自定义SpringIOC(亲手实践)
上一篇文章,我们介绍了SpringIOC容器的核心组件及其作用,下面我们来动手仿写一个SpringIOC容器,让我们对SpringIOC容器理解地更加透彻!Start Go Go Go!
自定义SpringIOC
对下面的配置文件进行解析,并自定义SpringIOC,对涉及到的对象进行管理。
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans>
<bean id="courseService" class="com.hopeful.service.impl.CourseServiceImpl">
<property name="courseDao" ref="courseDao"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="courseDao" class="com.hopeful.dao.impl.CourseDaoImpl"></bean>
</beans>1) 创建与Bean相关的pojo类
- PropertyValue类: 用于封装 bean 的属性,体现到上面的配置文件就是封装 bean 标签的子标签 property 标签数据。
java
/**
* 该类用来封装bean标签下的property子标签的属性
* 1.name属性
* 2.ref属性
* 3.value属性: 给基本数据类型及string类型数据赋的值
**/
public class PropertyValue {
private String name;
private String ref;
private String value;
public PropertyValue() {
}
public PropertyValue(String name, String ref, String value) {
this.name = name;
this.ref = ref;
this.value = value;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getRef() {
return ref;
}
public void setRef(String ref) {
this.ref = ref;
}
public String getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(String value) {
this.value = value;
}
}- MutablePropertyValues类: 一个bean标签可以有多个property子标签,所以再定义一个MutablePropertyValues类,用来存储并管理多个PropertyValue对象。
java
package com.mashibing.framework.beans;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 该类用来存储和遍历多个PropertyValue对象
**/
public class MutablePropertyValues implements Iterable<PropertyValue>{
//定义List集合,存储PropertyValue的容器
private final List<PropertyValue> propertyValueList;
//空参构造中 初始化一个list
public MutablePropertyValues() {
this.propertyValueList = new ArrayList<PropertyValue>();
}
//有参构造 接收一个外部传入的list,赋值propertyValueList属性
public MutablePropertyValues(List<PropertyValue> propertyValueList) {
if(propertyValueList == null){
this.propertyValueList = new ArrayList<PropertyValue>();
}else{
this.propertyValueList = propertyValueList;
}
}
//获取当前容器对应的迭代器对象
@Override
public Iterator<PropertyValue> iterator() {
//直接获取List集合中的迭代器
return propertyValueList.iterator();
}
//获取所有的PropertyValue
public PropertyValue[] getPropertyValues(){
//将集合转换为数组并返回
return propertyValueList.toArray(new PropertyValue[0]); //new PropertyValue[0]声明返回的数组类型
}
//根据name属性值获取PropertyValue
public PropertyValue getPropertyValue(String propertyName){
//遍历集合对象
for (PropertyValue propertyValue : propertyValueList) {
if(propertyValue.getName().equals(propertyName)){
return propertyValue;
}
}
return null;
}
//判断集合是否为空,是否存储PropertyValue
public boolean isEmpty(){
return propertyValueList.isEmpty();
}
//向集合中添加
public MutablePropertyValues addPropertyValue(PropertyValue value){
//判断集合中存储的propertyvalue对象.是否重复,重复就进行覆盖
for (int i = 0; i < propertyValueList.size(); i++) {
//获取集合中每一个 PropertyValue
PropertyValue currentPv = propertyValueList.get(i);
//判断当前的pv的name属性 是否与传入的相同,如果相同就覆盖
if(currentPv.getName().equals(value.getName())){
propertyValueList.set(i,value);
return this;
}
}
//没有重复
this.propertyValueList.add(value);
return this; //目的是实现链式编程
}
//判断是否有指定name属性值的对象
public boolean contains(String propertyName){
return getPropertyValue(propertyName) != null;
}
}- BeanDefinition类: 用来封装 bean 信息的,主要包含id(即 bean 对象的名称)、class(需要交由spring管理的类的全类名)及子标签property数据。
java
/**
* 封装Bean标签数据的类,包括id与class以及子标签的数据
**/
public class BeanDefinition {
private String id;
private String className;
private MutablePropertyValues propertyValues;
public BeanDefinition() {
propertyValues = new MutablePropertyValues();
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getClassName() {
return className;
}
public void setClassName(String className) {
this.className = className;
}
public MutablePropertyValues getPropertyValues() {
return propertyValues;
}
public void setPropertyValues(MutablePropertyValues propertyValues) {
this.propertyValues = propertyValues;
}
}2) 创建注册表相关的类
BeanDefinition 对象存取的操作, 其实是在BeanDefinitionRegistry接口中定义的,它被称为是BeanDefinition的注册中心。
java
//源码
public interface BeanDefinitionRegistry extends AliasRegistry {
void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException;
void removeBeanDefinition(String beanName) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
BeanDefinition getBeanDefinition(String beanName) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
boolean containsBeanDefinition(String beanName);
String[] getBeanDefinitionNames();
int getBeanDefinitionCount();
boolean isBeanNameInUse(String beanName);
}BeanDefinitionRegistry继承结构图如下:
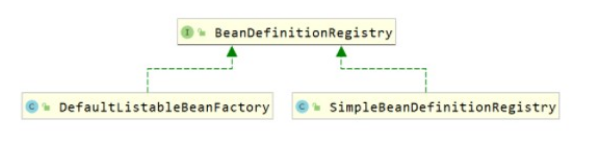
BeanDefinitionRegistry接口的子实现类主要有以下两个:
-
DefaultListableBeanFactory:在该类中定义了如下代码,就是用来注册bean
javaprivate final Map<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256); -
SimpleBeanDefinitionRegistry:在该类中定义了如下代码,就是用来注册bean
javaprivate final Map<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(64);
- 自定义BeanDefinitionRegistry接口定义了注册表的相关操作,定义如下功能:
java
public interface BeanDefinitionRegistry {
//注册BeanDefinition对象到注册表中
void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition);
//从注册表中删除指定名称的BeanDefinition对象
void removeBeanDefinition(String beanName) throws Exception;
//根据名称从注册表中获取BeanDefinition对象
BeanDefinition getBeanDefinition(String beanName) throws Exception;
//判断注册表中是否包含指定名称的BeanDefinition对象
boolean containsBeanDefinition(String beanName);
//获取注册表中BeanDefinition对象的个数
int getBeanDefinitionCount();
//获取注册表中所有的BeanDefinition的名称
String[] getBeanDefinitionNames();
}- SimpleBeanDefinitionRegistry类, 该类实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry接口,定义了Map集合作为注册表容器。
java
public class SimpleBeanDefinitionRegistry implements BeanDefinitionRegistry {
private Map<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new HashMap<String, BeanDefinition>();
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName,beanDefinition);
}
@Override
public void removeBeanDefinition(String beanName) throws Exception {
beanDefinitionMap.remove(beanName);
}
@Override
public BeanDefinition getBeanDefinition(String beanName) throws Exception {
return beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
}
@Override
public boolean containsBeanDefinition(String beanName) {
return beanDefinitionMap.containsKey(beanName);
}
@Override
public int getBeanDefinitionCount() {
return beanDefinitionMap.size();
}
@Override
public String[] getBeanDefinitionNames() {
return beanDefinitionMap.keySet().toArray(new String[1]);
}
}3) 创建解析器相关的类
BeanDefinitionReader 接口
- BeanDefinitionReader 用来解析配置文件并在注册表中注册 bean 的信息。定义了两个规范:
- 获取注册表的功能,让外界可以通过该对象获取注册表对象;
- 加载配置文件,并注册bean数据
java
/**
* 该类定义解析配置文件规则的接口
**/
public interface BeanDefinitionReader {
//获取注册表对象
BeanDefinitionRegistry getRegistry();
//加载配置文件并在注册表中进行注册
void loadBeanDefinitions(String configLocation) throws Exception;
}XmlBeanDefinitionReader类
- XmlBeanDefinitionReader 是专门用来解析 xml 配置文件的。该类实现 BeanDefinitionReader 接口并实现接口中的两个功能。
java
/**
* 该类是对XML文件进行解析的类
**/
public class XmlBeanDefinitionReader implements BeanDefinitionReader {
//声明注册表对象(将配置文件与注册表解耦,通过Reader降低耦合性)
private BeanDefinitionRegistry registry;
public XmlBeanDefinitionReader() {
registry = new SimpleBeanDefinitionRegistry();
}
@Override
public BeanDefinitionRegistry getRegistry() {
return registry;
}
//加载配置文件
@Override
public void loadBeanDefinitions(String configLocation) throws Exception {
//使用dom4j解析xml
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
//获取配置文件,类路径下
InputStream is = XmlBeanDefinitionReader.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(configLocation);
//获取document文档对象
Document document = reader.read(is);
Element rootElement = document.getRootElement();
//解析bean标签
parseBean(rootElement);
}
private void parseBean(Element rootElement) {
//获取所有的bean标签
List<Element> elements = rootElement.elements();
//遍历获取每个bean标签的属性值和子标签property
for (Element element : elements) {
String id = element.attributeValue("id");
String className = element.attributeValue("class");
//封装到beanDefinition
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = new BeanDefinition();
beanDefinition.setId(id);
beanDefinition.setClassName(className);
//获取property
List<Element> list = element.elements("property");
MutablePropertyValues mutablePropertyValues = new MutablePropertyValues();
//遍历,封装propertyValue,并保存到mutablePropertyValues
for (Element element1 : list) {
String name = element1.attributeValue("name");
String ref = element1.attributeValue("ref");
String value = element1.attributeValue("value");
PropertyValue propertyValue = new PropertyValue(name,ref,value);
mutablePropertyValues.addPropertyValue(propertyValue);
}
//将mutablePropertyValues封装到beanDefinition
beanDefinition.setPropertyValues(mutablePropertyValues);
System.out.println(beanDefinition);
//将beanDefinition注册到注册表
registry.registerBeanDefinition(id,beanDefinition);
}
}
}4) 创建IOC容器相关的类
1) BeanFactory接口
在该接口中定义 IOC 容器的统一规范和获取bean对象的方法。
java
/**
* IOC容器父接口
**/
public interface BeanFactory {
Object getBean(String name)throws Exception;
//泛型方法,传入当前类或者其子类
<T> T getBean(String name ,Class<? extends T> clazz)throws Exception;
}2) ApplicationContext 接口
该接口的所有的子实现类对 bean 对象的创建都是非延时的,所以在该接口中定义 refresh() 方法,该方法主要完成以下两个功能:
- 加载配置文件。
- 根据注册表中的 BeanDefinition 对象封装的数据进行 bean 对象的创建。
java
/**
* 定义非延时加载功能
**/
public interface ApplicationContext extends BeanFactory {
//进行配置文件加载,并进行对象创建
void refresh();
}3) AbstractApplicationContext类
- 作为 ApplicationContext 接口的子类,所以该类也是非延时加载,所以需要在该类中定义一个Map集合,作为bean对象存储的容器。
- 声明 BeanDefinitionReader 类型的变量,用来进行 xml 配置文件的解析,符合单一职责原则。
- BeanDefinitionReader 类型的对象创建交由子类实现,因为只有子类明确到底创建BeanDefinitionReader 哪儿个子实现类对象。
java
/**
* ApplicationContext接口的子实现类
* 创建容器对象时,加载配置文件,对bean进行初始化
**/
public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext implements ApplicationContext {
//声明解析器变量
protected BeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader;
//定义存储bean对象的Map集合
protected Map<String,Object> singletonObjects = new HashMap<>();
//声明配置文件类路径的变量
protected String configLocation;
@Override
public void refresh() {
//加载beanDefinition对象
try {
beanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocation);
//初始化bean
finishBeanInitialization();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//bean初始化
protected void finishBeanInitialization() throws Exception {
//获取对应的注册表对象
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = beanDefinitionReader.getRegistry();
//获取beanDefinition对象
String[] beanNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
//进行bean的初始化
getBean(beanName);
}
};
}4) ClassPathXmlApplicationContext类
该类主要是加载类路径下的配置文件,并进行 bean 对象的创建,主要完成以下功能:
- 在构造方法中,创建 BeanDefinitionReader 对象。
- 在构造方法中,调用 refresh() 方法,用于进行配置文件加载、创建 bean 对象并存储到容器中。
- 重写父接口中的 getBean() 方法,并实现依赖注入操作。
java
/**
* IOC容器具体的子实现类,加载XML格式配置文件
**/
public class ClassPathXmlApplicationContext extends AbstractApplicationContext{
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String configLocation) {
this.configLocation = configLocation;
//构建解析器对象
this.beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader();
this.refresh();
}
//跟据bean的对象名称获取bean对象
@Override
public Object getBean(String name) throws Exception {
//判断对象容器中是否包含指定名称的bean对象,如果包含就返回,否则自行创建
Object obj = singletonObjects.get(name);
if(obj != null){
return obj;
}
//自行创建,获取beanDefinition对象
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = beanDefinitionReader.getRegistry();
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = registry.getBeanDefinition(name);
//通过反射创建对象
String className = beanDefinition.getClassName();
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(className);
Object beanObj = clazz.newInstance();
//CourseService与UserDao存依赖,所以要将UserDao一同初始化,进行依赖注入
MutablePropertyValues propertyValues = beanDefinition.getPropertyValues();
for (PropertyValue propertyValue : propertyValues) {
//获取name属性值
String propertyName = propertyValue.getName();
//获取Value属性
String value = propertyValue.getValue();
//获取ref属性
String ref = propertyValue.getRef();
//ref与value只能存在一个
if(ref != null && !"".equals(ref)){
//获取依赖的bean对象,拼接set set+Course
Object bean = getBean(ref);
String methodName = StringUtils.getSetterMethodFieldName(propertyName);
//获取所有方法对象
Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
if(methodName.equals(method.getName())){
//执行该set方法
method.invoke(beanObj,bean);
}
}
}
if(value != null && !"".equals(value)){
String methodName = StringUtils.getSetterMethodFieldName(propertyName);
//获取method
Method method = clazz.getMethod(methodName, String.class);
method.invoke(beanObj,value);
}
}
//在返回beanObj之前 ,需要将对象存储到Map容器中
this.singletonObjects.put(name,beanObj);
return beanObj;
}
@Override
public <T> T getBean(String name, Class<? extends T> clazz) throws Exception {
Object bean = getBean(name);
if(bean == null){
return null;
}
return clazz.cast(bean);
}
}5) 自定义IOC容器测试
第一步: 将我们写好的自定义IOC容器项目,安装到maven仓库中,使其他项目可以引入其依赖
xml
//依赖信息
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.hopeful</groupId>
<artifactId>user_defined_springioc</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>第二步: 创建一个新的maven项目,引入上面的依赖
第三步: 完成代码编写
- dao
java
public interface CourseDao {
public void add();
}
public class CourseDaoImpl implements CourseDao {
//value注入
private String courseName;
public String getCourseName() {
return courseName;
}
public void setCourseName(String courseName) {
this.courseName = courseName;
}
public CourseDaoImpl() {
System.out.println("CourseDaoImpl创建了......");
}
@Override
public void add() {
System.out.println("CourseDaoImpl的add方法执行了......" + courseName);
}
}- service
java
public interface CourseService {
public void add();
}
public class CourseServiceImpl implements CourseService {
public CourseServiceImpl() {
System.out.println("CourseServiceImpl创建了......");
}
private CourseDao courseDao;
public void setCourseDao(CourseDao courseDao) {
this.courseDao = courseDao;
}
@Override
public void add() {
System.out.println("CourseServiceImpl的add方法执行了......");
courseDao.add();
}
}- applicationContext.xml
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans>
<bean id="courseService" class="com.mashibing.test_springioc.service.impl.CourseServiceImpl">
<property name="courseDao" ref="courseDao"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="courseDao" class="com.mashibing.test_springioc.dao.impl.CourseDaoImpl">
<property name="courseName" value="java"></property>
</bean>
</beans>- Controller
java
public class CourseController{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.创建Spring的容器对象
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//2.从容器对象中获取CourseService对象
CourseService courseService = context.getBean("courseService", CourseService.class);
//3.调用UserService的add方法
courseService.add();
}
}在此,我们就已经实现了专属自己的IOC容器,是不是突然发现平时感觉很高深的Sping IoC容器也不是那么复杂!离大佬又近了一步,哈哈!
6) 案例中使用到的设计模式
- 工厂模式:这个使用工厂模式 + 配置文件的方式。
- 单例模式:Spring IOC管理的bean对象都是单例的,此处的单例不是通过构造器进行单例的控制的,而是spring框架对每一个bean只创建了一个对象。
- 模板方法模式:AbstractApplicationContext 类中的 finishBeanInitialization() 方法调用了子类的 getBean() 方法,因为 getBean() 的实现和环境息息相关。
- 迭代器模式。对于 MutablePropertyValues 类定义使用到了迭代器模式,因为此类存储并管理PropertyValue 对象,也属于一个容器,所以给该容器提供一个遍历方式。