1. 导包
python
import numpy as np
import h5py
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from testCases_v2 import *
from dnn_utils_v2 import sigmoid, sigmoid_backward, relu, relu_backward
% matplotlib inline
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (5.0, 4.0) # set default size of plots
plt.rcParams['image.interpolation'] = 'nearest'
plt.rcParams['image.cmap'] = 'gray'
% reload_ext autoreload
% autoreload 2
np.random.seed(1)2. 整体流程图
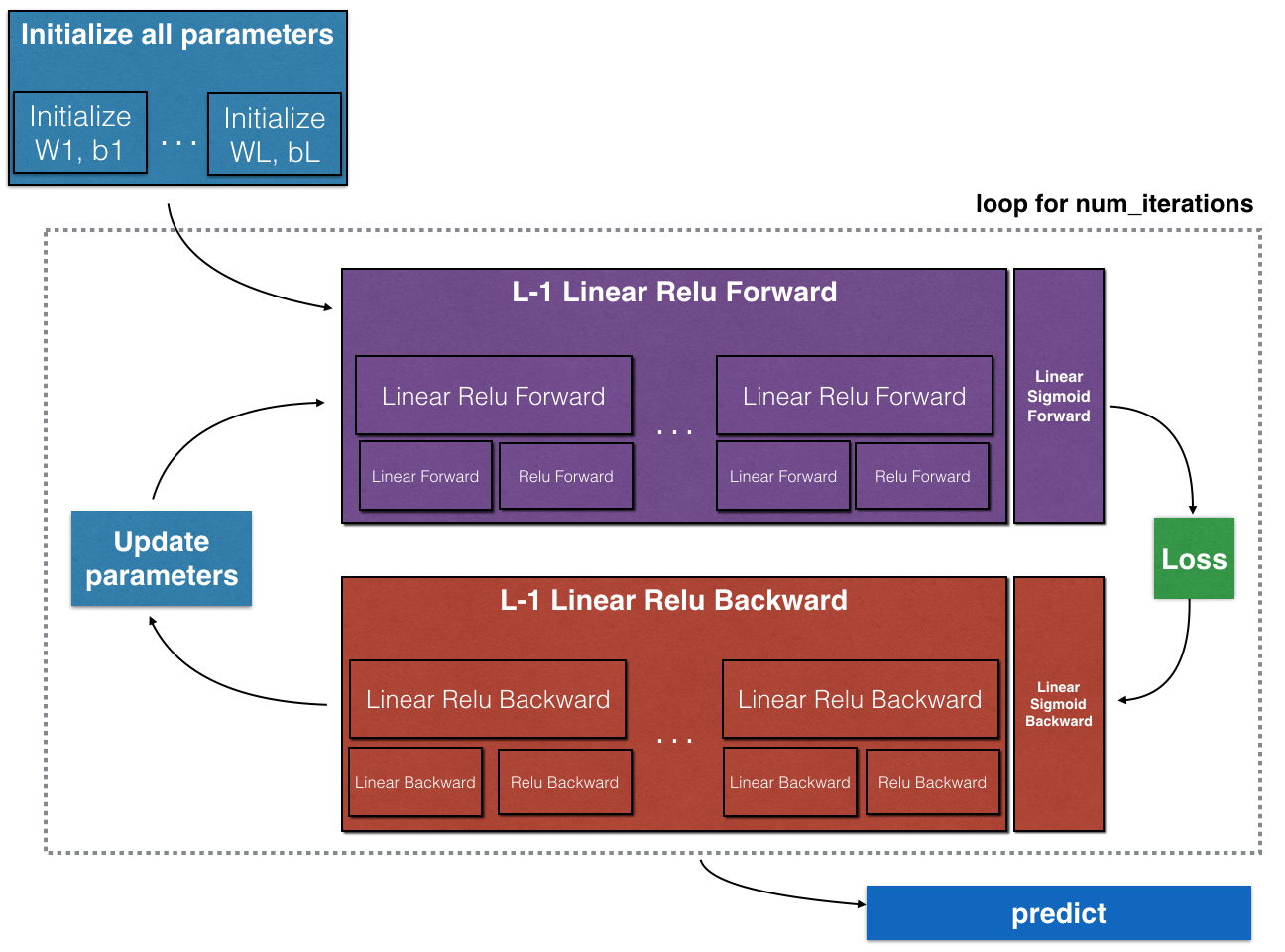
3. 初始化
3.1 创建2层神经网络
python
def initialize_parameters(n_x, n_h, n_y):
"""
Argument:
n_x -- size of the input layer
n_h -- size of the hidden layer
n_y -- size of the output layer
Returns:
parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters:
W1 -- weight matrix of shape (n_h, n_x)
b1 -- bias vector of shape (n_h, 1)
W2 -- weight matrix of shape (n_y, n_h)
b2 -- bias vector of shape (n_y, 1)
"""
np.random.seed(1)
W1 = np.random.randn(n_h, n_x) * 0.01
b1 = np.zeros((n_h, 1))
W2 = np.random.randn(n_y, n_h) * 0.01
b2 = np.zeros((n_y, 1))
parameters = {"W1": W1,
"b1": b1,
"W2": W2,
"b2": b2}
return parameters3.2 隐藏层神经网络
python
def initialize_parameters_deep(layer_dims):
"""
Arguments:
layer_dims -- python array (list) containing the dimensions of each layer in our network
Returns:
parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters "W1", "b1", ..., "WL", "bL":
Wl -- weight matrix of shape (layer_dims[l], layer_dims[l-1])
bl -- bias vector of shape (layer_dims[l], 1)
"""
np.random.seed(3)
parameters = {}
L = len(layer_dims) # number of layers in the network
for l in range(1, L):
parameters['W' + str(l)] = np.random.randn(layer_dims[l], layer_dims[l - 1]) * 0.01
parameters['b' + str(l)] = np.zeros((layer_dims[l], 1))
return parameters4. 前向传播
4.1 线性前向传播
python
def linear_forward(A, W, b):
"""
Implement the linear part of a layer's forward propagation.
Arguments:
A -- activations from previous layer (or input data): (size of previous layer, number of examples)
W -- weights matrix: numpy array of shape (size of current layer, size of previous layer)
b -- bias vector, numpy array of shape (size of the current layer, 1)
Returns:
Z -- the input of the activation function, also called pre-activation parameter
cache -- a python dictionary containing "A", "W" and "b" ; stored for computing the backward pass efficiently
"""
Z = np.dot(W, A) + b
cache = (A, W, b)
return Z, cache4.2 激活函数
python
def linear_activation_forward(A_prev, W, b, activation):
"""
Implement the forward propagation for the LINEAR->ACTIVATION layer
Arguments:
A_prev -- activations from previous layer (or input data): (size of previous layer, number of examples)
W -- weights matrix: numpy array of shape (size of current layer, size of previous layer)
b -- bias vector, numpy array of shape (size of the current layer, 1)
activation -- the activation to be used in this layer, stored as a text string: "sigmoid" or "relu"
Returns:
A -- the output of the activation function, also called the post-activation value
cache -- a python dictionary containing "linear_cache" and "activation_cache";
stored for computing the backward pass efficiently
"""
if activation == "sigmoid":
Z, linear_cache = linear_forward(A_prev, W, b)
A, activation_cache = sigmoid(Z)
elif activation == "relu":
Z, linear_cache = linear_forward(A_prev, W, b)
A, activation_cache = relu(Z)
cache = (linear_cache, activation_cache)
return A, cache隐藏层前向传播
python
# GRADED FUNCTION: L_model_forward
def L_model_forward(X, parameters):
"""
Implement forward propagation for the [LINEAR->RELU]*(L-1)->LINEAR->SIGMOID computation
Arguments:
X -- data, numpy array of shape (input size, number of examples)
parameters -- output of initialize_parameters_deep()
Returns:
AL -- last post-activation value
caches -- list of caches containing:
every cache of linear_relu_forward() (there are L-1 of them, indexed from 0 to L-2)
the cache of linear_sigmoid_forward() (there is one, indexed L-1)
"""
caches = []
A = X
L = len(parameters) // 2
for l in range(1, L):
A_prev = A
A, cache = linear_activation_forward(A_prev, parameters['W' + str(l)], parameters['b' + str(l)],
activation="relu")
caches.append(cache)
AL, cache = linear_activation_forward(A, parameters['W' + str(L)], parameters['b' + str(L)],
activation="sigmoid")
caches.append(cache)
return AL, caches5. 损失函数
python
def compute_cost(AL, Y):
"""
Implement the cost function defined by equation (7).
Arguments:
AL -- probability vector corresponding to your label predictions, shape (1, number of examples)
Y -- true "label" vector (for example: containing 0 if non-cat, 1 if cat), shape (1, number of examples)
Returns:
cost -- cross-entropy cost
"""
m = Y.shape[1]
cost = - np.sum(Y * np.log(AL) + (1 - Y) * np.log(1 - AL)) / m
cost = np.squeeze(cost) # To make sure your cost's shape is what we expect (e.g. this turns [[17]] into 17).
return cost6. 反向传播
6.1 线性反向传播
python
def linear_backward(dZ, cache):
"""
Implement the linear portion of backward propagation for a single layer (layer l)
Arguments:
dZ -- Gradient of the cost with respect to the linear output (of current layer l)
cache -- tuple of values (A_prev, W, b) coming from the forward propagation in the current layer
Returns:
dA_prev -- Gradient of the cost with respect to the activation (of the previous layer l-1), same shape as A_prev
dW -- Gradient of the cost with respect to W (current layer l), same shape as W
db -- Gradient of the cost with respect to b (current layer l), same shape as b
"""
A_prev, W, b = cache
m = A_prev.shape[1]
dW = np.dot(dZ,A_prev.T)/m
db = np.sum(dZ, axis = 1).reshape(dZ.shape[0], 1) / m
dA_prev = np.dot(W.T,dZ)
return dA_prev, dW, db6.2 反向激活函数
python
# GRADED FUNCTION: linear_activation_backward
def linear_activation_backward(dA, cache, activation):
"""
Implement the backward propagation for the LINEAR->ACTIVATION layer.
Arguments:
dA -- post-activation gradient for current layer l
cache -- tuple of values (linear_cache, activation_cache) we store for computing backward propagation efficiently
activation -- the activation to be used in this layer, stored as a text string: "sigmoid" or "relu"
Returns:
dA_prev -- Gradient of the cost with respect to the activation (of the previous layer l-1), same shape as A_prev
dW -- Gradient of the cost with respect to W (current layer l), same shape as W
db -- Gradient of the cost with respect to b (current layer l), same shape as b
"""
linear_cache, activation_cache = cache
if activation == "relu":
dZ = relu_backward(dA, activation_cache)
dA_prev, dW, db = linear_backward(dZ, linear_cache)
elif activation == "sigmoid":
dZ = sigmoid_backward(dA, activation_cache)
dA_prev, dW, db = linear_backward(dZ, linear_cache)
return dA_prev, dW, db6.3 L层神经网络 *
python
# GRADED FUNCTION: L_model_backward
def L_model_backward(AL, Y, caches):
"""
Implement the backward propagation for the [LINEAR->RELU] * (L-1) -> LINEAR -> SIGMOID group
Arguments:
AL -- probability vector, output of the forward propagation (L_model_forward())
Y -- true "label" vector (containing 0 if non-cat, 1 if cat)
caches -- list of caches containing:
every cache of linear_activation_forward() with "relu" (it's caches[l], for l in range(L-1) i.e l = 0...L-2)
the cache of linear_activation_forward() with "sigmoid" (it's caches[L-1])
Returns:
grads -- A dictionary with the gradients
grads["dA" + str(l)] = ...
grads["dW" + str(l)] = ...
grads["db" + str(l)] = ...
"""
grads = {}
L = len(caches) # the number of layers
m = AL.shape[1]
Y = Y.reshape(AL.shape) # after this line, Y is the same shape as AL
dAL = - (np.divide(Y, AL) - np.divide(1 - Y, 1 - AL))
current_cache = caches[L - 1]
grads["dA" + str(L - 1)], grads["dW" + str(L)], grads["db" + str(L)] = linear_activation_backward(dAL, current_cache, 'sigmoid')
for l in reversed(range(L - 1)):
current_cache = caches[l]
dA_prev_temp, dW_temp, db_temp = linear_activation_backward(grads["dA" + str(l + 1)], current_cache, 'relu')
grads["dA" + str(l)] = dA_prev_temp
grads["dW" + str(l + 1)] = dW_temp
grads["db" + str(l + 1)] = db_temp
return grads6.4 更新参数
python
def update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate):
"""
Update parameters using gradient descent
Arguments:
parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters
grads -- python dictionary containing your gradients, output of L_model_backward
Returns:
parameters -- python dictionary containing your updated parameters
parameters["W" + str(l)] = ...
parameters["b" + str(l)] = ...
"""
L = len(parameters) // 2 # number of layers in the neural network
for l in range(L):
parameters["W" + str(l+1)] = parameters["W" + str(l+1)] - learning_rate * grads["dW" + str(l+1)]
parameters["b" + str(l+1)] = parameters["b" + str(l+1)] - learning_rate * grads["db" + str(l+1)]
return parameters7 - Conclusion
Congrats on implementing all the functions required for building a deep neural network!
We know it was a long assignment but going forward it will only get better. The next part of the assignment is easier.
In the next assignment you will put all these together to build two models:
- A two-layer neural network
- An L-layer neural network
You will in fact use these models to classify cat vs non-cat images!
python
# GRADED FUNCTION: L_layer_model
def L_layer_model(X, Y, layers_dims, learning_rate=0.0075, num_iterations=3000, print_cost=False): #lr was 0.009
"""
Implements a L-layer neural network: [LINEAR->RELU]*(L-1)->LINEAR->SIGMOID.
Arguments:
X -- data, numpy array of shape (number of examples, num_px * num_px * 3)
Y -- true "label" vector (containing 0 if cat, 1 if non-cat), of shape (1, number of examples)
layers_dims -- list containing the input size and each layer size, of length (number of layers + 1).
learning_rate -- learning rate of the gradient descent update rule
num_iterations -- number of iterations of the optimization loop
print_cost -- if True, it prints the cost every 100 steps
Returns:
parameters -- parameters learnt by the model. They can then be used to predict.
"""
np.random.seed(1)
costs = [] # keep track of cost
# Parameters initialization.
### START CODE HERE ###
parameters = initialize_parameters_deep(layers_dims)
### END CODE HERE ###
# Loop (gradient descent)
for i in range(0, num_iterations):
# Forward propagation: [LINEAR -> RELU]*(L-1) -> LINEAR -> SIGMOID.
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line of code)
AL, cache = L_model_forward(X, parameters)
### END CODE HERE ###
# Compute cost.
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line of code)
cost = compute_cost(AL, Y)
### END CODE HERE ###
# Backward propagation.
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line of code)
grads = L_model_backward(AL, Y, cache)
### END CODE HERE ###
# Update parameters.
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line of code)
parameters = update_parameters(parameters,grads,learning_rate)
### END CODE HERE ###
# Print the cost every 100 training example
if print_cost and i % 100 == 0:
print("Cost after iteration %i: %f" % (i, cost))
if print_cost and i % 100 == 0:
costs.append(cost)
# plot the cost
plt.plot(np.squeeze(costs))
plt.ylabel('cost')
plt.xlabel('iterations (per tens)')
plt.title("Learning rate =" + str(learning_rate))
plt.show()
return parameters