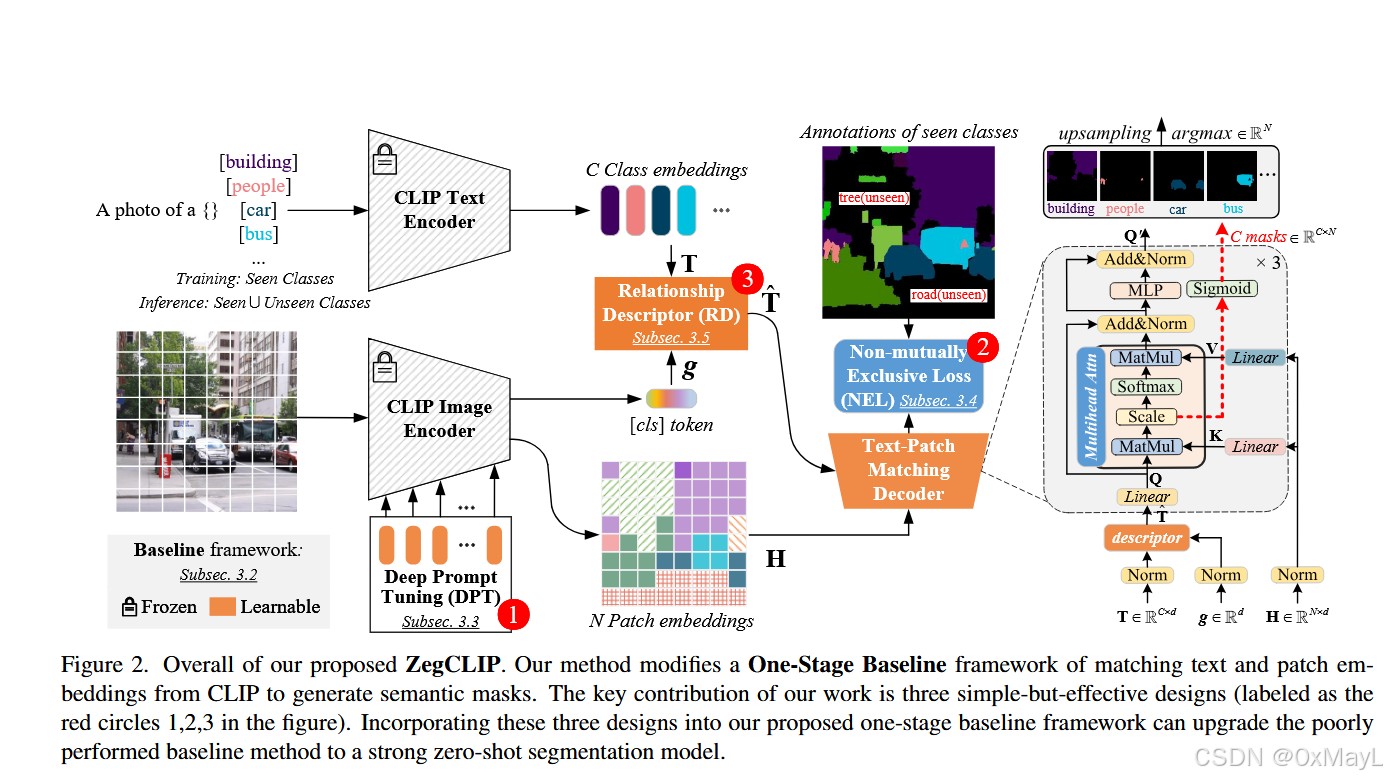
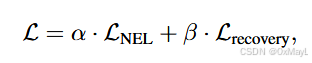Zegclip
- 获取图像的特殊编码:使用prompt tuning的技术,目的是减少过拟合和计算量。
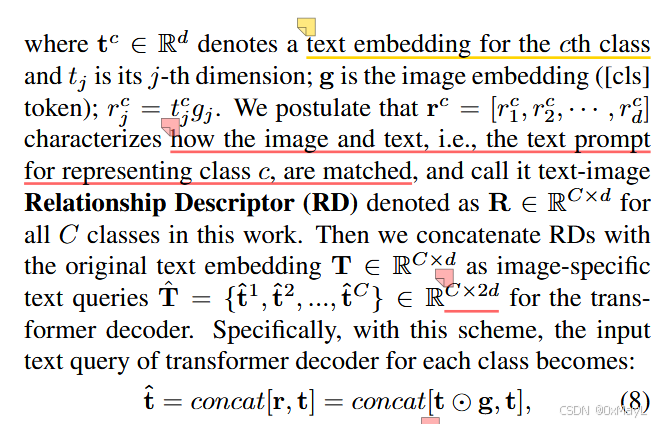
- 调整文本编码:使用RD关系描述符,将每一个文本对应的[cls] token和图像对应的[cls] token作哈密顿积,最后文本[cls]token
形式化任务
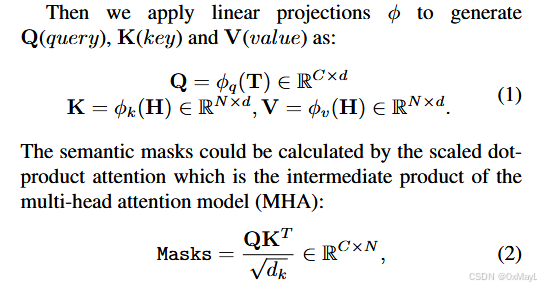
- 文本的[cls] token 和每一个patch token 进行一一匹配,这一点是通过交叉注意力实现 的,通过
argmax操作得到最后的分割结果
图像编码:prompt tuning
- P作为prompt token
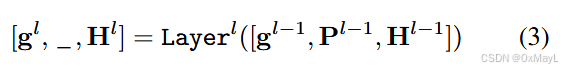
文本编码:RD关系描述符
While being quite intuitive, we find this design could lead to severe overfitting. We postulate that this is because the matching capability between the text query and image patterns is only trained on the seen-class datasets.
Non-mutually Exclusive Loss (NEL)
"the class space will be different from the training scenario, making the logit of an unseen class poorly calibrated with the other unseen classes." (Zhou 等, 2023, p. 5) (pdf) 🔤类空间将与训练场景不同,使得看不见的类的 logit 与其他看不见的类的校准很差。🔤
- 动机:unseen class相比seen class的概率很差,不适合进行softmax
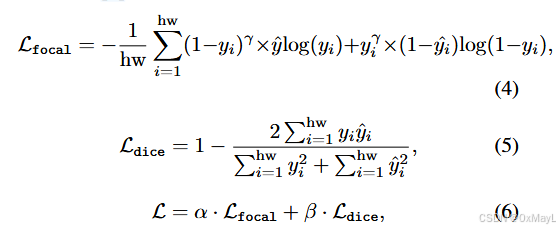
inductive和transductive训练设置
- inductive:训练只用seen类,完全不了解unseen class的name ,完全不知道unseen class的标注信息,测试时预测seen类和unseen类
- transductive:训练分为两个阶段 ,全程都知道seen和unseen class的name ,但是unseen class的标注信息完全不知道 。第一个阶段只在seen class上训练,然后预测unseen class的标注信息,生成伪标签。第二个阶段使用unseen class的为标签和seen class的ground truth进行训练,测试与inductive一致。
"In the "transductive" setting, we train our ZegCLIP model on seen classes in the first half of training iterations and then apply self-training via generating pseudo labels in the rest of iterations." (Zhou 等, 2023, p. 6) (pdf) 🔤在"转导"设置中,我们在训练迭代的前半部分在看到的类上训练我们的 ZegCLIP 模型,然后在其余迭代中通过生成伪标签来应用自训练。🔤
CLIP-RC
- RLB:VIT的特殊编码
- RAM:Text encoder的特殊编码+对齐
- 损失函数:Recovery Decoder With Recovery Loss
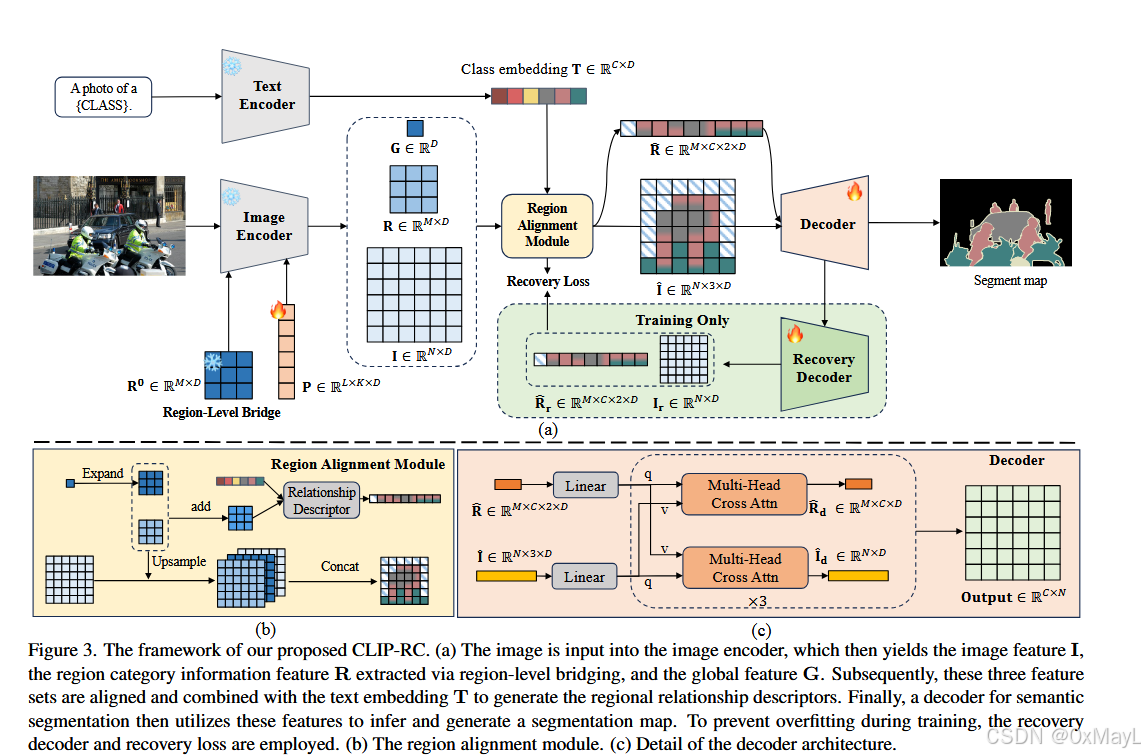
RLB
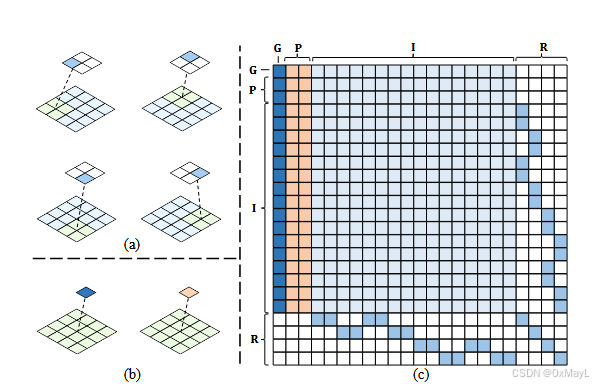
- VIT的输入结构
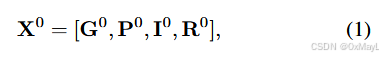
- VIT的输出结构
- G是图像token(1,D),P是prompt token(K,D),I是patch token(N,D),R是作者引入的region token(M,D)。
R的理解和掩码设计
-
作者认为每一个R中的token对应了NMNM\frac{\sqrt{N}\sqrt{M}}{\sqrt{N}\sqrt{M}}N M N M 个patches
-
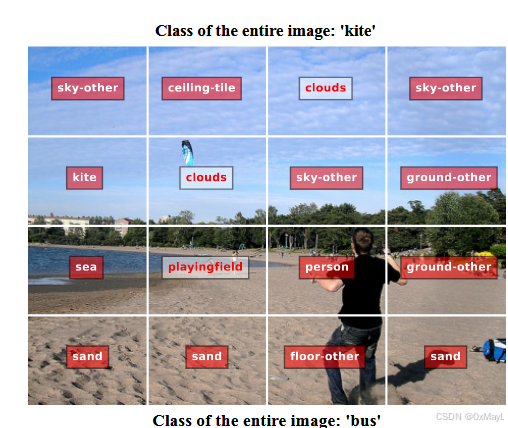
例子:假设N=4,M=2,图像中2x2的区域对应一个R的token
-
多了个掩码矩阵,一个R的token对应这些patch,其他的patch不需要参与计算,所以说有个掩码矩阵
-
输出结果正常抛弃prompt token 。
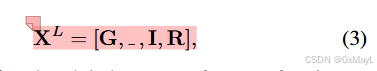
RLB
对齐图像编码
- image特征对齐为:(N,3D)
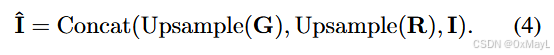
区域描述符(特殊编码text encoder)
- 得到特殊编码:(M,C,2D)

Decoder头
- 先把I^\hat{I}I^和R^\hat{R}R^进行线性层映射到D维度(N,D)和(M,C,D)
- 正常交叉注意力
- 得到I和R形状不变
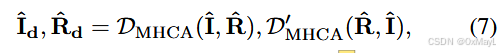
where, DMHCA and D′ MHCA denotes the decoder for semantic segmentation with multi-head cross attention, and ˆId ∈ RN×D and ˆRd ∈ RM×C×D are the image features and region-specific text queries respectively, used for segmentation. The segmentation map Output ∈ RC×N is obtained by averaging the outputs:
- Output:(M,C,D),然后对M维度平均 得到最后的掩码矩阵。

损失函数
- NLS+Recovery Loss
- 完全一模一样架构的decoder(辅助头)
Then, during training, a recovery decoder recovers the features extracted by the decoder into features with strong generalization. The network architecture of the recovery decoder is completely identical to that of the semantic segmentation decoder. They are recovered as follows:
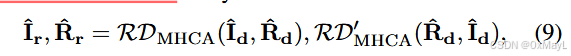
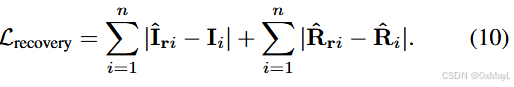
- 这里的I指的是原始CLIP提取的图像特征 ,已经被冻结,R指的是关系描述符,也就是文本特征 。