使用 Trea cn 设计 爬虫程序 so esay
在现代数据驱动的时代,网络爬虫已成为数据采集的重要工具。传统的爬虫开发往往需要处理复杂的HTTP请求、HTML解析、URL处理等技术细节。而借助 Trea CN 这样的AI辅助开发工具,我们可以更高效地构建功能完善的爬虫程序。
本文将通过实际案例,展示如何使用 Trea CN 快速开发一个遵循robots协议的Python网络爬虫。
文章目录
- [使用 Trea cn 设计 爬虫程序 so esay](#使用 Trea cn 设计 爬虫程序 so esay)
-
- 环境准备:安装必要的依赖包
- [使用 Trea](#使用 Trea)
- [写一个爬虫 代码](#写一个爬虫 代码)
- [技术深度解析:urllib.parse 核心功能](#技术深度解析:urllib.parse 核心功能)
环境准备:安装必要的依赖包
bash
pip install requests beautifulsoup4 lxml html5lib各包说明:
| 库名 | 功能描述 | 特点 |
|---|---|---|
requests |
HTTP请求库 | 简洁易用,功能强大 |
beautifulsoup4 |
HTML/XML解析库 | 语法直观,容错性强 |
lxml |
高性能XML/HTML解析器 | 速度快,功能丰富 |
html5lib |
纯Python HTML5解析器 | 解析最准确,但速度较慢 |
使用 Trea
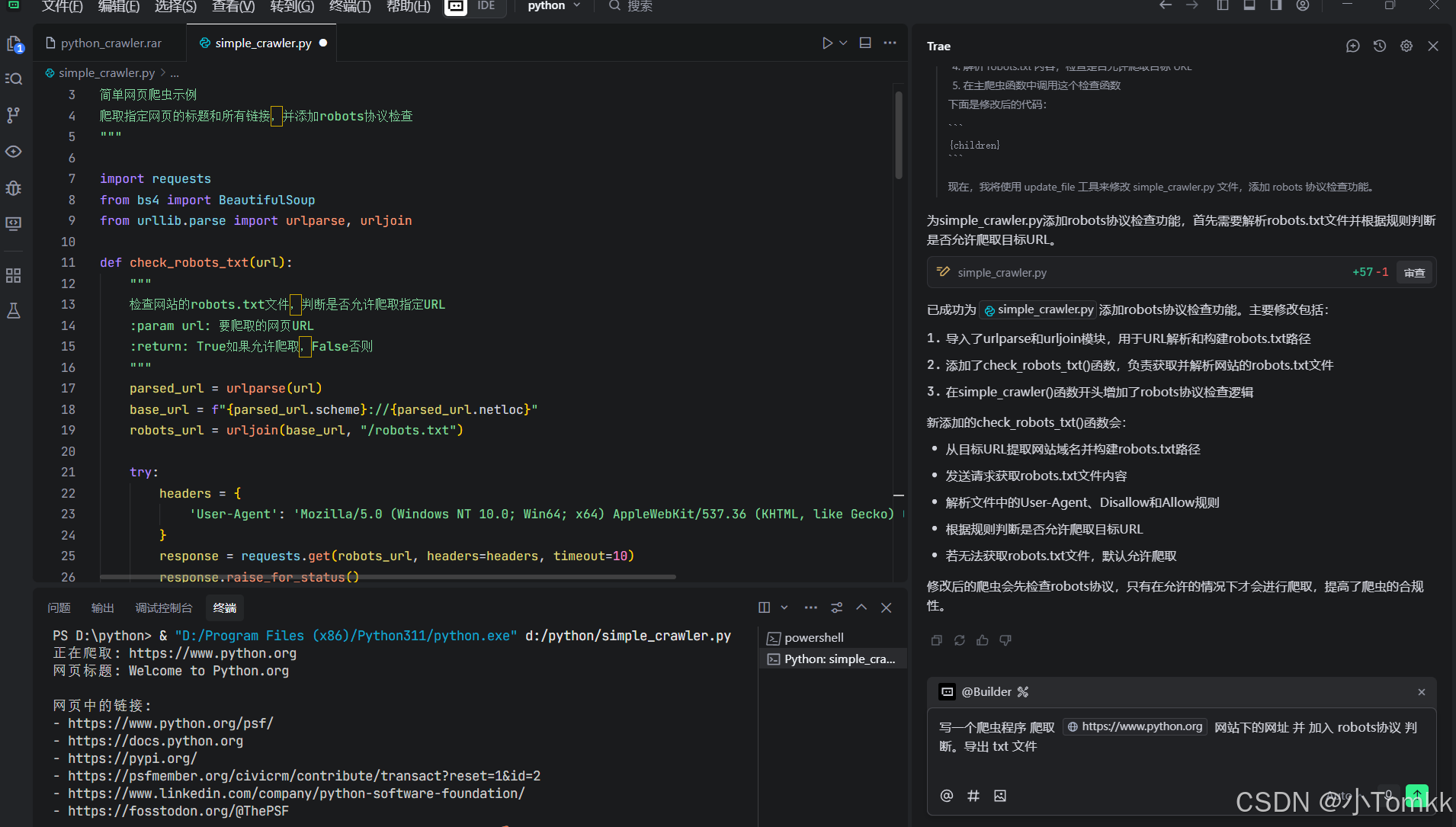
写一个爬虫 代码
python
#!/usr/bin/env python3
"""
简单网页爬虫示例
爬取指定网页的标题和所有链接,并添加robots协议检查
"""
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
from urllib.parse import urlparse, urljoin
def check_robots_txt(url):
"""
检查网站的robots.txt文件,判断是否允许爬取指定URL
:param url: 要爬取的网页URL
:return: True如果允许爬取,False否则
"""
parsed_url = urlparse(url)
base_url = f"{parsed_url.scheme}://{parsed_url.netloc}"
robots_url = urljoin(base_url, "/robots.txt")
try:
headers = {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/91.0.4472.124 Safari/537.36'
}
response = requests.get(robots_url, headers=headers, timeout=10)
response.raise_for_status()
# 默认允许爬取
allow = True
user_agent = "Mozilla/5.0"
# 解析robots.txt
lines = response.text.split('\n')
current_user_agent = None
for line in lines:
line = line.strip()
if not line or line.startswith('#'):
continue
if line.lower().startswith('user-agent:'):
current_user_agent = line.split(':', 1)[1].strip().lower()
elif current_user_agent in ['*', user_agent.lower()]:
if line.lower().startswith('disallow:'):
disallow_path = line.split(':', 1)[1].strip()
if disallow_path == '/' or parsed_url.path.startswith(disallow_path):
allow = False
break
elif line.lower().startswith('allow:'):
allow_path = line.split(':', 1)[1].strip()
if parsed_url.path.startswith(allow_path):
allow = True
break
return allow
except requests.exceptions.RequestException:
# 如果无法获取robots.txt,默认允许爬取
return True
def simple_crawler(url):
"""
简单爬虫函数
:param url: 要爬取的网页URL
"""
try:
# 检查robots.txt
if not check_robots_txt(url):
print(f"根据robots.txt协议,不允许爬取 {url}")
return
# 发送HTTP请求
headers = {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/91.0.4472.124 Safari/537.36'
}
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers, timeout=10)
response.raise_for_status() # 检查请求是否成功
# 解析HTML内容
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, 'html.parser')
# 获取网页标题
title = soup.title.string if soup.title else '无标题'
print(f"网页标题: {title}")
# 获取所有链接
print("\n网页中的链接:")
links = []
for link in soup.find_all('a', href=True):
href = link['href']
if href.startswith('http'): # 只显示完整URL
print(f"- {href}")
links.append(href)
# 将结果写入txt文件
with open('crawl_results.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(f"网页标题: {title}\n\n")
f.write("网页中的链接:\n")
for link in links:
f.write(f"- {link}\n")
print("\n爬取结果已保存到 crawl_results.txt 文件")
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
print(f"请求出错: {e}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"发生错误: {e}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 示例:爬取Python官网
target_url = "https://www.python.org"
print(f"正在爬取: {target_url}")
simple_crawler(target_url)代码已经上传
代码仓库
完整代码已上传至GitHub:SmartCrawler
技术深度解析:urllib.parse 核心功能
1. urlparse() - URL解析神器
urlparse() 函数能够将复杂的URL分解成易于处理的组件:
from urllib.parse import urlparse
解析复杂URL
python
url = "https://www.python.org/downloads/release/python-3-11/?tab=source#files"
parsed = urlparse(url)
print(f"🌐 协议: {parsed.scheme}") # https
print(f"🏠 域名: {parsed.netloc}") # www.python.org
print(f"📁 路径: {parsed.path}") # /downloads/release/python-3-11/
print(f"⚙️ 参数: {parsed.params}") # (空)
print(f"🔍 查询: {parsed.query}") # tab=source
print(f"📍 锚点: {parsed.fragment}") # files输出效果
bash
🌐 协议: https
🏠 域名: www.python.org
📁 路径: /downloads/release/python-3-11/
⚙️ 参数:
🔍 查询: tab=source
📍 锚点: files2. urljoin() - URL智能拼接器
urljoin() 函数能够智能处理基础URL与相对路径的组合:
python
from urllib.parse import urljoin
base_url = "https://www.python.org/downloads/"
# 演示各种路径拼接场景
test_cases = [
("release/", "相对路径拼接"),
("/about/", "绝对路径拼接"),
("../community/", "上级目录拼接"),
("https://docs.python.org/", "完整URL覆盖")
]
print("🔗 URL拼接示例:")
for path, description in test_cases:
result = urljoin(base_url, path)
print(f" {description}: {path} → {result}")输出效果
bash
🔗 URL拼接示例:
相对路径拼接: release/ → https://www.python.org/downloads/release/
绝对路径拼接: /about/ → https://www.python.org/about/
上级目录拼接: ../community/ → https://www.python.org/community/
完整URL覆盖: https://docs.python.org/ → https://docs.python.org/实际应用场景
爬虫中的URL处理最佳实践
python
from urllib.parse import urlparse, urljoin
def normalize_and_validate_url(base_url, found_url):
"""
标准化和验证URL
:param base_url: 基础URL
:param found_url: 发现的URL
:return: 处理后的URL或None
"""
# 使用urljoin处理相对路径
full_url = urljoin(base_url, found_url)
# 使用urlparse进行验证
parsed = urlparse(full_url)
# 验证URL合法性
if not all([parsed.scheme, parsed.netloc]):
return None
# 只接受HTTP/HTTPS协议
if parsed.scheme not in ['http', 'https']:
return None
# 移除锚点,避免重复爬取
clean_url = f"{parsed.scheme}://{parsed.netloc}{parsed.path}"
if parsed.query:
clean_url += f"?{parsed.query}"
return clean_url
# 使用示例
base = "https://www.python.org/about/"
test_urls = ["../downloads/", "mailto:admin@example.com", "javascript:void(0)", "/community/"]
for url in test_urls:
result = normalize_and_validate_url(base, url)
status = "✅ 有效" if result else "❌ 无效"
print(f"{status}: {url} → {result}")总结与展望
通过本文的实践案例,我们看到了如何使用 Trea CN 高效开发一个功能完善的网络爬虫。主要收获包括:
✨ 核心优势
- AI辅助开发:Trea CN 的智能提示大幅提升编码效率
- 协议遵守:自动检查robots.txt,确保合规爬取
- 错误处理:完善的异常处理机制,提高程序健壮性
- 结果管理:智能化的数据提取和保存功能
🚀 技术要点
- URL处理:urllib.parse 模块的灵活运用
- 智能解析:BeautifulSoup的高效HTML解析
- 友好爬取:合理的延迟机制和User-Agent设置
- 日志记录:完整的运行状态监控
🔮 未来方向
- 随着AI技术的发展,像Trea CN这样的智能开发工具将会:
- 提供更精准的代码生成
- 支持更复杂的业务逻辑自动化
- 实现更智能的错误诊断和修复
- 集成更多的开发生态工具