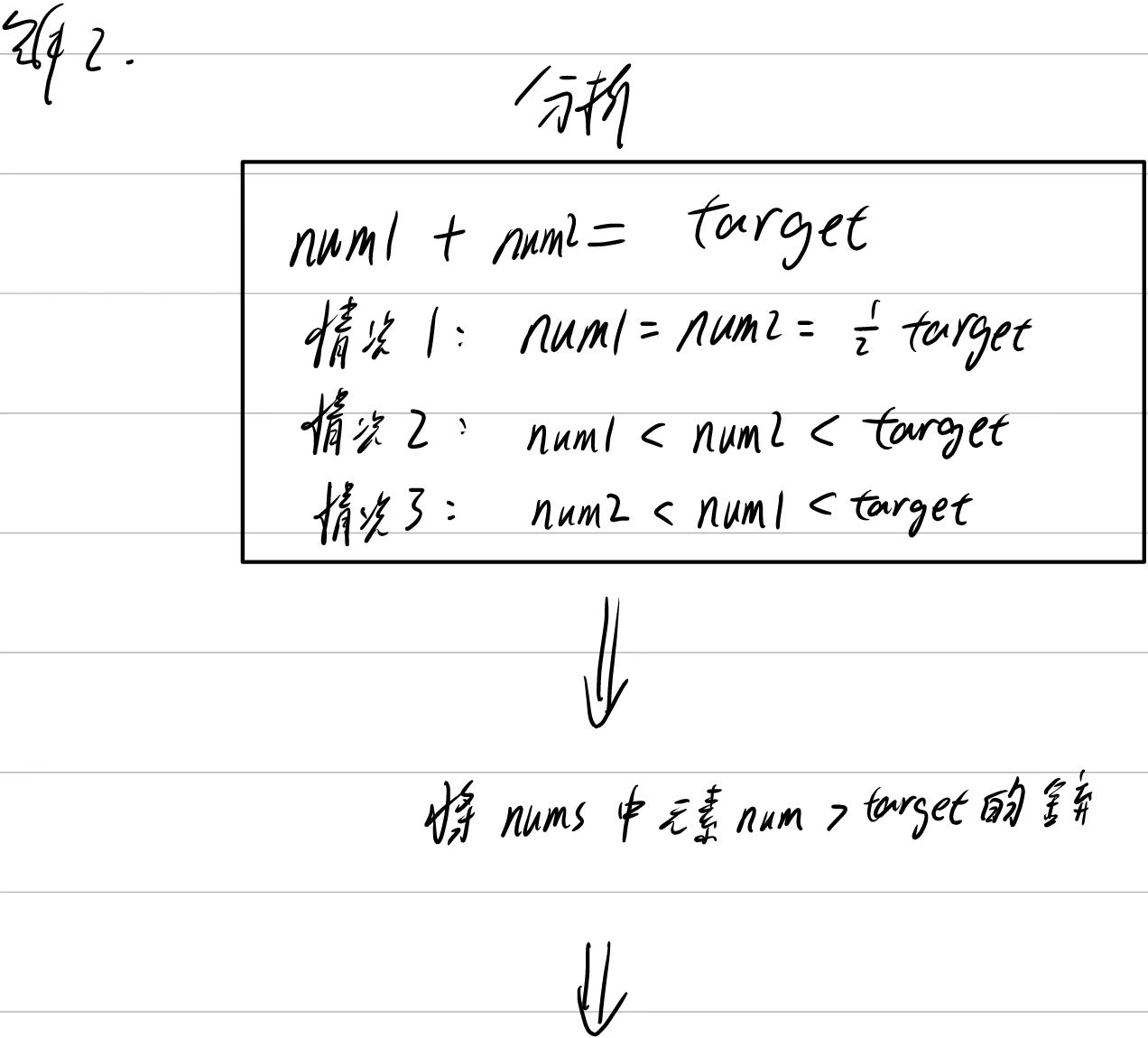
};错误想法
将大于target的部分舍弃缩小数组【没有考虑到有负数的情况】
cpp
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
vector<int> new_nums = nums;
for(vector<int>::iterator it = new_nums.begin(); it != new_nums.end(); ) { //删除比target大的元素
if(*it > target){
it = new_nums.erase(it); //删除,erase会返回下一个迭代器位置
}
else
it++;
}
vector<int> s1; //保存结果【两个数】
for(vector<int>::iterator it1 = new_nums.begin(); it1 != new_nums.end()-1; it1++){
for(vector<int>::iterator it2 = it1+1; it2 != new_nums.end(); it2++){
if(*it1+*it2 == target){
s1.push_back(*it1);
s1.push_back(*it2);
}
}
}
vector<int> s2; //保存结果【寻找下标】
int num = 0;
for(vector<int>::iterator it = nums.begin(); it != nums.end(); it++,num++){
if(*it == s1[0] || *it == s1[1])
s2.push_back(num);
}
return s2;
}
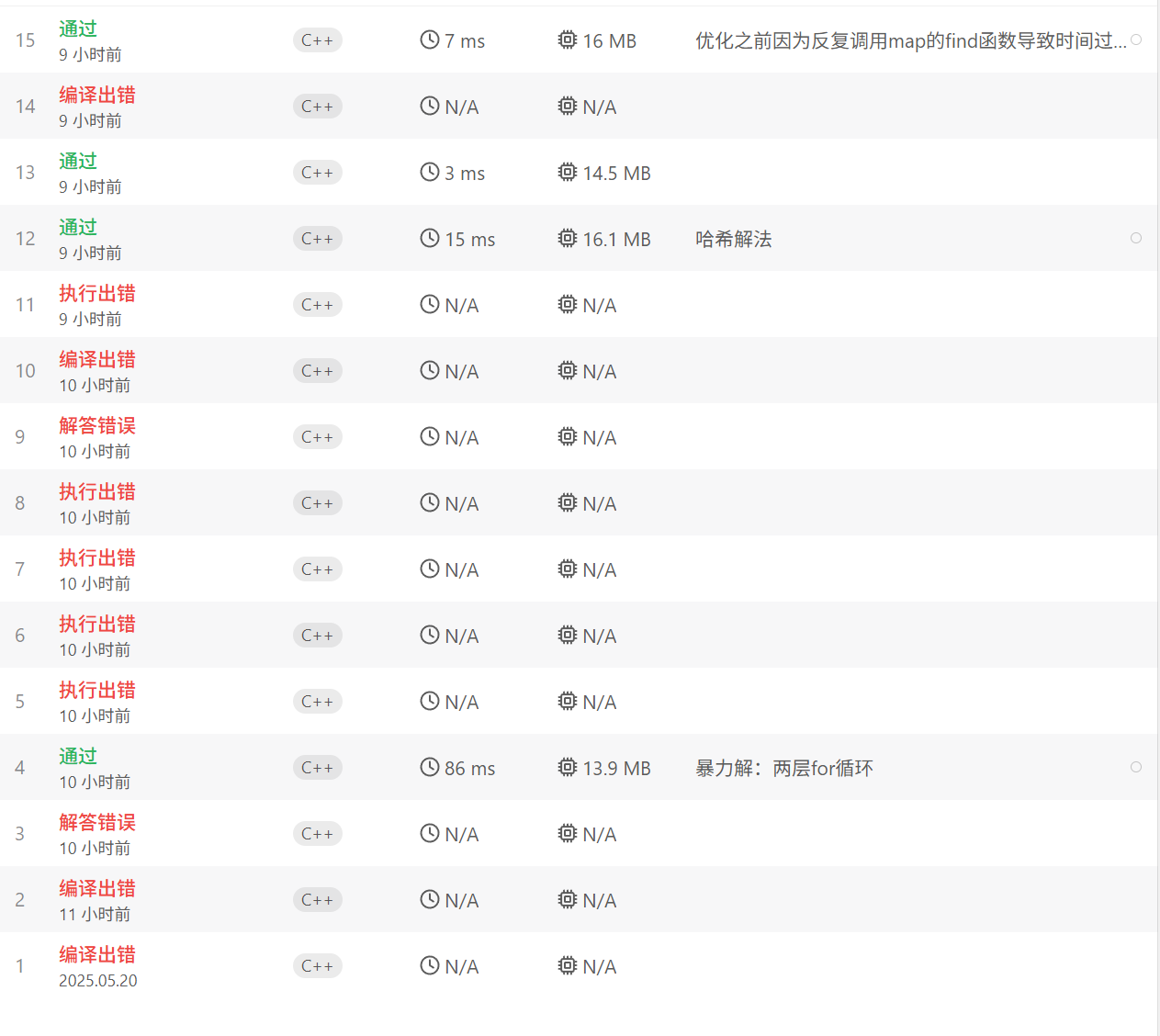
};看题解【想不到】

分析
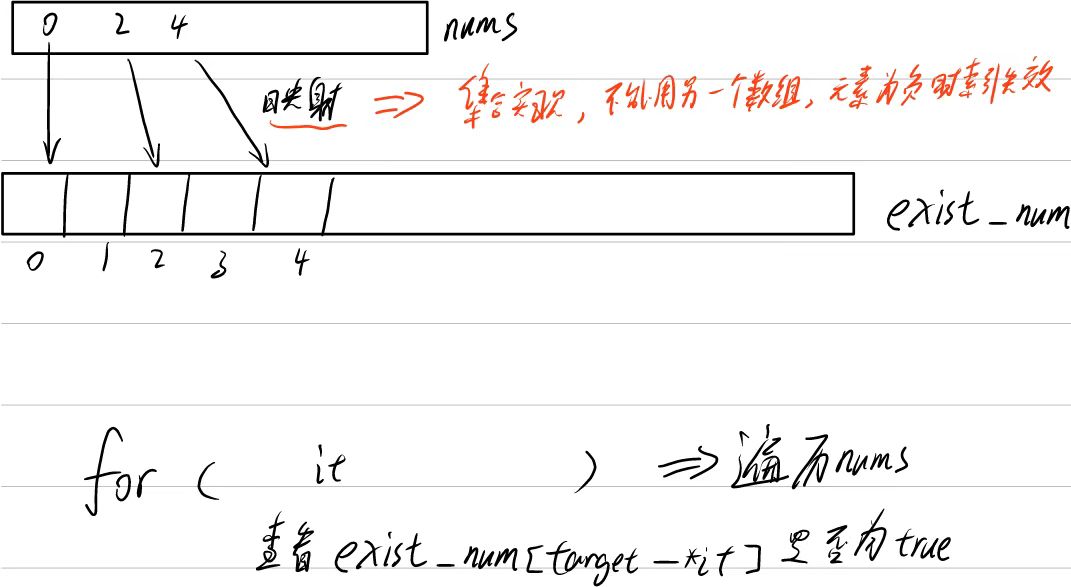
自己写
【注,最好直接用临时变量储存find得到的迭代器,不然反复调用find也很浪费时间】
cpp
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
map<int,int> exist_num;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++){ //映射到哈希表中<key,index>
exist_num[nums[i]] = i;
}
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++){ //查找target-nums[i]是否存在
map<int,int>::iterator index = exist_num.find(target-nums[i]);
if(index != exist_num.end() && i != index->second) //存在并且不是同一元素(下标不一致)
return {index->second,i};
}
return {};
}
};
2. 两数相加
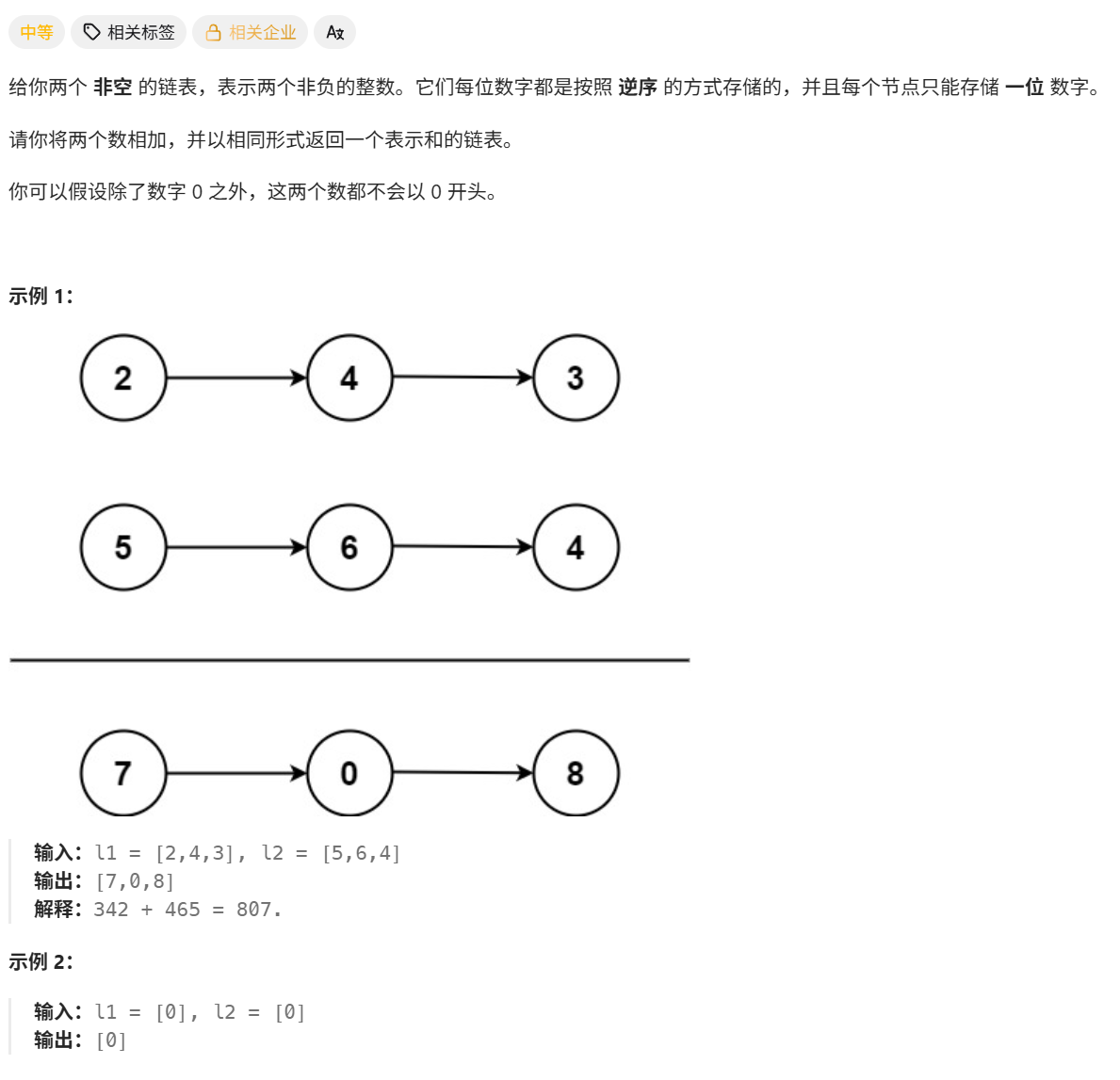
自己做
分析

解
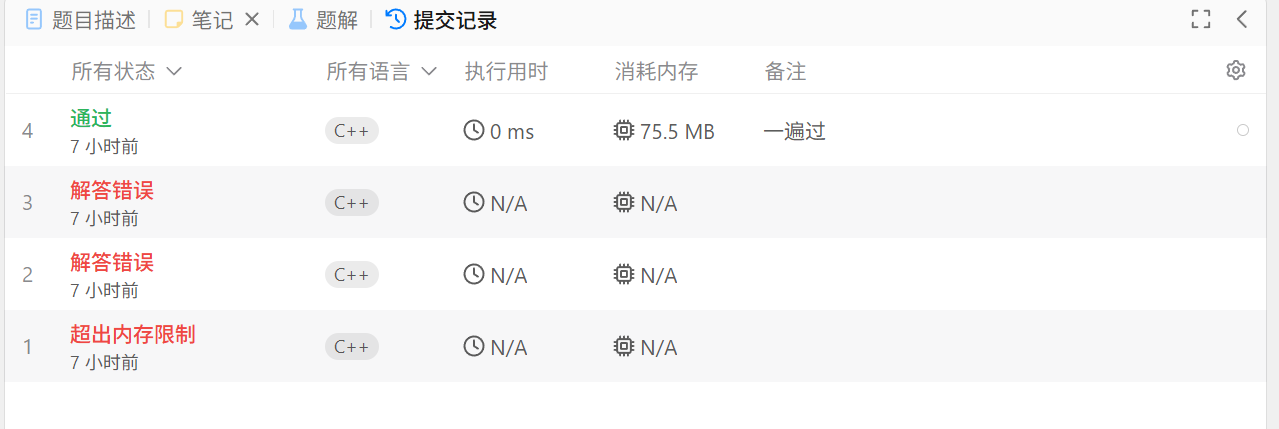
cpp
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
ListNode *p1 = l1,*p2 = l2; //遍历结点
ListNode *p3 = new ListNode((p1->val + p2->val) % 10); //个位相加
int add =(p1->val + p2->val) / 10; //进位
p1 = p1->next;
p2 = p2->next;
ListNode *pr = p3; //尾插用的指针
while(p1 != nullptr || p2 != nullptr){
ListNode *p = nullptr;
if(p1 != nullptr && p2 != nullptr){ //二者都不为空的情况
p = new ListNode((p1->val + p2->val + add) % 10); //创建新节点保存结果:保存余位
add = (p1->val + p2->val + add) / 10; //保存进位
p1 = p1->next;
p2 = p2->next;
}
else if(p1 != nullptr){ //p1不为空、p2为空
p = new ListNode((p1->val + add) % 10); //创建新节点保存结果:保存余位
add = (p1->val + add) / 10; //保存进位
p1 = p1->next;
}
else if(p2 != nullptr){ //p2不为空、p1为空
p = new ListNode((p2->val + add) % 10); //创建新节点保存结果:保存余位
add = (p2->val + add) / 10; //保存进位
p2 = p2->next;
}
pr->next = p; //尾插
pr = pr->next;
}
if(add != 0){ //p1为空、p2为空外还有进位
ListNode *p = new ListNode(add);
pr->next = p; //尾插
pr = pr->next;
}
return p3;
}
};
3. 无重复字符的最长子串

自己做
分析
遗漏点:string也是容器,也可以使用size、begin、end这些(之前的笔记没补上)

解法1:暴力解
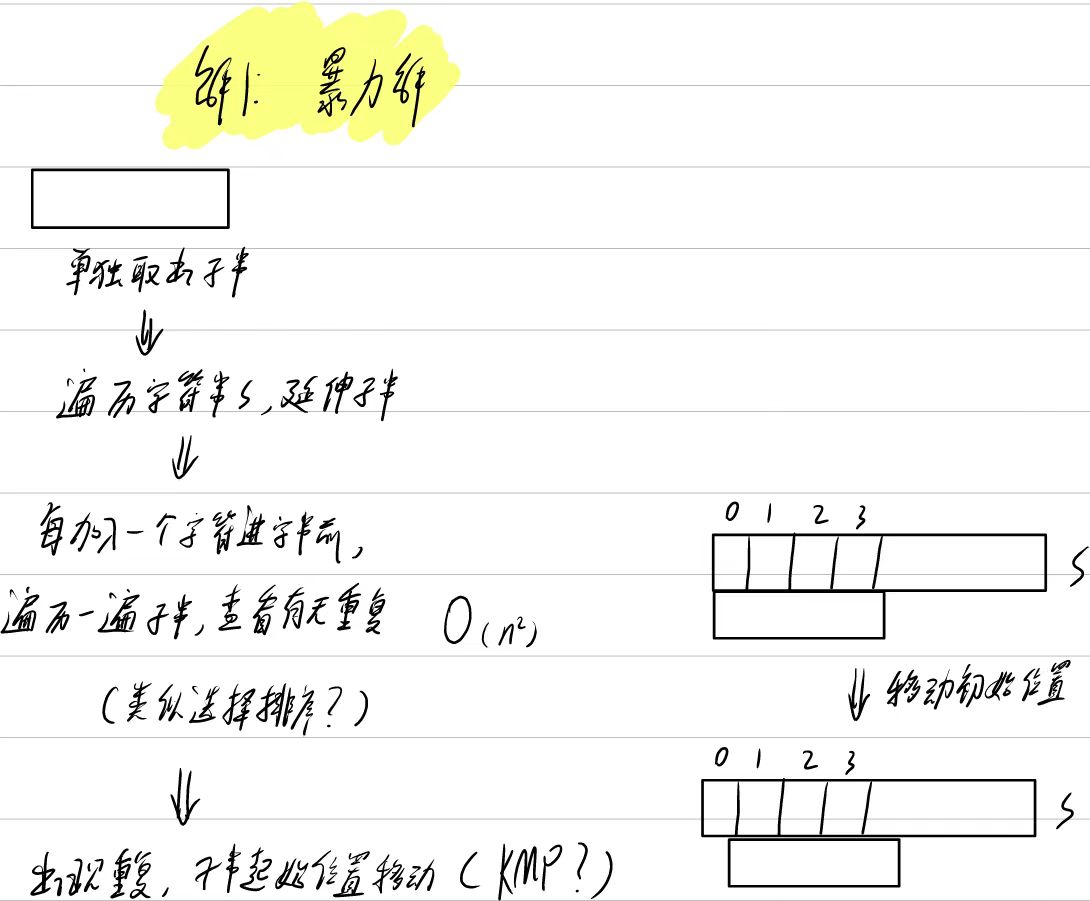
cpp
class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {
int max = 0; //记录最大值
string c; //子串
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {
c = s[i]; //子串起始位置从i开始
bool exist_double = false; //判断是否重复
for (int j = i + 1; j < s.size() && exist_double == false; j++) { //子串扩展
for (int z = 0; z < c.size(); z++) {
if (s[i + c.size()] == c[z]) //子串的下一个字符s[i+c.size()]与子串存在重复
exist_double = true; //存在重复,调整起始位置
}
//不存在重复
if (!exist_double)
c += (s[i + c.size()]); //拼接子串
}
//判断该轮取得的子串大小
if (c.size() > max)
max = c.size();
}
return max; //返回子串大小
}
};解法2:滑动窗口
这里我自己写的还不如暴力解
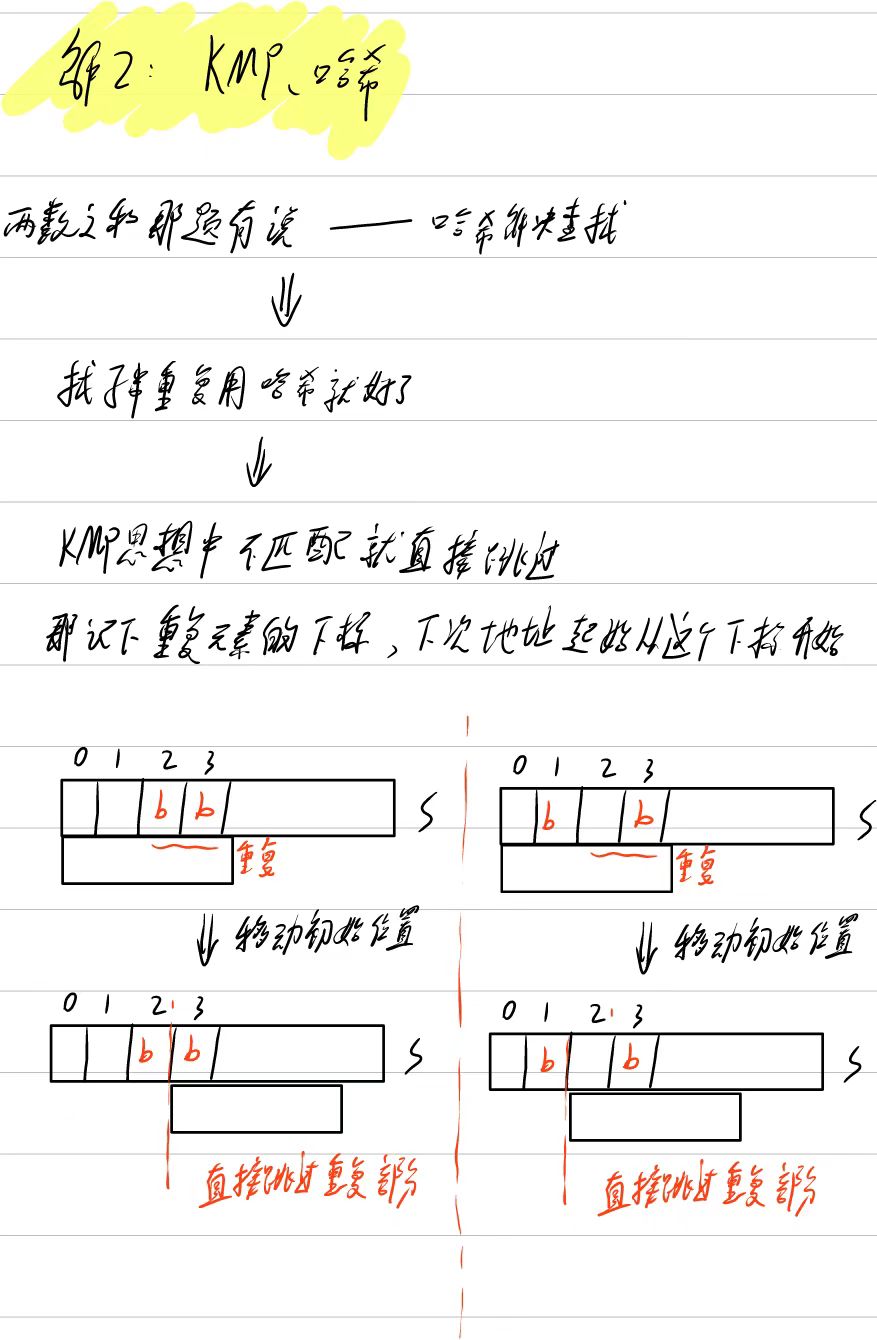
cpp
class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {
int max = 0; //记录最大值
string c; //子串
map<char, int> m; //哈希记录子串<word,index>,其中index为字符串s的下标
int index = 0; //子串c的起始下标
while (index + c.size() < s.size()) {
c = s[index]; //子串起始位置从index开始
m[s[index]]=index; //插入哈希表
for (int j = index + 1; j < s.size(); j++) { //子串扩展
map<char, int>::iterator it = m.find(s[j]); //哈希查找
if (it != m.end()) { //子串的下一个字符s[i+c.size()]与子串存在重复【在哈希表中找到元素】
index = it->second+1; //更改索引,跳出重复值
m.clear(); //清空哈希表
break; //本次查找失败,直接进入下一轮【跳出for循环】
}
else { //不存在重复
c += s[j]; //拼接子串
m[s[j]] = index; //插入哈希表
}
}
//判断该轮取得的子串大小
if (c.size() > max)
max = c.size();
}
return max; //返回子串大小
}
};效率低原因:
嵌套循环结构 和频繁的哈希表清空操作
看题解【敲不出】

知识点unordered_set:
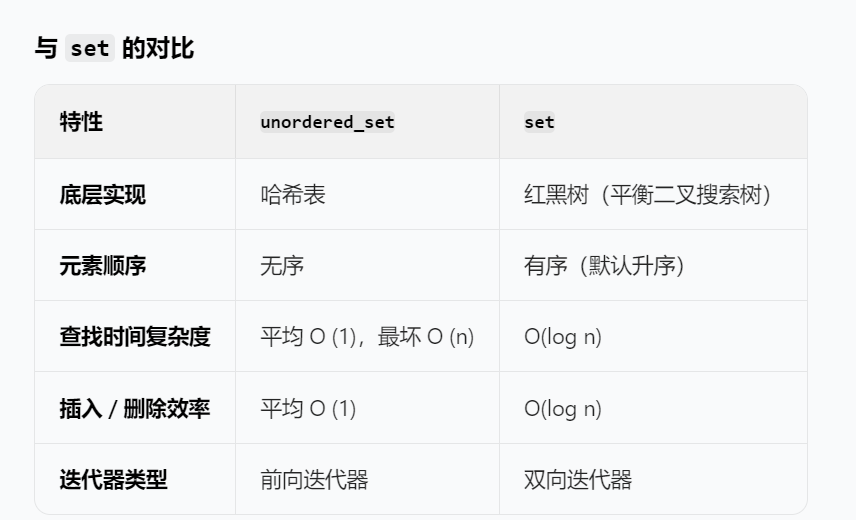
仿写官方思路
cpp
class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {
unordered_set<char> c;
int rear = -1;
int max = 0;
for(int front = 0; front < s.size(); front++){
if(front != 0){ //左指针移动
c.erase(s[front - 1]); //删除移出哈希表的数据
}
while(rear + 1 < s.size() && !c.count(s[rear+1])){
//右指针移动
c.insert(s[rear+1]); //插入哈希表
rear++;
}
if(rear - front + 1 > max)
max = rear - front + 1;
}
return max;
}
};优化自己的实现
cpp
class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {
int max = 0;
unordered_map<char, int> m;
int front = 0, rear = 0; //首位指针
cout << s.size() << endl;
//往哈希表中设置第一个元素
if (s.size() != 0) { //预防空字符串
m[s[rear]] = rear;
max++; //已经添加一个字符进去了,即最大值最小也是1
while (rear < s.size() - 1) {
unordered_map<char, int>::iterator it = m.find(s[rear + 1]); //查看下一个元素是否已经在哈希表中
if (it != m.end()) { //在哈希表中找到元素【有重复】
int old = front; //记录旧位置
front = it->second + 1; //偏移起始位置
//移除窗口以外的值【front偏移了,前面的值都要删除】
for (int i = old; i < front; i++) {
m.erase(s[i]);
}
}
//无重复,或重复问题被front偏移解决
m[s[rear + 1]] = rear + 1; //修改哈希表【重新修改值】
rear++;
if (rear - front + 1 > max)
max = rear - front + 1;
}
}
return max;
}
};【注:这过程中发现了之前都没有注意到的------size()返回的是无符号整数,而int是有符合整数,所以当我设置while循环的时候,往往出现size()返回的是0,结果设置的size()-1就变的极大,同理,设置rear从-1开始,结果rear转为无符号整数后就废了】
今天结束总结
之前做的博客笔记帮大忙了,刚学完的很多都有些忘了,还好之前做好了笔记可以来回翻