文章目录
-
- 盒模型:Box-Model。
- [浮动:float 第一种打破文档流的规则的方式](#浮动:float 第一种打破文档流的规则的方式)
- 定位:第二种打破文档流的规则的方式
- 布局
盒模型:Box-Model。
在css中,将任意一个元素,都视作一个盒子(可以层层嵌套)。
总宽度=内容区域宽+左右内边距+左右边框+左右外边距
总高度=内容区高宽+上下内边距+上下边框+上下外边距
在CSS中,所有的HTML元素都可以被看作是一个盒子,这个盒子由内容区、内边距(padding)、边框(border)和外边距(margin)组成。通过盒模型,浏览器能够确定元素的大小以及元素与其他元素之间的间距。
具体来说,盒模型由以下几个部分构成:
1、内容区(Content):这是盒子的核心区域,包含元素的文本、图片等内容。它的大小由元素的 width 和 height 属性决定。
2、内边距(Padding):位于内容区和边框之间的区域。它为内容提供了空白空间,不影响元素的实际大小,但会影响盒子的总体占用空间。
3、边框(Border):包围内边距的边框区域,可以设置不同的宽度、样式和颜色。它会占用空间并影响元素的整体尺寸。
4、外边距(Margin):在元素的边框之外,创建元素之间的间距。外边距不会影响元素的尺寸,但会影响元素的定位。
margin:外边距 ,可以单独分别指定四个方向的边距:
html
margin-left: 10px;
margin-right: 20px;
margin-top: 30px;
margin-bottom: 40px;padding:内边距,也可以单独指定四个方向的。
html
padding-top: 10px;
padding-bottom: 20px;
padding-left: 30px;
padding-right: 40px;写的参数不同,代表的不同:
java
4:上,右,下,左
3:上,左右,下
2:上下,左右
1:上下左右代码示例:
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>盒模型</title>
<style>
.outer{
/* 内容区域 */
width: 300px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
border: 10px solid green;
/* 外边距:margin */
margin:30px;
/* 内边距: */
padding: 30px;
/*四个单独写:分别指定上下左右外边距,每个方向都可以单独指定*/
/* margin-top: 30px;
margin-bottom: 30px;
margin-left: 30px;
margin-right: 30px; */
/*写四个 顺时针方向 上右下左 */
/* margin: 10px 20px 30px 40px; */
/* 写三个 :上 左 右 */
/* margin: 10px 20px 30px; */
/* 写两个 上下 左右 */
/*四个单独写:分别指定上下左右内边距,每个方向都可以单独指定 */
/* padding-top: 20px;
padding-bottom: 20px;
padding-left: 20px;
padding-right: 20px; */
/*分别指定上下左右边框,每个方向都可以单独指定 */
/* border-top: 10px solid green;
border-bottom: 10px solid green;
border-left: 10px solid green;
border-right: 10px solid green; */
/* 边框的宽度、style、color可以直接写四个方向的 */
/* border-width: 10px 10px 10px 10px;
border-style: solid solid solid solid;
border-color: green; */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="outer"></div>
</body>
</html>如何给块元素添加背景图片
background-img
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.outer{
width: 800px;
height: 900px;
background-color: pink;
background-image: url(./imgs/壁纸.jpeg);
/* 平铺模式 */
/* 不平铺 */
background-repeat:no-repeat ;
/* 横向平铺 */
/* background-repeat: repeat-x; */
/* 纵向平铺 */
/* background-repeat: repeat-y; */
/* 大小 宽 高 */
/* 背景图的尺寸 */
/* background-size: 30px 30px; */
/* background-size: auto 50px; */
/* 缩放到背景图片正好能被包含,确保整个背景图片都显示在元素背景中,
以最小边为基础(缩放),图片不会被裁剪,但这可能导致元素中留有空白区域。 */
background-size: contain;
/* 缩放到正好覆盖整个元素背景 */
/* background-size: cover; */
/* 控制位置 */
/* background-position: 10px 100px; */
/* background-position: center; */
/* background-position: 10% center; */
/* 或者 上面四个background合并成一条语句,最常用: */
background: url(imgs/壁纸.jpeg) no-repeat center center
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="outer"></div>
</body>
</html>浮动:float 第一种打破文档流的规则的方式
入门示例:
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>浮动</title>
<style>
.d1{
width:10px;
height: 20px;
background-color: pink;
}
.d2{
width:30px;
height: 40px;
background-color: green;
}
.d3{
width:35px;
height: 45px;
background-color: yellow;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="d1"></div>
<div class="d2"></div>
<div class="d3"></div>
</body>
</html>如上示例代码我们写了三个盒子,div是块元素,要占满一整行的,显示效果如下:
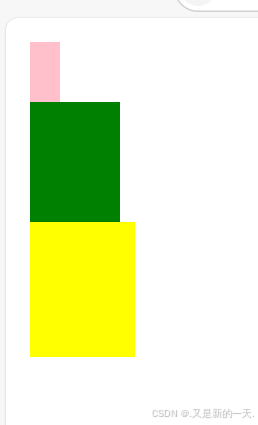
上述效果其实就是文档流的默认规则
文档流的默认规则:
1.块元素从下向右排列,独占一行。
2.行内元素从左右排列,无大小。
打破文档流的默认规则:
比如我们想要两个框并列,就需要打破文档流的默认规则,采用的方式:浮动
浮动:float,浮动顺序与声明的顺序无关,与boday里面的结构有关
给上述代码每个盒子部分里面添加浮动,代码如下:
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>浮动</title>
<style>
.d1{
width:10px;
height: 20px;
background-color: pink;
/* 添加浮动,向左浮动 */
float: left;
}
.d2{
width:30px;
height: 40px;
background-color: green;
float: left;
}
.d3{
width:35px;
height: 45px;
background-color: yellow;
float: left;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="d1"></div>
<div class="d2"></div>
<div class="d3"></div>
</body>
</html>浮动的意义:打破文档流的默认规则
浮动的缺点(副作用):
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>浮动</title>
<style>
.d1{
width:10px;
height: 20px;
background-color: pink;
/* 添加浮动,向左浮动 */
float: left;
}
.d2{
width:30px;
height: 40px;
background-color: green;
float: left;
}
.d3{
width:35px;
height: 45px;
background-color: yellow;
float: left;
}
.d4{
width: 10px;
height: 10px;
background-color: blueviolet;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="d1"></div>
<div class="d2"></div>
<div class="d3"></div>
<div class="d4"></div>
</body>
</html>我们加入第四个盒子,不设置浮动,则遵循默认文档流规则,前三个盒子相当于浮动起来了,相当于浮动起来的把没有浮动的盖住了。
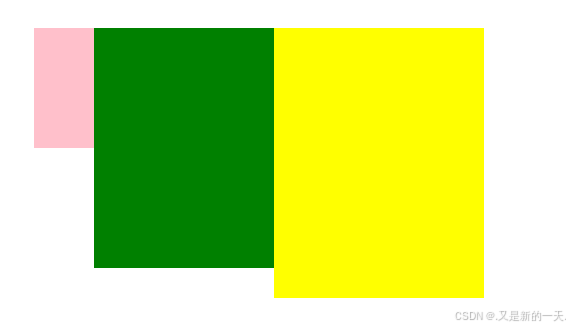
右键检查,会发现是存在我们新建立的第四个盒子的,只是被盖住了:

实际开发中,这通常不是我们想要的效果。我们通常会需要在下一行继续显示,解决上述浮动副作用的办法:
清除浮动:clear
清除浮动的三个规则:
1.必须使用块元素。(用div最好,因为他本身没有任何样式)
2.必须在所有浮动元素的后面。
3.必须和浮动元素是兄弟
代码示例:
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>浮动</title>
<style>
.d1{
width:10px;
height: 20px;
background-color: pink;
/* 添加浮动,向左浮动 */
float: left;
}
.d2{
width:30px;
height: 40px;
background-color: green;
float: left;
}
.d3{
width:35px;
height: 45px;
background-color: yellow;
float: left;
}
.d4{
width: 20px;
height: 20px;
background-color: blueviolet;
}
.clear{
clear: both;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="d1"></div>
<div class="d2"></div>
<div class="d3"></div>
<div class="clear"></div>
<div class="d4"></div>
</body>
</html>显示结果:

浮动应用实例---横向菜单
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>横向菜单</title>
<style>
.nav {
/* 列表的格式类型设置成空 */
list-style-type: none;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
/* 将nav下面的li向左浮动,实现横向排布 */
.nav>li {
float: left;
background-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5);
padding: 8px 20px;
}
/* 设置鼠标悬停效果 */
.nav>li:hover {
background-color: chocolate;
}
/* 设置超链接的装饰和颜色 */
.nav>li>a {
text-decoration: none;
color: #fff;
}
/* 清浮动的另外一种"完美方式" */
.nav::after {
content: "";
/* display:表示将元素显示成什么格式 */
display: block;
clear: both;
width: 0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<ul class="nav">
<li><a href="#">首页</a></li>
<li><a href="#">设备列表</a></li>
<li><a href="#">产品列表</a></li>
<li><a href="#">公司介绍</a></li>
<li><a href="#">关于我们</a></li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>展示效果:
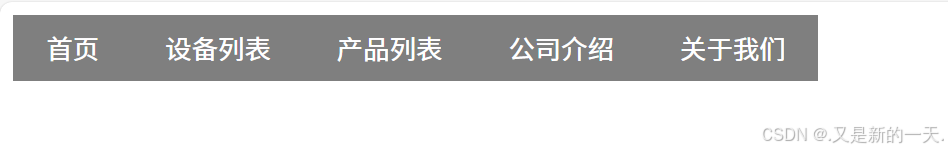
display:表示将元素显示成什么格式
定位:第二种打破文档流的规则的方式
position:
1.static:静态定位,不定位,默认文档流(没啥用)
2.absolute: 绝对定位。上下左右:top、left、right、bottom
3.relative:相对定位
4.fixed:固定定位
定位的参照物:
1.绝对定位:最近的祖先元素中,非static定位的元素。如果没有,则以body为参照。
2.相对定位:以其自身未偏移前的位置为参照物。
3.固定定位:以用户的视区为参照物。
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.outer {
width: 140px;
height: 140px;
background-color: pink;
/* position: absolute; 用于定位
下面四个用于指定具体的位置:
在有尺寸的情况下这四个不能同时生效,只能有两个生效,左上/右下/左下..这种...
具体生效几个取决于我们自己,如果指定了宽高,只能两个生效
如果把高度和宽度去掉,那么四个方位都能生效
top:200px;
left:100px;
right:100px;
bottom:100px;
*/
margin-top: 200px;
margin-left: 100px;
}a
.inner {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: gold;
position: fixed;
top: 20px;
left: 30px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="outer">
<div class="inner"></div>
</div>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
<p>段落</p>
</body>
</html>布局
一个html页面的设计编写过程,就是布局的过程。
圣杯布局
上下左右,可以根据自己的需要删减。

html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>圣杯布局</title>
<style>
/* 整个页面,占满可视区域 */
html,body{
height: 100%;
margin: 0;
}
/* 布局,div默认占满一整行,所有只设置height即可 */
.layout{
height: 100%;
}
/* 设置上部 */
.header{
height: 100px;
background-color: pink;
}
/* 设置中 */
.center{
/* 计算中间的高度:可视区域100%-上部区域-下部区域,-两边必须有空格 */
height: calc(100% - 200px);
background-color:aquamarine;
}
/* 设置下 */
.footer{
height: 100px;
background-color: violet;
}
/* 中间的div水平排序:浮动 */
.center>div{
float:left;
}
/* 清除浮动 */
.center::after{
content: "";
display: block;
clear: both;
width: 0;
}
/* 设置中间部分的左、中、右 */
.center>.lft{
width: 120px;
height: 100%;
background-color: aqua;
}
.center>.rgt{
width: 200px;
height: 100%;
background-color: gold;
}
.center>.main{
width: calc(100% - 320px);
height: 100%;
background-color: blueviolet;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="layout">
<!-- 上 -->
<div class="header"></div>
<!-- 中 -->
<div class="center">
<!-- 中又分成左中右: -->
<div class="lft"></div>
<div class="main"></div>
<div class="rgt"></div>
</div>
<!-- 下 -->
<div class="footer"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>实现效果:上、(左中右)、下
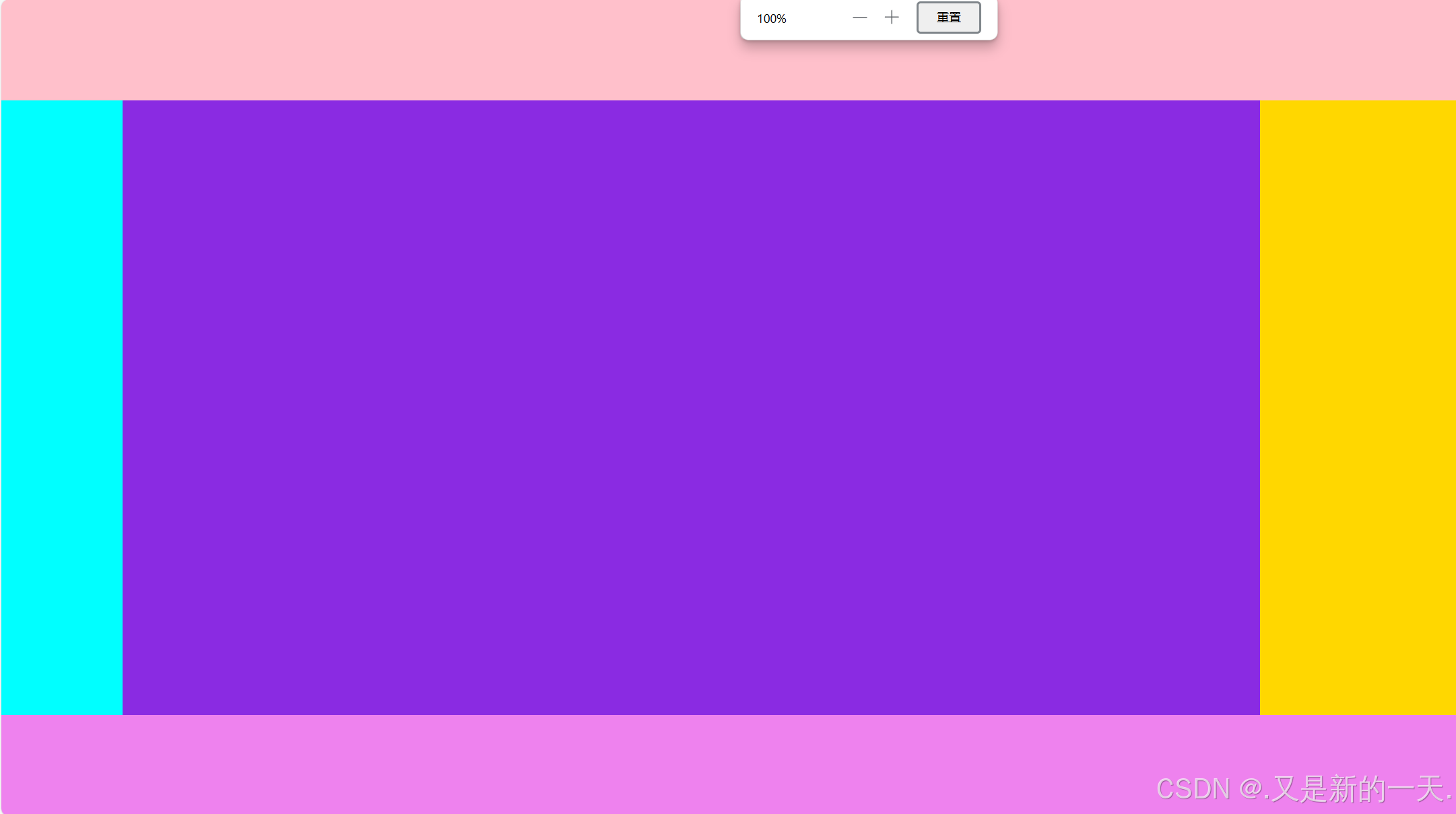
可以根据自己需要删减。
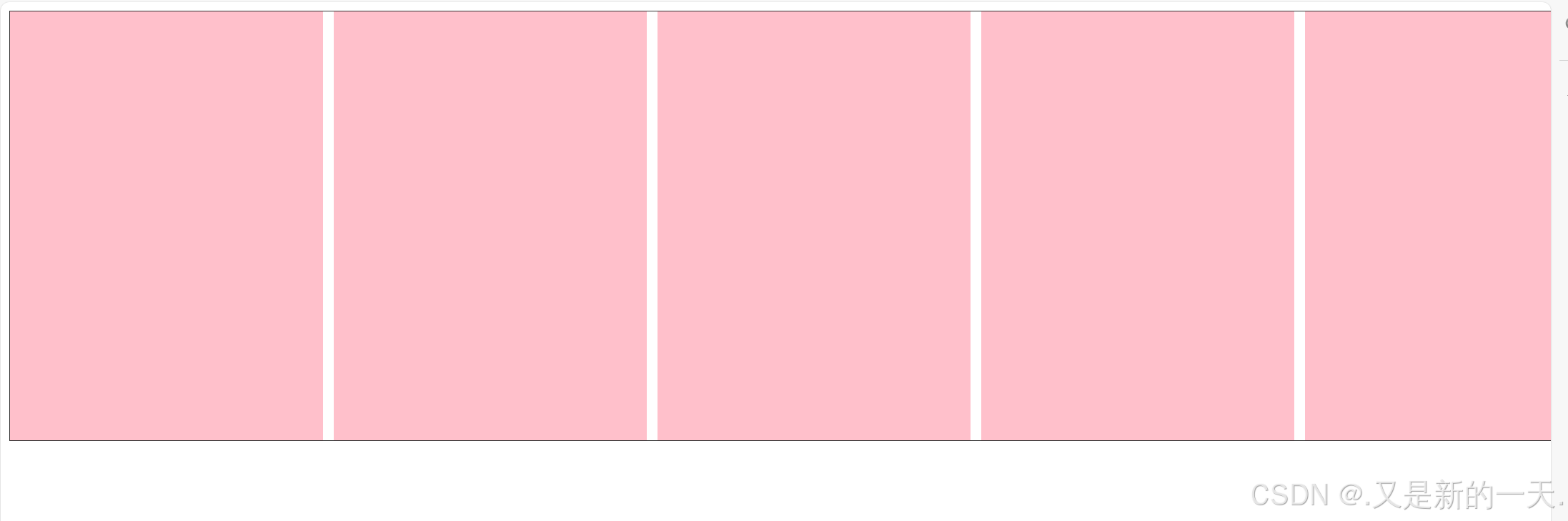
等分布局(很常见)
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>等分布局</title>
<style>
.outer {
width: 1500px;
height: 400px;
border: 1px solid #333;
margin: 0 auto;
}
/* 向左浮动 */
.outer>.item {
float: left;
background-color: pink;
/*五等分 */
width: calc(20% - 8px);
height: 100%;
margin-right: 10px;
}
.outer>.item:last-child {
margin-right: 0;
}
/* 清除浮动 */
.outer::after {
content: "";
display: block;
clear: both;
width: 0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="outer">
<div class="item"></div>
<div class="item"></div>
<div class="item"></div>
<div class="item"></div>
<div class="item"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>实现效果如下: