在 JavaScript 中,内置对象(Built-in Objects)是指由 ECMAScript 标准定义、浏览器或 JavaScript 引擎自带的对象,无需额外引入即可直接使用。这些对象提供了丰富的功能,涵盖数据处理、DOM 操作、日期处理等多个领域。
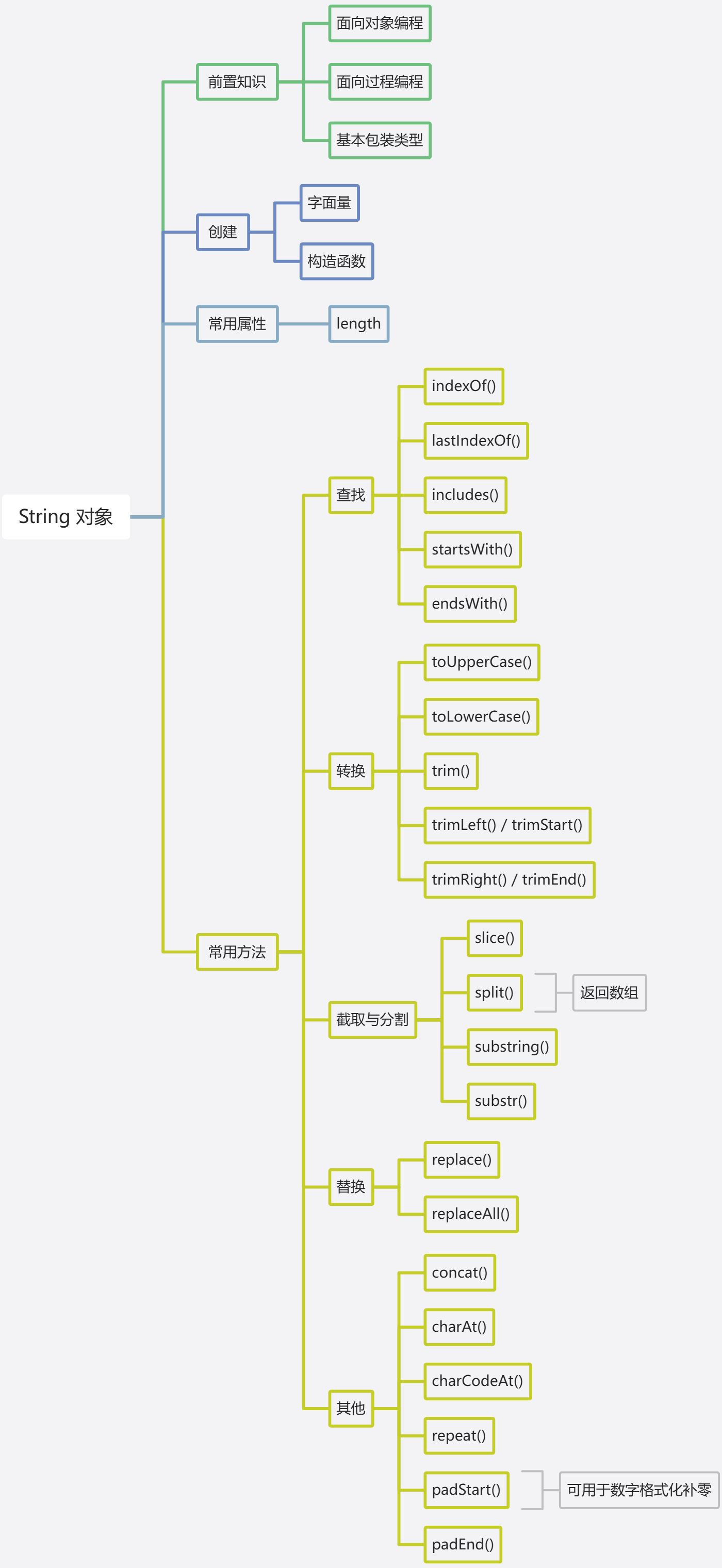
JavaScript中一共有26个内置对象,本章主要介绍 - String对象。
在开始之前需要了解的概念
面向对象编程(OOP)
定义:一种以 "对象" 为中心的编程思想,将数据(属性)和操作数据的方法封装在对象中,注重 "做什么"(目标)而非 "怎么做"(步骤)。
核心特性:
- 封装:将属性和方法封装在对象中,隐藏内部细节。
- 继承:子类可复用父类的属性和方法(减少重复代码)。
- 多态:不同对象对同一方法可有不同实现(增强灵活性)。
示例(用对象封装圆的功能):
javascript
// 面向对象:用类封装属性和方法
class Circle {
// 构造函数:初始化属性
constructor(radius) {
this.radius = radius; // 数据(属性)
}
// 方法:操作数据
calculateArea() {
return Math.PI * this.radius **2;
}
calculateCircumference() {
return 2 * Math.PI * this.radius;
}
}
// 使用:创建对象(实例)
const circle = new Circle(5);
console.log("面积:", circle.calculateArea());
console.log("周长:", circle.calculateCircumference());面向过程编程(POP)
定义:一种以 "过程" 为中心的编程思想,通过一步步编写函数(过程)实现功能,注重 "怎么做"(步骤)。
特点:
- 代码按步骤拆分,用函数实现独立功能。
- 数据与函数分离,函数通过参数接收数据并处理。
- 适合简单逻辑,代码直观但可复用性差。
示例(计算圆的面积和周长):
javascript
// 面向过程:按步骤编写函数
function calculateArea(radius) {
return Math.PI * radius * radius;
}
function calculateCircumference(radius) {
return 2 * Math.PI * radius;
}
// 使用
const r = 5;
console.log("面积:", calculateArea(r));
console.log("周长:", calculateCircumference(r));JavaScript中的基本包装类型(Primitive Wrapper Types)
JavaScript 中,基本数据类型(<font style="color:rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.85) !important;">string</font>、<font style="color:rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.85) !important;">number</font>、<font style="color:rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.85) !important;">boolean</font>)本身不是对象,但为了让它们能使用对象的方法(如 <font style="color:rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.85) !important;">str.trim()</font>),JS 引擎在后台创建了临时对象,这些对象称为 "基本包装类型"。
原理:
当基本类型调用方法时,JS 会自动完成以下步骤:
- 创建对应的包装对象(如
<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">new String(str)</font>)。 - 调用包装对象的方法。
- 立即销毁包装对象。
javascript
const str = "hello";
str.toUpperCase(); // "HELLO"
// 等价于:
const temp = new String("hello"); // 临时包装对象
temp.toUpperCase(); // "HELLO"
temp = null; // 销毁临时对象三种基本包装类型:
- String : 对应
<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">string</font>类型,如<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">new String("abc")</font>。 - Number : 对应
<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">number</font>类型,如<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">new Number(123)</font>。 - Boolean : 对应
<font style="color:rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.85) !important;">boolean</font>类型,如<font style="color:rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.85) !important;">new Boolean(true)</font>。
注意事项:
- 基本类型与包装对象的区别:
javascript
const str1 = "hello"; // 基本类型(string)
const str2 = new String("hello"); // 包装对象(object)
console.log(str1 === str2); // false(类型不同)- 避免手动创建包装对象:这可能会导致类型判断错误(如
<font style="color:rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.85) !important;">typeof new String("a")</font>为<font style="color:rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.85) !important;">object</font>,而非<font style="color:rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.85) !important;">string</font>)。
内置对象 - String
<font style="color:rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.85);">String</font> 是 JavaScript 中处理文本数据的内置对象,用于创建和操作字符串。
它既是基本数据类型(<font style="color:rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.85);">string</font>)的包装对象,也提供了丰富的方法处理字符串。
String 对象的创建
- 字面量形式(推荐):直接使用单引号、双引号或反引号定义,实际是基本数据类型。
javascript
const str1 = "hello"; // 基本类型 string
const str2 = `world`; // 模板字符串(支持换行和变量插入)- 构造函数形式 :通过
<font style="color:rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.85);">new String()</font>创建,返回对象类型。
javascript
const strObj = new String("hello"); // 引用类型 object
console.log(typeof strObj); // "object"String 对象的常用属性
- 属性 :
<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">length</font> - **功能:**返回字符串的长度(字符数量)。
- 示例
javascript
const str = "hello";
console.log(str.length); // 5
const emptyStr = "";
console.log(emptyStr.length); // 0String对象的常用方法
查找与判断方法
- indexOf(searchValue, fromIndex)]
- 功能 :从
<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">fromIndex</font>(默认 0)开始,查找<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">searchValue</font>首次出现的索引,未找到返回<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">-1</font>。 - 示例 :
javascript
const str = "hello world";
console.log(str.indexOf("o")); // 4(首次出现的索引)
console.log(str.indexOf("o", 5)); // 7(从索引5开始查找)
console.log(str.indexOf("xyz")); // -1(未找到)- lastIndexOf(searchValue, fromIndex)
- 功能 :从
<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">fromIndex</font>(默认字符串末尾)开始,反向查找<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">searchValue</font>最后一次出现的索引。 - 示例 :
javascript
const str = "hello world";
console.log(str.lastIndexOf("o")); // 7(最后一次出现的索引)- includes(searchValue, fromIndex)
- 功能 :判断字符串是否包含
<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">searchValue</font>,返回布尔值。 - 示例 :
javascript
const str = "hello";
console.log(str.includes("ll")); // true
console.log(str.includes("xyz")); // false
console.log(str.includes("e", 2)); // false(从索引2开始不包含"e")- startsWith(searchValue, fromIndex)
- 功能 :判断字符串是否以
<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">searchValue</font>开头(从<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">fromIndex</font>位置开始算)。 - 示例 :
javascript
const str = "hello world";
console.log(str.startsWith("hello")); // true
console.log(str.startsWith("world", 6)); // true(从索引6开始以"world"开头)- endsWith(searchValue, fromIndex)
- 功能 :判断字符串是否以
<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">searchValue</font>结尾(<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">length</font>可选,指定字符串的前<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">length</font>个字符)。 - 示例 :
javascript
const str = "hello world";
console.log(str.endsWith("world")); // true
console.log(str.endsWith("hello", 5)); // true(前5个字符是"hello")转换与格式化方法
- toUpperCase()
- 功能:将字符串转换为大写。
- 示例 :
javascript
const str = "Hello World";
console.log(str.toUpperCase()); // "HELLO WORLD"- toLowerCase()
- 功能:将字符串转换为小写。
- 示例 :
javascript
console.log(str.toLowerCase()); // "hello world"- trim()
- 功能 :去除字符串首尾的空格(包括换行符
<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">\n</font>、制表符<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">\t</font>等空白字符)。 - 示例 :
javascript
const str = " hello \n";
console.log(str.trim()); // "hello"(首尾空白被移除)- trimStart() / trimLeft()
- 功能:仅去除字符串开头的空白。
- 示例 :
javascript
console.log(str.trimStart()); // "hello \n"(仅开头空白被移除)- trimEnd() / trimRight()
- 功能:仅去除字符串结尾的空白。
- 示例 :
javascript
console.log(str.trimEnd()); // " hello"(仅结尾空白被移除)截取与分割方法
- slice(startIndex, endIndex)
- 功能 :截取从
<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">startIndex</font>到<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">endIndex</font>(不包含<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">endIndex</font>)的子串,支持负数索引(从末尾计算)。 - 示例 :
javascript
const str = "abcdef";
console.log(str.slice(1, 4)); // "bcd"(索引1到3)
console.log(str.slice(2)); // "cdef"(从索引2到末尾)
console.log(str.slice(-3)); // "def"(从倒数第3个到末尾)- substring(startIndex, endIndex)
- 功能 :类似
<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">slice</font>,但不支持负数索引,且<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">startIndex</font>大于<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">endIndex</font>时会自动交换。 - 示例 :
javascript
console.log(str.substring(4, 1)); // "bcd"(自动交换为1到4)- substr(startIndex, endIndex)
- 功能 :从
<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">startIndex</font>开始,截取长度为<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">length</font>的子串(注意:部分浏览器可能不推荐使用,建议用<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">slice</font>替代)。 - 示例 :
javascript
console.log(str.substr(2, 3)); // "cde"(从索引2开始,截取3个字符)- split(separator, limit)
- 功能 :按
<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">separator</font>分割字符串为数组,<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">limit</font>限制返回的数组长度。 - 示例 :
javascript
const str = "apple,banana,orange";
console.log(str.split(",")); // ["apple", "banana", "orange"]
console.log(str.split(",", 2)); // ["apple", "banana"](只取前2个)
console.log(str.split("")); // ["a","p","p","l","e",",",...](分割为单个字符)替换方法
- replace(pattern, replacement)
- 功能 :替换第一个匹配
<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">pattern</font>(字符串或正则表达式)的子串为<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">replacement</font>。 - 示例 :
javascript
const str = "hello world";
console.log(str.replace("world", "there")); // "hello there"(替换第一个匹配)
console.log(str.replace(/o/g, "*")); // "hell* w*rld"(正则全局替换所有"o")- replaceAll(pattern, replacement)
- 功能 :替换所有匹配
<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">pattern</font>的子串(<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">replace</font>需配合正则<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">g</font>修饰符才能全局替换)。 - 示例 :
javascript
console.log(str.replaceAll("l", "x")); // "hexxo worxd"(替换所有"l")其他实用方法
- charAt(Index)
- 功能 :返回索引
<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">index</font>处的字符(类似<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">str[index]</font>,但<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">str[index]</font>在部分旧环境可能不支持)。 - 示例 :
javascript
const str = "hello";
console.log(str.charAt(1)); // "e"- charCodeAt()
- 功能 :返回索引
<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">index</font>处字符的 Unicode 编码。 - 示例 :
javascript
console.log(str.charCodeAt(0)); // 104("h"的Unicode编码)- concat(str1, str2)
- 功能 :拼接多个字符串,返回新字符串(通常推荐用
<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">+</font>或模板字符串替代,更简洁)。 - 示例 :
javascript
const str1 = "hello";
const str2 = "world";
console.log(str1.concat(" ", str2)); // "hello world"- padStart(targetLength, padString)
- 功能 :在字符串开头填充
<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">padString</font>,直到总长度为<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">targetLength</font>。 - 示例 :
javascript
const num = "123";
console.log(num.padStart(5, "0")); // "00123"(总长度5,不足补"0")- padEnd(targetLength, padString)
- 功能 :在字符串结尾填充
<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">padString</font>,直到总长度为<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">targetLength</font>。 - 示例 :
javascript
console.log(num.padEnd(5, "x")); // "123xx"- repeat(count)
- 功能 :将字符串重复
<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">count</font>次,返回新字符串。 - 示例 :
javascript
console.log("ab".repeat(3)); // "ababab"字符串的不可变性
字符串是不可变的:一旦创建,其字符无法被直接修改,任何修改操作都会返回新字符串。
javascript
let str = "hello";
str[0] = "H"; // 无效操作
console.log(str); // 仍为 "hello"
// 正确修改方式:创建新字符串
str = "H" + str.slice(1); // "Hello"